Antibiotics that interferes with nucleic acid
3- Antibiotics that interferes with nucleic acid a.SulphonamidesAmongst the first successful chemotherapeutic agent.
It usually combined with trimethoprim
Because of its adverse effects it use restricted to specific indications
The sulphonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic with a wide spectrum against most G+ve and many G-ve organisms.
Nocardia, chlamydia and some protozoa are inhibited.
Some enteric bacteria such as E.coli, klebsiella, salmonella, shigella and enterobacter are inhibited.
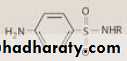
The M.O. require PABA in order to form nucleic acid. Sulphonamides are structural analoges of PABA that competitively inhibit dihydrofolic acid synthase which ultimately impair DNA formation. The bacteria produce its own folic acid, human take folic acid from diet .sulphonamide inhibit folic acid synthesis therefore are toxic to bacteria but not to human.
Sulphonamide Mech. of action
Pharmacokinetics
Sulfonamide for systemic use are absorbed rapidly from the gut ,metabolic path is acetylation and the capacity is geneticaly determined. The excretion through the kidney.(sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim) = co trimoxazole, both are bacteriostatic. T1/2 of 10 h ,it should be reduced in renal impairment.
Suphonamides
Calssification
Systemic use
(sulfamethoxazole+trimethoprim ) Co-trimoxazole,treat pneumonia due to pneumocystis carini in immunosuppressed patients,treatment of toxoplasmosis,
urinary tract infection (UTI)
dysentry due to shigellosis
Topical application
Silver sulfadiazine
Infected burns, leg ulcers, bed sores.against pseudomonads
Sulfasalazine is a combination of sulfapyridine+5-amino salicylic acid its used in ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis.
sulfacetamide: ophthalmic eye drop for bacterial infection of eye.
Sulphonamides (adverse effects)* crystalluria * hypersensitivity
Sulphonamides (adverse effects)* hemolytic anemia in G6PD deficiency* kernicterus in newborn bec. Sulpha drugs displace bilirubin from binding site on serum albumin and the free pass to CNS bec. Babys BBB is not fully developed.
Trimethoprim
Following its extensive use in combination with sulphonamides, trimethoprim has emerged as a useful broad-spectrum antimicrobial against G+ve, G-ve, T1/2: 10 hrs, excrete in urine.NOTE: if you give vitamin B12 with sulphonamide you are weaken the effect of it.
Trimethoprim is effective as sole therapy in treating urinary and respiratory tract infections, and for prophylaxis of urinary tract infections.
Trimethoprim (adverse effects)
Skin rash
Anorexia
Nausea
Vomiting
Abdominal pain
And diarrhoea
Cotrimoxazole
Combination of trimethoprim with sulfamethoxazole ,they shows greater antimicrobial activity because of their synergistic activity,broad spectrum of antibactrial action,effect in treating UTI,RTI,GIT infections Shigella,salmonella,Toxoplasmosis resistance is less ,it administered orally,IV,use in prostatitis,cross BBB,both drug and metabolite are excreted in urine.Adverse effects: skin rash,nausea&vomitting,glossitis& stomatitis,hyperkalemia,megaloblastic anemia,the hematologic effect may be reversed by folinic acid.
Urinary tract Antiseptics/Antimicrobials
UTI:E.Coli is the most common pathogen causing about 80% of upper and lower UTI . In addition to Cotrimoxazole & Quinolones UTI may be treated by agents called UT Antiseptics including nitro furantoin and the quinolone nalidixic acid . These drugs not achieve antibacterial levels in the circulation but they are concentrated in the urine.3- Antibiotics that interferes with nucleic acid b.Quinolones
All the fluoroquinolones are bactericidal. Like aminoglycosides, the quinolones exhibit concentration-dependent bacterial killing.Act principally by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase, thus preventing the supercoiling of DNA, a process that is necessary for compacting chromosomes into the bacterial cell.
Pharmacokinetics
Well absorbed from gut,and widly distributed in tissue, mechanism of inactivation(hepatic metabolism,renal and biliary excretion).some are potent liver enzyme inhibitor and impair the metabolic inactivation of warfarin,theophylline and sulphonylurea.Quinolones
It has become common practice to classify the fluoroquinolones into 4
generations.
First generation (naldixic acid): it’s the first drug used in UTI bec. Its concentrated in the urine . and it has no systemic effect but fluorinated quinolone used in systemic infection.
Second generation (Ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin): is effective against G-ve organism against chlamydia,mycoplasma,used in UTI, RTI, GIT, Gonorrhea & septicemia, osteomyelitis, pseudomonas infection in cystic fibrosis, anthrax.
Third generation (levofloxacin): RTI(streptococcus pneumonia) once daily ,and used in UTI.
Fourth generation (moxifloxacin): against G+ve activity and anaerobic, its weakly active against pseudomonas.it used prophylacticalybefore trans urethral surgery to lower post surgical UTI.
Quinolones
Adverse effectsGastrointestinal disorder
Allergic reactions
CNS effects
Connective tissue problems, its not use in pregnant, lactating female, in children, in adolescents less than eighteen years bec. of damaging growing cartilage and arthropathy.
3- Antibiotics that interferes with nucleic acid C- Azoles
This group includesantibacterial and antiprtozoal (Metronidazole and Tinidazole)
antifungal (Fluconazole, itraconazole, clotrimazole)
anthelminthic drugs (Albendazole, Mebendazole)
Metronidazole
Mechanism of action
Is converted into an active form by reduction of its nitro group; this binds to DNA and prevents nucleic acid formation. It is bactriostatic.
Pharmacokinetics:
is well absorbed after oral or rectal administration, distributed widely, eliminated in urine, T1/2 :8 hrs.
Metronidazole
Clinical uses (active against a wide range of anaerobic bacteria, and protozoa).Treatment of sepsis to which anaerobic organisms, e.g. Bacteriodes spp and anaerobic cocci ,post surgical infection and intra abdominal septicemia,osteomylitis and abscess of brain and lung.
Antibiotic-associated pseudomembraneous colitis
Trichomoniasis of the urogenital tract in both sexes
Amoebiasis(entamoeba histolytica)
Giardiasis
Acute ulcerative gingivitis and dental infection
Anaerobic vaginosis
Metronidazole
Side effectsGIT disorders
Allergic reactions
Peripheral neuropathy
Disulfiram-like effect
Furred tongue with un pleasant metalic taste
CNS effect headache, dizziness
Tinidazole
Is very similar to metronidazole but has a longer T half life=13hs
Used as single dose for treatment of giardiasis, trichomonisasis and acute ulcerative gingivitis, in which tinidazole 2gm by mouth as single dose best than course of metronidazole.