Hookworms
Ancylostoma duodenaleIntroduction
The hookworms cause hookworm disease, which is one of the five major parasitic disease in China(malaria, shistosomiasis, filariasis, kala- azar and hookworm disease). At least two species of hookworms infect man, Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale. They live in small intestine.Morphology
Adults:They look like an odd piece thread and are about 1cm. They are white or light pinkish when living. ♀is slightly larger than♂.The male’s posterior end is expanded to form a copulatory bursa. cylindrical with the head bent sharply backwards giving them a hooked appearance.
Morphology
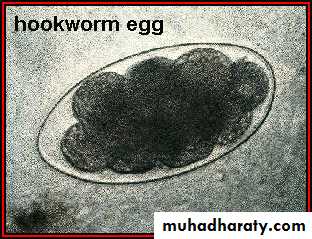
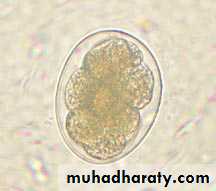
Eggs:60×40 µm in size, oval in shape, shell is thin and colorless. Content is 2-8cells.
Ancylostoma duodenale
• Egg
• AdultAncylostoma duodenale
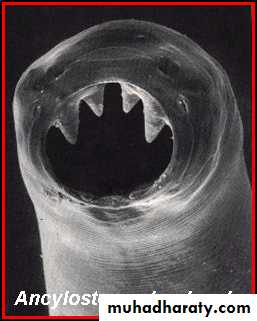
Scanning electron micrograph of the mouth capsule of Ancylostoma duodenale, note the presence of four "teeth," two on each side.
Ancylostoma duodenale
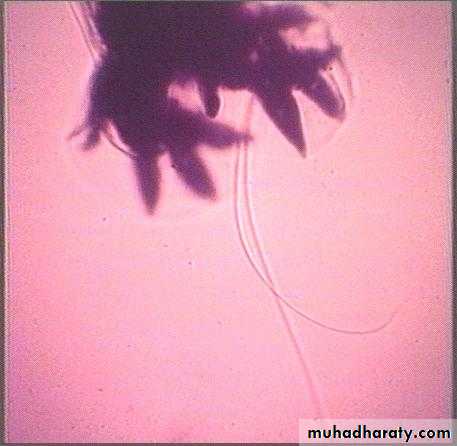
• Ancylostoma duodenale - copulatory bursa and spines of male(a side view)
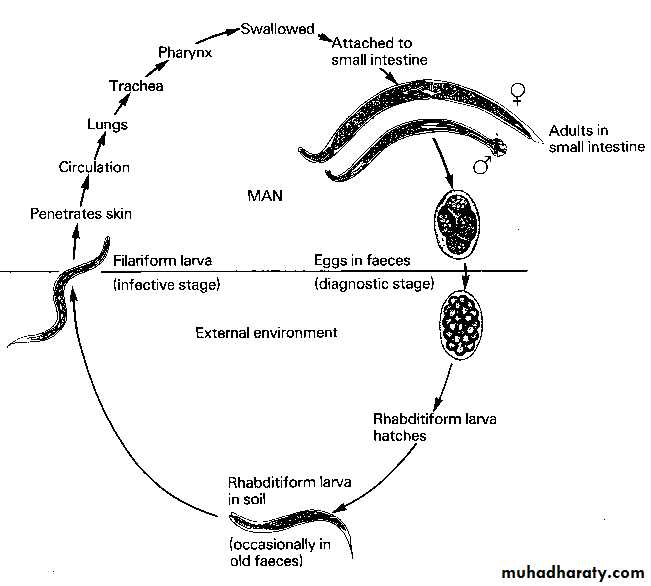
Ancylostoma duodenaleFinal host: man
Inf. Stage: Larva 3 or filariform larva.Diagnosis stage : egg in stool.
Inf. Route: by skin
Food: blood and tissue fluid
Site of inhabitation: small intestine
Life span: Ad 15years, Na 3-7years
Blood-lung migration:
skin, cavum, right heart, lungs
Life cycle
Diagnosis
Stool examinationThis is based on finding the eggs in the faeces.
An estimation of worm load is often necessary for any correlation of the anaemia with the hookworm infection.