Pain sensation
Pain sensation
Pain is a protective mechanism.
Pain occurs whenever any tissues are being damaged, and it causes the individual to react to remove the pain stimulus.
Types of Pain
Two major types: fast pain and slow pain.Fast pain (acute pain or sharp pain):
-Is felt within about 0.1 second after a pain stimulus is applied. In general, fast pain is elicited by the mechanical and thermal types of stimuli. Fast-sharp pain is not felt in most deeper tissues of the body.
The fast-sharp pain can be localized much more exactly in the different parts .
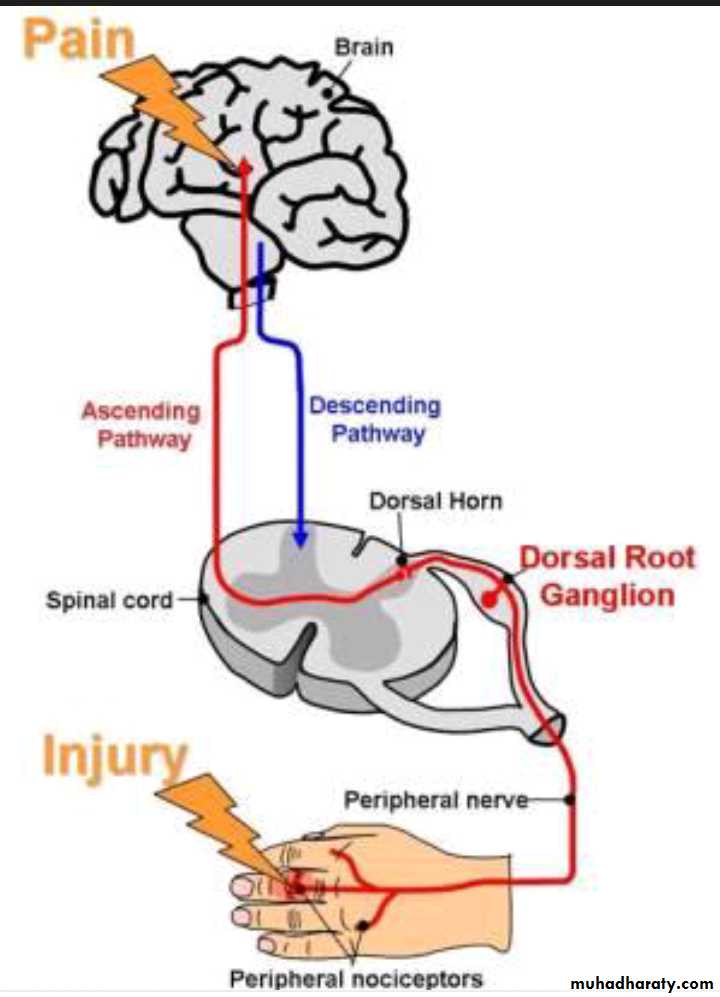
Transmitted to the spinal cord by small type A-d fibers.
It is believed that glutamate is the neurotransmitter substance secreted in the spinal cord at the type A d pain nerve fiber endings.
Slow pain
(Chronic pain or aching pain),begins only after 1 second or more and then increases slowly over many secondsThis type of pain is usually associated with tissue destruction. It can lead to prolong suffering. It can occur both in the skin and in almost any deep tissue or organ.
Localization of pain is poor.
The slow-chronic type of pain is transmitted to the spinal cord by type C fibers ,and secretes substance P which concerned with slow-chronic pain.
Pain Receptors and Their Stimulation
nociceptors(pain receptors), are all free nerve endings. They are widespread in the skin as well as in certain internal tissues, such as the periosteum, the arterial walls, the joint surfaces and other deep tissues pain receptors adapt very little and sometimes not at all, because it allows the pain to keep the person apprised of a tissue-damaging stimulus as long as it persists.Stimuli:
Pain can be elicited by multiple types of stimuli. They are classified as mechanical, thermal, and chemical pain stimuli.Thermal Stimulusfor Pain
The average person begins to perceive pain when the skin is heated above 45°C and the tissues begin to be damaged by heat
chemical types of pain stimuli
The chemical substances stimulating the slow type of pain that occurs after tissue injury (bradykinin, serotonin, histamine, potassium ions, acids, and proteolytic enzymes) . that excite the chemical pain receptors.
Tissue Ischemia as a Cause of Pain.
When blood flow to a tissue is blocked, the tissue often becomes very painful within a few minutes.For instance, if a blood pressure cuff is placed around the upper arm and inflated until the arterial blood flow ceases, can cause muscle pain the causes of pain is accumulation of large amounts o lactic acid in the tissues, formed as a consequence of anaerobic metabolism (metabolism without oxygen).
Muscle spasm
Muscle spasm is also a common cause of pain, and it is the basis of many clinical pain syndromes. By stimulating mechanosensitive pain receptors, and it might also result from the indirect effect of muscle spasm to compress the blood vessels and cause ischemia.
Analgesic System in the Brain and Spinal Cord (pain suppression)
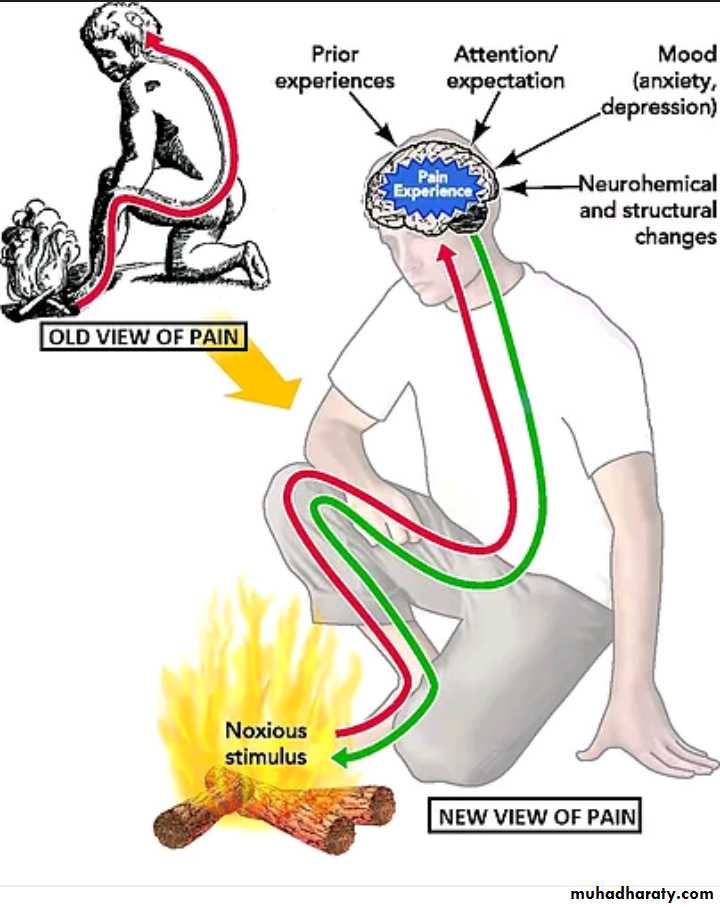
The degree to which a person reacts to pain varies.This results partly from a capability of the brain itself to suppress input of pain signals to the nervous system by activating a pain control system, called an analgesia system. Several transmitter substances are involved in the analgesia system; enkephalin, serotonin.
The serotonin causes local cord neurons to secrete enkephalin which cause both presynaptic and postsynaptic inhibition of incoming type C and type Ad pain fibers.
Brain’s Opiate System—Endorphins and Enkephalins
It was assumed that the “morphine receptors” of the analgesia system must be receptors for some morphine-like neurotransmitter that is naturally secreted in the brain. Therefore, these are natural opiate of the brain.Among the more important of these opiate-like substances are beta-endorphin, met-enkephalin, and dynorphin.
Activation of the analgesia system by nervous signals entering the periaqueductal gray and periventricular areas, or inactivation of pain pathways by morphine-like drugs, can almost totally suppress many pain signals entering through the peripheral nerves.
Inhibition of Pain
Stimulation of large type A -b sensory fibers from peripheral tactile receptors can depress transmission of pain signals from the same body area.This presumably results from local lateral inhibition in the spinal cord.
It explains why such simple maneuvers as rubbing the skin near painful areas is often effective in relieving pain. And it probably also explains why liniments are often useful for pain relief.
This mechanism and the simultaneous psychogenic excitation of the central analgesia system are probably also the basis of pain relief by acupuncture.
Visceral Pain
The viscera have sensory receptors only for pain.
One of the most important differences between surface pain and visceral pain is that highly localized types of damage to the viscera seldom cause severe pain. Conversely, any stimulus that causes diffuse stimulation of pain nerve endings throughout a viscous causes pain that can be severe. Diffused pain dull aching usually referred pain. Essentially all visceral pain is transmitted by small type C pain fibers and, therefore, can transmit only the chronic-aching-suffering type of pain.Causes of Visceral Pain:
Ischemia.Chemical Stimuli.
Spasm of a Hollow Viscus
Over distention of a Hollow Viscus
Spasm of a Hollow Viscus
Often pain from a spastic viscus occurs in the form of cramps, with the pain increasing to a high degree of severity and then subsiding. This process continues intermittently, once every few minutes. each time a peristaltic wave travels along an overly excitable spastic gut, a cramp occurs.The cramping type of pain frequently occurs in appendicitis, gastroenteritis, constipation, menstruation, ect
Over distention of a Hollow Viscus.
Extreme overfilling of a hollow viscus also can result in pain; presumably because of overstretch of the tissues themselves.Over distention can also collapse the blood vessels that pass into its wall, thus perhaps promoting ischemic pain.Insensitive Viscera.
A few visceral areas are almost completely insensitive to pain of any type.These include the parenchyma of the liver, brain and the alveoli of the lungs. Yet the liver capsule is extremely sensitive to both direct trauma and stretch, and the bile ducts are also sensitive to pain. In the lungs, both the bronchi and the parietal pleura are very sensitive to pain.
Referred Pain
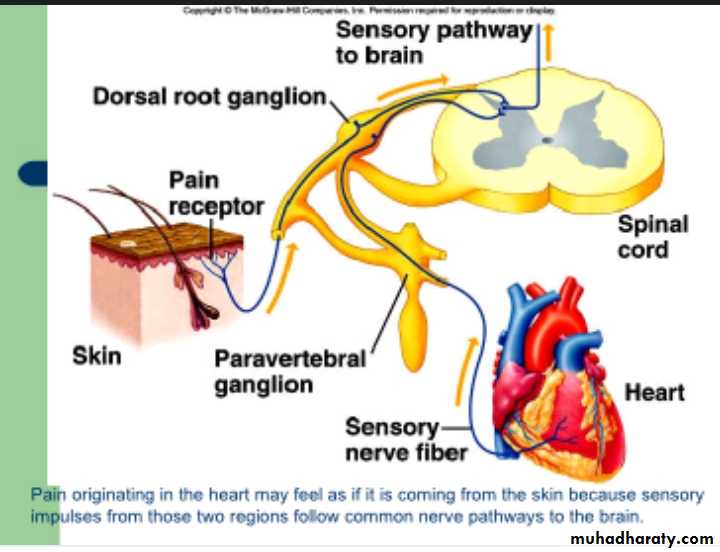
Person feels pain in a part of the body that is away from the tissue causing the pain.When visceral pain is referred to the surface of the body, the person generally localizes it in the dermatomal segment from which the visceral organ originated in the embryo.
When the visceral pain fibers are stimulated, pain signals from the viscera are conducted through at least some of the same neurons that conduct pain signals from the skin, the brain therefore interprets the information coming from visceral receptors as having arisen from receptors on the body surface, this is the convergence projection theory
The heart originated in the neck and upper thorax, so that the heart’s visceral pain fibers enter the spinal cord between segments C-3 and T-5. Therefore, pain from the heart is referred to the side of the neck, over the shoulder, over the pectoral muscles, down the arm, and into the substernal area of the upper chest. These are the areas of the body surface that send their own somatosensory nerve fibers into the C-3 to T-5 cord segments
Hyperalgesia
Increase in sensitivity of the pain receptorsHeadache
Headaches are a type of pain referred to the surface of the head from deep head structures. Some headaches result from pain stimuli arising inside the cranium, but others result from pain arising outside the cranium, such as from the nasal sinuses.The brain tissues themselves are almost totally insensitive to pain.
Conversely, stretching the dura atthe base of the brain can cause intense pain that is recognized as headache. Also, almost any type of traumatizing, crushing, or stretching stimulus to the blood vessels of the meninges can cause headache.