Diagnosis and Treatment Planning - Removable Partial DenturePart-II
Assis.Prof.Radhwan Himmadi HasanB.D.S. , M.Sc. , Ph.D.
2018
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
1
LEC 2
صناعة نظري \ رابع اسنان كركوك
د. رضوان
2\4\2018
374
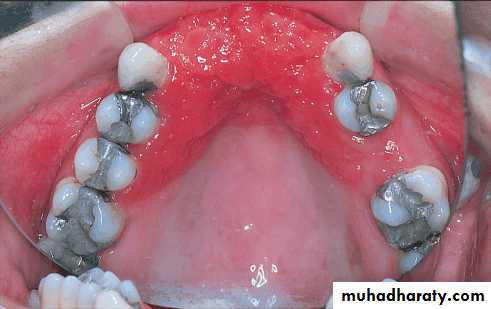
Diagnostic impressions and casts
A diagnostic procedure is incomplete unless it includes the evaluation of accurate diagnostic casts.Permits analysis of contour of both hard and soft tissues of the mouth
Determines the type of restorations to be placed on the abutment teeth
Determines the need for the correction of exostoses, frena, tuberosities, and undercuts
The casts are surveyed, the proposed design is drawn on the casts.4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan2
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan3
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan4
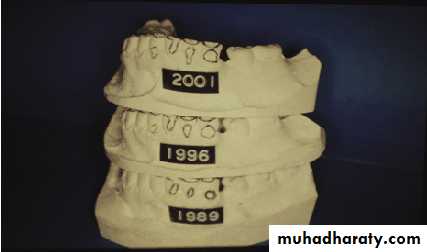
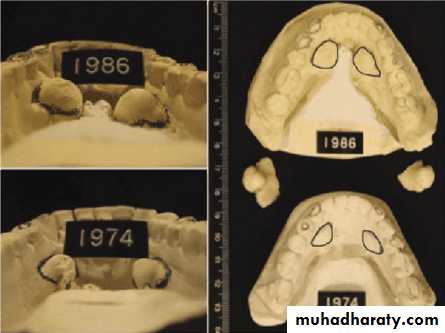
Diagnostic casts are valuable for research purposes and forensic information as they provide observable, precise geometry of the teeth and jaws
Occlusion constantly changes, and comparison of the changes on stone casts provide valuable information to the practitioner and can be used to educate the patient.
The designed casts serve as a blue print for the placement of restorations, the re contouring of teeth, and preparation of rest seats.
Aid in the presentation of proposed treatment plan to the patient.
The mounted diagnostic casts permit analysis of the patients occlusion, adequacy of inter arch space, and of the presence of over erupted or malposed teeth and tuberosity interferences.4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
5
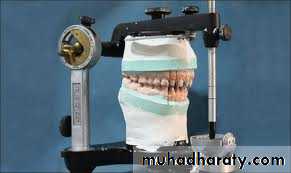
Mounting of diagnostic casts
Objective:To position the casts of dental arches on an articulator so that the casts have the same relationship as do the mandible to maxilla in the patient skull.
Three distinct phases of the procedure are
Orientation of the maxillary cast to the condylar elements of articulator by means of a face- bow transfer.4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
6
Orientation of the mandibular cast at the patients centric jaw relation by means of an accurate centric jaw relation record
Verification of these relationships by means of additional centric jaw relation records and comparison of occlusal contacts on the articulator with those in mouth.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan7
Centric jaw relation record
It is the most posterior relation of the mandible to the maxilla at the established vertical relation.It is a bone to bone relation of the mandible to the maxilla in terminal hinge closure.
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
8
Definitive oral examination
It should includeA thorough examination made of a dry field in good light
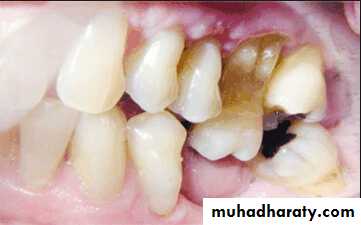
Carious lesions and defective restorations are correlated with radiographic and other diagnostic findings
All teeth that appear questionable clinically or radiographically are tested for pulp vitality.
The teeth are tested for sensitivity to percussion and mobility
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
9
Periodontal examination that includes
Determination of pocket depth, examination for evidence of infection or inflammation, the amount of attached gingiva of the prospective abutment teeth is madeThe oral mucosa is examined visually and with palpation for evidence of pathologic change
The examination is made for the presence of tori, exostoses, sharp or prominent bony areas , soft or hard tissue undercuts, enlarged tuberosities.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan10
Evaluation of pulp
Electric pulp tester in conjunction with thermal tests should be used to detect pulpitis or necrosis.The success of endodontic treatment must be assured before an affected tooth is selected as an abutment.
Full crown restorations are indicated for endodontically treated abutment teeth.
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
11
Evaluation of sensitivity to percussion
Positive in case ofTooth movement caused by a prosthesis or the occlusion
A tooth or restoration in traumatic occlusion
Periapical or pulpal abscess
Acute pulpitis
Gingivitis or periodontitis
Cracked tooth syndrome
A removable partial denture should not be constructed until the cause discovered and the sensitivity is eliminated.
The use of a percussion sensitive tooth as an abutment would result in early failure of the treatment.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan12
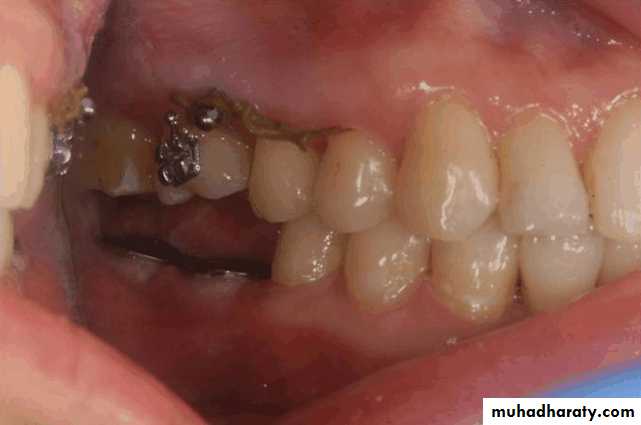
Evaluation of mobile teeth
Mobile tooth as an abutment tooth – poor prognosisThe causes for mobility
Trauma from occlusion- reversibleInflammatory changes in the periodontal ligament- may be reversed if the inflammation is eliminated
Loss of alveolar bone support – not reversible
A tooth with less than a 1:1 crown/root ratio is not suitable as an abutment tooth, indicated for extraction or can be used as an over denture abutment.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan13
Indications for splinting of abutment
teethIndicated when all remaining teeth have reduced support because of
Periodontal diseaseTeeth with short ,tapered roots
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan14
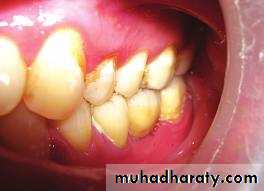
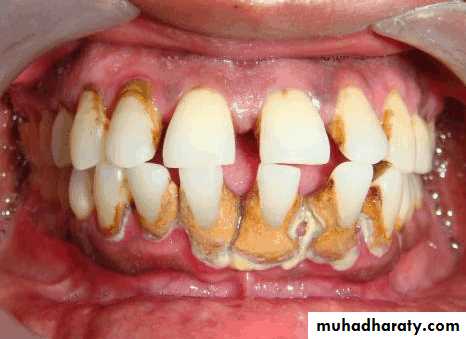
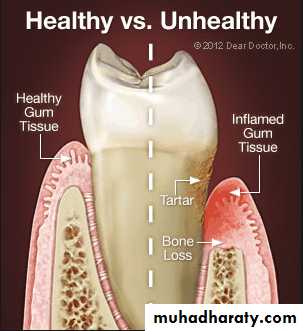
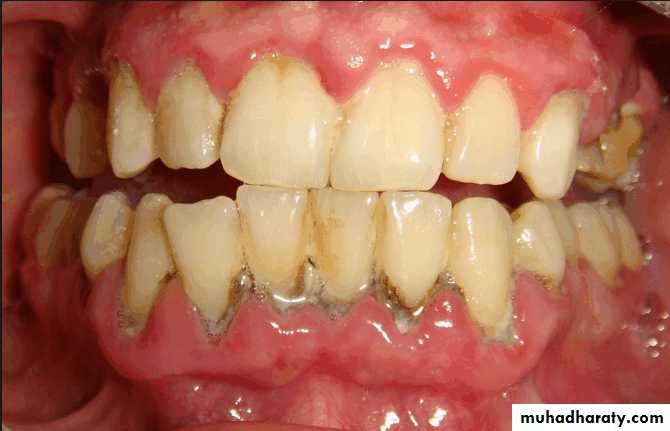
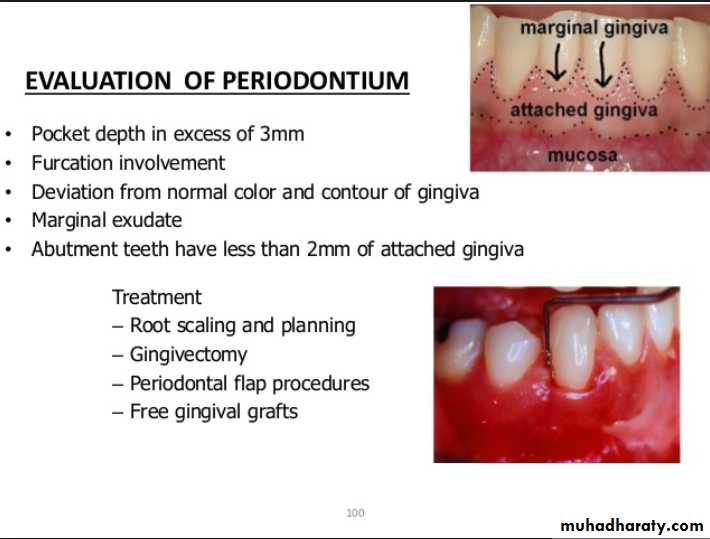
Evaluation of periodontium
Periodontal disease is one of the main etiologic factors in the loss of the teethA removable partial denture placed in the presence of active periodontal disease will contribute significantly to the rapid progression of the disease and the loss of the remaining teeth.
The causative factors must be eliminated, the disease process must be controlled before the fabrication of the prosthesis.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
15
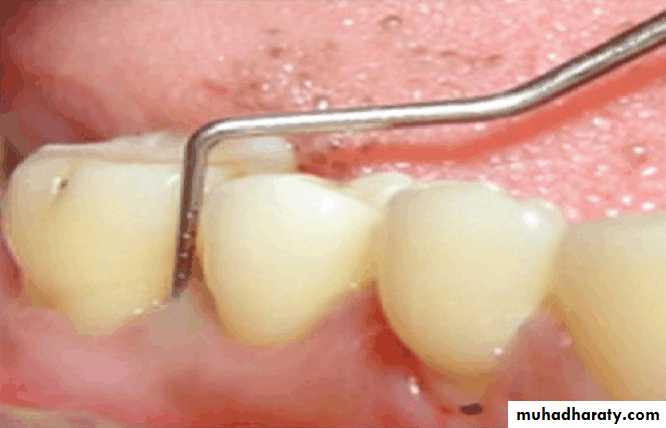
Examination findings that indicate possible need for periodontal treatment include
Pocket depth in excess of 3 mmFurcation involvement
Deviations from normal color and contour in gingiva, indicating gingivitisMarginal exudate
Potential abutment teeth with less than 2 mm of attached gingiva
Pulling of muscle or frena on attached gingiva
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
16
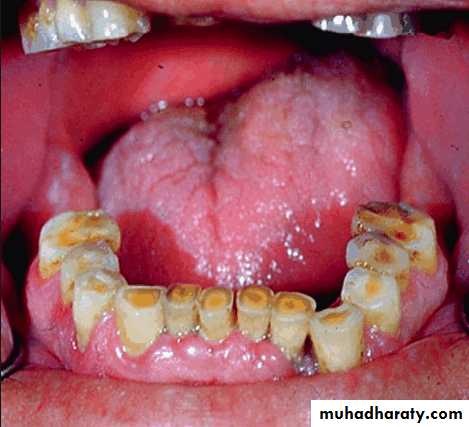
Evaluation of oral mucosa
Pathologic changes:Any ulceration, swelling , or color change that might indicate malignant or pre malignant changes should be recognized and evaluated through biopsy or referral.
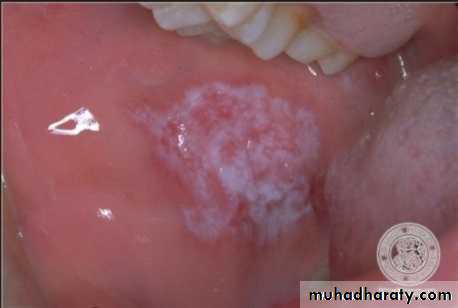
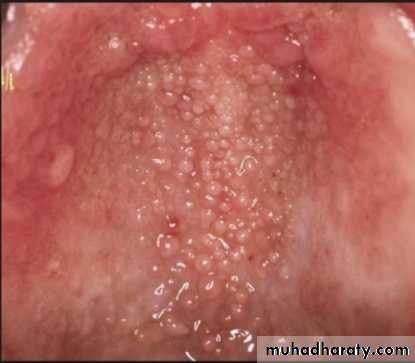
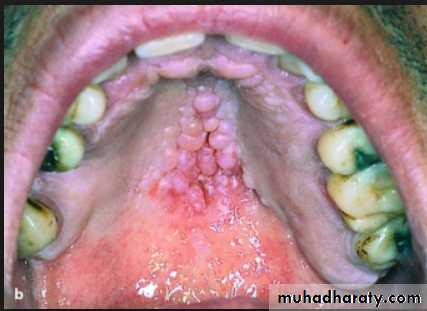
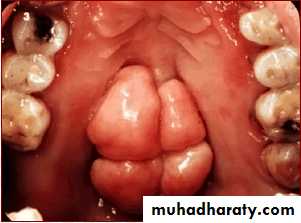
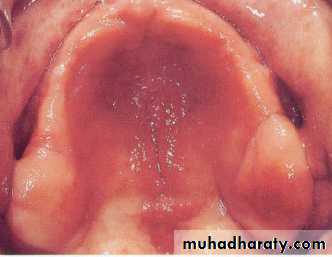
Palatal papillary hyperplasia:
Caused by inflammatory response in the sub mucosa, consists of numerous papillary growths.Food debris, fungi, bacteria collect in the crevices and may give rise to secondary infection.
If the patient will not be able to keep the lesion adequately clean, it should be removed.
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
17
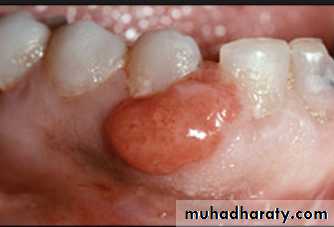
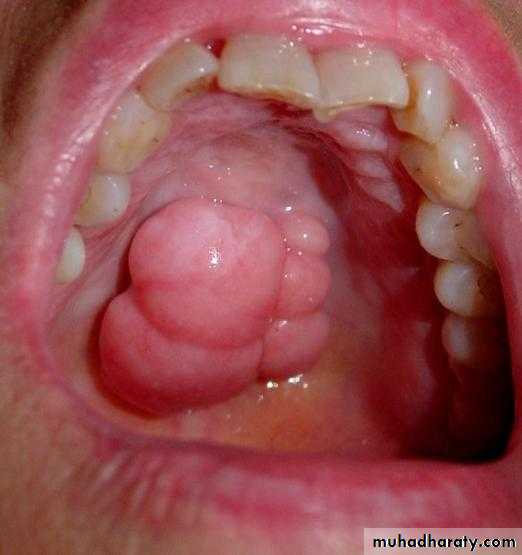
• Tissue reactions to the wearing of a prosthesis
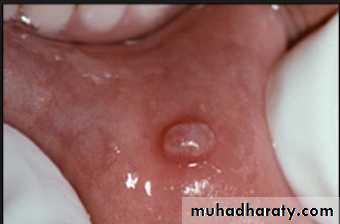
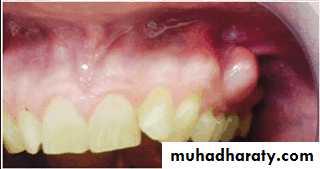
Epulis fissuratum: denture granuloma
It is a tumor like hyperplasic growth caused by an ill- fitting or overextended border of removable prosthesis
It may occur in double fold of tissue with one fold on the tissue side and one on the polished side of the denture border
Surgical removal – formation of scar tissue - not good for proper border seal
If the irritation is removed – resolves on its own4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan18
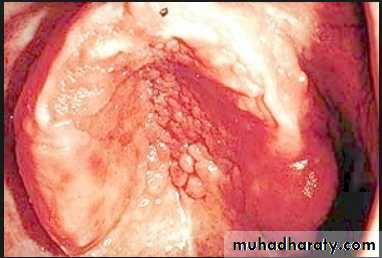
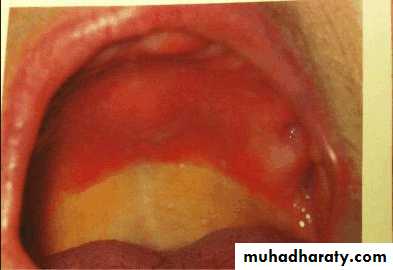
Denture stomatitis
Characterized by generalized erythema, usually including all the tissues covered by the prosthesis.Occurs under metal as well as acrylic resin denture bases, usually under maxillary prosthesis.
Frequently the mucosa is swollen and smooth – patient complaints of burning or itching.
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
19
Contributing factors:, poor fit of the prosthesis, poor oral hygiene, continuous wearing of prosthesis
Candida albicans has been shown to be present in much higher percentages of denture stomatitis patients than normal patients.
Treatment :
Remove causative factornystatin, good oral hygiene
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
20
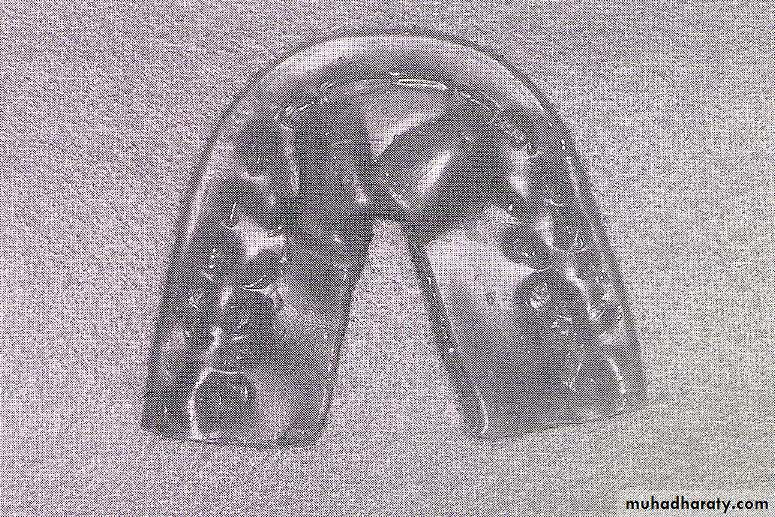
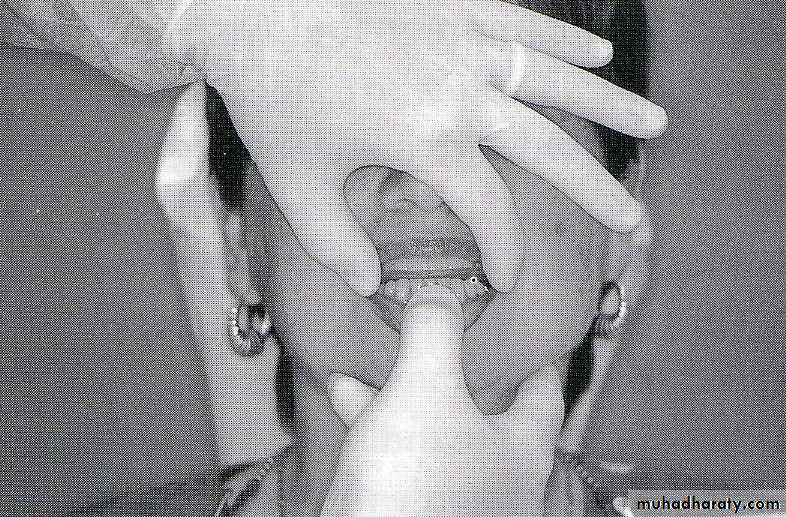
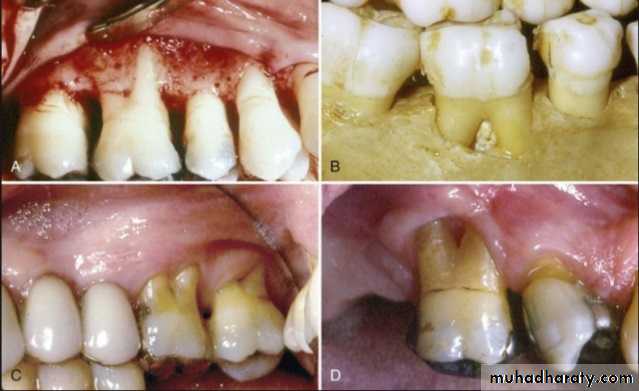
Evaluation of hard tissue abnormalities
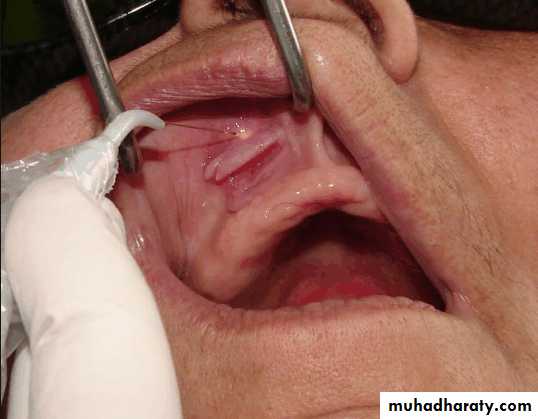
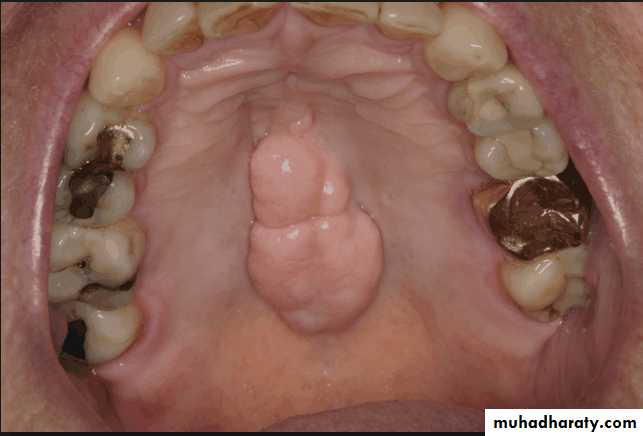
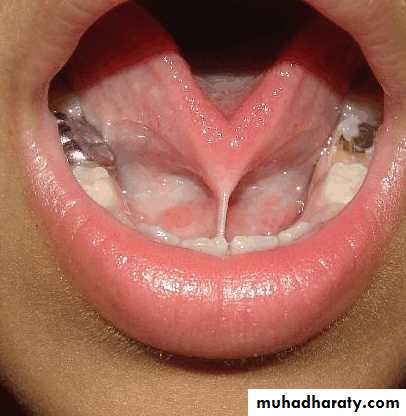
Torus palatinus:
Removal is not necessary unless it is so large that interferes with the design and construction of the prosthesis.If removal is deemed necessary, acrylic resin surgical splint should be constructed pre operatively.
Splint is used to adapt and support the mucosal flaps in contact with the bone.
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
21
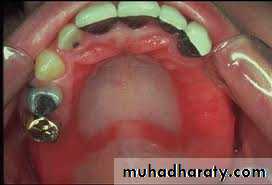
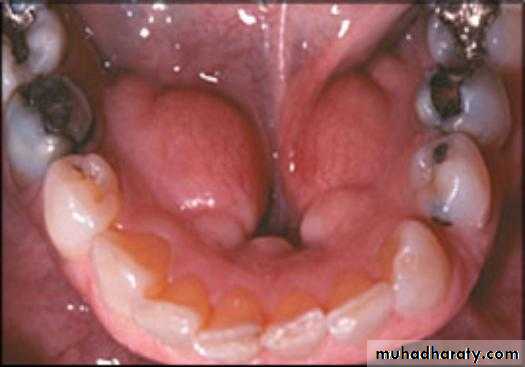
Torus mandibularis:
Usually occurs bilaterally, on the lingual surface of body of the mandible.
Tori should be removed if the patient is to wear the removable partial denture with any degree of comfort.
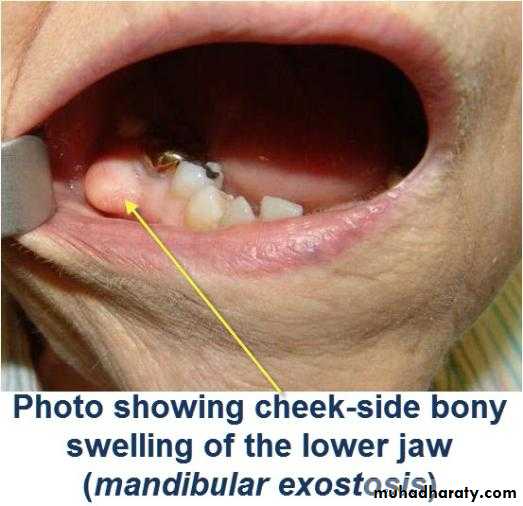
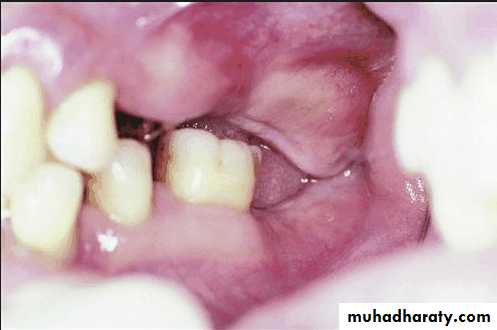
Exostoses and undercuts:
That are present in residual ridge areas that prevent the proper extension of the denture borders should be evaluated and , if necessary, surgically corrected.4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
22
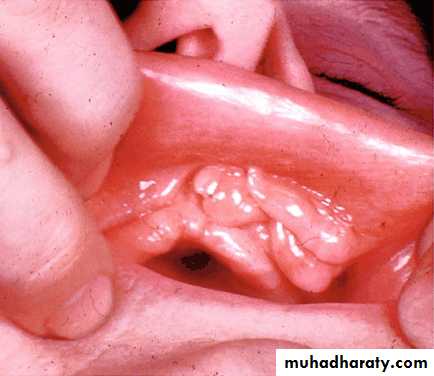
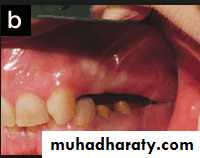
Mandibular / Maxillary tuberosity:
A bony protuberance at the distal end of the third molar areaThe soft tissue covering is thin, traumatized by the insertion and removal of removable partial denture.
1-relieve
2-path of insertion
3-One side surgical correction
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan23
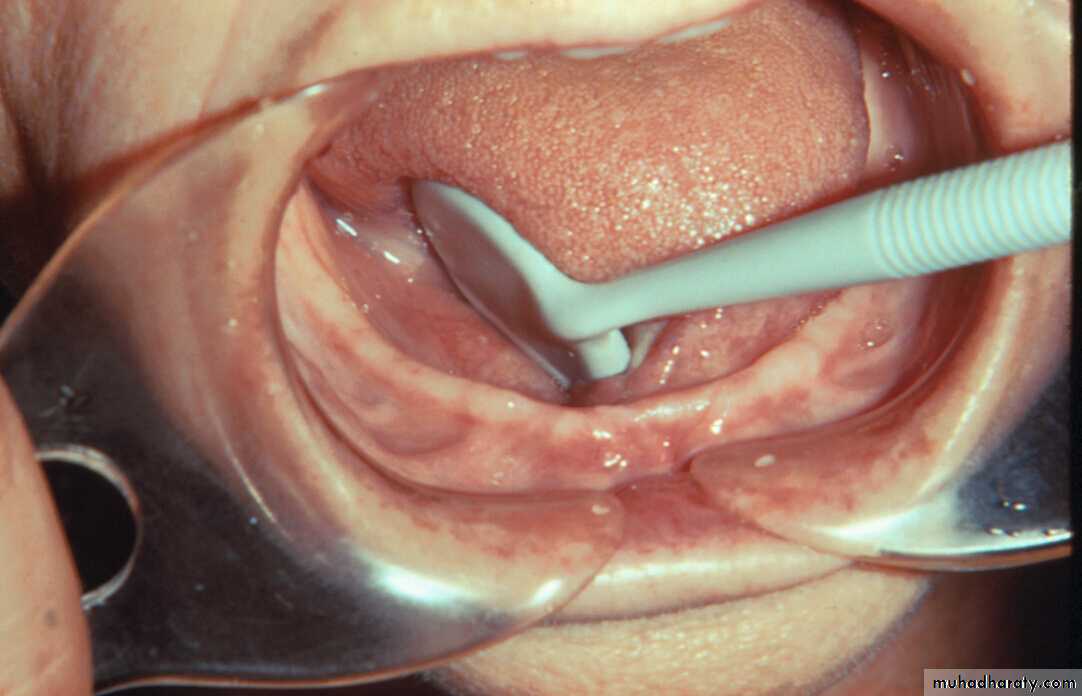
Evaluation of soft tissue abnormalities
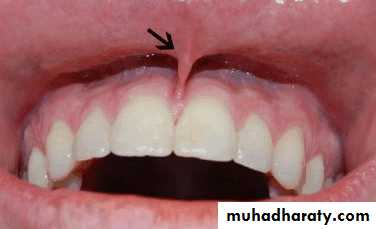
Various tissue conditions can present problems in the design and construction of removable partial denture.Labial and lingual frena as well as un supported and hyper mobile gingiva should be evaluated to determine whether surgical correction will improve the prognosis of the treatment
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
24
Evaluation of quantity and quality of saliva
If the mouth is dry, the patient will probably be uncomfortable wearing a removable partial denture.The denture bases will drag across the tissues during placement and removal if the lubricating effect of the saliva is not present.
A lubricating saliva substitute can help make the prosthesis more tolerable for the treatment.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
25
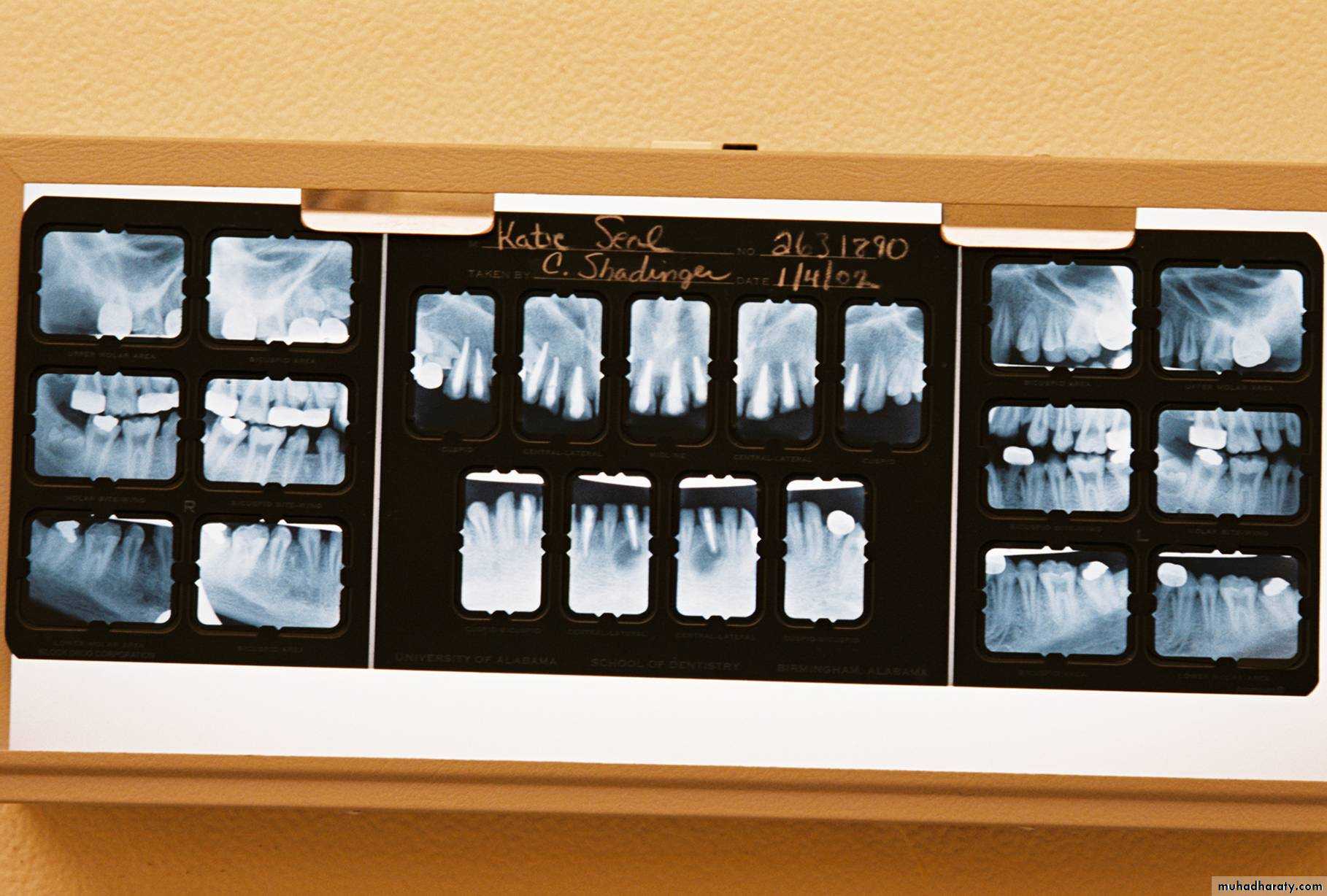
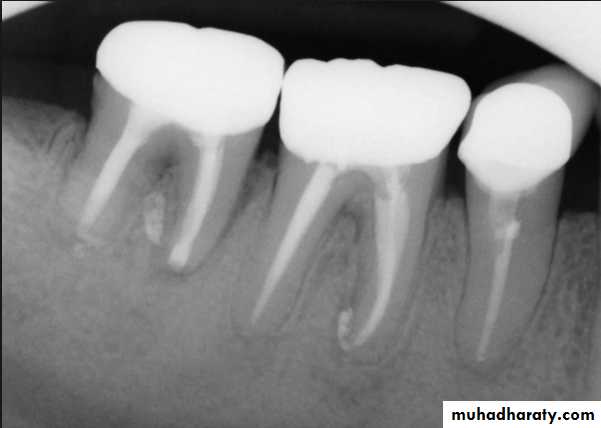
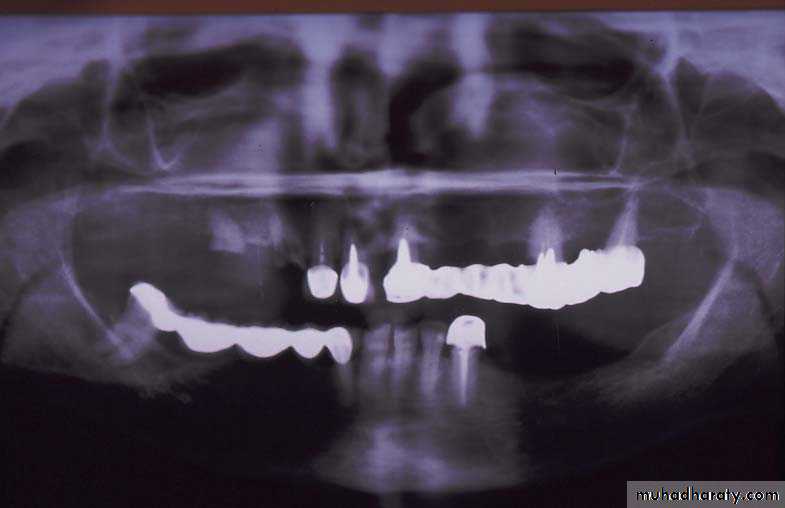
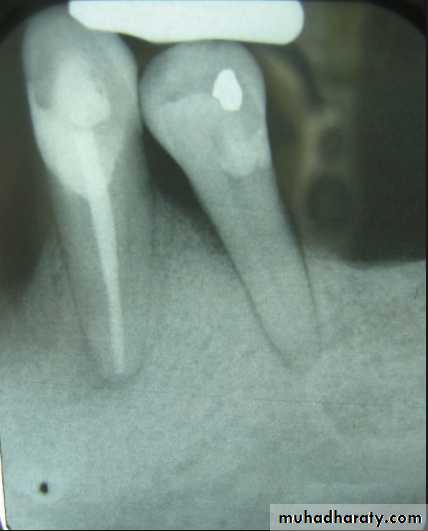
Evaluation of radiographic survey
All prospective abutment teeth must be critically evaluated4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan26
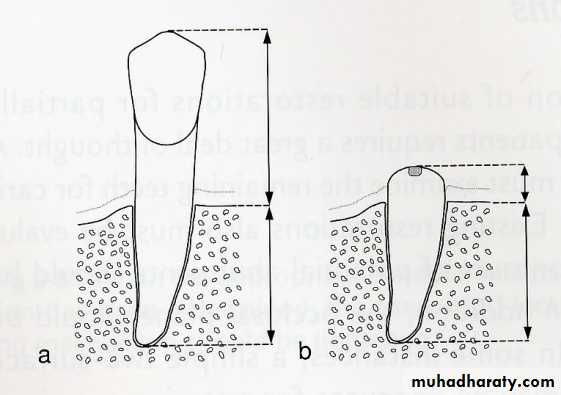
Root size, length and form
Teeth with large or long roots - Greater periodontal supportTapered or conical roots- un favorable
Multi rooted teeth with divergent roots are stronger abutment teeth than single rooted, multi rooted teeth with fused roots.4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan27
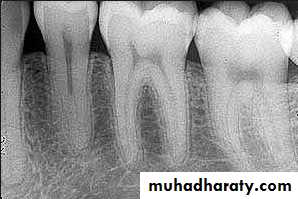
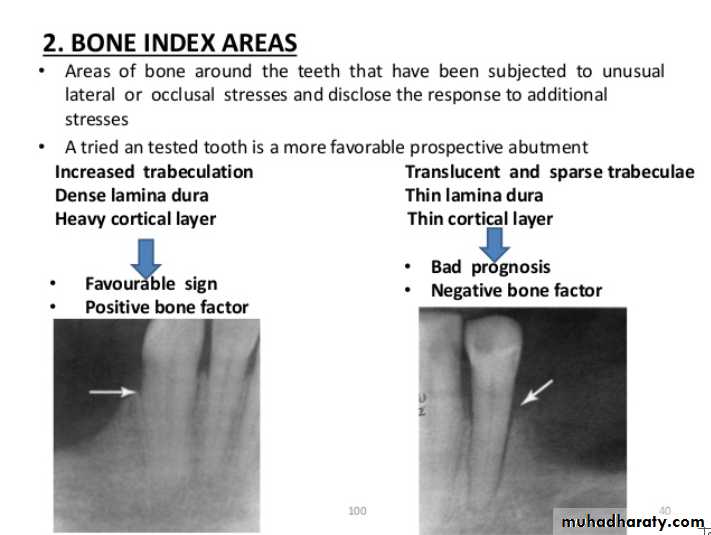
Signs of positive bone factor
A supportive trabecular patternHeavy cortical layer
Dense lamina dura
Normal bone height
Normal periodontal ligament space.
If retrograde bone changes occur, the patient has a negative bone factor ; prognosis is poor.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
28
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan29
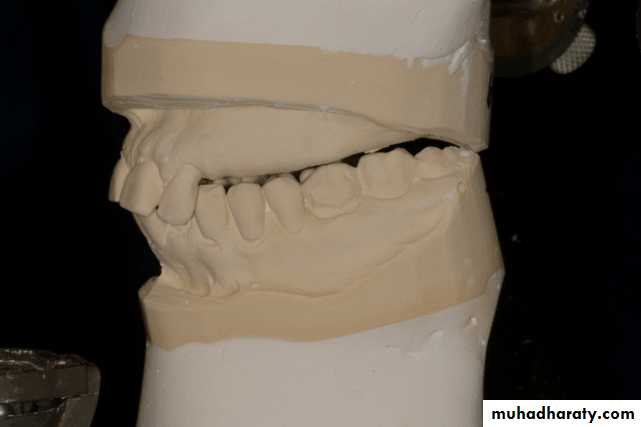
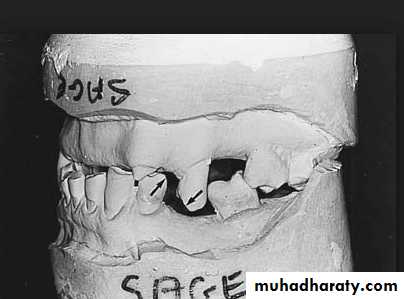
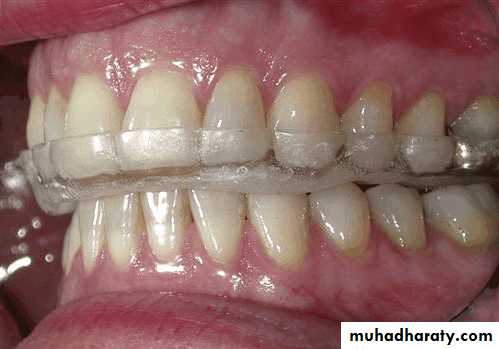
Evaluation of mounted diagnostic casts
Potential problems such as insufficient inter arch distance, irregularity or mal position of the occlusal plane, extruded or malposed teeth, and unfavorable maxillomandibular relationships are more apparent in accurately mounted casts because the lips, cheeks, and skull block out good visual access to the teeth in the mouth.4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan30
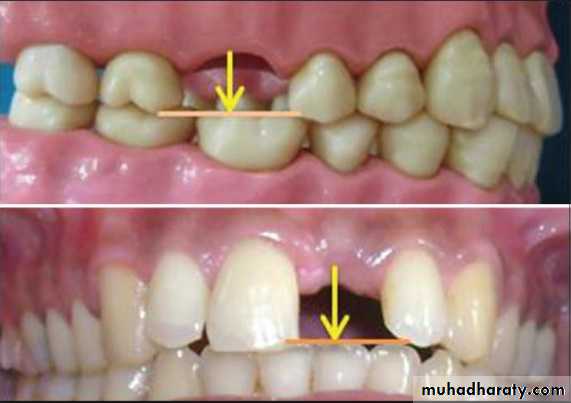
Interarch space
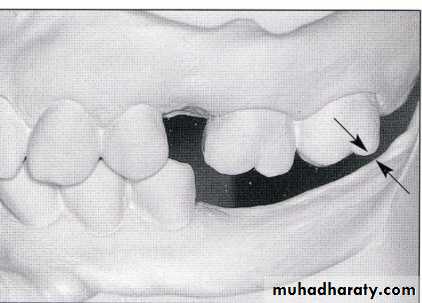
Lack of sufficient inter-arch distance- difficult for placing the teethFrequently it is caused by maxillary tuberosity that is too large in vertical height- surgical reduction vertical height is necessary for satisfactory replacement of the missing teeth.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan31
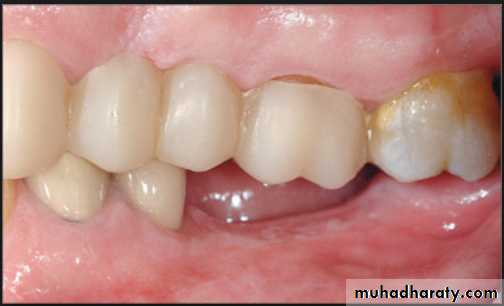
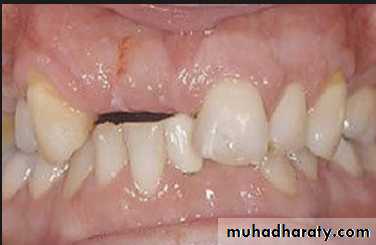
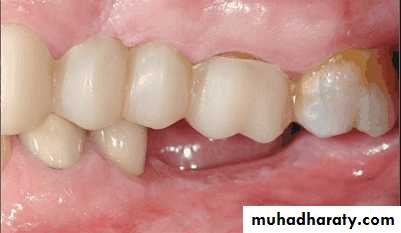
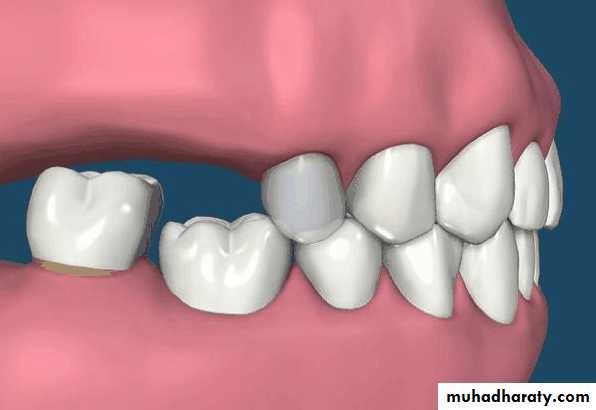
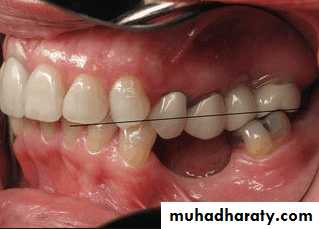
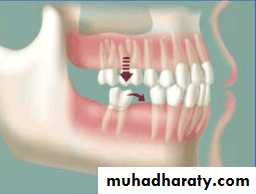
• Treatment over erupted teeth
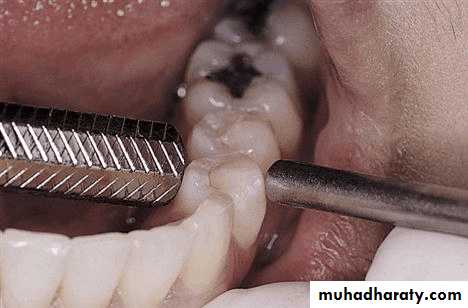
• If the tooth is extruded above the occlusal plane because of lack of an antagonist –• Treatment
• Moderately extrude tooth – aprox 2mm - enameloplasty.
• If the extrusion is greater than 2 mm or if the tooth does not lend itself to enameloplasty, the placement of a crown is indicated.
• If size of pulp prevent the required tooth reduction endodontic therapy
• If clinical crown length is inadequate crown lengthning
• Orthodontic treatment
• Severely extruded teeth – contacting the opposing ridge & if alveolar bone followed eruption remove the tooth and recontour the bone is necessary
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
32
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
33
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan34
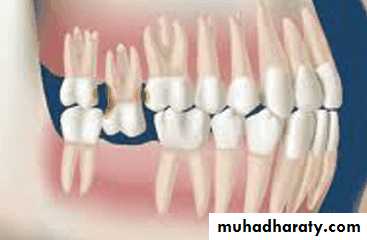
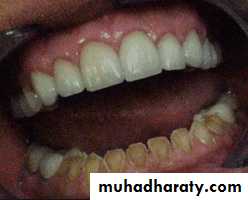
Occlusal plane
Occlusion plane may be irregular because of extrusionOne or more unopposed teeth.
Such conditions require corrective procedures if an acceptable occlusion is to be developed.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
35
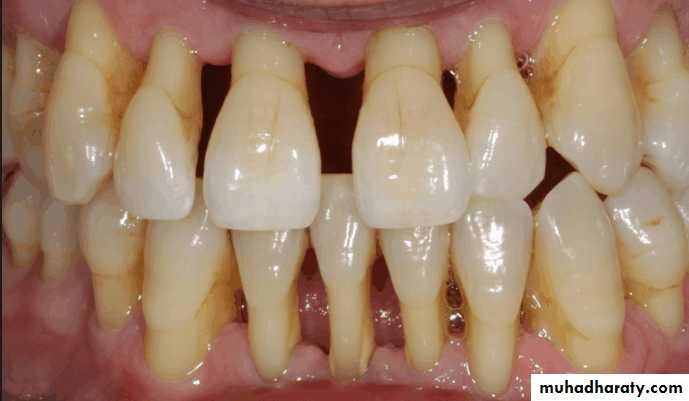
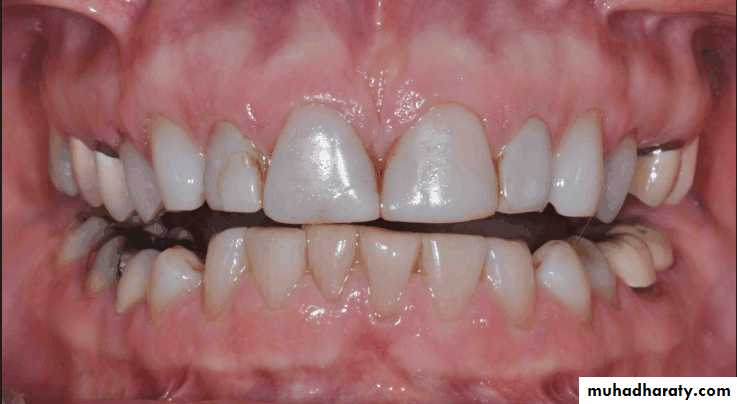
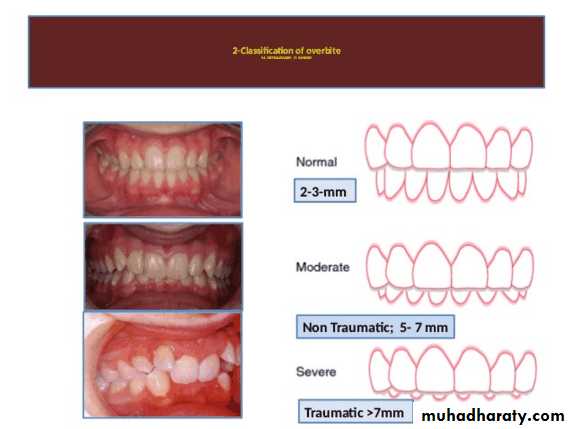
Traumatic vertical overlap
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
36
Clinical symptoms of traumatic vertical overlap
AbrasionMobility
Migration of the teeth
Inflammation , ulceration of the gingiva and palatal mucosa
Early recognition of problems and treatment with orthodontic or combined orthodontic and orthognathic surgical procedures are the treatment of choice
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
37
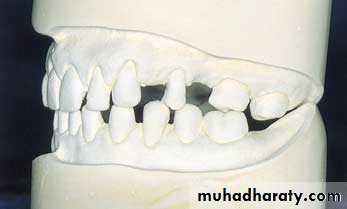
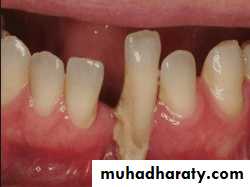
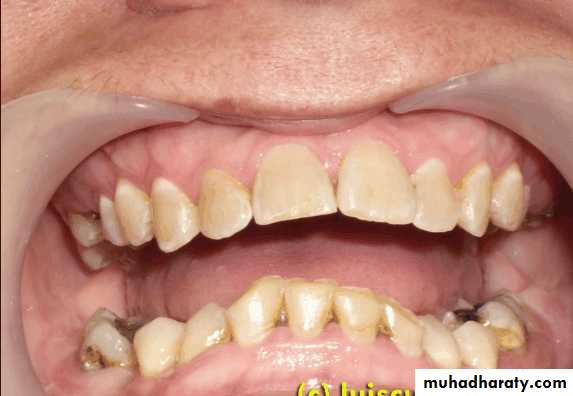
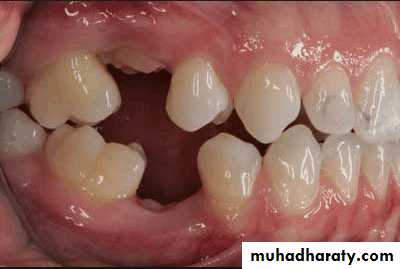
Tipped or malposed teeth
Limited orthodontic procedures for minor tooth movement can be used to upright the tipped tooth to allow the placement of an artificial tooth of more normal size.Orthodontic appliances, rubber ligature used to correct the position
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
38
Occlusion
The information obtained from the analysis of occlusion should be correlated with other clinical findings.The common finding is the presence of occlusal interferences.
Partially edentulous patients have greater probability of having premature contacts because of drifting and migration.
The most common causes of Bruxism
Occlusal interferences between centric jaw relation and centric occlusion,Balancing side contacts.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
39
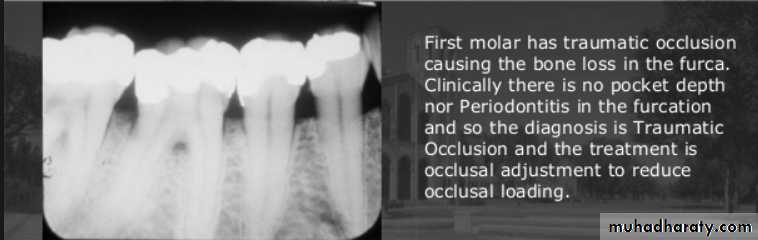
Clinical symptoms of traumatic occlusion
Excessive wear of teethMobility, tooth migration,
Pain during and after occlusal contact.
Muscle spasm,& joint symptoms.
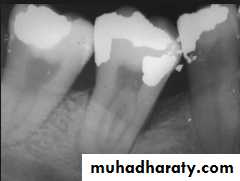
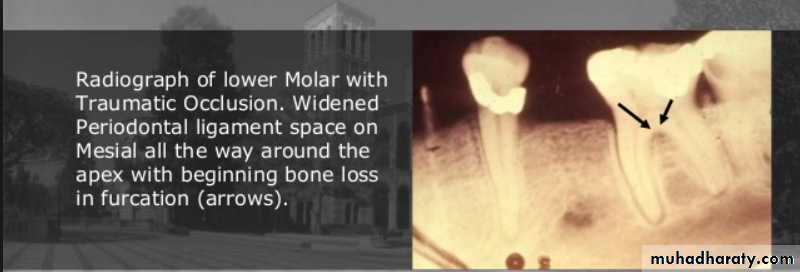
Radiographic findings
Widening of periodontal space with either thickening or loss of lamina dura
Periapical or Furcation radiolucency
Resorption of alveolar bone
Root resorption
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
40
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan41
Development of treatment plan
The treatment of partially edentulous patient can be divided in to five phases.Phase 1 :
Collection and evaluation of the diagnostic data, including a diagnostic mounting and analysis of diagnostic castsImmediate treatment to control pain or infection
Biopsy or referral of the patient
Development of treatment plan
Initiation of education and motivation of patient.
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
42
Phase 2:
Removal of deep caries and placement of temporary restorationsExtirpation of inflamed or necrotic pulp tissues
Removal of non retainable teeth
Periodontal treatment
Construction of interim prosthesis for function or esthetics
Occlusal equilibration
Reinforcement of education and motivation of patient
4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
43
Phase 3 :
Preprosthetic surgical procedures
Definitive endodontic procedures
Definitive restoration of teeth, including placement of cast metallic restorationsFixed partial denture construction
Reinforcement of education and motivation of patient4/2/2018
Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
44
Phase 4 :
Construction of removable partial dentureReinforcement of education and motivation of patient
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
45
Phase 5 :
Post insertion care
Periodic recallReinforcement of education and motivation of patient
4/2/2018Dr.Radhwan Himmadi Hasan
46