Breast
Dr. Sura Obay AL-DewachiBreasts ( Mammary glands )
The breasts are originated from the skin.They resemble the sweat glands in structure & development & they are regarded as modified sweat glands .
Each breast consists of 15-25 lobes. Each lobe is drained by a duct that emerges at the nipple as an independent opening.
The lobes are separated by interlobular connective tissue & adipose tissue . The lobes are sub-divided into lobules by layer of connective tissue & adipose tissue .
Each lobe has an excretory lactiferous ducts that opens independently at the nipple .
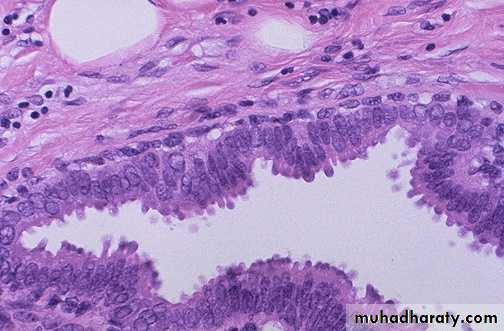
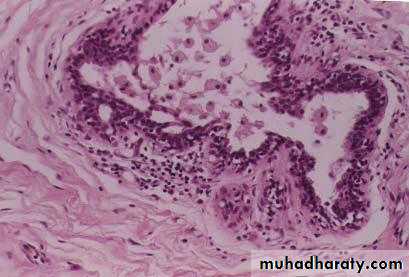
The ductolobular system is composed of dual layers of epithelia resting on basement membrane and enveloped by stroma.
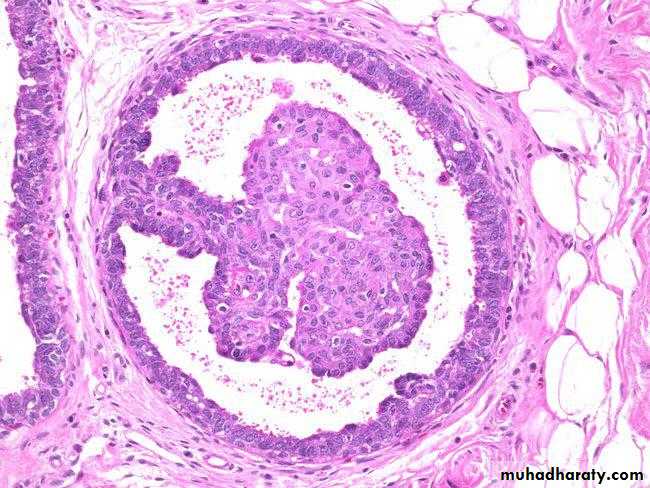
• Duct with double layer
• Normal Breast
Congenital abnormalities :
• Poly mastia : It is the presence of more than two breasts. These may occur any where along the milk-line which extends from the axilla to the groin .• Polythelia : It is the presence of accessory nipples .
Inflammation of the breast
Acute mastitis:It is usually a bacterial infection (staph. And strepto coccus).
Seen most commonly in early weeks of lactation.
Bacteria invade the breast through the small fissures (cracks) in the nipple of lactating woman.
Abscess can result.
Patients have redness, swelling, pain, and tenderness. The axillary lymph nodes are frequently swollen & show reactive hyperplasia .
Micro. : There is an acute suppurative inflammation & with abscess formation.
Chronic mastitis
• Chronic mastitis due to bacterial infection is uncommon .• Most cases are due to incomplete resolution of acute mastitis in the lactating breast
• or due to chronic breast abscess,
• Tuberculosis (very rare) rare but may occur secondary to tuberculosis of the lungs .
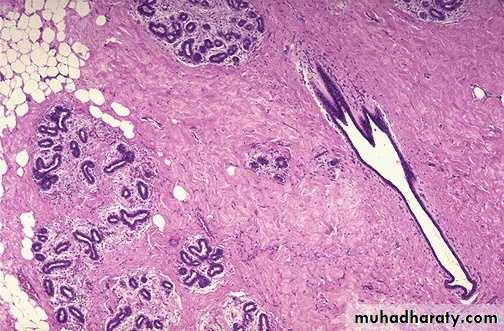
Traumatic fat necrosis of the breast :
• It is caused by a trauma to the breast (accidental or surgical) which cause disruption of fat cells & allow the escape of fat globule into the surrounding tissue.
• Microscopically: necrotic fatty cells surrounded by neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells and lipid filled macrophages, enclosed by fibrous tissue.
• The clinical importance of fat necrosis is that may present as a hard mass that can be misdiagnosed as carcinoma on physical examination, however , it is benign and not associated with increase risk of malignancy.
Mammary duct ectasia
Non bacterial inflammation of the breast associated with inspassation of breast secretion in the main excretory ducts.Ductal dilatation with ductal rupture leads to reactive changes in the surrounding breast substances.
It is usually occur in women near menopause who have born children.
Dilated ducts are filled with fat and cellular debris leading to thick cheesy nipple discharge.
Histologically: ducts are filled with granular debris, lipid laden macrophages, epithelial cells destruction, with prominance of lymphocytes and plasma cells infiltration in periductal stroma.
The importance of mammary duct ectasia that it cause retraction of skin and nipple resembling changes caused by cancer.
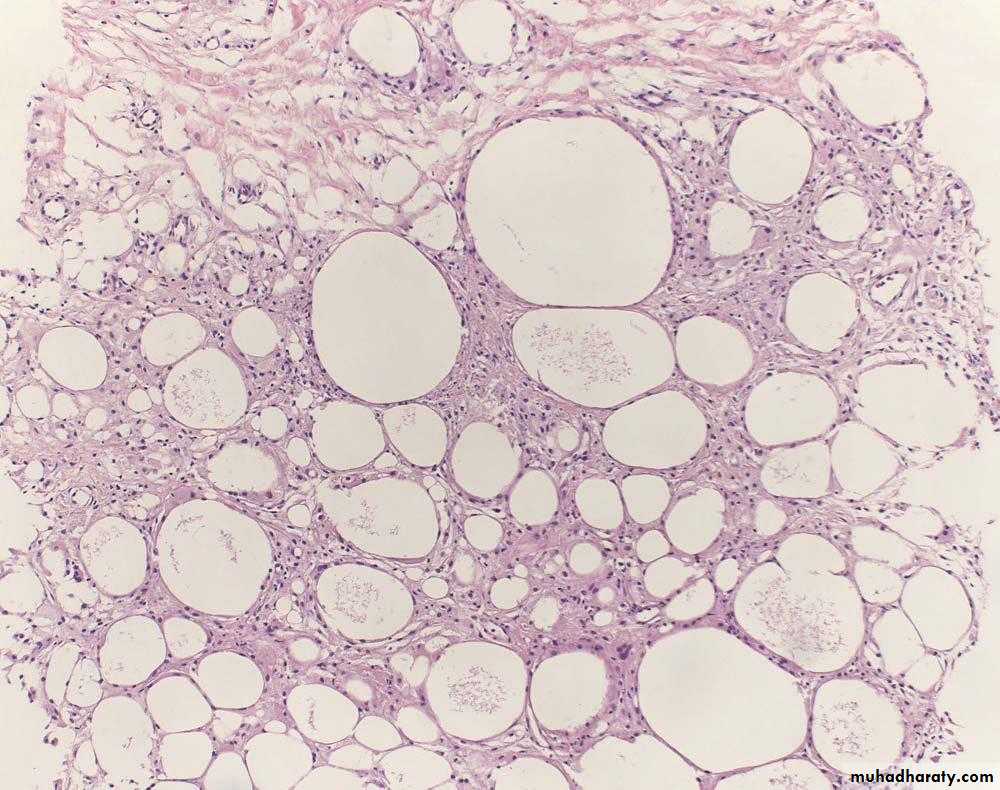
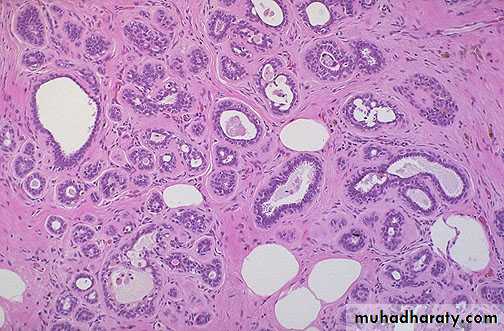
Fibrocystic changes
• It may occur at any age from puberty onwards but is common about the time of menopause & afterwards .• Structural changes : It consists of :
• Fibrosis :
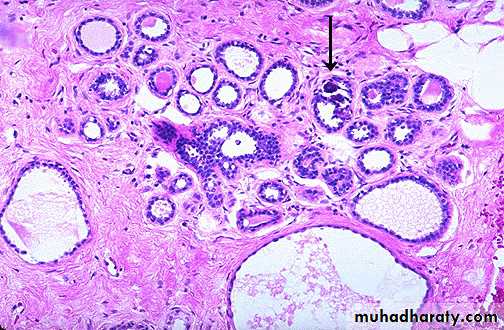
• Cyst formation : It occurs as a result of dilatation of ducts . The cysts are lined by flattened cuboidal epithelium. Some cysts may show metaplasia of the lining epithelial cells which become large , columnar with eosinophilic cytoplasm & it is called apocrine metaplasia .
• c. Adenosis : There is formation of new breast lobules as a result of proliferation of the breast epithelium of ducts & acini. There may be increase in the fibrous stroma producing distortion of the acinar pattern & eventually sclerosis . This is called sclerosing adenosis .
Fibrocystic Disease of Breast :
It is characterized by proliferation of the epithelium & connective tissue of the breast with cystic dilatation of the ducts , due to ovarian hormonal imbalance .The nature of the fibrocystic changes :
The cyclic changes in the ovary , with alternating oestrogen & progesterone secretion , produce effects not only in the endometrium but also in the breasts.Thus there is overgrowth of both epithelium & stroma during the cycle with a return to normal at the end of each cycle. As a result of hormonal imbalance either the epithelium or the stroma or both may remain in an abnormal proliferative state to produce nodular , lumpy or cystic breasts .
Non-Proliferative Breast Changes (Fibrocystic Changes)
Clinical Presentation
Palpable lump
Mammographic calcification
Nipple discharge
Morphology
Cysts formation, apocrine metaplasia
Fibrosis
Adenosis.
No risk for carcinoma
• Fibrocystic disease
• Fibrocystic disease, adenosis, fibrosis, cystic change
• Fibrocystic disease, apocrine change
Proliferative Breast Diseases Without Atypia
MorphologyProliferation of ductal epithelium and/or stroma in form of
• Epithelial hyperplasia
• Sclerosing adenosis
Mild risk for carcinoma
• Epithelial hyperplasia• Sclerosing adenosis
• Epitheliosis :
• The essential feature is increase in the thickness of the epithelium of the wall of ducts & acini due to hyperplasia of the epithelium of ducts & acini . Thus the cells are several layers in depth & the lumen may be completely obliterated by this proliferation .• Proliferative Breast Diseases With Atypia
Morphology
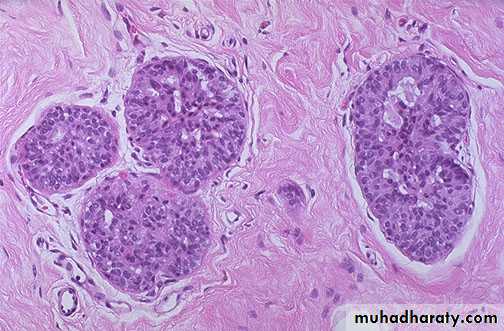
Atypical ductal hyperplasia
Atypical lobular hyperplasia
moderate risk for carcinoma
Tumours of the breast
• Benign tumours
• The main tumours are :
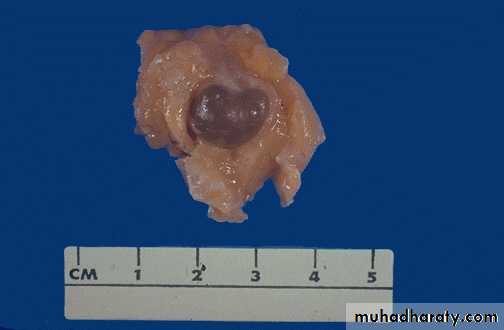
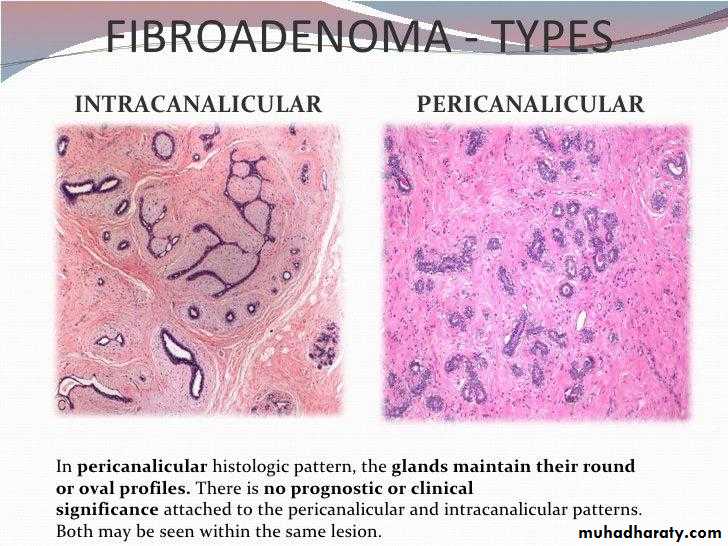
• Fibroadenoma :
• It is the commonest benign tumour of the breast .
• It consists of both stromal & epithelial elements.
• Fibroadenoma is small well circumscribed rounded mass & movable.
• Presents as
• Palpable mass in young women
• Mammographic density or calcification in old women
• Microscopically :
• Types :• Pericanalicular : It consists of fibrous tissue surrounding groups of epithelial acini
• Intracanalicular : It is composed of fibrous tissue surrounding epithelial clefts which represent compressed ducts
• . Mixed
•
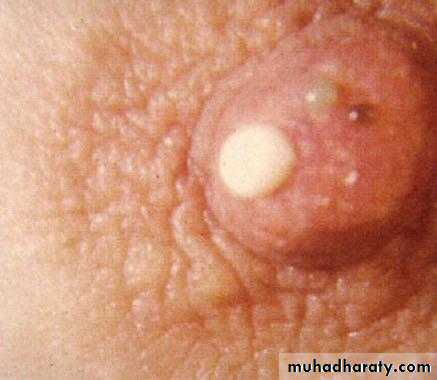
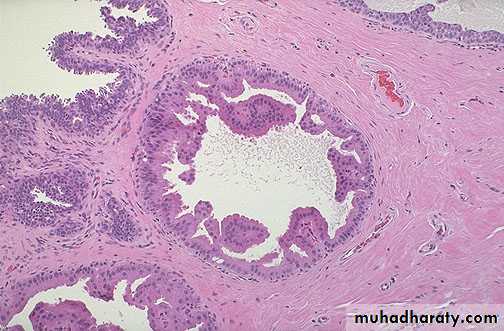
2. Duct papilloma :
It occurs as a pedunculated tumour which forms within a distended duct.
It consists of a branching fibro vascular stromal core covered by cuboidal epithelium.
It causes blood discharge from the nipple.