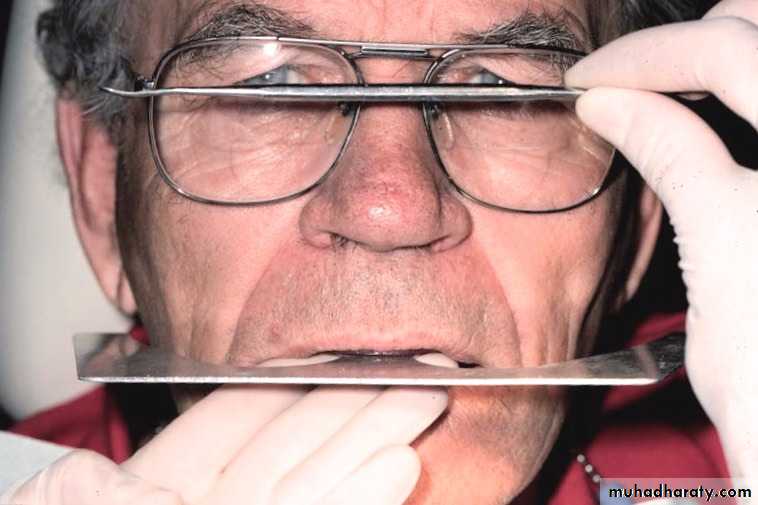
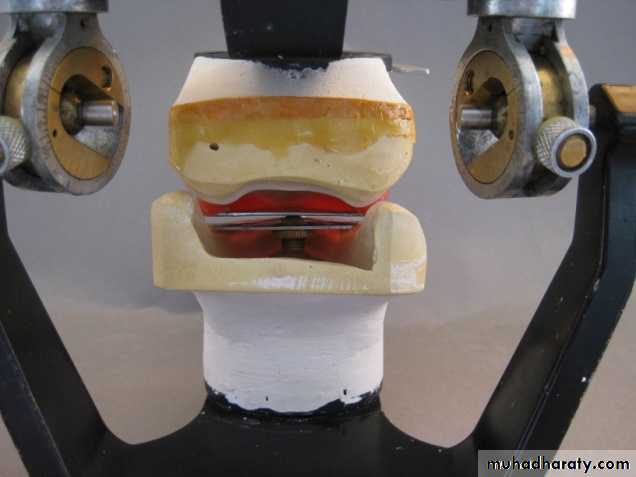
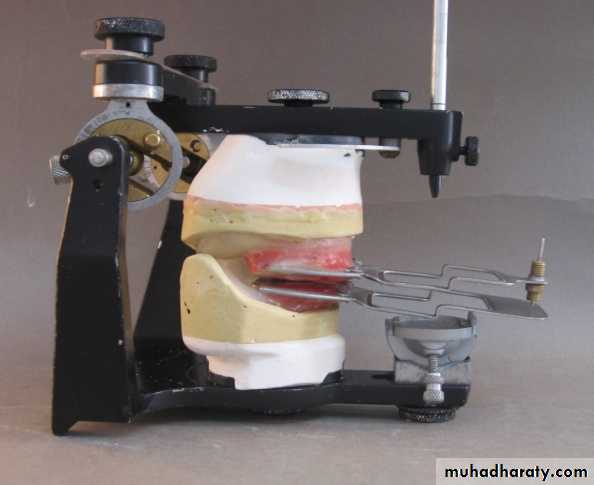
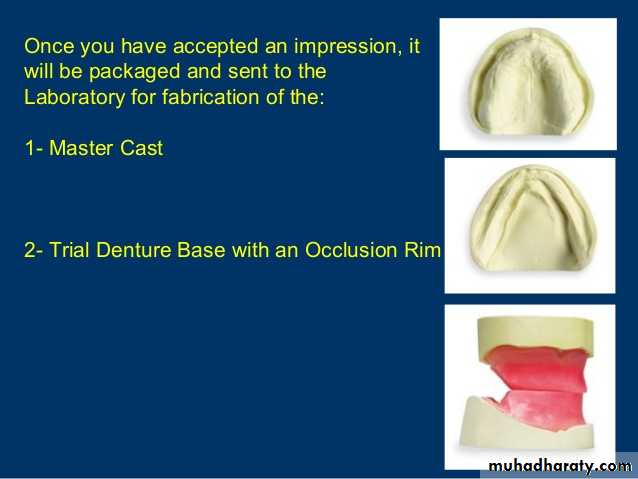
MAXILLOMANDIBULAR RELATIONSHIP
2017Try- in of the occlusion rims
Checked for:retention
stability &
interferences
Level & inclination of the occlusal plane
• Using maxillary occlusion rim• Using mandibular occlusion rim
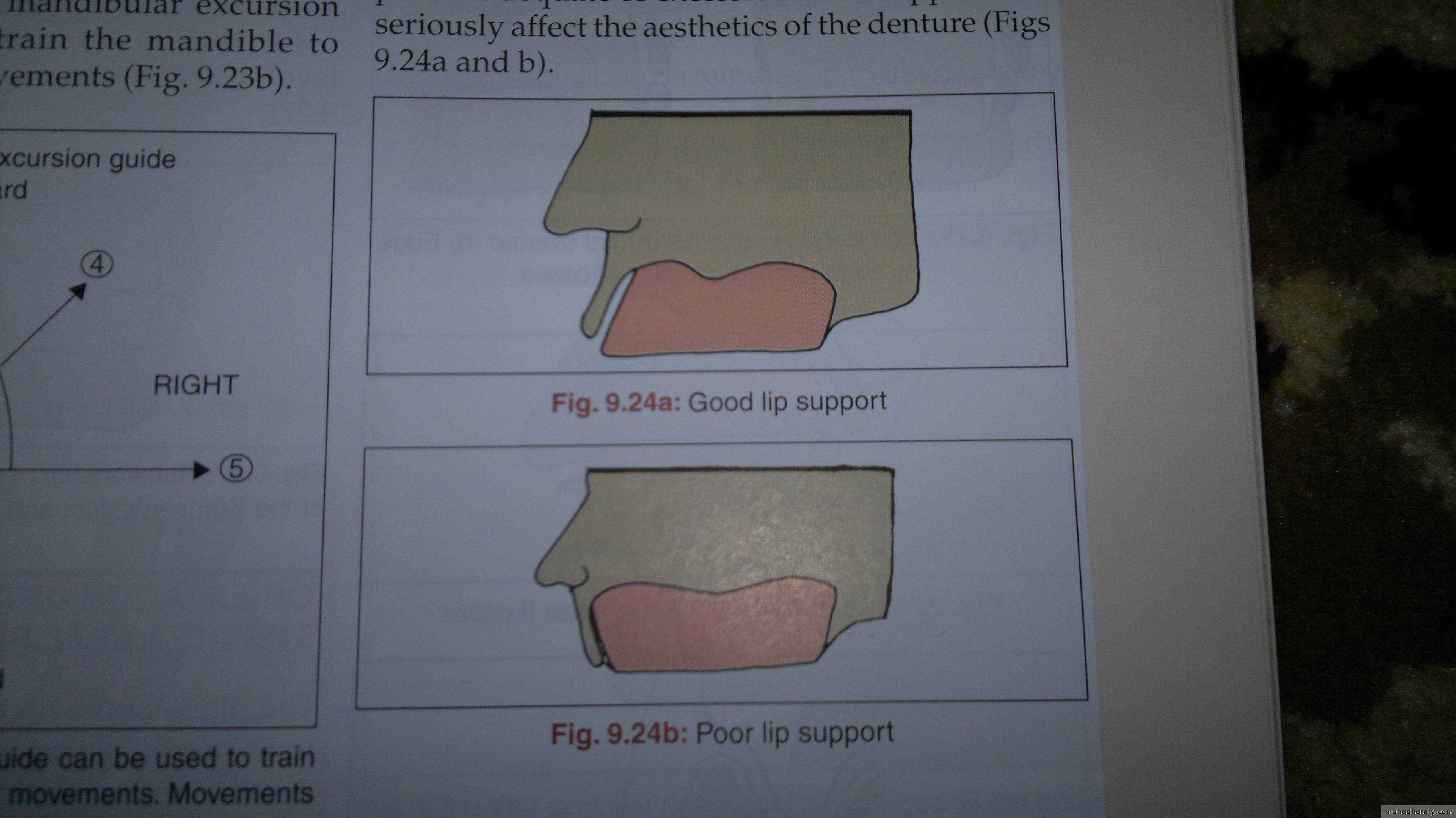
Establishing the labial form of the occlusion rim
Following facial landmark used as a guide:Fullness of the upper lip
Philtrum
Nasolabial fold
Buccal corridor
Maxillary Occlusion Rim Adjustment
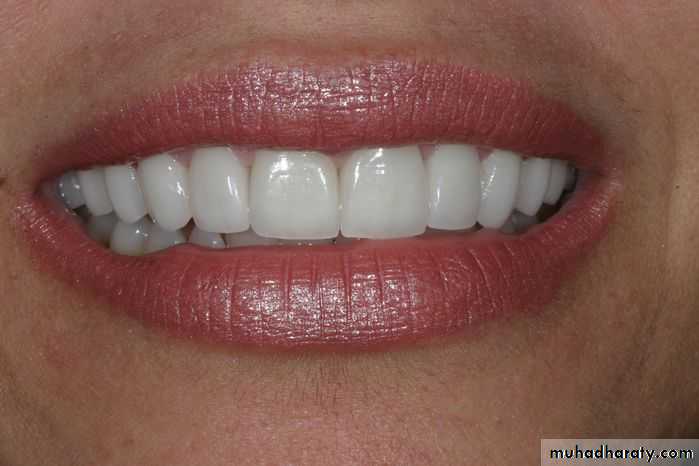
Anterior height 1-2 mm below the lip at rest/when the patient slightly smilesOcclusion Rim Angulation
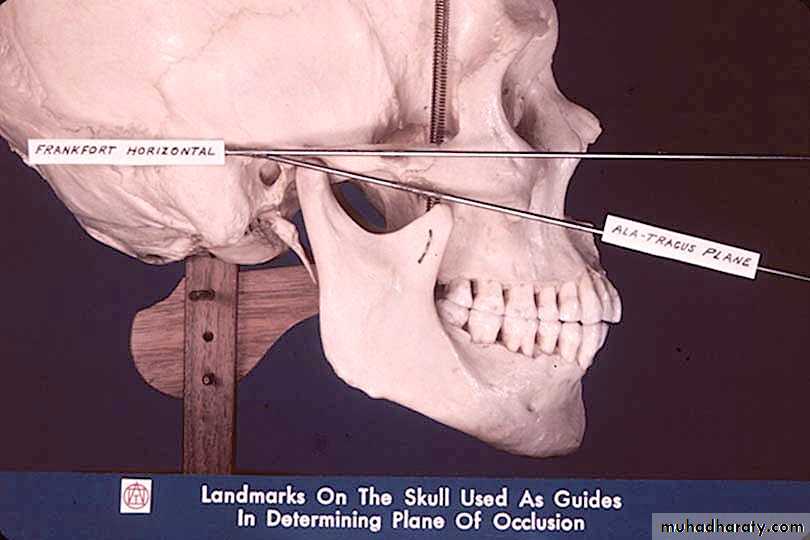
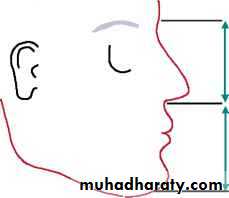
Occlusal plane parallel to the ala-tragus line
Occlusion Rim Occlusal Plane
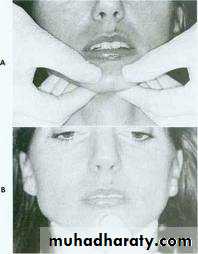
Mediolaterally, parallels the pupilsFox plane can be used
Mandibular Rim Height
Anterior height even with the corners of mouth when lip is relaxedAdjusting the Anterior occlusal plane
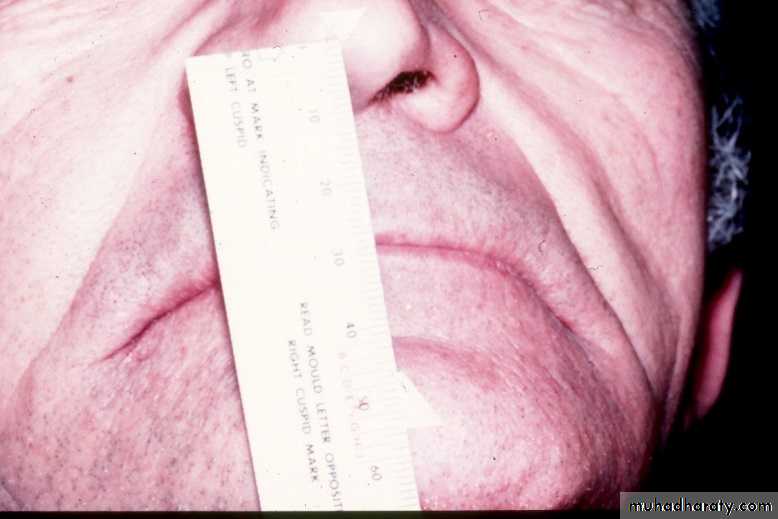
Incisal visibility: 1-2 mm below the upper lipInter-pupillary line
Using maxillary occlusion rim
Adjusting the Anterio-posterior occlusal plane
Parallel to the Ala-Tragus line, (using fox bite )Using maxillary occlusion rim
Establishing the occlusal plane of the lower occlusion rim so that it meets the upper occlusion rim evenly.
Maxillomandibular relationship
Definition: Any spatial relationship of maxilla to mandible.Classsification: (Boucher)
• Vertical relations.• Horizontal relations.
Establishing Jaw Relation
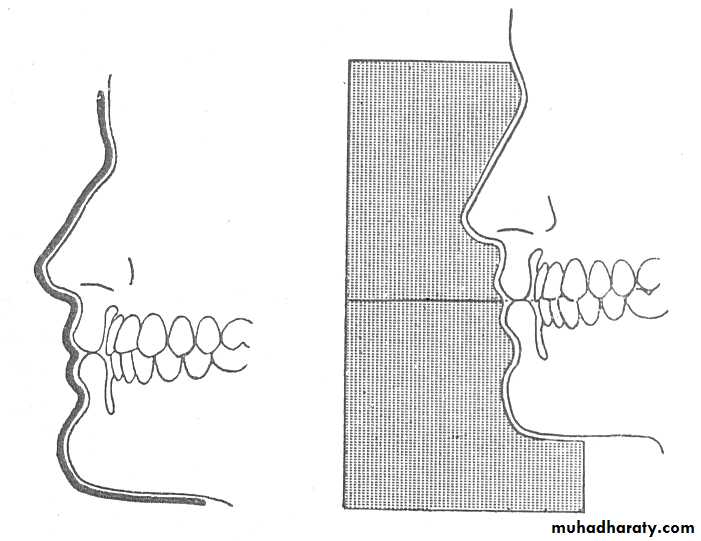
VERTICAL RELATIONS (VD)
Vertical dimension (VD)It is the relation of mandible to the maxilla in a vertical plane
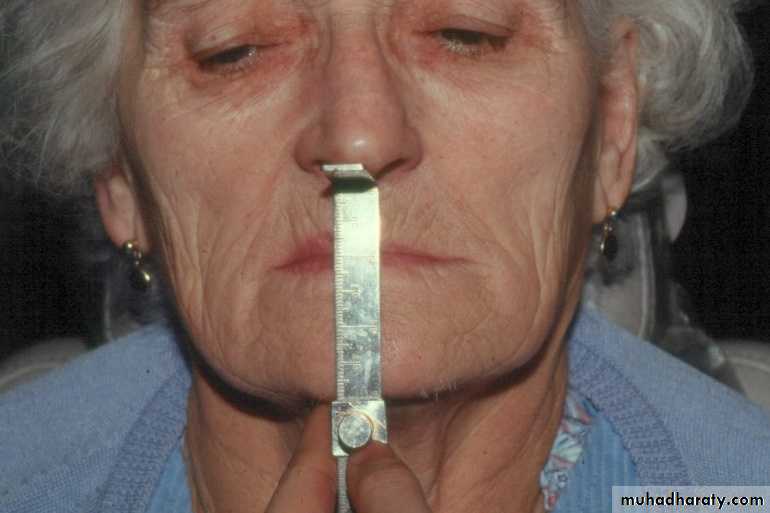
Definition: distance between two selected anatomic or marked points (usually one on the tip of the nose & the other on upon the chin), one on a fixed & one on a movable member.
• Rest vertical dimension (RVD)
• Occlusal vertical dimension (OVD)• Inter occlusal dimension (IOD) or rest space or freeway space (FWS).
Types
RVD It is the distance between two selected points measured when the mandible is in physiologic rest position.
OVD It is the VD of face when the teeth or occlusal rims are in contact in centric occlusion.
Established by occlusal stops of teeth or occlusion rim
Affected by tooth loss, wear, etc.
Types
FWS (IOD)
FWS (Freeway space) It is the difference between the RVD and OVDIn natural teeth, it ranges from 1-8 mm.
In complete dentures, a space of 2-4 mm at the premolar region is tolerated well by most pt.
FWS = RVD – OVD
FWS = 2 to 4 mmPhysiologic Rest Position
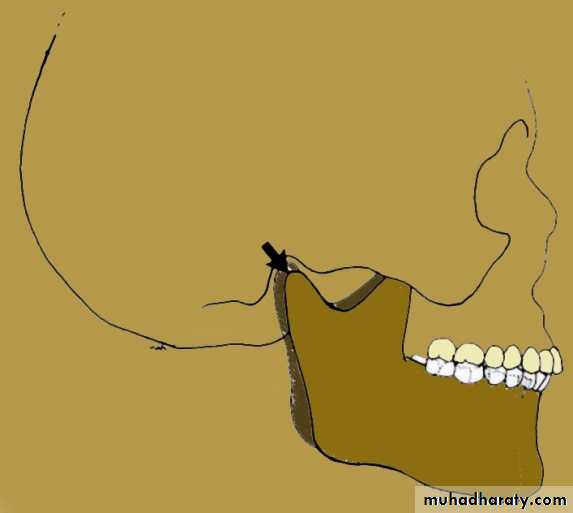
It is the postural position of the mandible when the individual is resting comfortably in an upright position and the associated muscles are in a state of minimal contractual activity.Factors affecting are:
• Tonicity of the jaw muscles
• Position of head
FWS (IOD)
The distance between the occluding surfaces of maxillary and mandibular teeth when the mandible is in the rest position.Methods of Measuring the VR
Mechanical Methodsand
Physiological Methods.
Mechanical Methods
• Ridge relation:2. Measurement of former dentures:
3. Pre-extraction records:
Profile radiographsProfile photographs
Articulated casts
Lead wire adaptation
Facial measurment
• Physiologic rest position
• Parting the lips after swallowing• Niswonger ’s method
• Phonetics
• Using the M sound
• Using H, S & J sounds
• Silverman ’s closest speaking space
• Facial expression & esthetic as guides
• Swallowing threshold
• Tactile sense
• Lytle ’s method (neuromuscular perception)
• Boos bimeter (power point)
• Patient s tactile sense as guide
• Electromyography
Physiologic Methods
Methods of Measuring the VR
Mechanical Methodsand
Physiological Methods.
Mechanical Methods
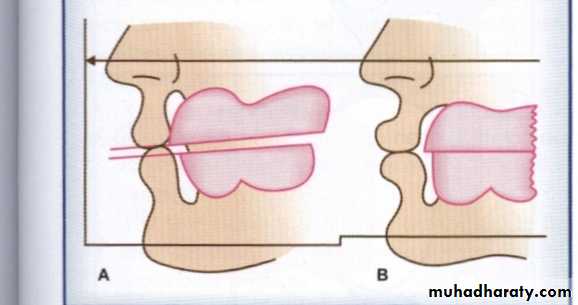
• Ridge relation:Parallelism of the ridges.
Sears suggested that correct OVD is at a point where the jaws are parallel with a 5 degree opening in the posterior region.
Disadvantages:
• Not reliable in case of marked resorption
• When teeth lost at irregular intervals; RR are not II.
Mechanical Methods
2. Measurement of former dentures:A Boley’s gauge is used to measure the distance between the border of the maxillary and mandibular denture, when the dentures are in occlusion. This measurement is used to determine the VDO.
Mechanical Methods
3. Pre-extraction records:Profile radiographs: Made with teeth in occlusion. These are compared with those made with occlusion rims in position.
Disadvantage: Time consuming, Image distortion, Radiation hazard.
Profile photographs
Articulated castsMechanical Methods
3. Pre-extraction records:Lead wire silhouettes ,outline,
Lead wires adapted to the pt’s profile before exo.
Outline is transferred to a cardboard & cut out.
After exo the cutout is placed against pt‘s profile to check VR.
Mechanical Methods
3. Pre-extraction records:Resin facemasks (Swenson’s method)
Made before exo, using a facial impression & cast
Not practical
Facial measurements
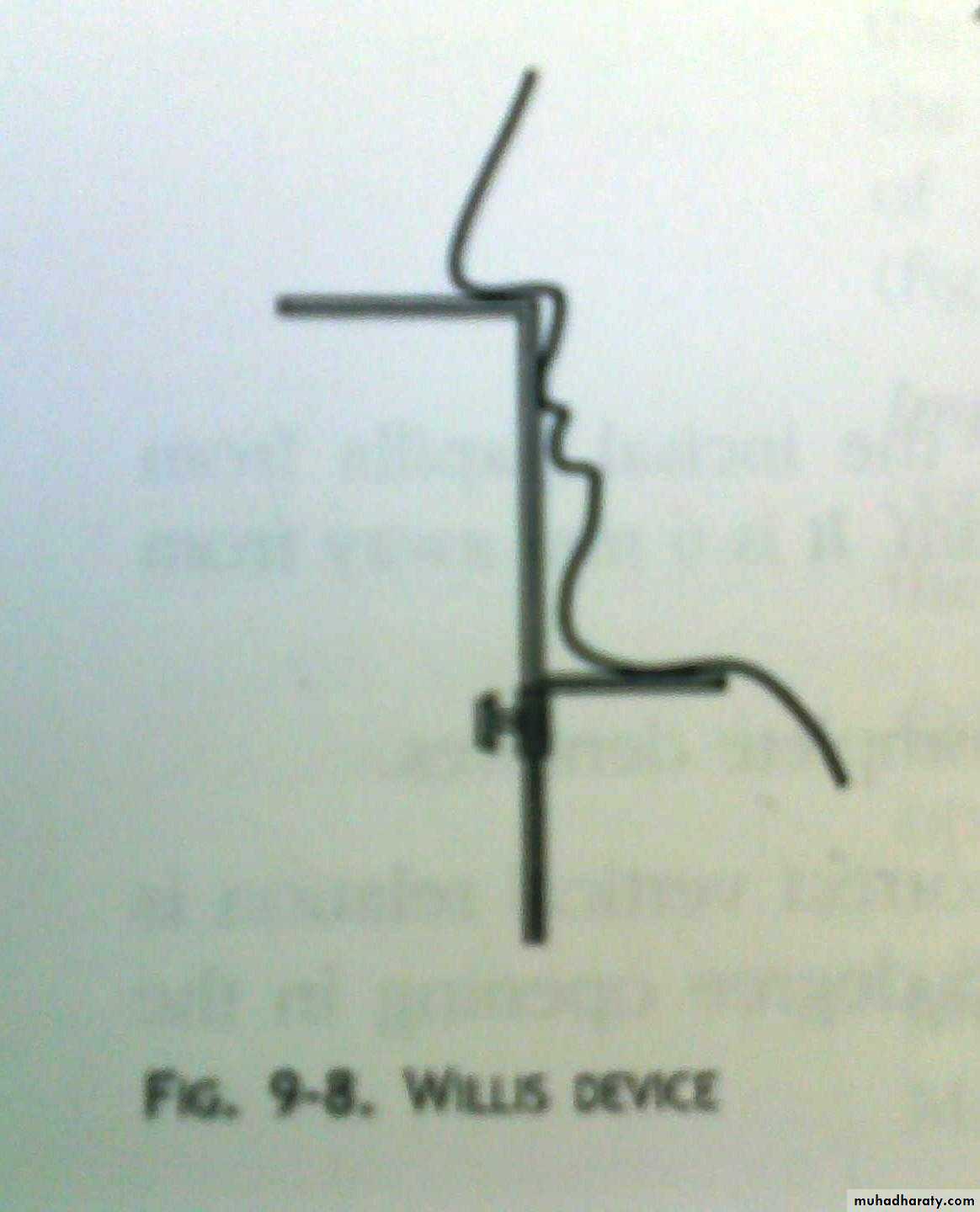
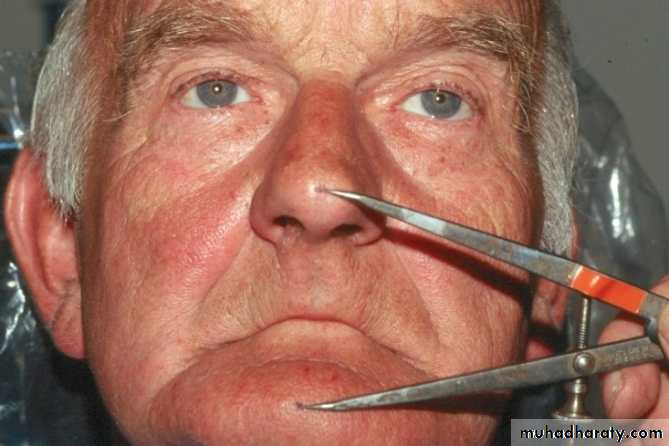
DakometerWillis gauge
sorensens
Mechanical Methods
3. Pre-extraction records:Facial measurements
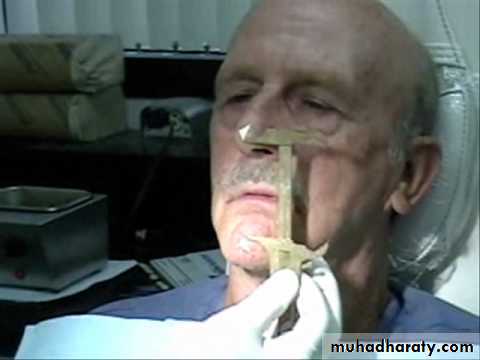
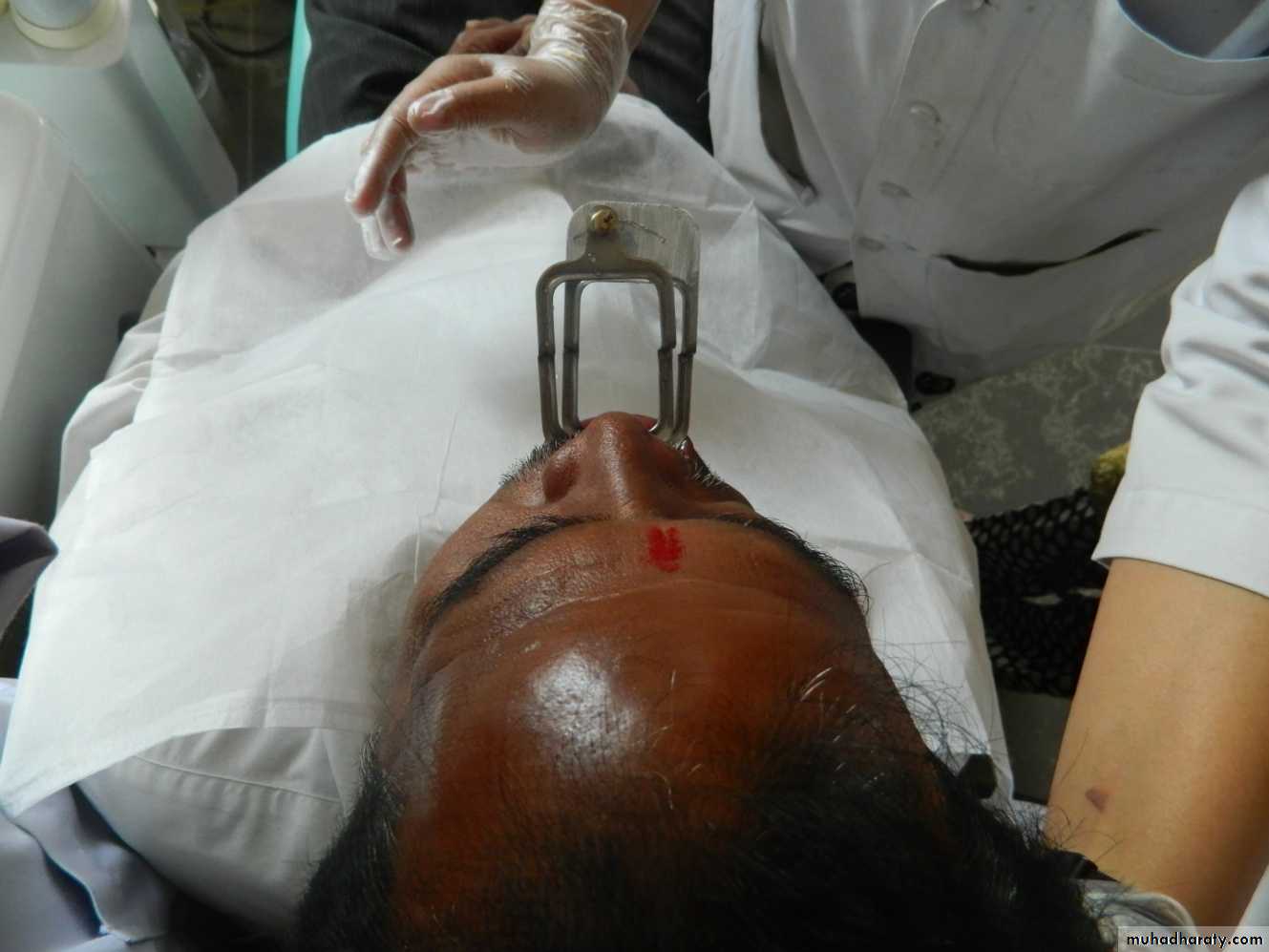
Dakometer: Positioned on the bridge of nose with compound.
Chin piece screwed till touches the front of chin.
Spring pressure gauge controls pr.
incisor attachment record the position of cent. incisors.
Mechanical Methods
3. Pre-extraction records:Facial measurements
Willis gauge
Sorensens
Methods of Measuring the VR
Mechanical Methodsand
Physiological Methods.
1. Physiologic rest position:
Swallow & relaxAfter the insertion of occlusion rims, Ask the patient to swallow and let the jaw relax.
The lips are carefully parted to see the amount of space between the occlusal rims.
Separate the lips without moving the jaws or lips.
This interocclusal rest space should be 2 to 4 mm.
Niswonger’s method
It is commonly used today.
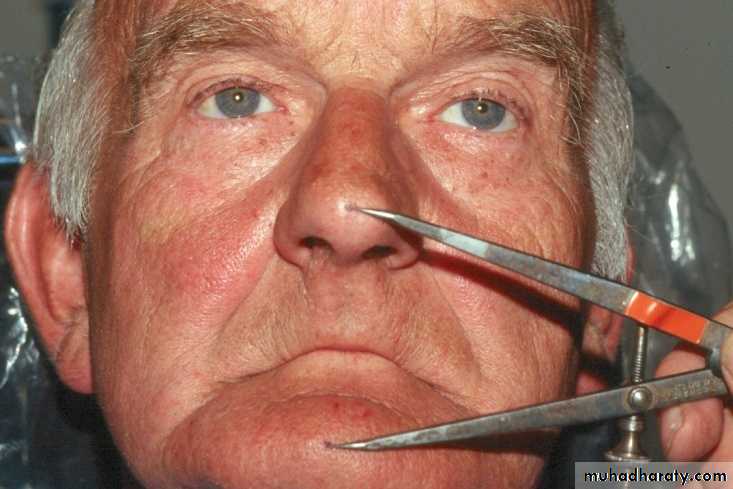
Two markings are made, (tip of the nose & prominent part of the chin).
The patient is instructed to swallow & relax.
The distances between the marks are recorded (RVD).
The occlusal rims are adjusted until the distance between the marks is 2 to 4 mm < original measurement (OVD) .
1. Physiologic rest position:
• Using the M sound
• Using Ch, S & J sounds• Using 33
• Using F or V sounds
2. Phonetics as guide
• Using the M sound
The patient repeats the letter ‘M’.
When the lip touches all jaw movements are stopped, & distance between the two points of reference are measured.
2. Phonetics as guide
• Using Ch., S & J sounds
• There should be 1 mm space between the occlusion rims in the anterior area at correct VDO• Using 33
• When repeating this word there should be enough space for the tip of the tongue to protrude between the anterior teeth.
2. Phonetics as guide
• Using F or V sounds• The max incisors/occlusion rims should lightly contact the lower lip at the vermillion border when pt pronounces V or F sound.
2. Phonetics as guide
• Silverman ’s closest speaking space• It is not freeway space.
• Freeway space establishes VD when muscles are at rest (static record).
• While it establishes VD when jaws are in the function of speech (dynamic record).
The 2 mm space between the incisors when pt pronounces words containing ‘S’ eg.
2. Phonetics as guide
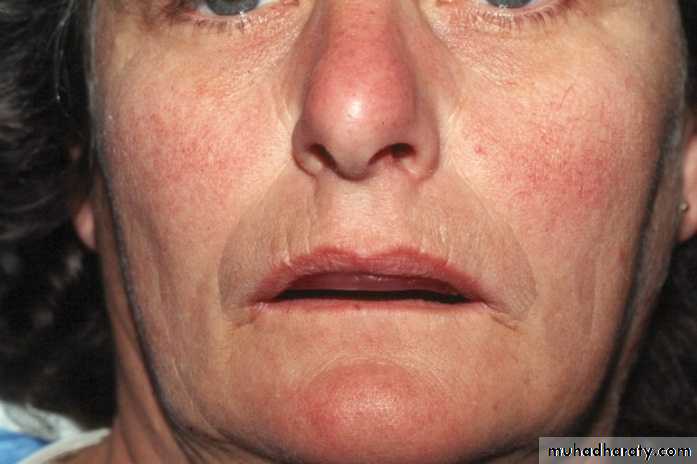
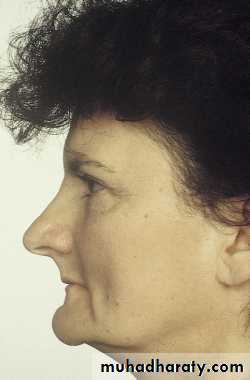
Facial estheticsIn normal relaxed position the lips are even antero-posteriorly & in slight contact.
The skin around the eyes and over the chin will be relaxed.
If face appears strained the VD may be more.
If corners of the mouth droop, making the chin appear too close to the nose, then VD may be too less.
3. Esthetic as guide
3. Facial expression & esthetics as guide:
3. Facial expression & esthetics as guide:
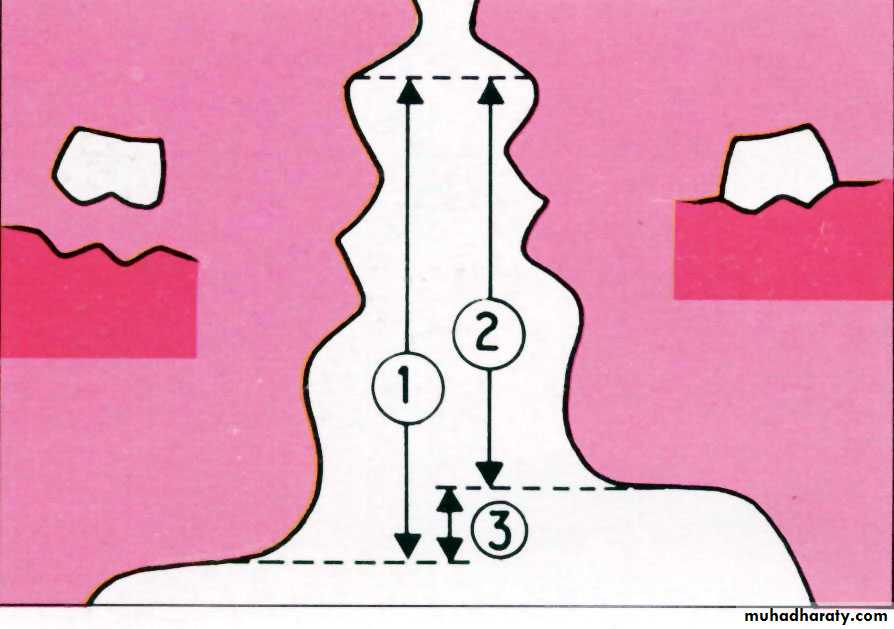
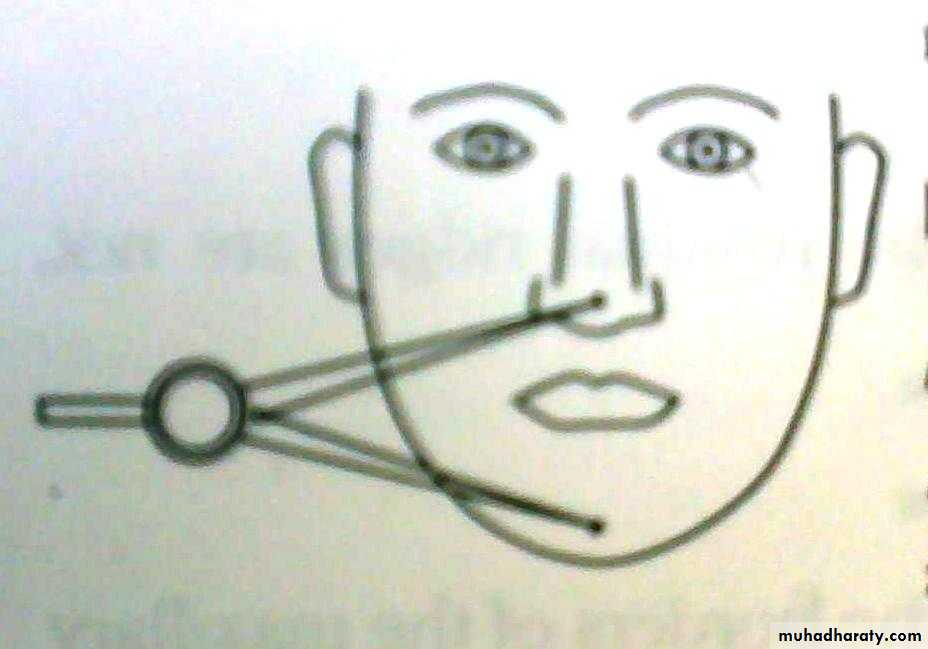
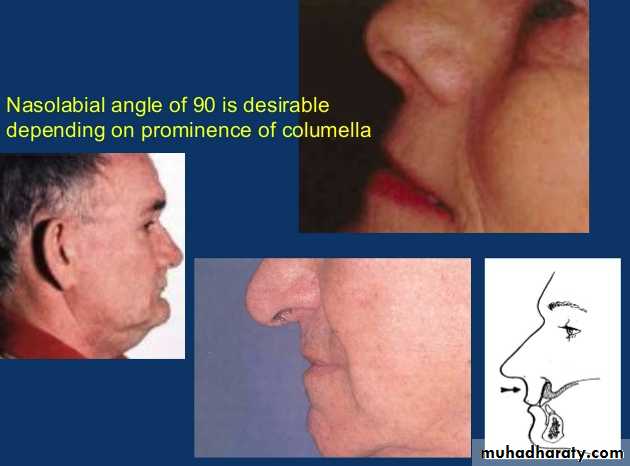
Willis method (facial proportions)Theoretically, distance between the outer canthus of the eye & corner of the mouth should be = to the distance between the lower border of the septum of the nose & lower border of the chin.
4. Swallowing threshold:
The technique is based on the fact that when a person swallows, the teeth come together with a very light contact at the beginning of the swallowing cycle.• Patient’ s tactile sense as guide:
• The patient’s tactile sense is used as a guide• Instruct the patient to stand upright and open the jaws wide until strain is felt in the muscles.
• When the opening becomes uncomfortable, ask him to close slowly until the jaws reach a comfortable relaxed position.
• Measure the distance and compare it.
• Boos bimeter :
• Boos (1940) stated: maximum biting force occurs at OVD.• Bimeter measuring the biting force. It is attached to the mand record base & a metal plate (cenral bearing point) to the maxillary.
• A screw is turned to adjust VR.
• The maximum power point is determined on the spring gauge indicates the correct VDO.Electromyography:
Rest position can be determined by recording the minimal activity of muscles of mastication.Disadvatages:
Not practicalRequires skill
Expensive
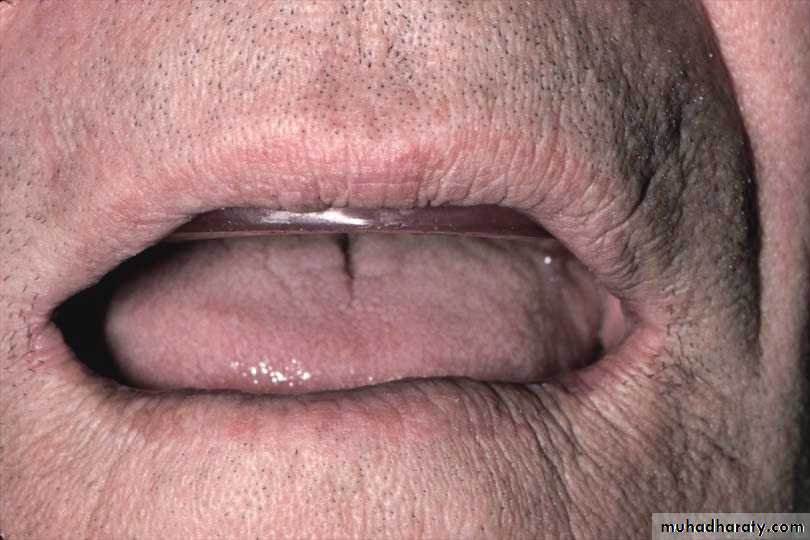
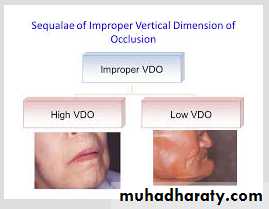
• Decreased chewing efficiency
• Cheek biting: flabby cheek t get trapped.
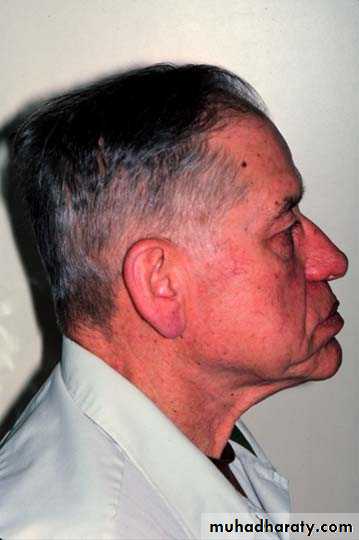
• Appearance: chin appears close to the nose, lips lose their fullness & Vermillion borders are reduced to a line, wrinkles on the face are deepened.
Effects of VD , freeway space
Angular cheilitis: a deep crease forms at the corner of the mouth. Constant wetness due to saliva leads to infection & sorness.
TMJ pain, clicking sounds, headache etc
Costen’s syndrome (now disputed) is due to prolonged overclosure.
Effects of VD , freeway space
• Discomfort & annoyance to the patient
• Trauma to underlying mucosa• Rapid resorption of alveolar bone
• Clicking of teeth
• Rapid wear of acrylic teeth
• Strained appearance (elongated face)
Effects of VD, freeway space
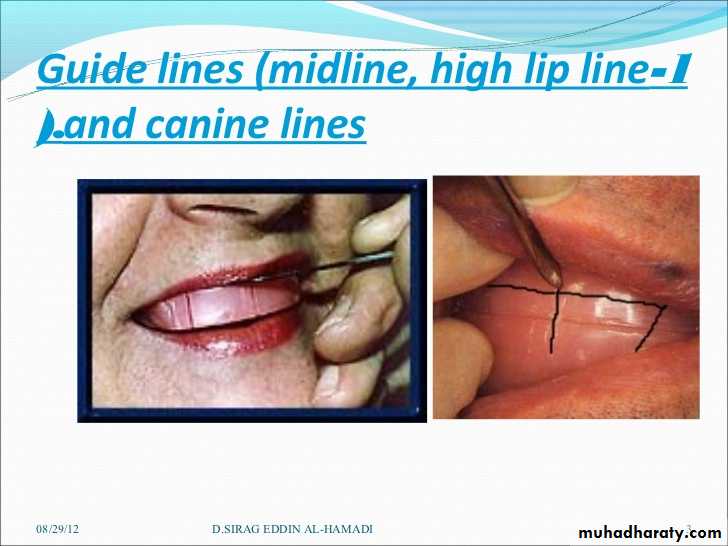
Mid line or center line
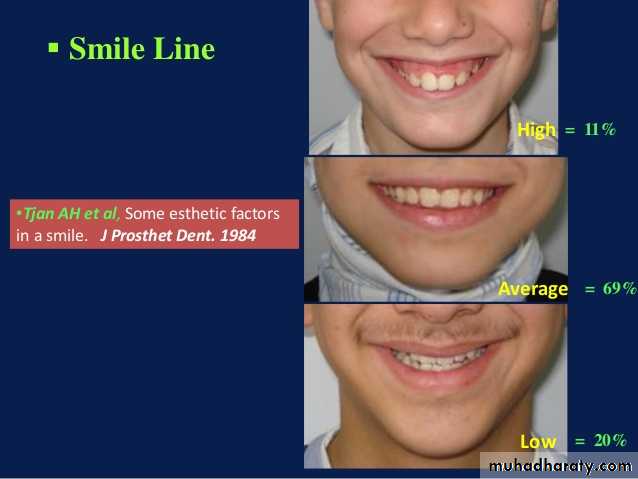
Canine linesHigh lip line (smile line)
Scribing guide lines on the wax occlusion rims
HORIZONTAL JAW RELATION
Horizontal jaw relation
Horizontal jaw relation is the relation that is established antero-posteriorly and medio-lateraly.It is classified as: 1. Centric relation2. Eccentric relation a. Protrusive relation b. Lateral relation i. Right lateral relation ii. Left lateral relation
Centric Occlusion
The relation of the mandible to maxilla in the maximum intercuspation of the teeth’.It is a tooth-tooth relation - a position of habitual closure.
Difficulties in Obtaining Mandiblular retrusion
• Biologic Difficulties• Psychological Difficulties
• Mechanical Difficulties
• Due to lack of coordination between muscles.
• In the edentulous state some pt assume a more prognathic position for convenience.• Old denture wearers assume habitual eccentric positions due to wear of teeth or due to a previous wrong centric.
Senility or other neuromuscular diseases.
1. Biologic difficulties
2. Psychological difficulties
When pt. fails to follow the instruction, dentist may get frustrated, more anxiety in the patient.Important point: dentist ……display his disappointment or frustration to the patient.
3. Mechanical difficulties
Due to ill fitting bases or interferences between bases.
Ill fitting base tend to shift around making observation difficult.
• Let the jaw relax, pull it back and close slowly on the back teeth.• Push the upper jaw out and then close on back teeth.
• Protrude and retrude the mandible repeatedly while pt hold the finger lightly against the chin.
Methods of Assisting the Patient to retrude the Mandible
• Turn the tongue backwards towards the posterior border of the upper denture & close the rims together until they meet.
• Swallow and close. Disadvantage is that pt can swallow in slight eccentric position also.
• Tapping rims together rapidly & repeatedly.
• Tilting the head backward tends to pull the mandible backwards bec. of tension of infrahyoid mus.
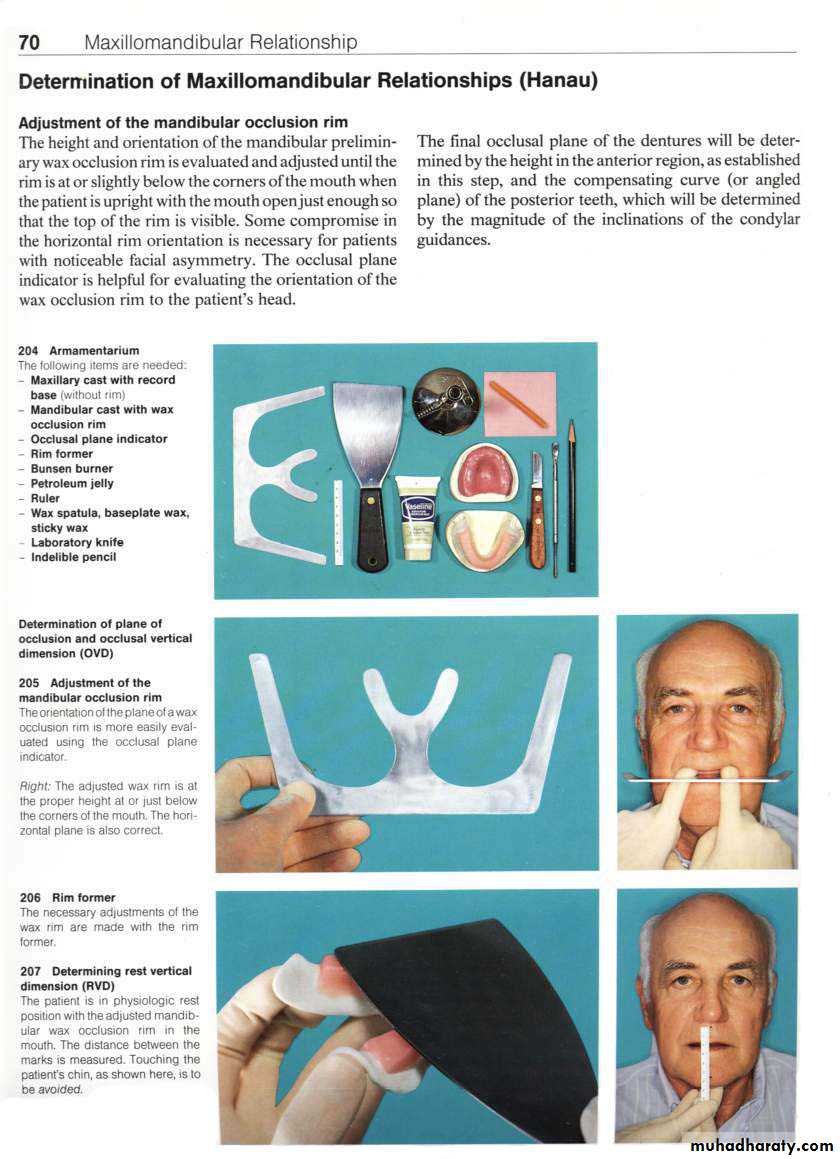
• Massaging or palpation of temporalis & masseter muscles to relax them.
• Boos stretch-relax exercises: open wide & relax, move the jaws to Lt & relax, Rt & relax, forward & relax. This help the pt to coordinate moements & follow the dentist instructions.
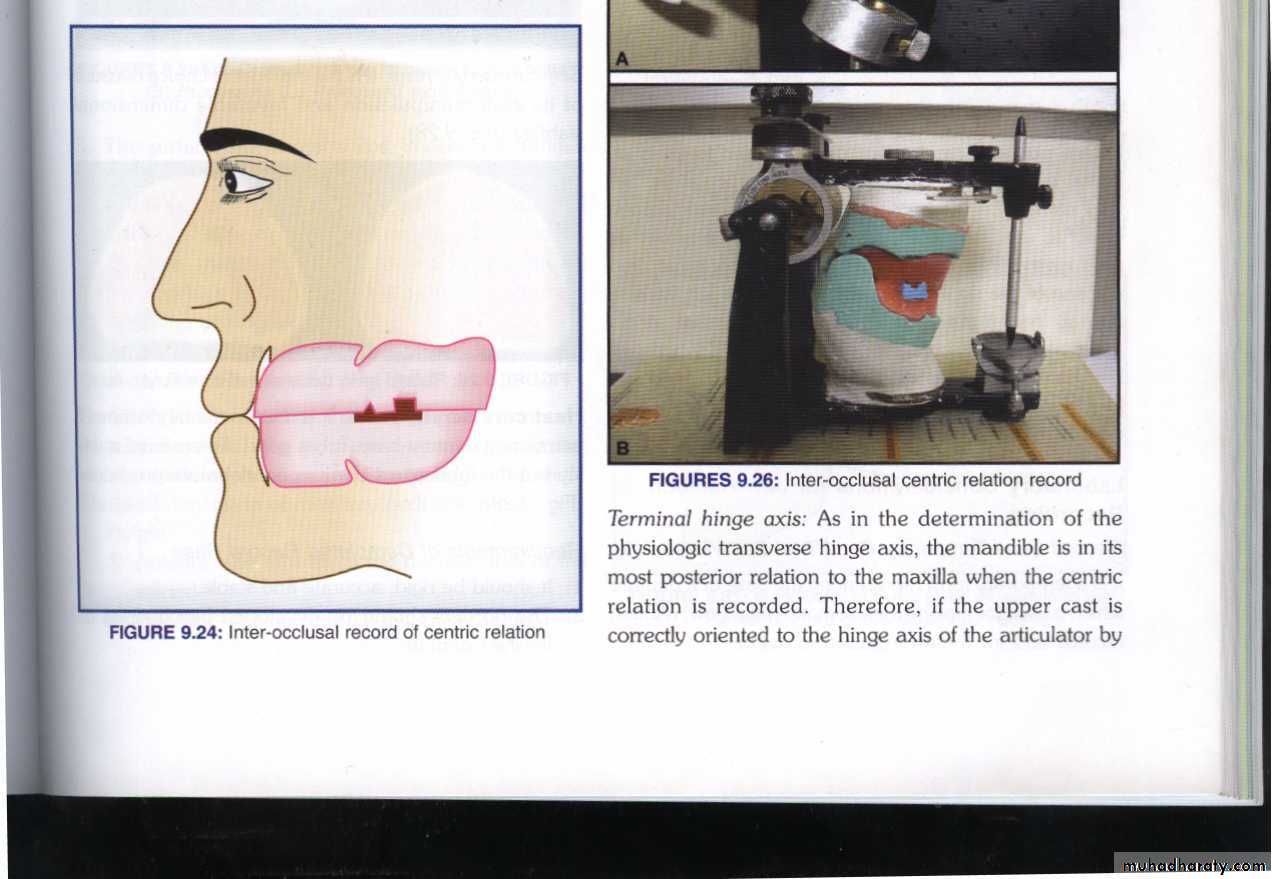
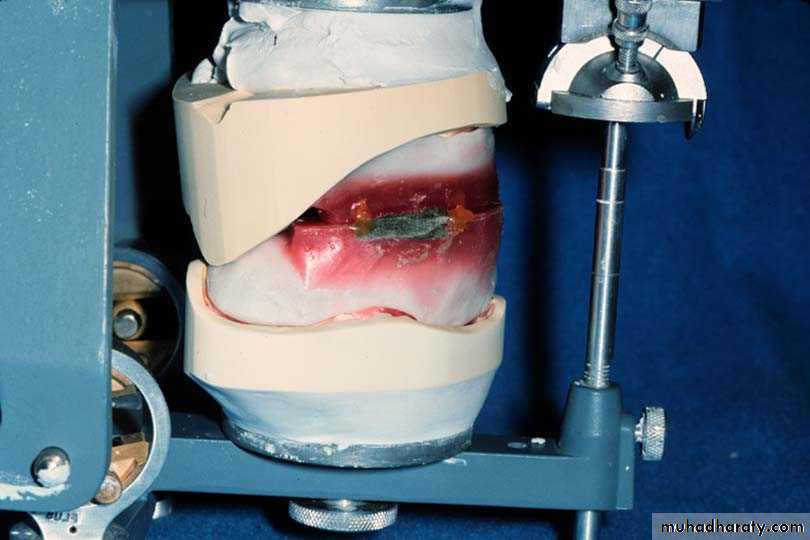
Methods of Recording Centric Relation
• Tactile or interocclusal check records• Functional (Chew-in) methods
• Needle house method.
• Patterson’s method.
• Meyer’s method.
• Excursive methods (Graphic method)
• Intra oral tracing
• Extra oral tracing
• Terminal hinge axis method
• Other methods
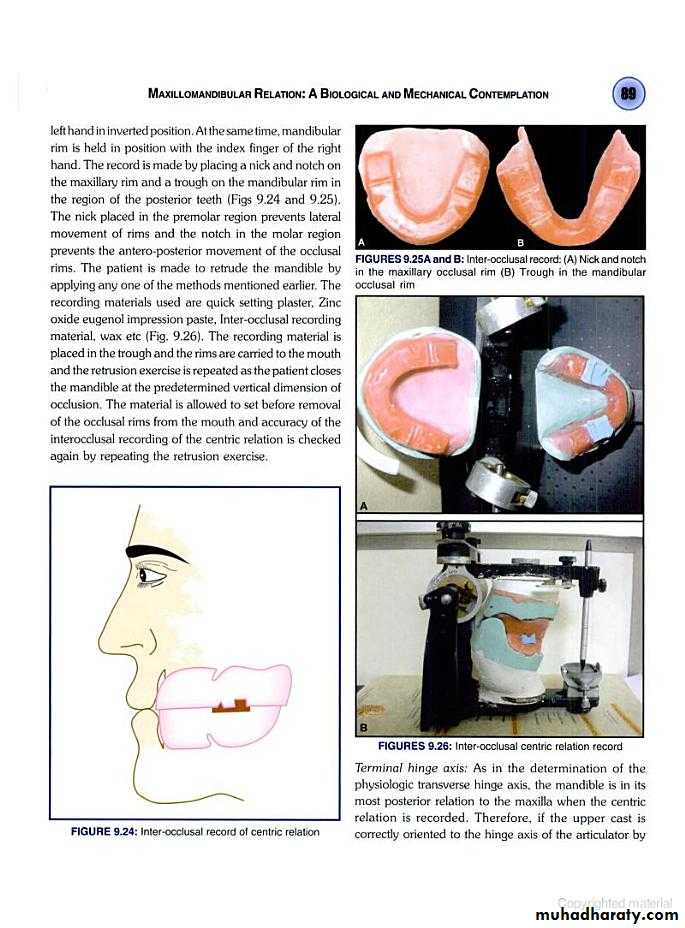
Bite registration…… interocclusal record.
Most widely used.Method
Training the pt. to retrude the mand.
Indexing the rim
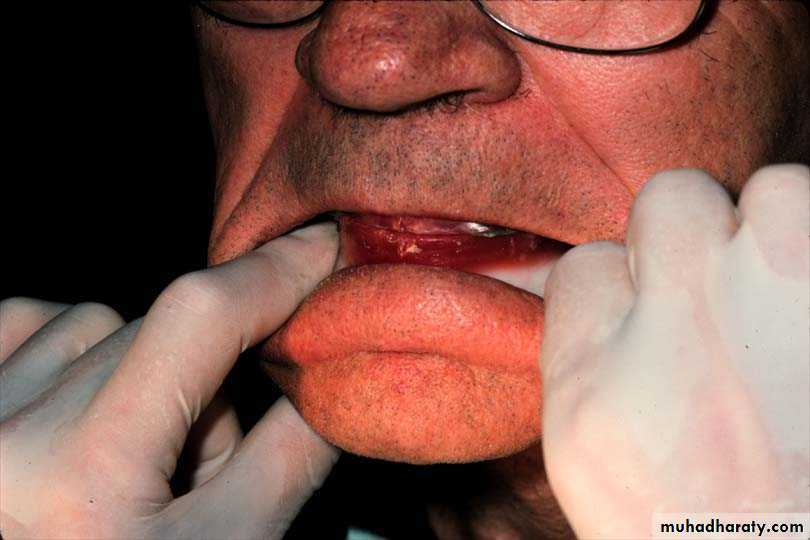
Recording centric
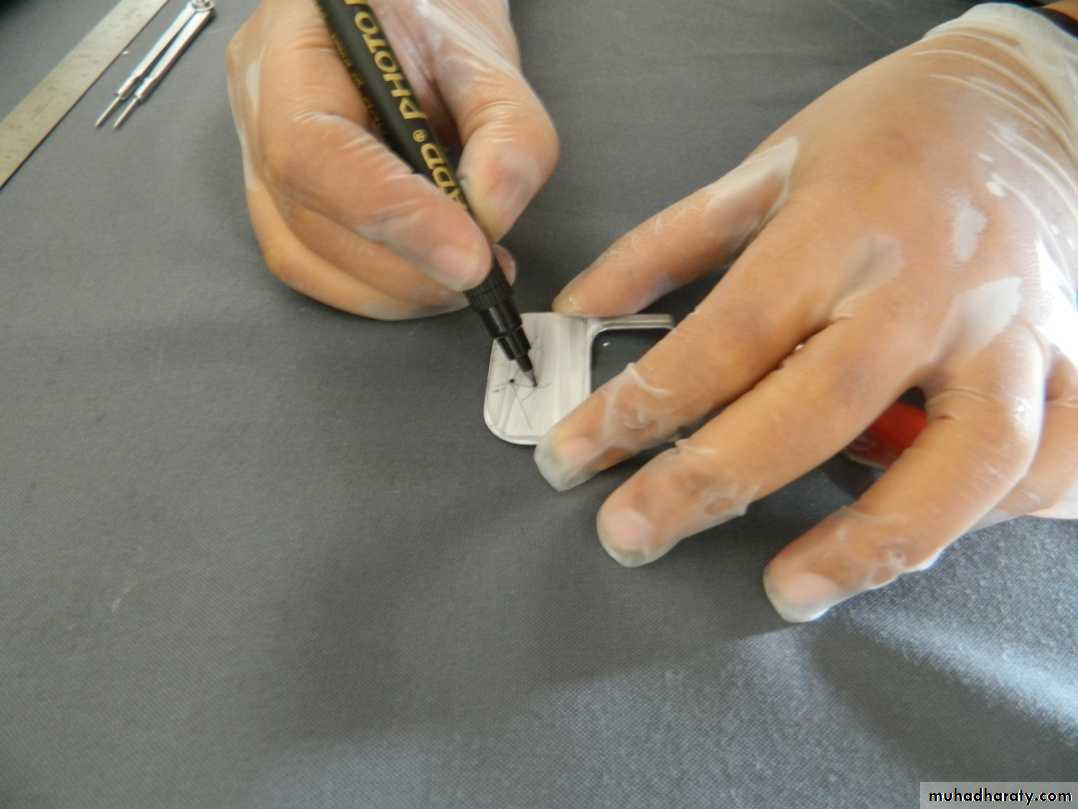
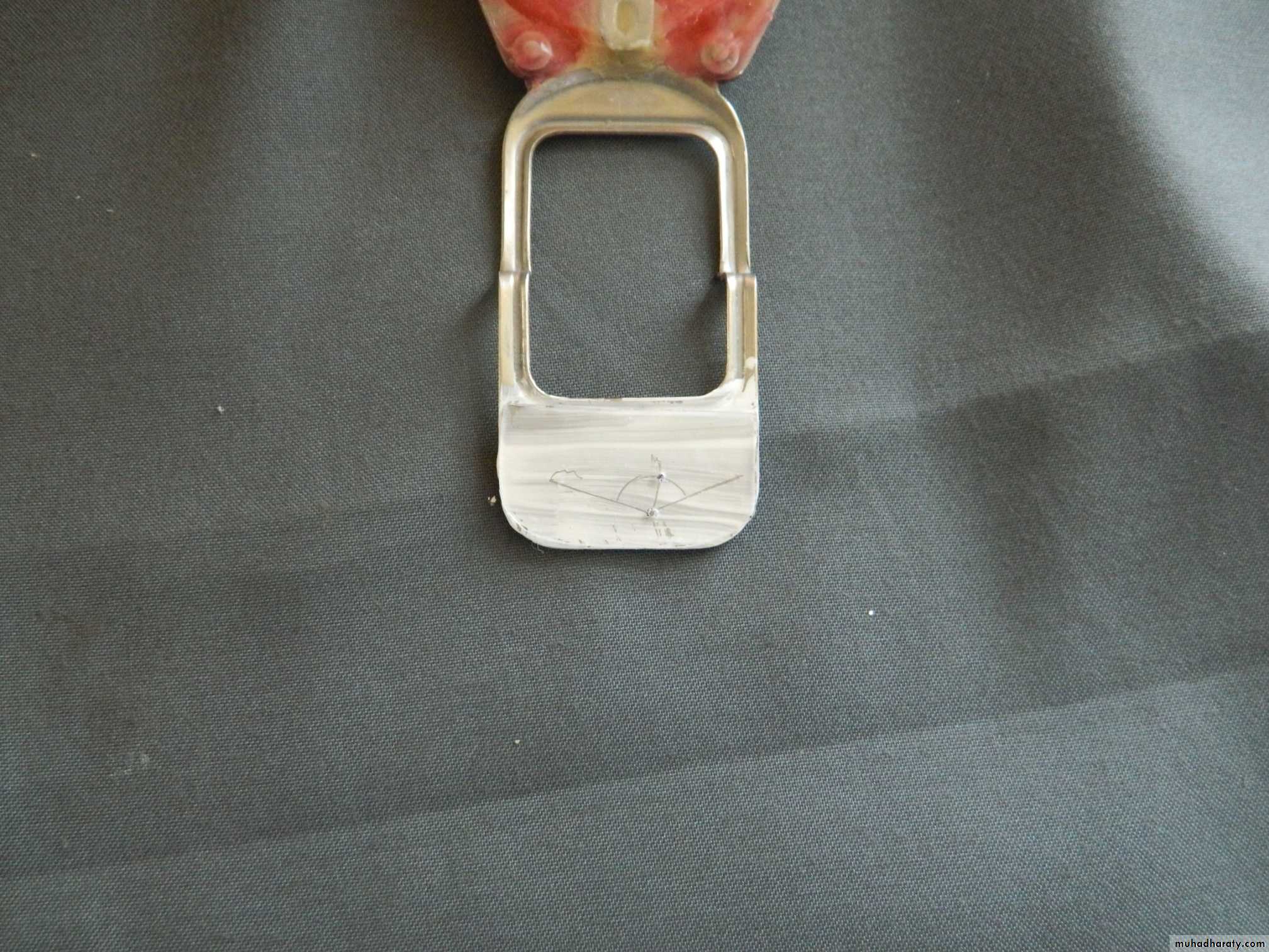
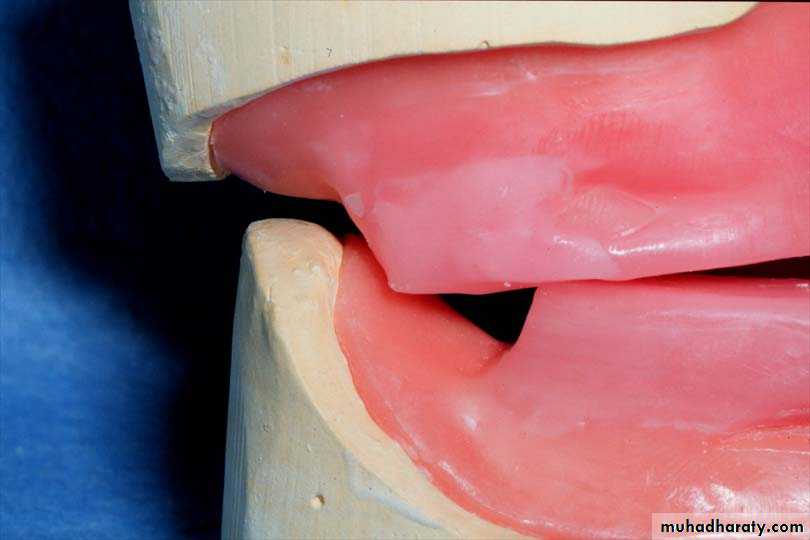
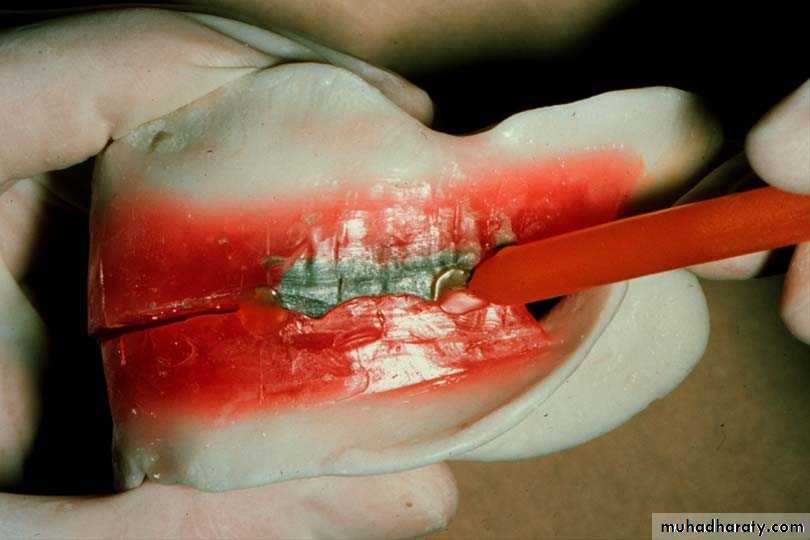
1. Interocclusal check records
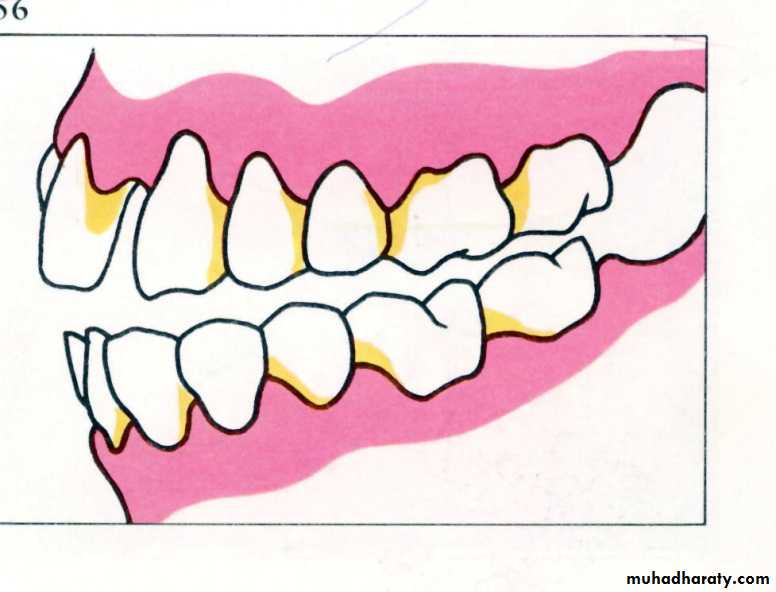
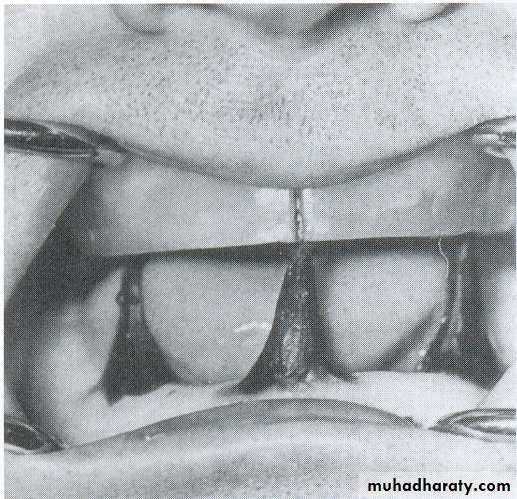
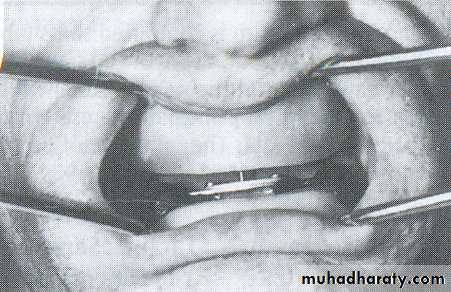
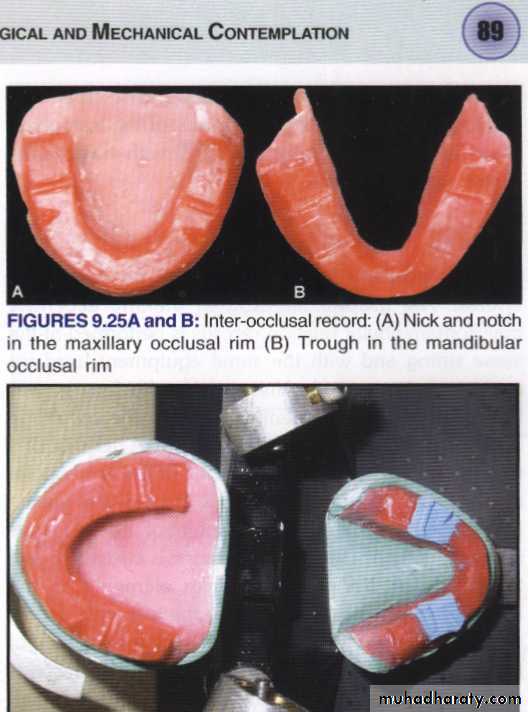
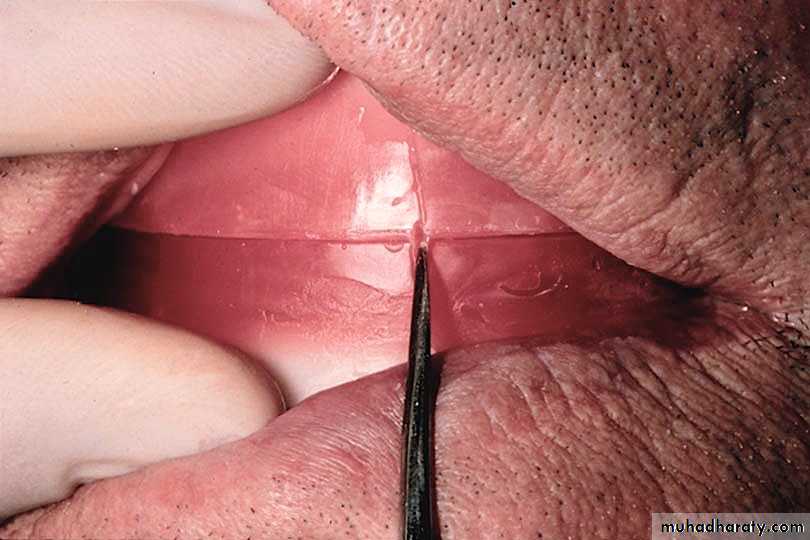
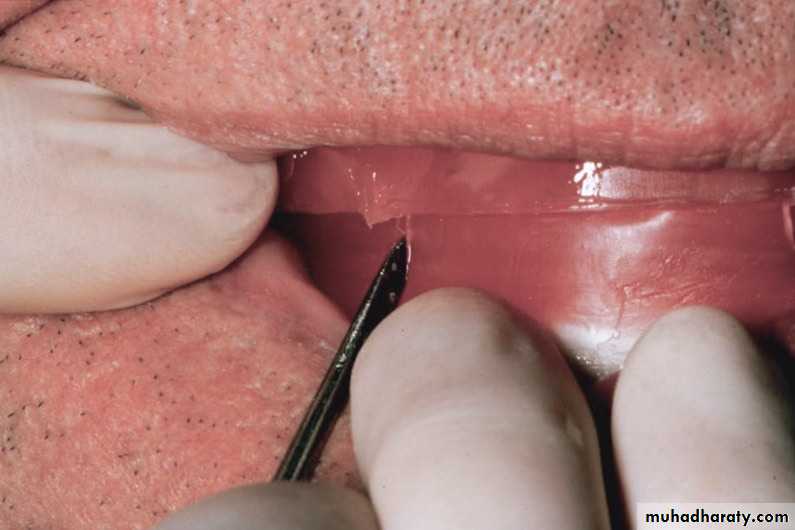
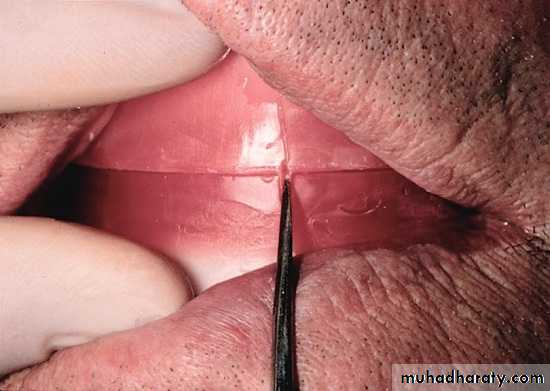
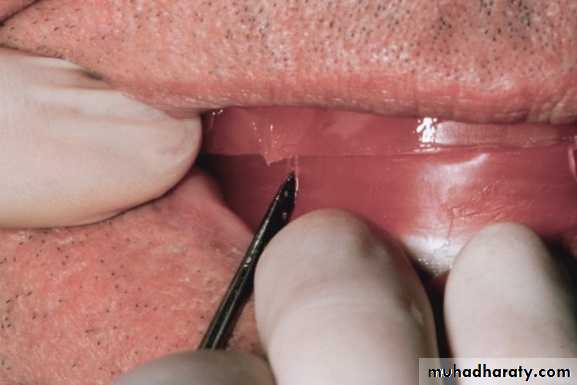
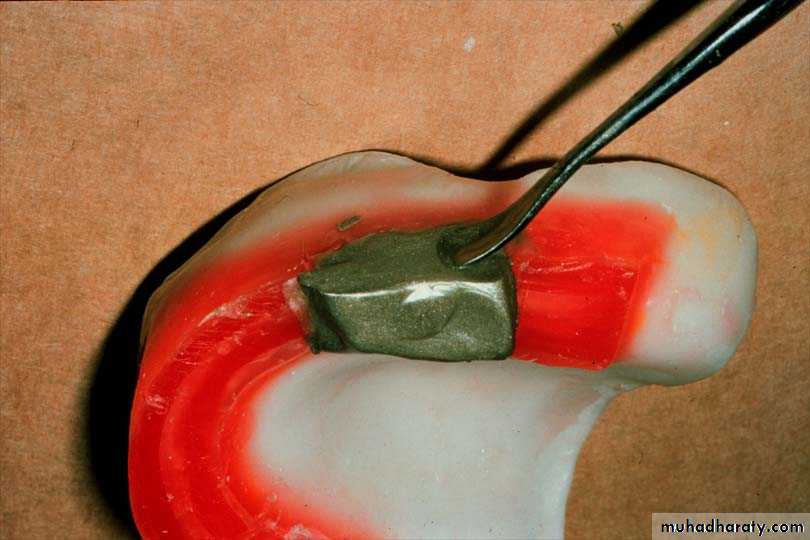
Nicks and notches created on the max. rim (premolar region) to (prevent lat. Movement)
A small section of the wax is removed from the lower rim (trough) to create space for registration material.The indices should be sharp & well defined.
Ensure Adequate Notch Depth
Too Shallow- no undercuts
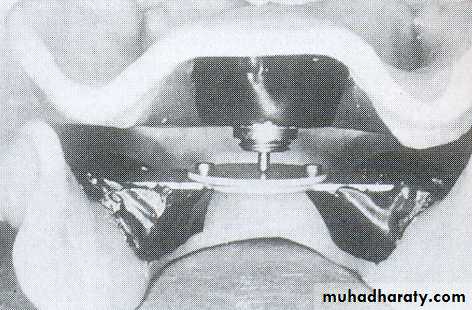
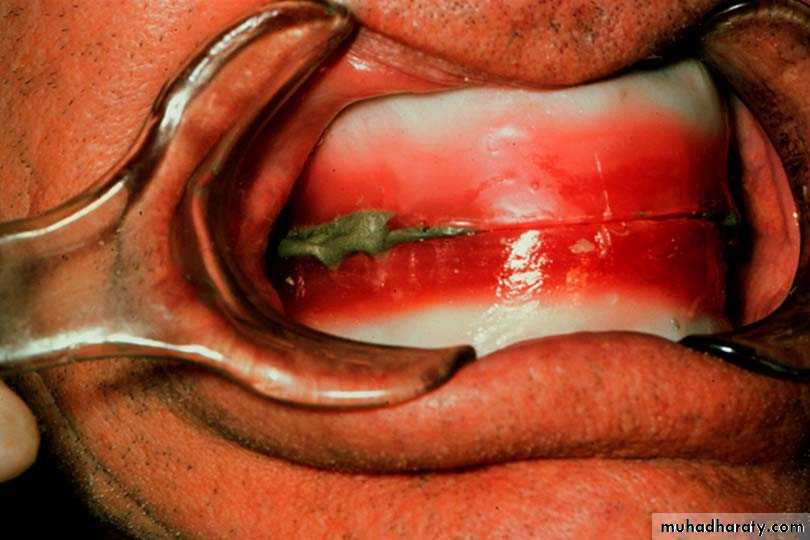
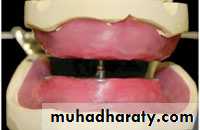
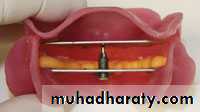
• Place 3 widely separated lines between the rims in the centric position• CRITICAL! Check that record base heels, record base/occlusion rims/casts do not touch
• Only contact should be rim to rim
• between record bases,
Bite registration material
Quick setting plaster.Bite registration ZOE paste,
Bite registration wax
Bite registration silicon
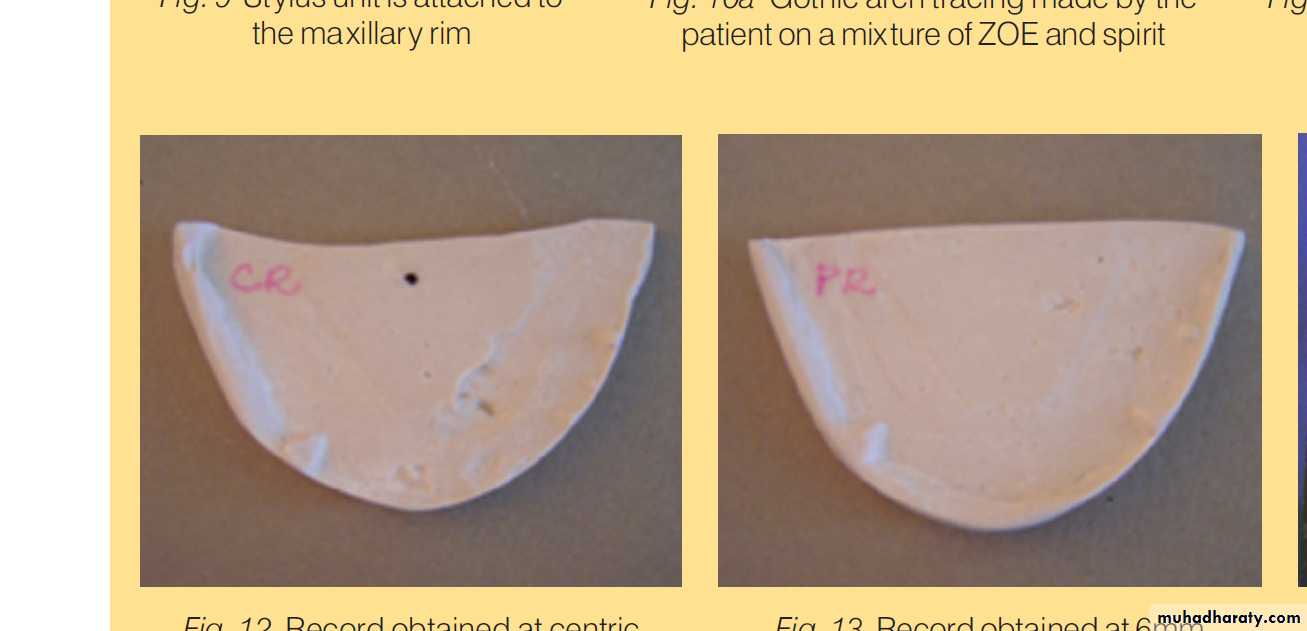
Nick and Notch method
Too shallow
2 mmMounting of the casts
`
Any Q?
2. Functional (chew-in) methodsMeyer’s method
Patterson’s method
Needles-House method
Meyer’s method
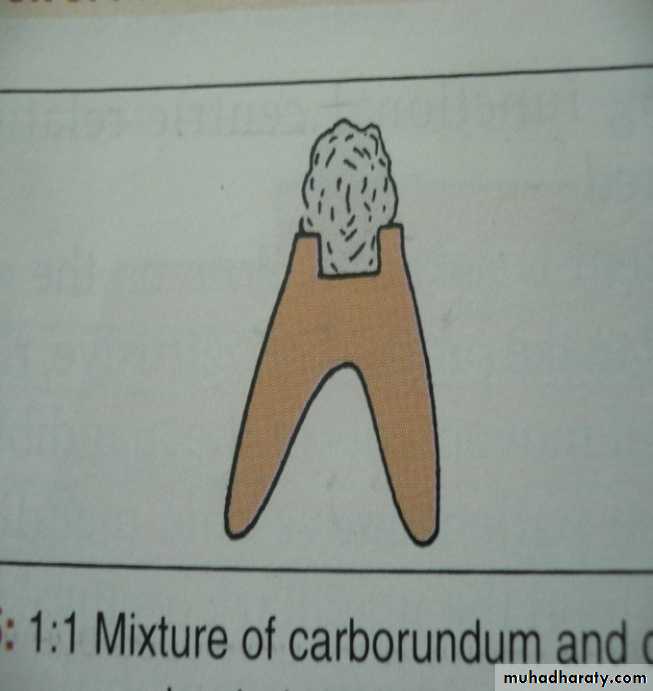
Soft wax - generated pathPlaster index made of wax path …. set the teeth
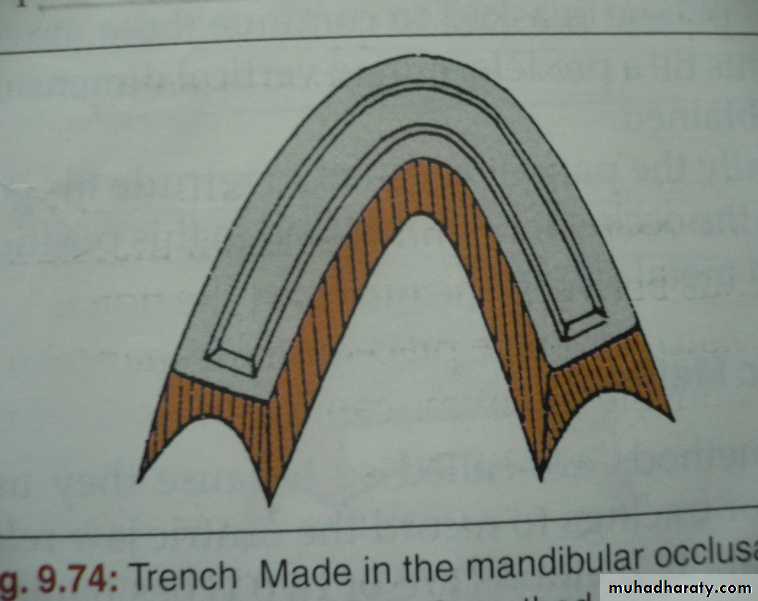
• Trench in lower wax occlusal rims
Fill with mixture of half plaster &Half carborundum in the trench
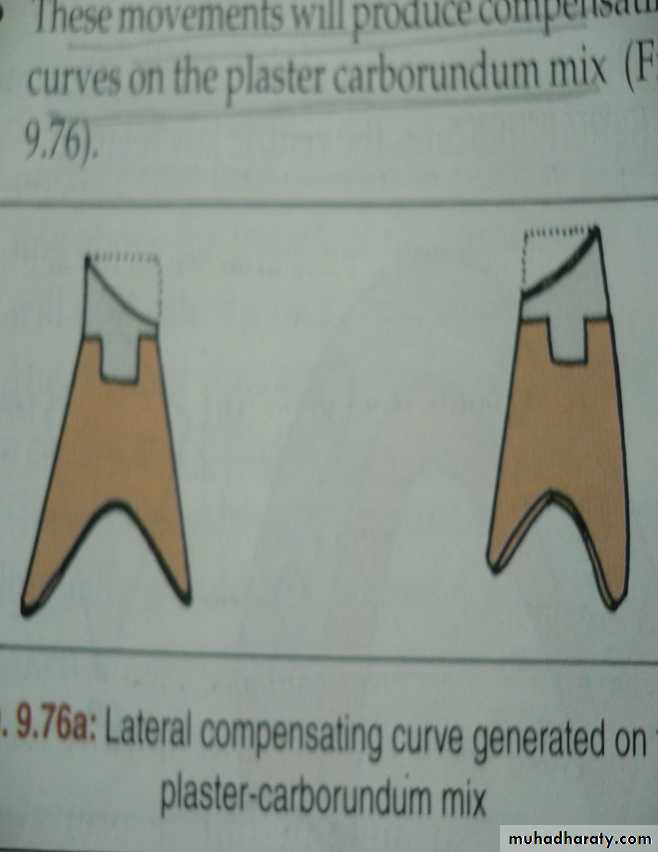
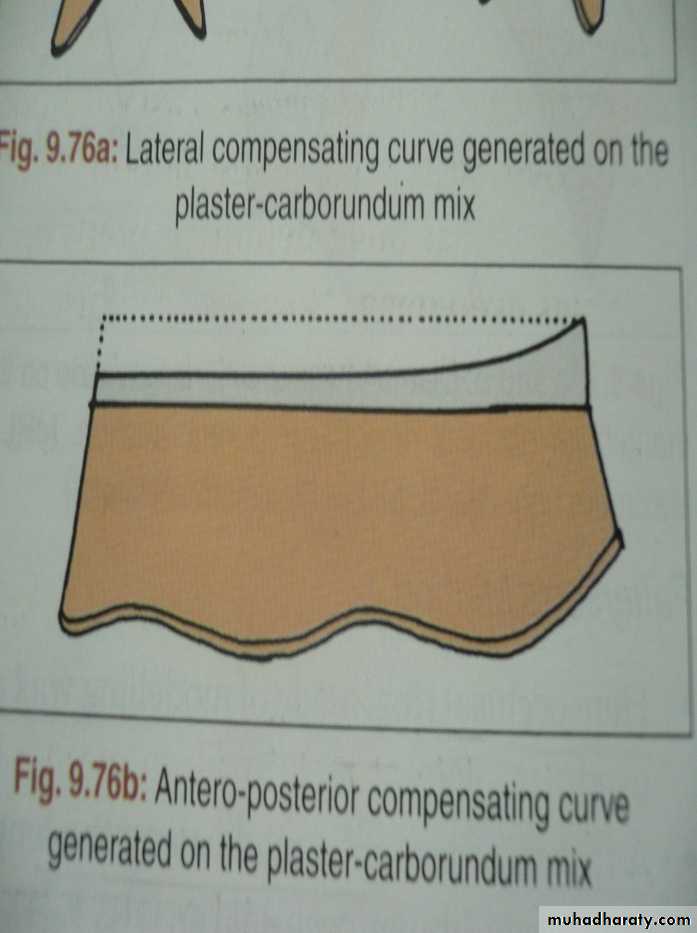
Compensating curve generated.
Needles-House method
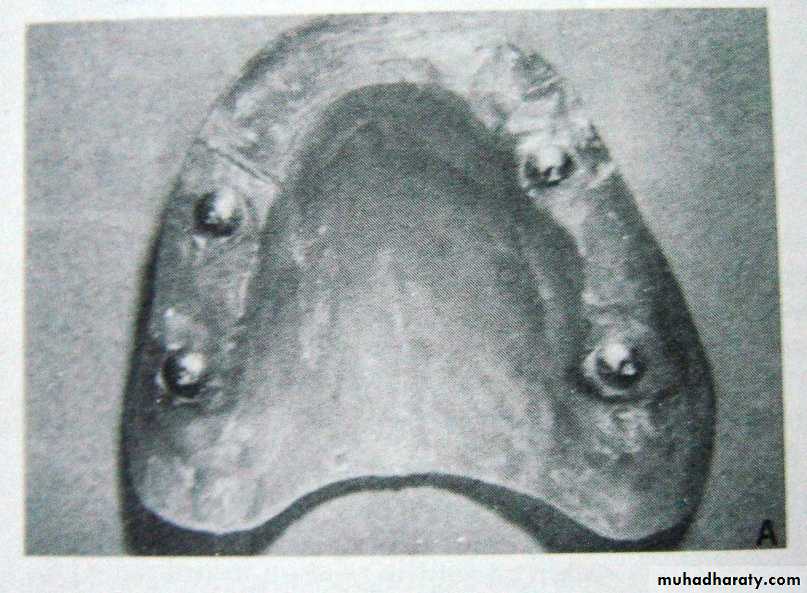
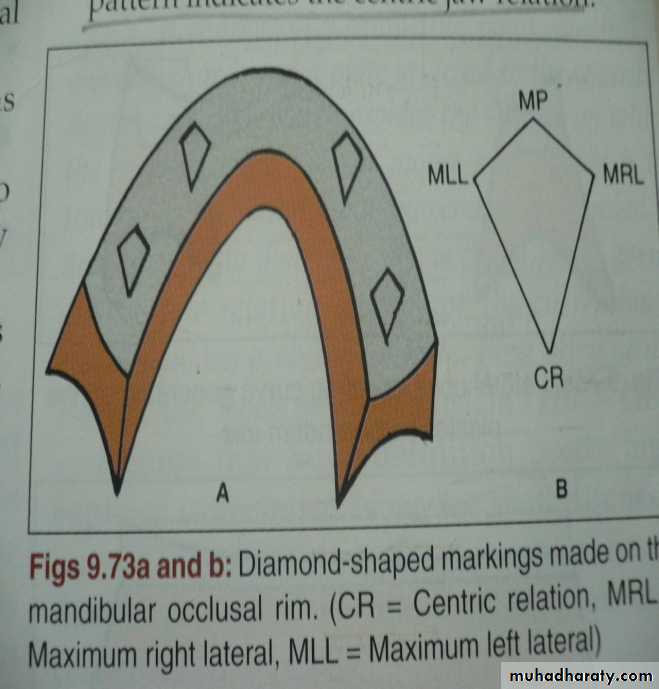
Four metal styli fixed on upper compound occlusion rims.Carve 4 diamond-shaped tracings on lower rim as mandibule move through various movements.
Records transferred only to Needle House articulator.3. Excursive (graphic) methods
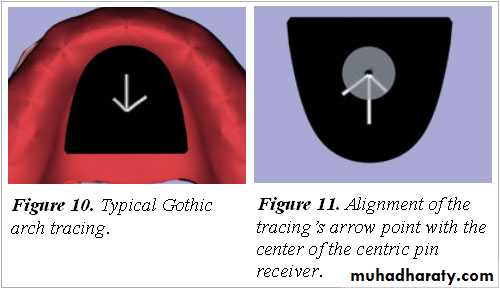
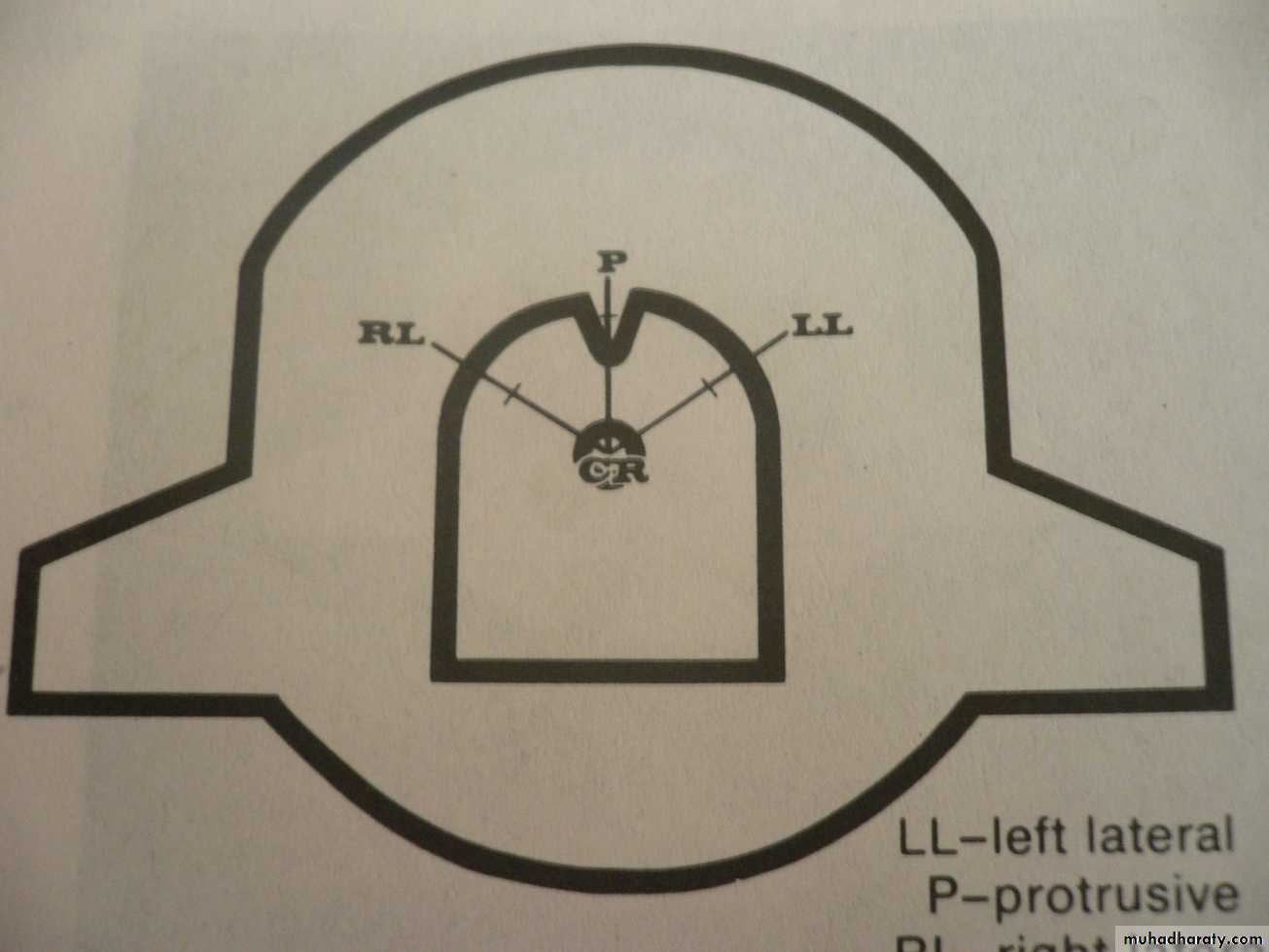
synonymsGothic arch tracing
Arrow point tracing or high tracer
Types
Intraoral (arrow points posteriorly)
Extraoral (arrow points anteriorly)
Uses
Verify centric relation
Obtain protrusive & lateral records
Before using tracing device:
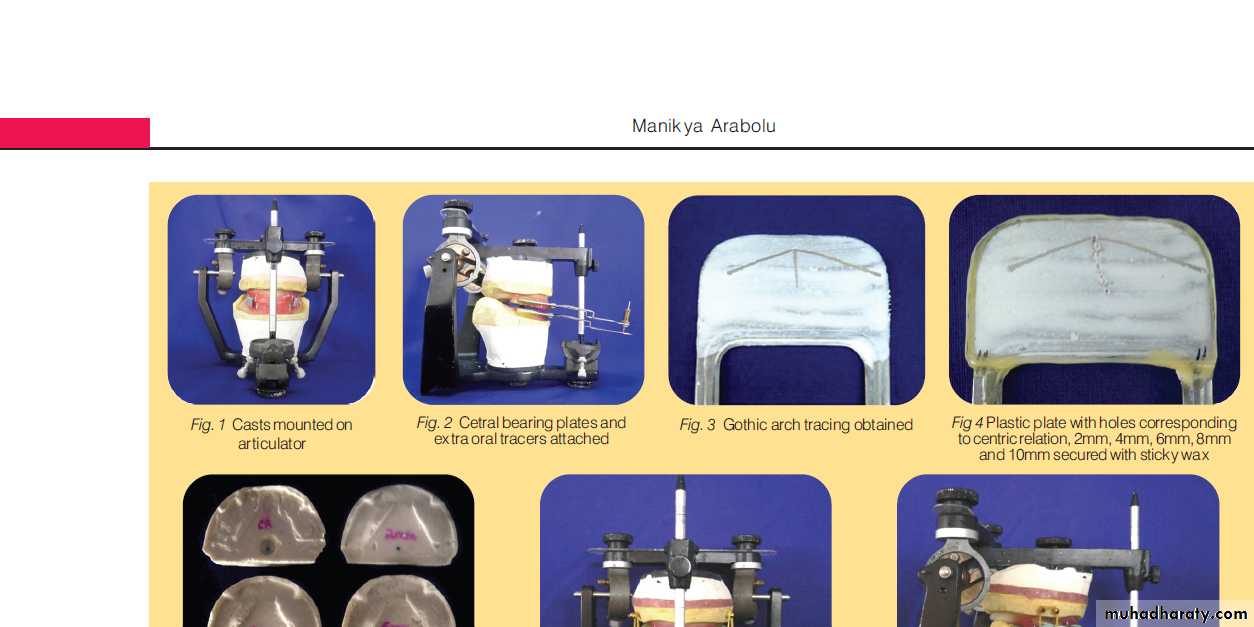
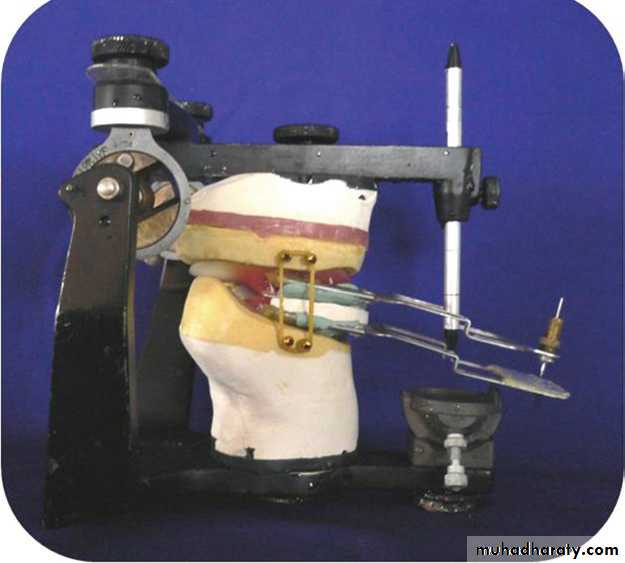
Occlusion rims mounted on articulator using tentative CRTracing devices attached to rims
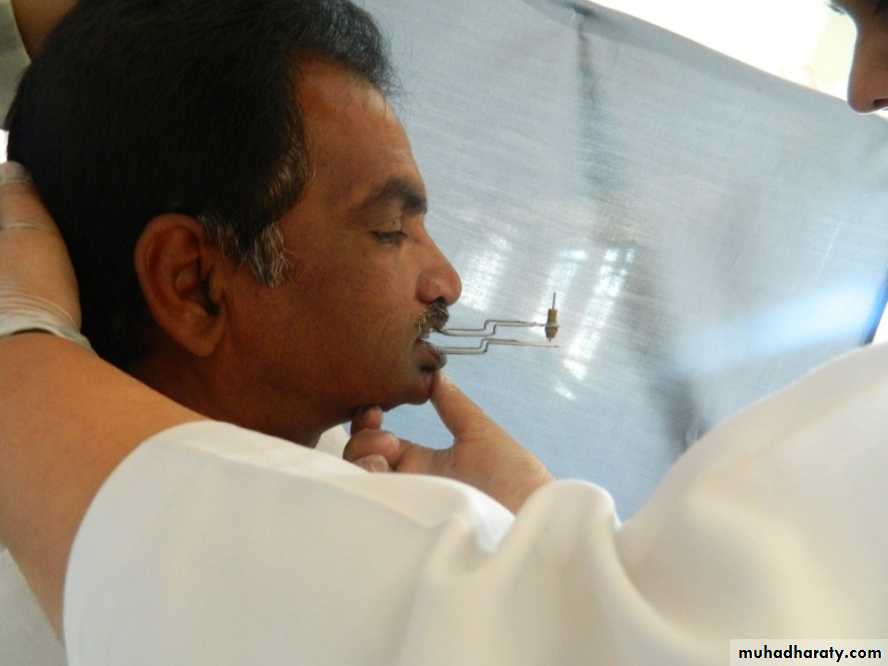
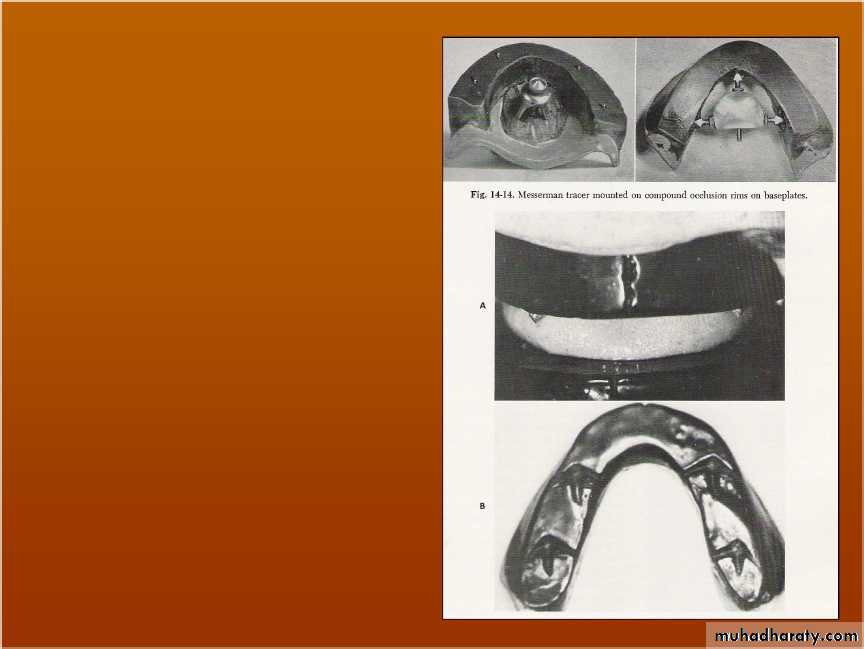
Intraoral tracing (IOT) assembly
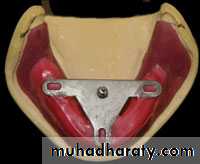
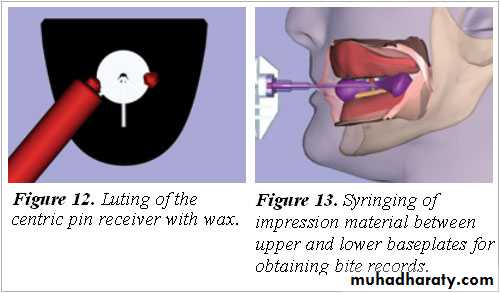
Central bearing plate … upper romBearing pin or stylus …. Lower rim
Plate cover w marking sub (carbon, ink or wax)
Height of pin adjusted by screw till it touches the plate
Pt instructed to perform protrusive, Lt lateral & Rt lateral several times.
Intraoral tracing (IOT)
Stylus traces an arrow point on the plate crroesponding to the movements.A sharp apex indicate accurate CR
Record transferred to the articulator & cheking the previous CR.
If previous CR is wrong, remount the cast w new record.
Advantages: strong enough to resist biting pr.Disadvantages:
• Being IOT, tracing is difficult to see, … guiding the pt dificult
• IOT is very small … difficult to find the apex.
Intraoral tracing (IOT)
Extraoral tracing (EOT)
Alwayas combined w IOT device to equalize pr.Plate attached to lower & pin to the upper rim.
Procedure is similar to IOT
Advantages:
• Tracing point is larger, apex better visualized.
• Since tracing is visible, pt guided more inteligently.
Extraoral tracing
Parts of arrow point tracer
• Tracing assembly: consist of tracing table & stylus.Stylus traces the Gothic arch on tracing table.
In EOT tracing assembly located outside the mouth, & in IOT located inside the mouth.
• Central bearing plate: consist of small fixed ball & a plate.
Located inside the mouth between 2 occluion rims.
They maintain the VR during mandibular movements.
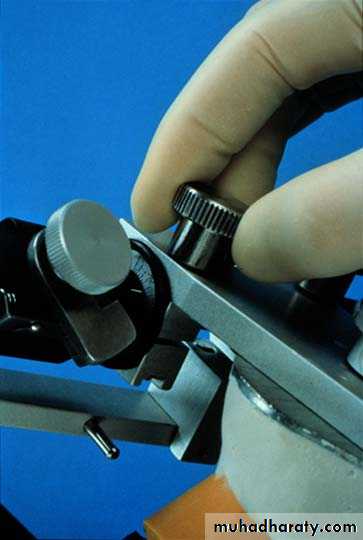
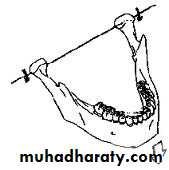
Terminal hinge axis
Kinematic facebow is used
Other methods
Strips of celloloid: after adjusting the rims strip of celloloid placed bet rims & pulled.If it pulls out easily … uneven contact … rims readjusted.
Disadvantages: present of unequall pr error
Deep beating or pooling of post portion of lower rim leaving the ant portion cold to maintain OVD.
Other methods
Softened wax placed on lower post teeth 7 upper post close into it.Advan: small sur contact instead of large flat wax sur.
Disadv: record sh be made at increase VD to avoid teeth contact.
Swallowing tech using soft cones of wax
2. Eccentric Jaw Relations
Eccentric relation: It is the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla other than the centric position.Eccentric relation a. Protrusive relation b. Lateral relation (Right & Left)
Importance necessary to program an adjustable articulator to simulate pt jaw movements.
Programmed articulator, helpful in constructing a balance denture occlusion.
Methods of recording
Functional
Excursive (graphic)
Direct check records
2. Eccentric Jaw Relations
Protrusive position
It is used to program the horizontal condylar guidance which together w the incisal guidance guides the Protrusive movement of the articulator.2. Eccentric Jaw Relations
Christensen’s phenomenon
Protrusive records are made byDirect protrusive check record:
Training the pt
Pt protrude by 5-6 mm & close
Position is record using suitable recording mat.
Graphic method using Gothic arch tracing
Ask the pt to protrude & close at a point 5-6 mm forward of the apex of arrow point (CR).Position is record using suitable recording medium.
Protrusive records are made by
Protrusive interocclusal record (Hanau)
Lateral jaw relations
When mandibule moved to one side, a separation observed between occlusion rims on the opposite side.This is result of downward displacement of condyle (balancing side)as it travels downward & medially along the medial slope of mand fossa (known as Bannett movement).
Application It is used to program the Lat condylar guidance which together w the incisal guidance guides the Lat movement of the articulator.
This can be done only in articulator that accepts Lat relation recorde.
Hanau semiadjustable articulator donot accept Lat relation records, a formula is used to drive the Lat condylar guidance.
Lateral jaw relations
Recorded Like protrusive relation using
FunctionalExcursive (graphic)
Direct check records
Recording Lateral jaw relations
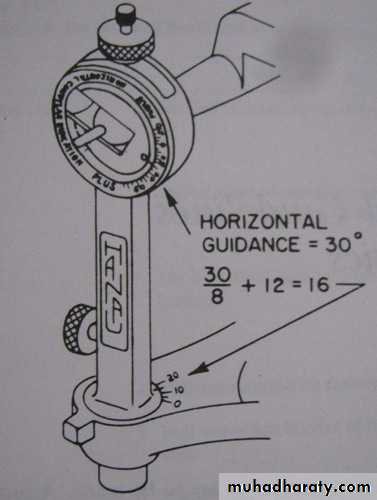
Hanau’s Formula: at 1930 Hanau recommended this formula:L = H/8 + 12
L = Lateral condylar inclination (in degree)H = Horizontal condylar inclination (in degree)