• StomachManal alahmad
Stomach
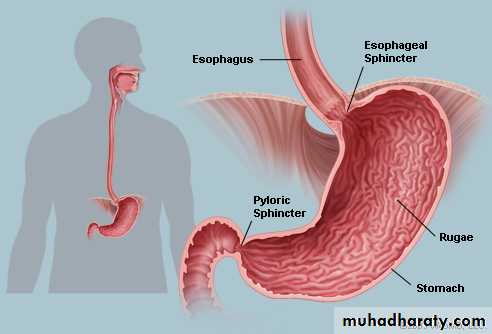
Is the most expanded part of the digestive tract, it is sac like structure.Functions of stomach:
1-Mechanical: store,mix and digest the food2-Chemical: secretion of enzymes and acids
3-absorptive function: absorbs water, alcohol and certain drugs
Stomach
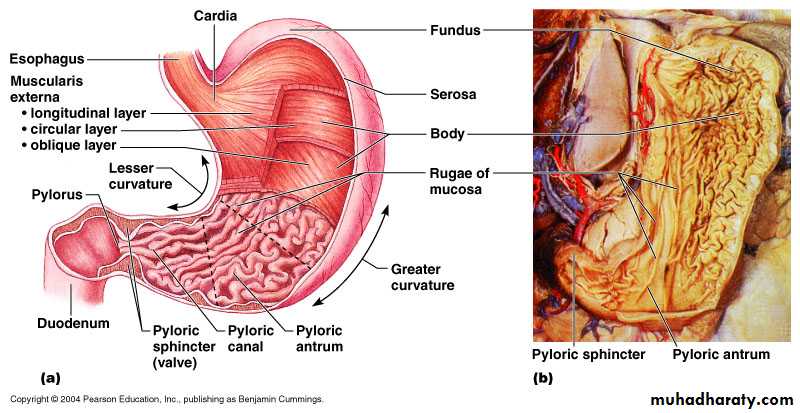
The Stomach is divided into 4 regions:Cardiac
fundusbody
Pylorus
Stomach
• The wall of stomach consists of 4 layers:• Mucosa
• Submucosa
• Muscularis Externa
• Serosa
Stomach
• Mucosa• Consists of:
• 1- Epithelium : simple columnar epithelium
• 2-Lamina propria: Ioose connective tissue
• 3-muscularis mucosae: smooth muscle (inner circular and outer longitudinal layers).
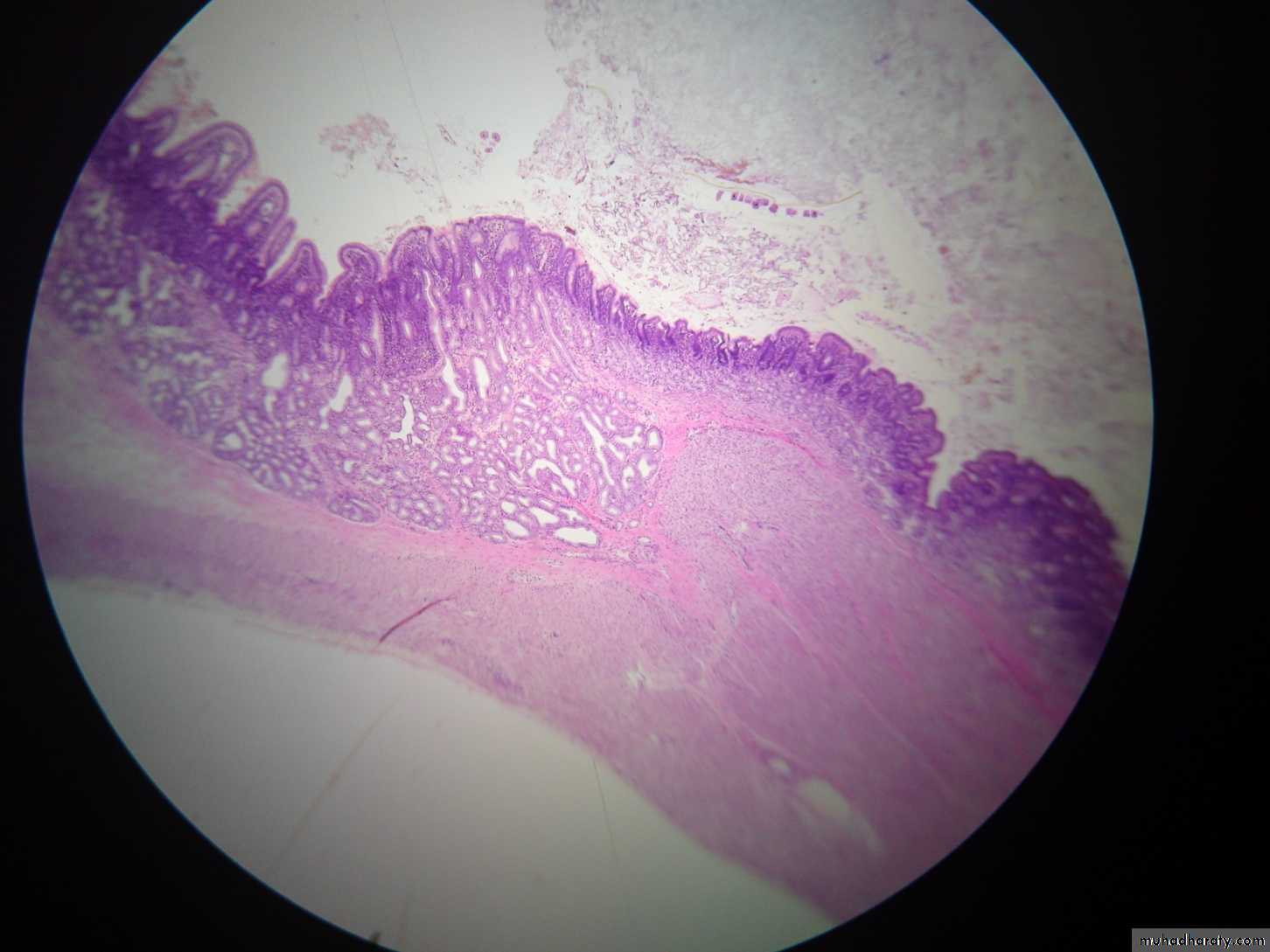
• Rugae: are longitudinal folds in the mucous layer that appear when the stomach is empty and these folds disappear when the stomach is filled
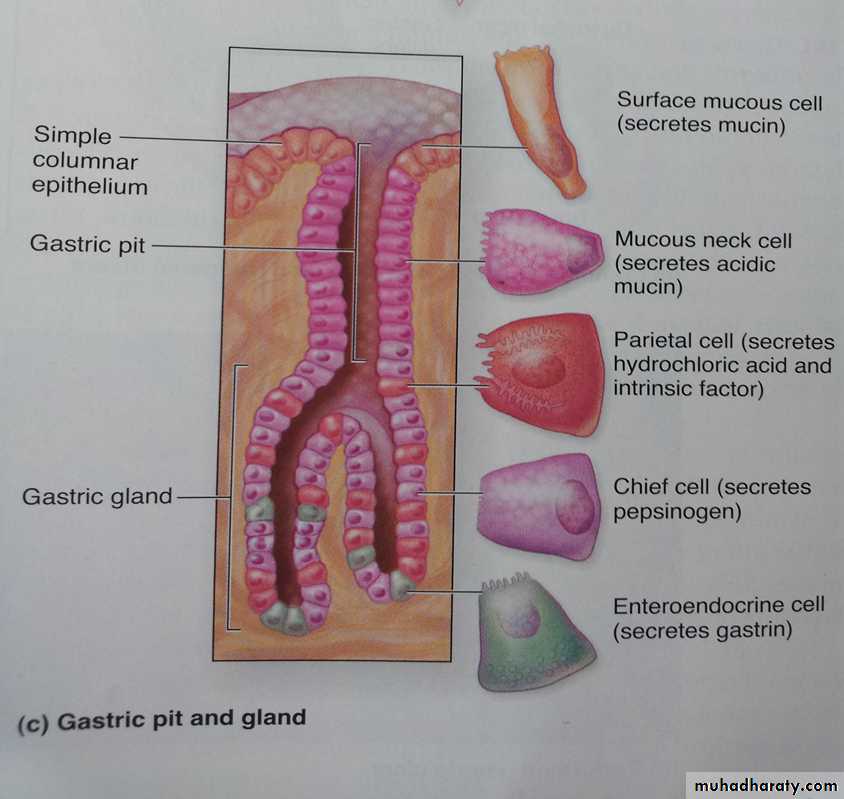
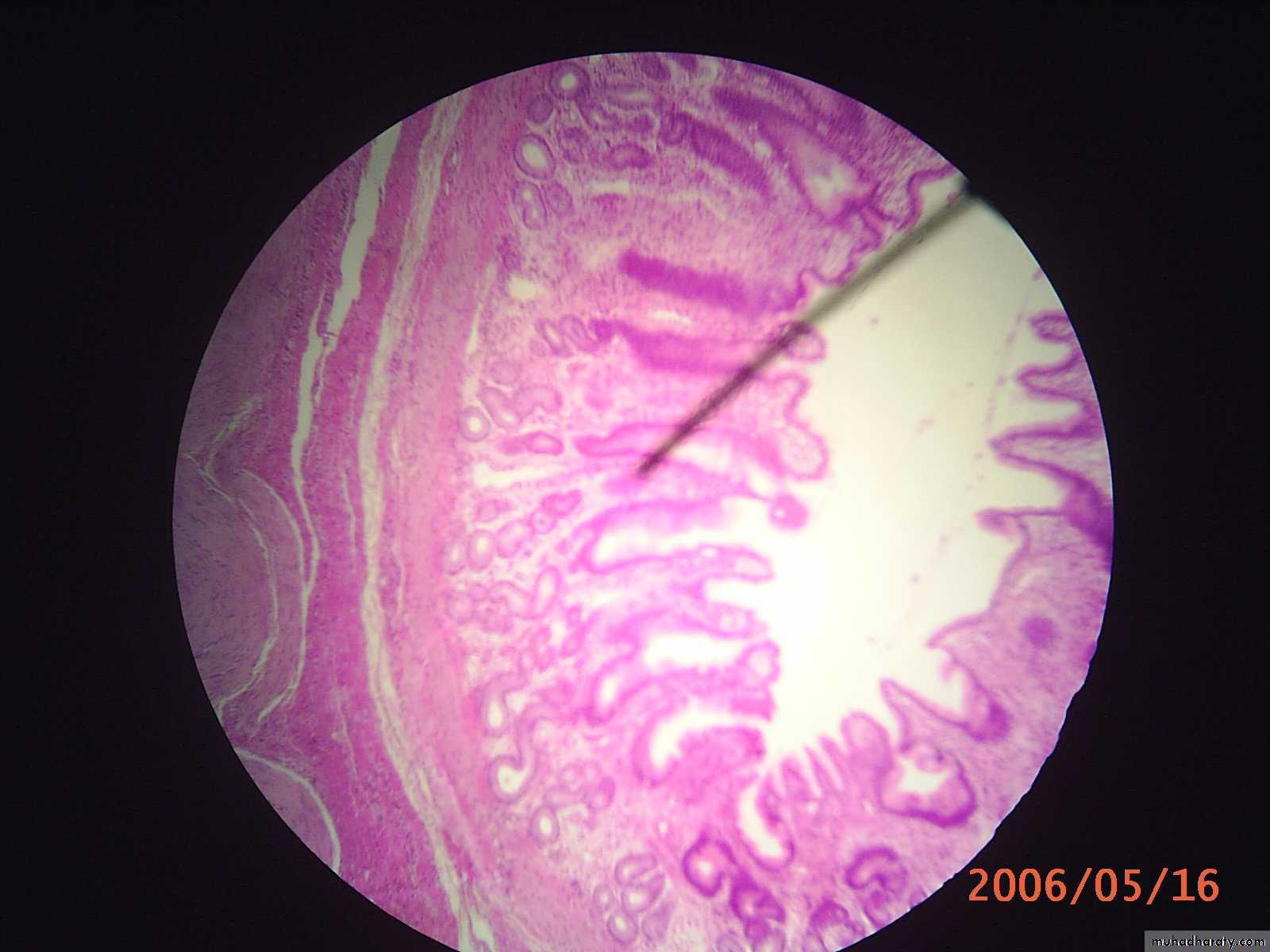
• Gastraic pits: are considered as ducts for gastric glands which occur in lamina propria
Cardio esophageal
junctionstratified sq. epith
columnar epthelium
Cardiac gland
Stomach
• Submucosa• the dense irregular collagenous connective tissue
this layer contains blood vessels
Stomach
• Muscularis Externa.• consists of 3 substantial layers of smooth muscle.
Inner oblique layer :
b. Middle circular layer :(is clearly evident along the entire stomach and especially pronounced pyloric region where it forms the pyloric sphincter)
Outer longitudinal layer:
• ****** Aurbach’s plexus is found between the circular and longitudinal layersStomach
• Serosa :loose areolar connective tissue covered by a mesothelium.
Stomach
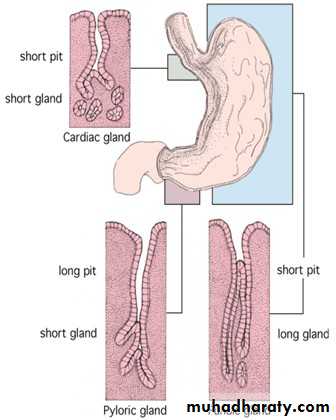
Gastric glands: it consists of isthmus , neck and base , it divided into
1-Gardiac glands:
2-Pyloric glands : *-long gastric pits and short glands
*- simple and tend to branch
3-Fundic glands: *-short gastric pits and long glands
*-simple ,tubular and branched
this gland is lined by 5 types of cells Mucus neck cells, Regenerative (Stem) cells, Parietal cells, Chief (Peptic) cells, Enteroendocrine cells .
Types cells in Gastric glands
Pyloric gland
• EpithPyloric gland
Lamina
propria
Gastric pit