د. احسان كيمياء حياتية 7\12\2017
عدد الاوراق ( 3 ) م\2\موصل lec: 6Gluconeogenesis
It is the term used to define all the pathways responsible for converting noncarbohydrate precursors to glucose or glycogen. These non carbohydrate precursors include glucogenic aminoacids,lactate and glycerol.Gluconeogenesis takes place in liver and kidney.
Gluconeogenesis meets the need of the body for glucose to supply energy especially for nervous system and erythrocytes.
It clears lactate produced by RBC and muscle. Also it is important to drain glycerol produced by adipose tissues.
Failure of gluconeogenesis is fatal.
Pathways of gluconeogenesis
Reversal of glycolysisThree reactions provides pathways for inversion of glycolysis
1.the mitochondrial pyruvate carboxylase convert pyruvate to oxaloacetate this is irreversible reaction expends ATP in the presence of biotin as a coenzyme.
Oxaloacetate does not cross the mitochondrial inner membrane and is converted to malate in the mitochondria by kreps cycle catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase ,malate is transported to the cytosol where it is converted back to oxaloacetate by the same enzyme!
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the carboxylation and phosphorylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate this is irreversible reaction requires GTP(guanosine
triphosphate) as phosphate donner.
2.The conversion of fructose 1 ,6 bisphosphate to fructose 6 phosphate this is catalyzed by fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase .
3.Conversion of glucose 6 phosphate to glucose via the action of glucose 6 phosphatase.
By the reversal of glycolysis and citric acid cycle glucose can be formed from the following non carbohydrate precursors :
1. Glucogenic aminoacids after transamination or deamination they yield either pyruvate or intermediates of citric acid as αketoglutarate ,oxaloacetate,or fumerate. Alanine is the most important aminoacid transported from the muscle to the liver during fasting ,it will be converted to pyruvate by transamination and enter into gluconeogenesis this cycle is called glucose –alanine cycle.
2.Lactate can be converted to pyruvate by the
lactate dehydrogenase .Lactate formed in RBC and skeletal muscle (anaerobicaly) transported to liver and kidney for gluconeogenesis,this prossess known as Cori cycle
3.Glycerol from fatty acid oxidation ,can enter the gluconeogenesis through its conversion into dihydroxyactone phosphate through the following pathways:
Hormonal control of carbohydrate metabolism
1.Glycolysis is stimulated by insulin and inhibited by glucagon and epinephrine.2.Glycogenesis is stimulated by insulin and inhibited by glucagon and epinephrine.
3.Glcogenolysis is stimulated by glucagon and epinephrine and inhibited by insulin.
4.Gluconeogenesis is stimulated by growth hormone ,glucocorticoids,glucagon and epinephrine,it is inhibited by insulin.
Blood glucose level
The concentration of blood glucose is regulated within narrow limits ranging from 3.3 mmol/L(60 mg/dl)in starvation ,up to 7.2 mmol/L(130 mg/dl) after the ingestion of a carbohydrate meal. A sudden decrease in blood glucose will cause convulsion due to the immediate brain dependence on a supply of glucose.
Glucosuria
Normally glucose is continuously filtered by the glomeruli but its completely reabsorbed in the renal tubules, therefore, normally there is no glucose in urine.This happen when venous blood glucose concentration is exceeding the renal threshold for glucose (171- 180 mg/dl).
The presence of glucose in urine (glucosuria) suggest :
1.Hyperglycemia when venous blood glucose concentration exceeds the renal threshold for glucose as occurs in diabetes mellitus.2.Reduction of renal threshold for glucose as occur in renal glucosuria which is harmless condition with no obvious cause for it. Also it could happen in normal pregnancy due to hypervolemia that occur during pregnancy.
Diabetes mellitus
It is a family of disorder that is characterized by hyperglycemia. These disorders differ in their etiology ,symptoms and complications. In Mosul 10-15 % of population have diabetes.Classification of diabetes
Type 1 diabetesType 2 diabetes
Gestational diabetes
Other specific types
Type 1
It usually represents about 5-10% of diabetes and is due to lack of insulin production by beta cell of pancreas. It manifests itself usually in childhood and adolescents. Treatment by insulin so it is called insulin dependent ,together with diet and exercise. It could be immune mediated in which there is auto antibodies that destruct the β cells.
And it could be ideopathic in which there is no obvious cause .
Type 2
It forms the most common cases and it is either due to insulin insufficiency or insulin resistance i.e decrease responsiveness to insulin by the cells. It is poly genic which mean that hereditary and environmental factors precipitate the disease (obesity , sedentary life style, over stress, increasing age, hypertension ,hyperlipidemia and others) usually affects obese people older than 40 years old treatment by oral drugs ,reducing body weight, diet, exercise ,if fail then insulin is used.Gestational diabetes
It is defined as diabetes diagnosed first time during pregnancy it affects about 4% of pregnant women . during pregnancy there is reduction of cellular response (insulin resistance). Most pregnant women compensate with increasing secretion of insulin , those who are unable to compensate may develop diabetes.It fades away after delivery ,but the woman becomes at risk at future of diabetes.
Other types of diabetes
Disease of exocrine pancreas such as cystic fibrosis.Endocrinopathies as cushing´s syndrome.
Drug triggered as glucocorticoids .
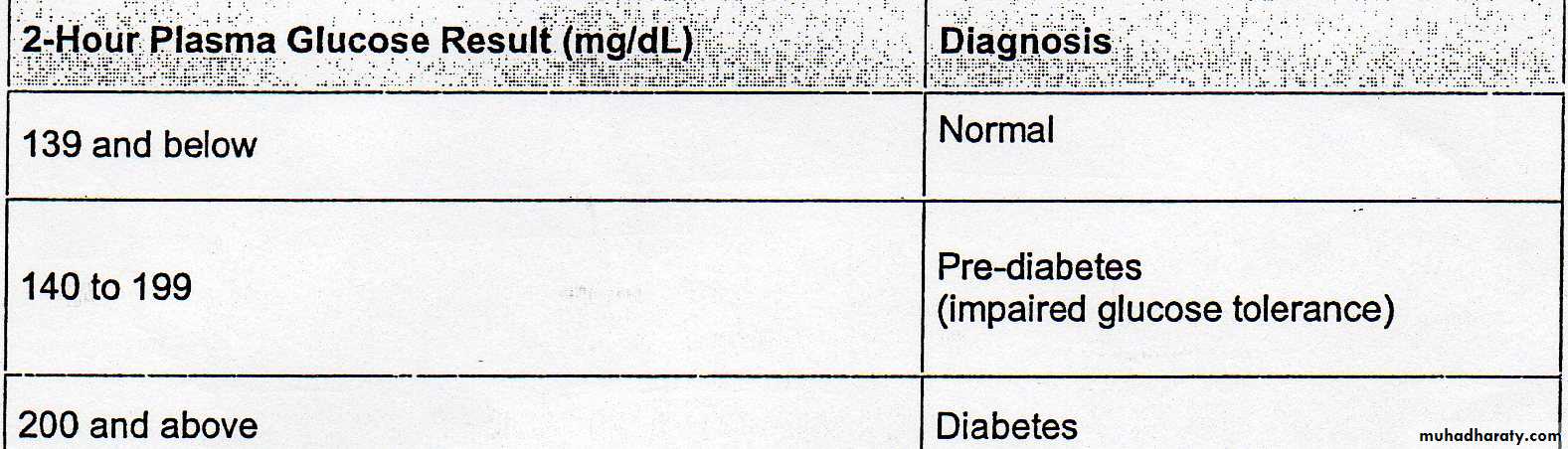
Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose ….prediabetes
They represent a borderline stage in which blood glucose is higher than normal and lower than diabetes. It is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.20-30% of those people will have overt diabetes within 10 years.Oral glucose tolerance test OGTT
Measure plasma glucose after 8 hours fasting and two hours after oral glucose load of 75 grams in 300 ml water . It is more precise .
Random plasma glucose measure glucose any time post prandial, if level of glucose exceeds 200mg% it is consider diabetes mellitus.