Breast ( Practical)
Dr. Sura Obay AL-DewachiNormal breast
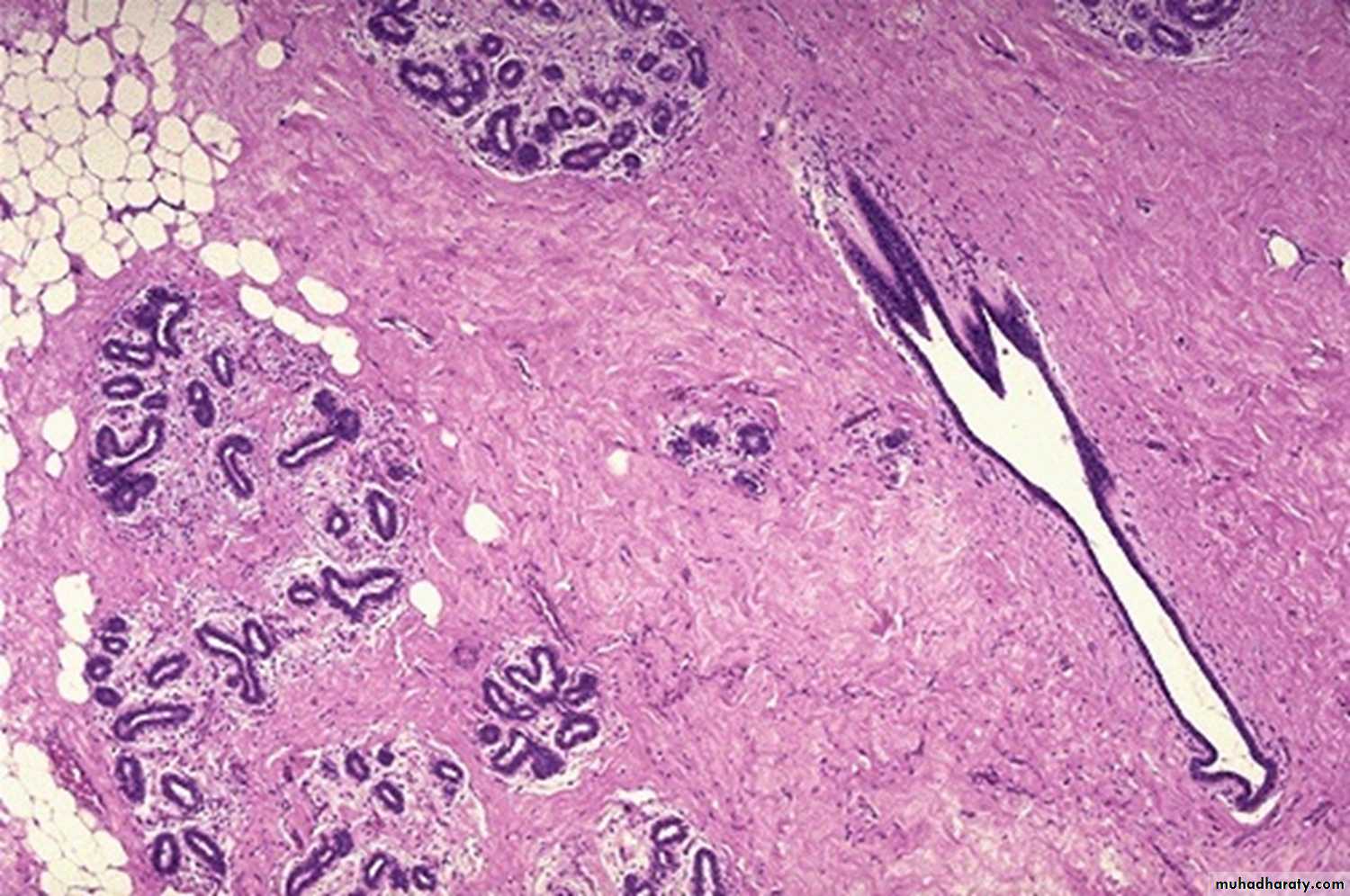
Traumatic fat necrosis of breast : lipid filled spaces surrounded by neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells and lipid filled macrophages, enclosed by fibrous tissue. :
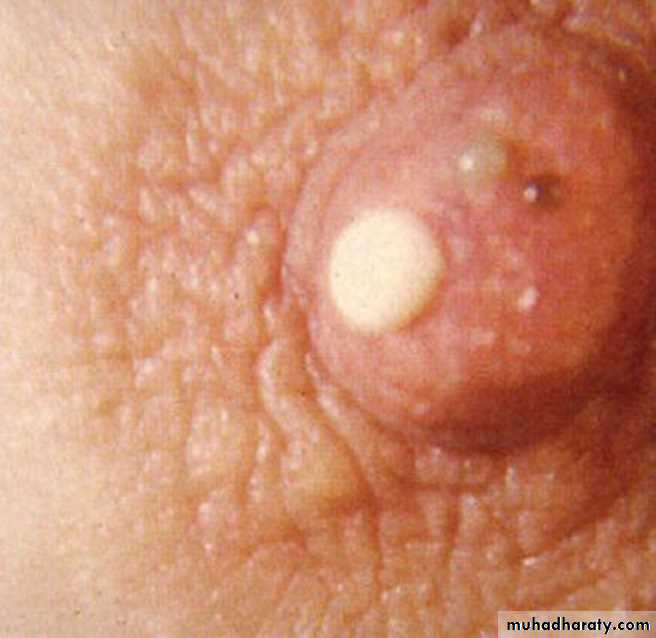
Thick cheesy nipple discharge(Mammary duct ectasia)
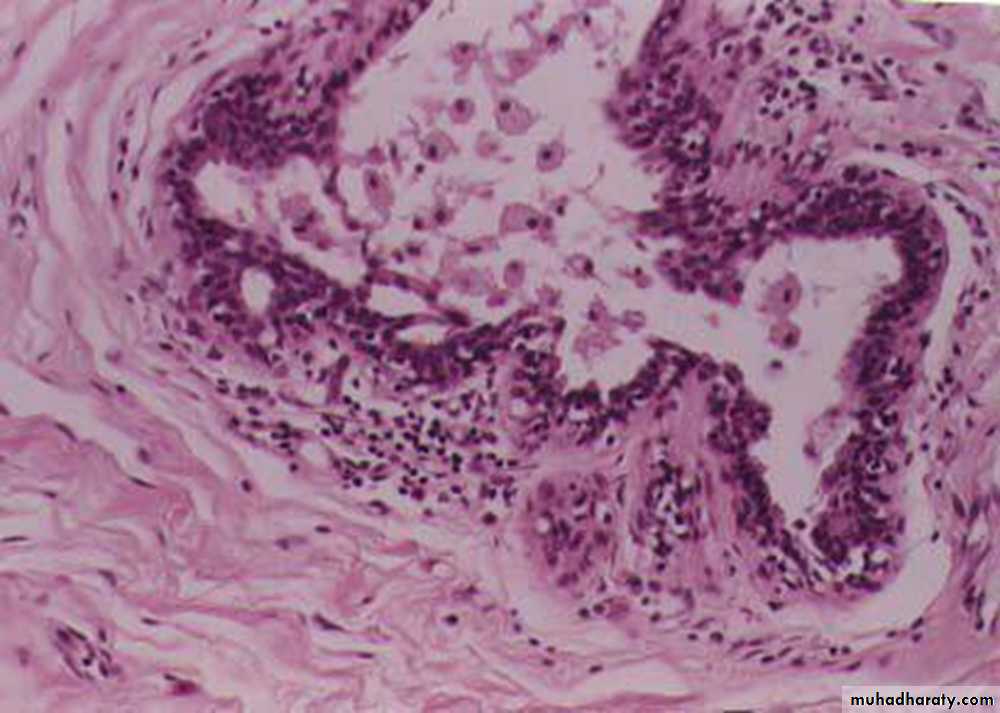
Mammary duct ectasia: irregularly dilated duct filled with lipid laden macrophages, with prominance of lymphocytes and plasma cells infiltration in periductal stroma.
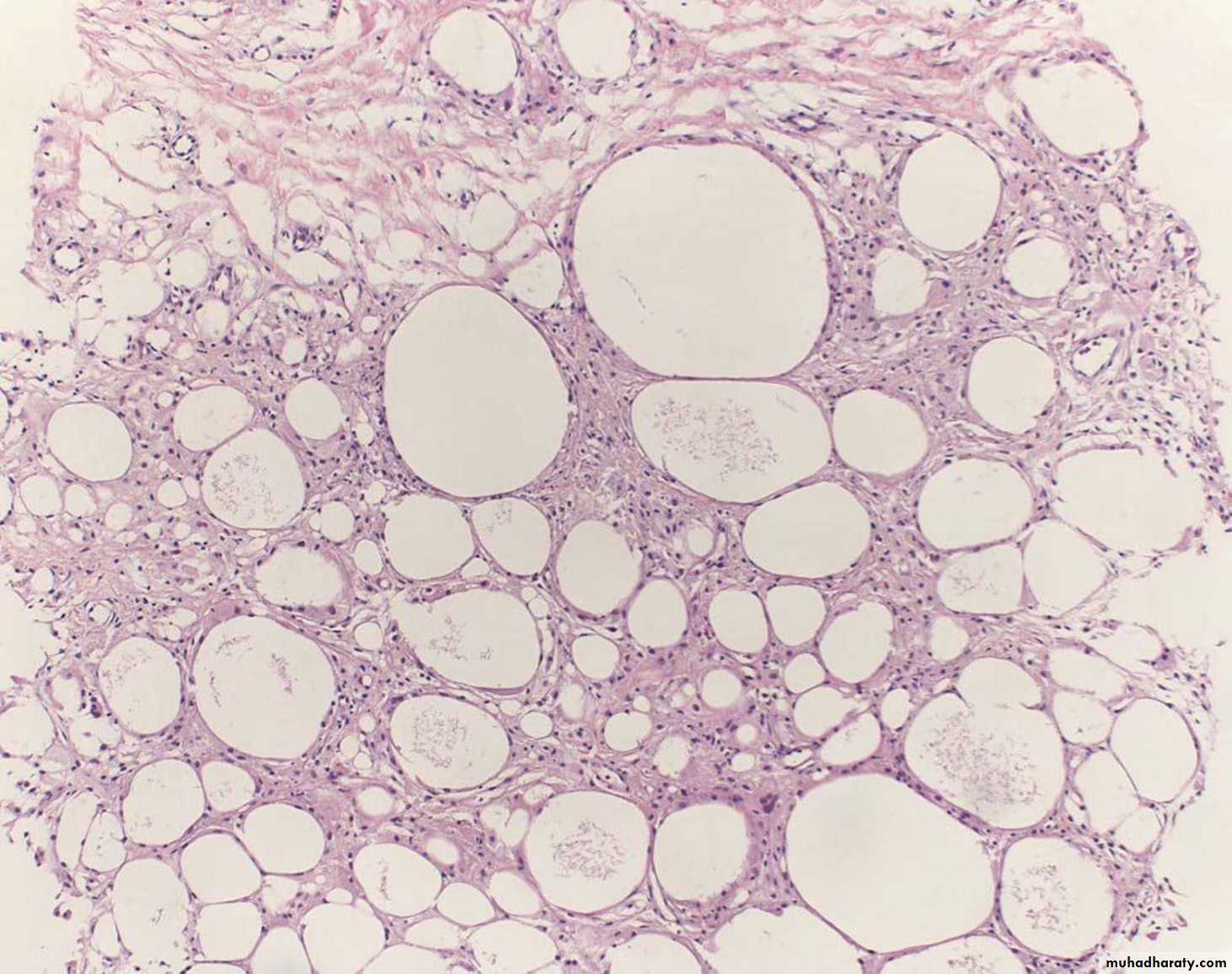
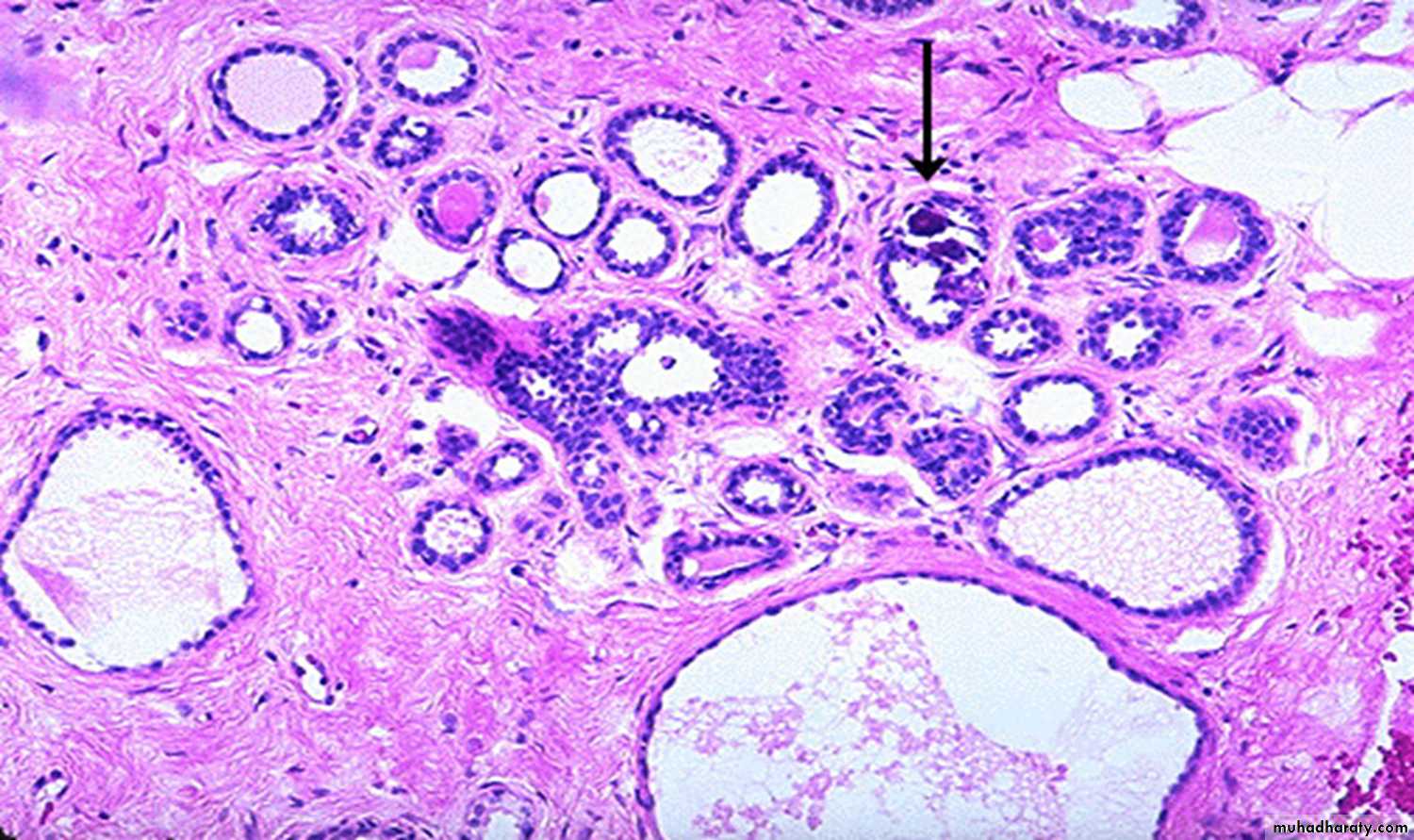
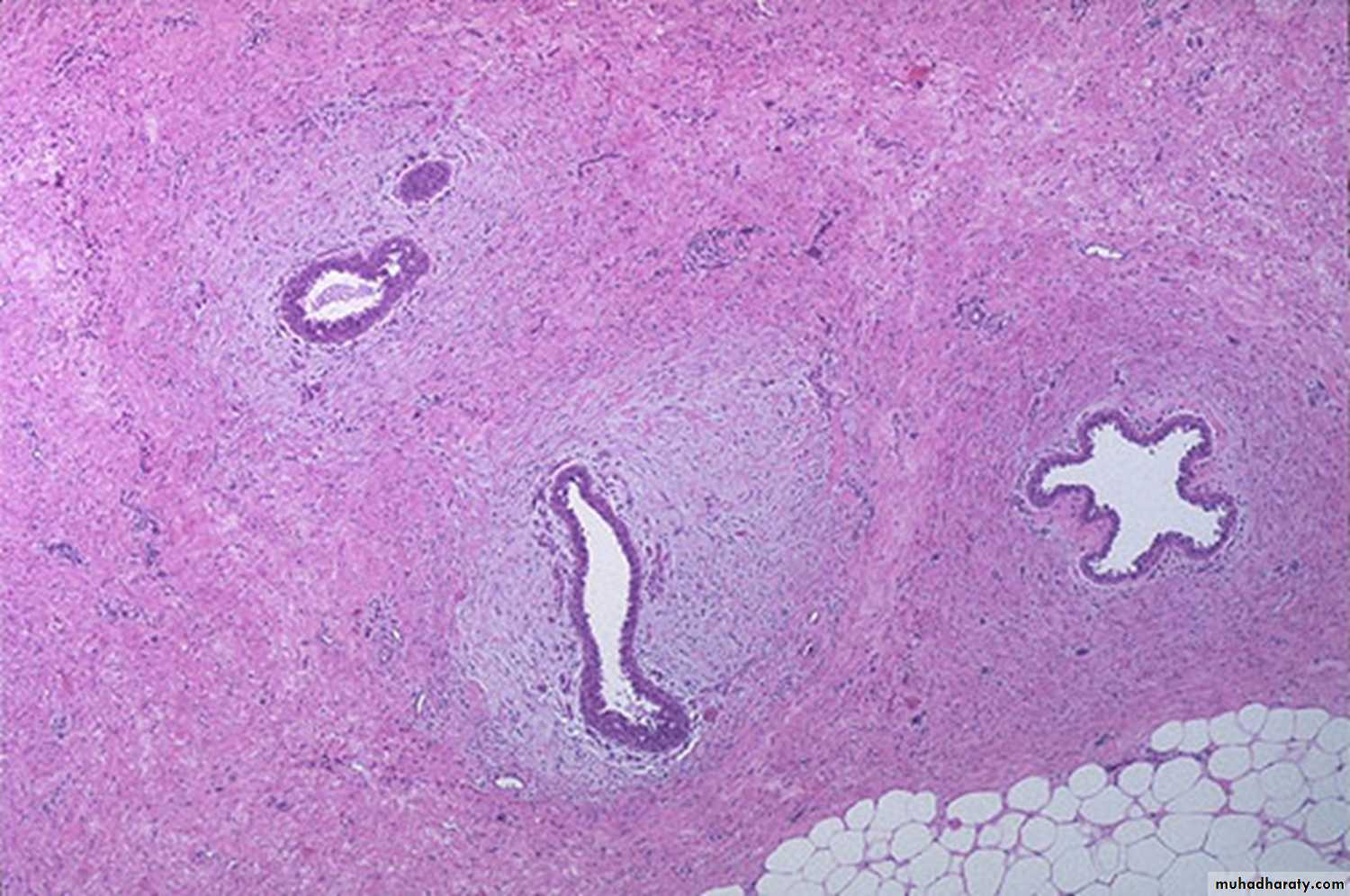
Fibrocystic disease: fibrosis, formation of cysts which are lined by flattened cuboidal epithelium, and adenosis.
Fibrocystic disease: metaplasia of the lining epithelial cells which become large , columnar with Eosinophilic cytoplasm (apocrine metaplasia)
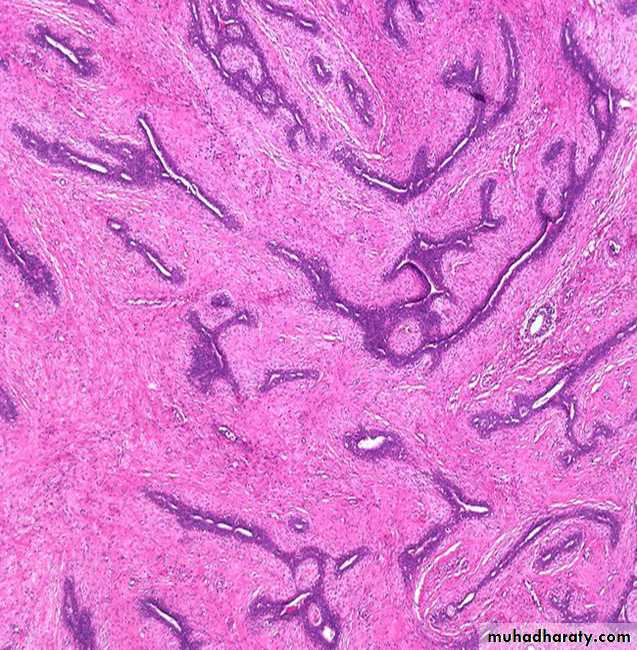
Fibroadenoma of the breast
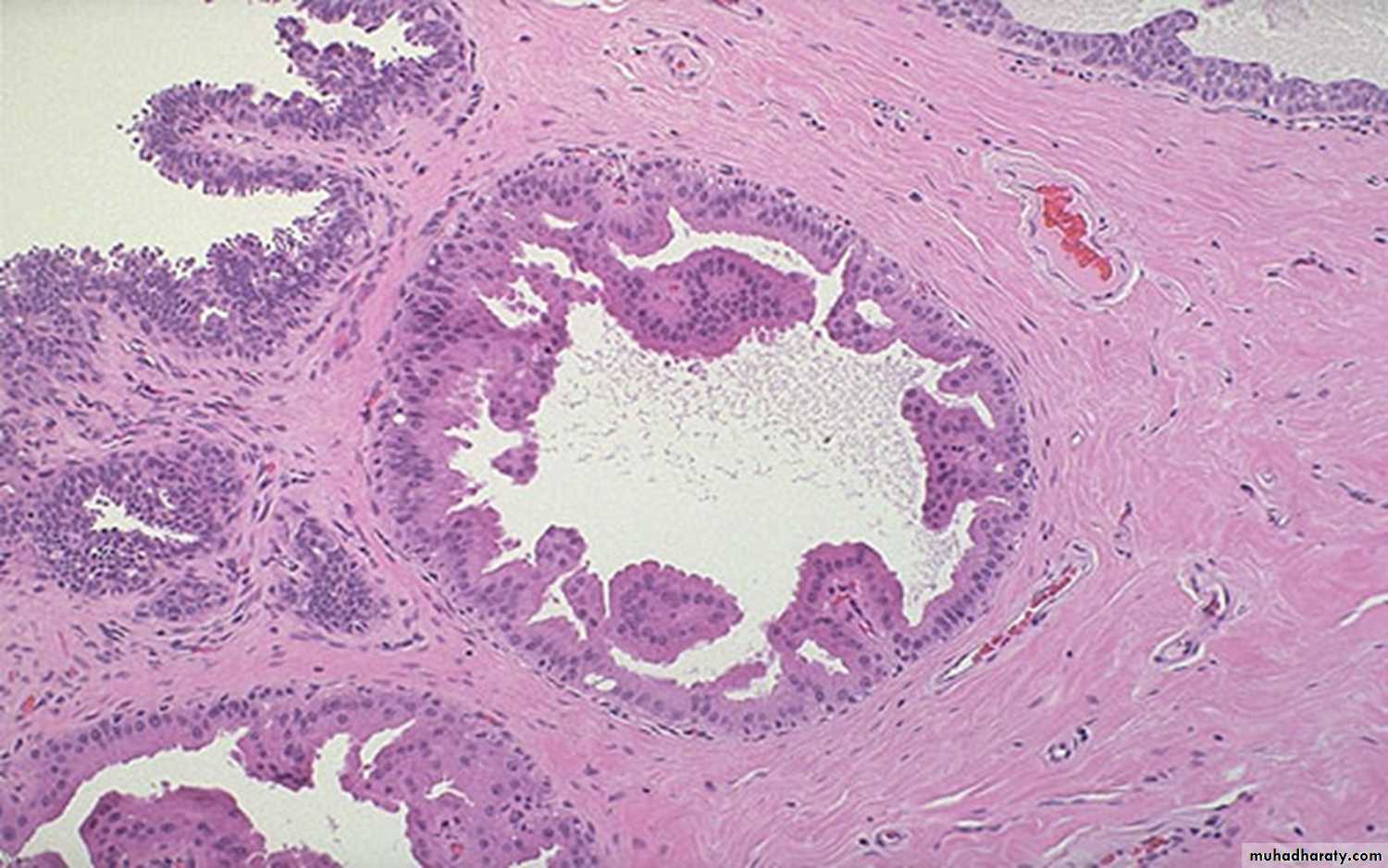
Intracanalicular fibroadenoma: stromal proliferation compresses the ducts which are irregular and reduced to slits.Duct papilloma: branching fibro vascular stromal core covered by cuboidal epithelium
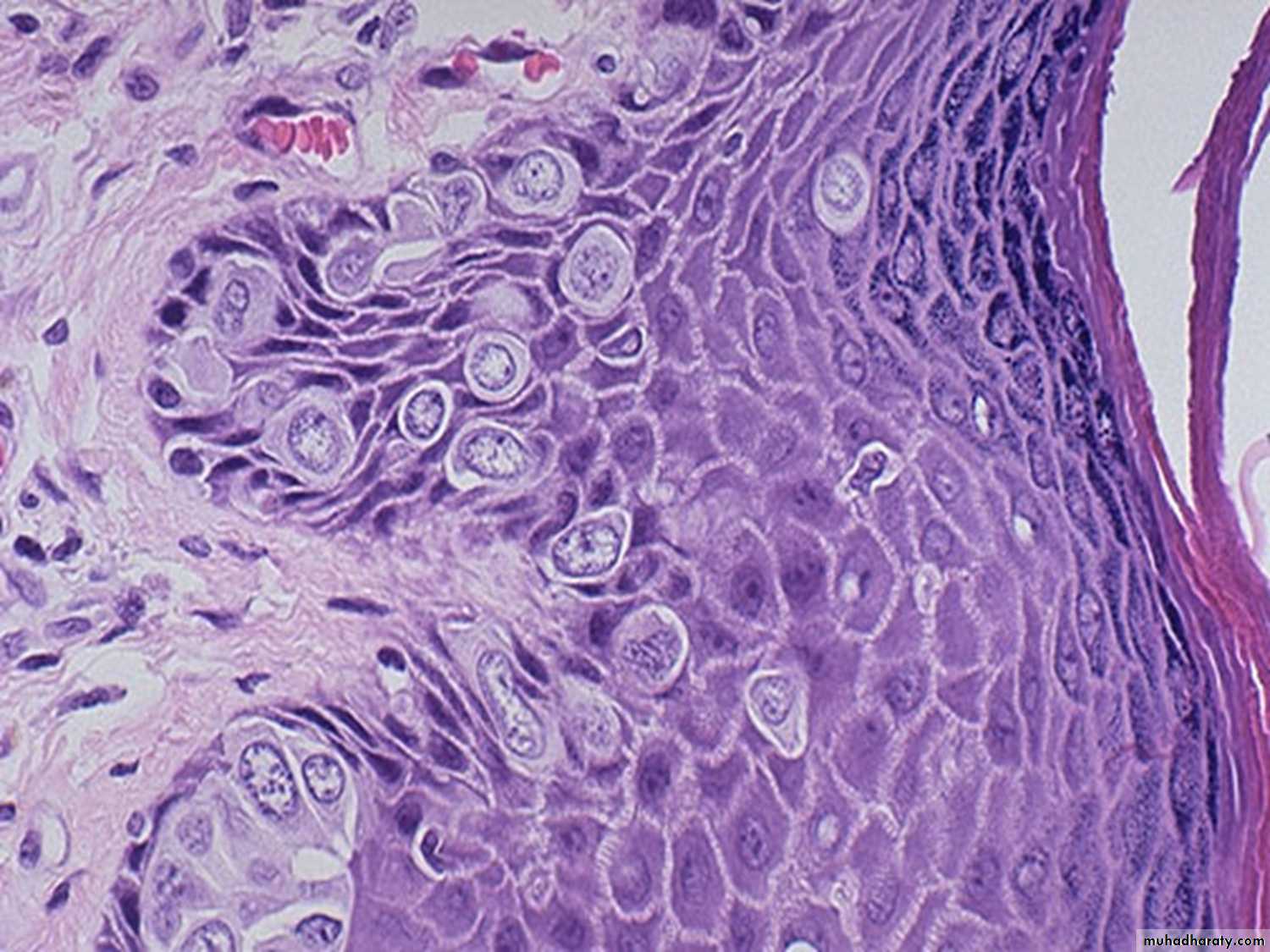
Paget disease of the breast: large cells with abundant clear cytoplasm and pleomorphic nuclei dot the epithelium
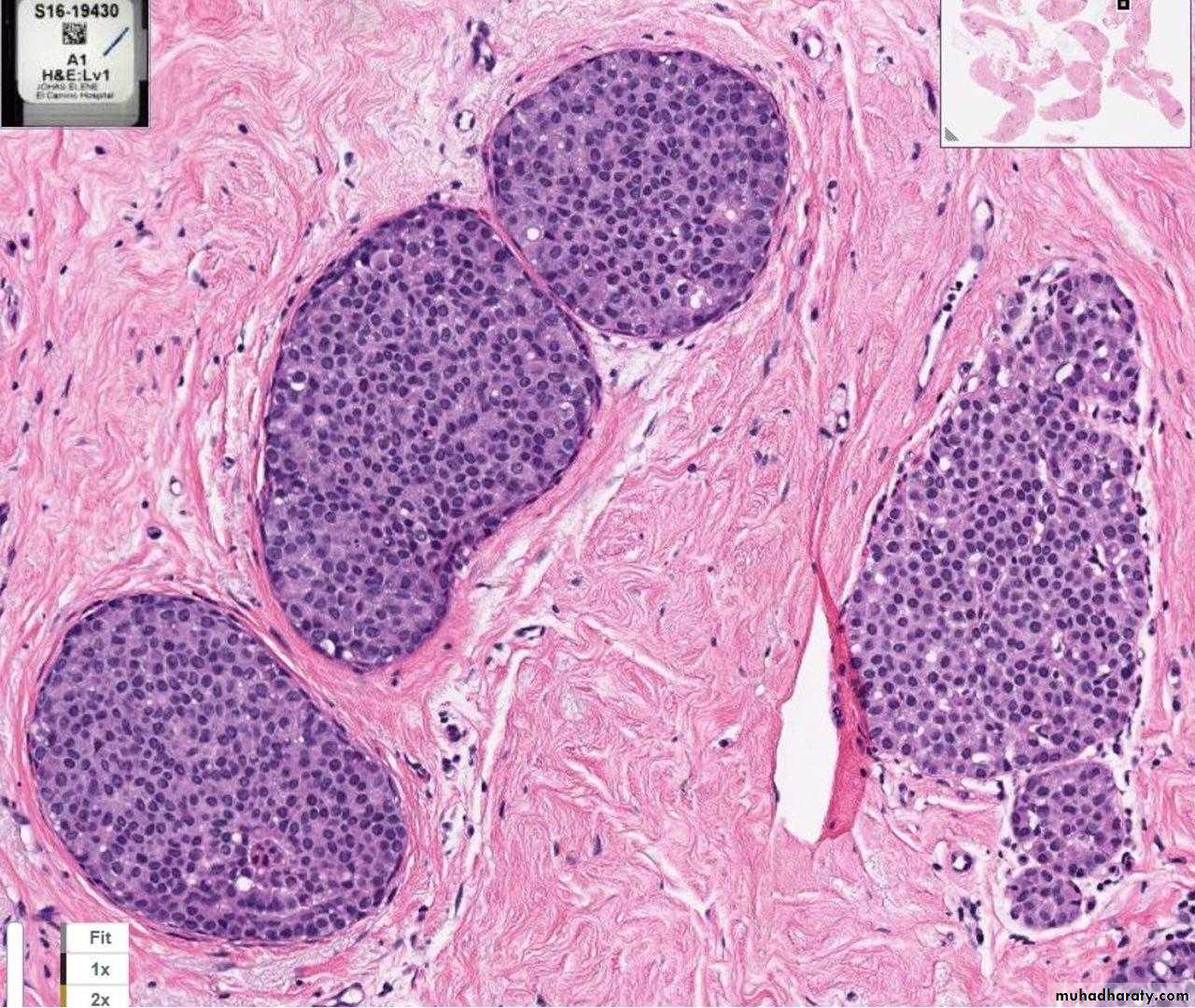
LCIS: TDLU filled and distended by proliferation of small uniform cells which are loosely cohesive, vacuolated cytoplasm.
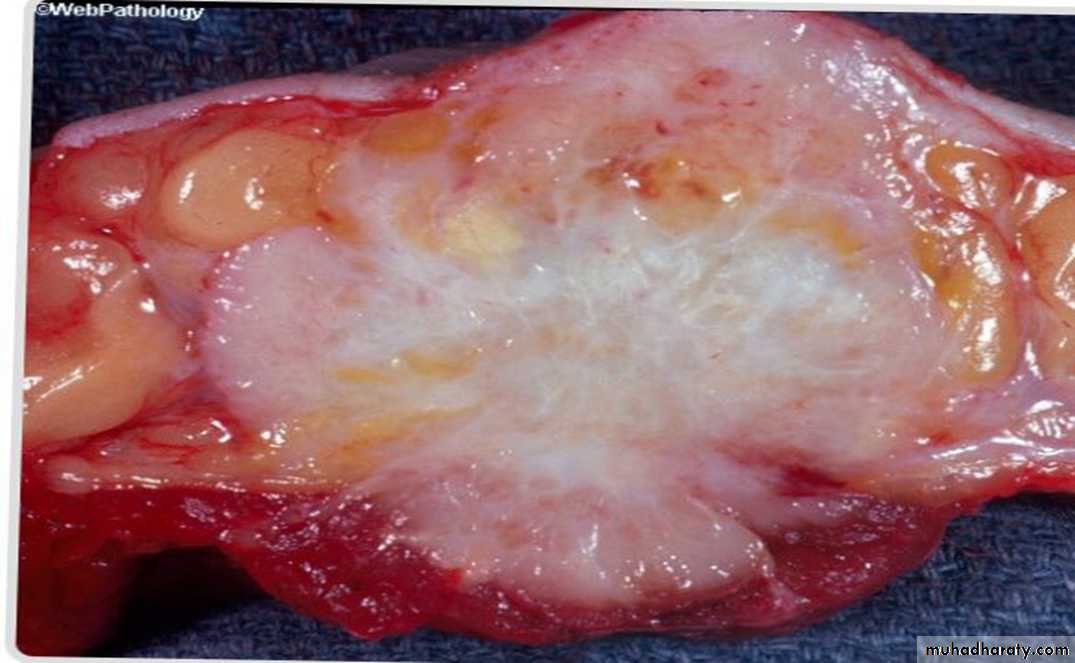
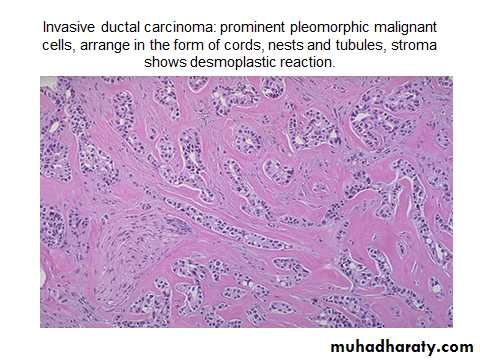
Invasive ductal carcinoma
• Solid mass• Irregular borders
• Gray- white in appearance
• Presence of yellow –white streaks of necrosis
• Foci of hemorrage
•
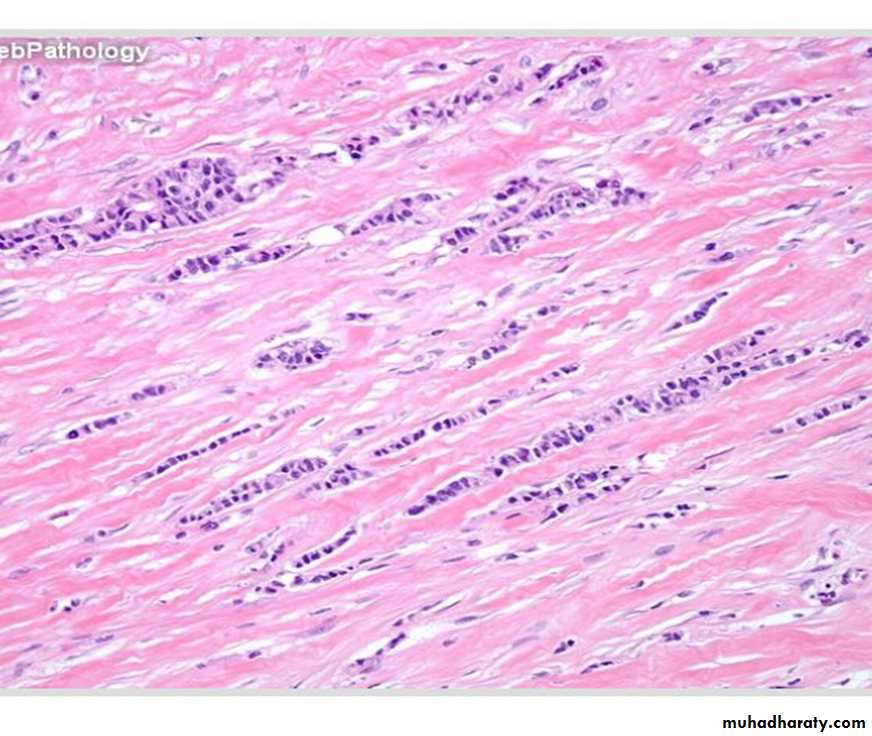
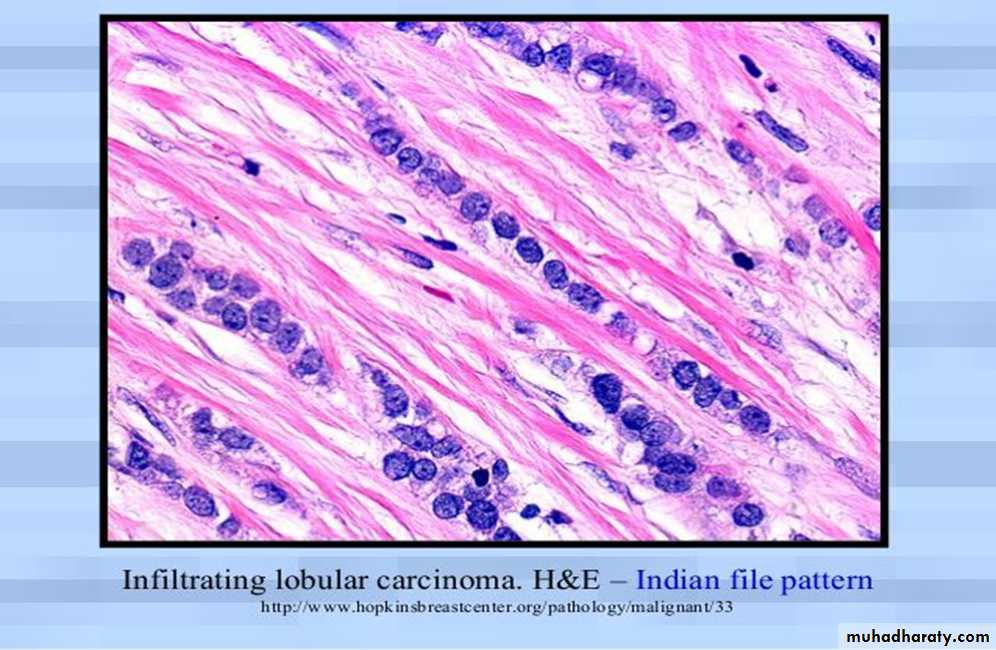
Invasive lobular carcinoma
• Absence of solid, alveolar ,papillary, or gland forming units.• The tumor cells are arranged in slender linear strands.
• Indian file pattern.
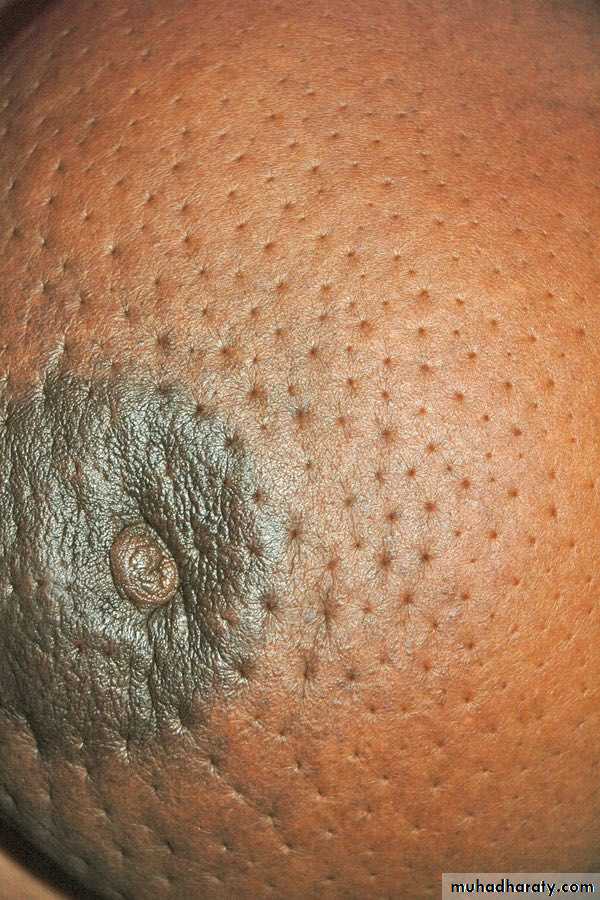
BREAST CARCINOA (peau d’ orange)
• Nipple retraction and peau d” orange appearance of surrounding skin• Skin of orange is due to dermal edema caused by obstruction of superficial lymphatics by the tumor.