METABOLIC RESPONSE
3. RESUSCITATION , surgical intervention and critical care can return the severly injured patients to asituation in which homeostasis become possible once again .1. HOMEOSTASIS is the foundation of normal physiology
2.As a result of modern understanding of homeostasis minimizing the response by MINIMALACCESS SURGERY & STRESS FREE PERIOPERALINE CARE .
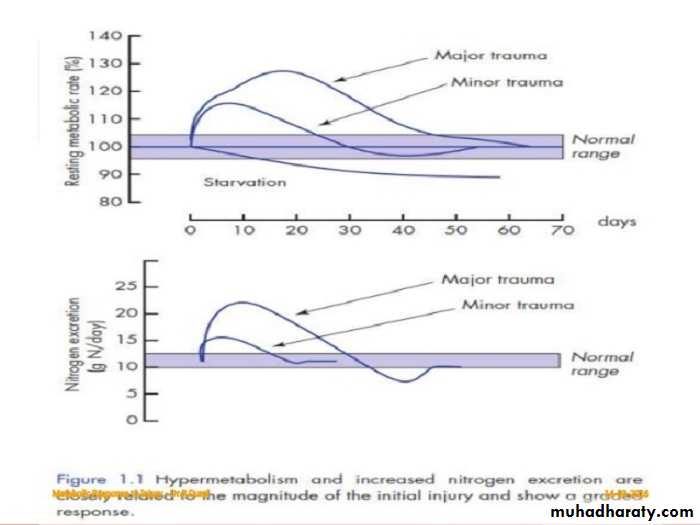
4. THE GRADED NATURE of injury response , (the more sever the injury the greater the response
5.MEDIATERS of the metabolic response to injury :-
A.NEUROENDOCRINE RESPONSE TO INJURY \ CRITICAL ILLNESS IS BIPHASIC :2
* ACUTE PHASE :characterised by actively secreating pituitary & elevated counter – regulatory hormones (cortisol , glutagon , adrenaline ) .
*CHORONIC PHASE : associated by hypothalamic suppression & low serum levels of the respective target organ hormones . Change contribute to chronic wasting .
B.Systemic inflammatery response syndrome following major injury
* is driven initially by proinflammatory cytokines (e.g IL1 , IL6 interleukin -1 and TNF and tumor necrosis factor alpha )3
* Is followed rapidly by increased plasma levels of cytokine antagenists and soluble receptors (IL1Ra,TNF-SR interleukin -1reseptor antagonist & TNF soluble reseptors )
*if prolonged or excession may evshe into acounter – inflammatory syndrome .
Important note on metabolic response :-
1 . Homeostasis : in emergency surgery cause amarked disturbance in homeostasis
4
2. Stress response , spinal cord , thalamus , hypothalamus & pituitary all form apart of the neuroendocrine pathaway .
3. Fluid & Electrolyte conservation :
conservation of sodium & water at renal tubule
4 .Stress response depends upon
Severity of injury5
Types of injury
To get speedy resolution avoid*secondary in sulits l3 is (ischemia , infection , in adequate oxygen .hypoxia.
*ongoing trauma e.g (compartment syndrome DVT (dap.v.thralz)Ongoing complation & secondary recovery ...
Hypothalamus6
TRAUMA spesis major operation
CRF
Anterior pituatory
ACTHAdrenals
cortisolReleaze of cortisole
5. The interplay of neuro , endocrine & infammatory factors :
Catechoamine – mediater .. fightor flight .. response7
Adrenal medulla
adrenalineHypothalamus
Nor-adrenaline from perpher neuro
Neuro hormonal response
Cortisol relazing hormone (CRH)AP (anterior – pituatory)
ACTHCortisol & glucocorhiods
CytokinesInflammatory response
6 .It is hyperglycemia & not hypoglycemia that occurs in stress response .7.IN Ebb (early) phase
8
Inflammatory mediaters and hormone mediators accumelate
Hypovolemic
Hypotension
Anaerobic metabolism
Lactic acid ↑ base deficit ↑BMR ↓ HR ↓ C:O ↓ O2 ↓ Bp ↓ urine ↓ temp ↓
A9
Hormone regulating ebb phase
Catecolamine cortisole aldosterone
Ebb (early) phasePurpose is to conserve circulating volume & energy store for recovery & repair
Achirenin of renin – angiostensin systemThe ebb phase (holding pattern)
B
10
Wounds healing
1. Normal wound healing :
Inflammatory phase of wound healing lasts for 2-3 days . Proliferative phase last from 3 days to 3 weeks ,remoeling phase last from end of 3 weeks to years
INFLAMMATORY PHASE
Also called exudate phase
1. Has no tonsile strength to the wound
2. It consist of vascular , cellular & enzymatic process
Platlet stick to damage new endothalmic
ADP + cytokines +sorozonin + protoglyandine + histamine
releazingCausing vasolar permeability in migration of inflammatory cells & macrophages .
Fibringen fibrine frame for fibroblastic11
Prolifrative phase
Fibroblast activting , collagen proucte , & new capillaries .
Remodelling phaseRe-arrangement of collagen fibers .
2 . Compatment syndromeOccurs usually in the lower limb , following closed injury , circumferenite burns & crush – injury . The patients complains of sever pain assosiated with sensory disturbance , & late stage absent periphere phase . In crush injuries , presentation maybe late , delayed may be dangerous . Then in become lymoglobin releaze from dead muscle result in myoglobinan → crush syndrome → acute renal failure )vndn such circumstance , ampulzine may be safer .
12
3 . Contrac → scars across joint .
4. Hypertrophic scar
5. Keleiod → exuberant scar
6 . Leg ulcer . Merjohns ulcer .
7. Necrotising soft tissue infection causative organisms are ;
Gram +ve (staph. Aerus )+gram –anaerobic (Ecoli .psudomans ,clostridium , bacctremia )& B- hemolytic streptoccoi . The two main type are (clostridial gass gangrine and streptoccoci orisin )
8 . Pressase sore → are bony prominme → ischemic → ulcer