Lec.1
HistologyHistology
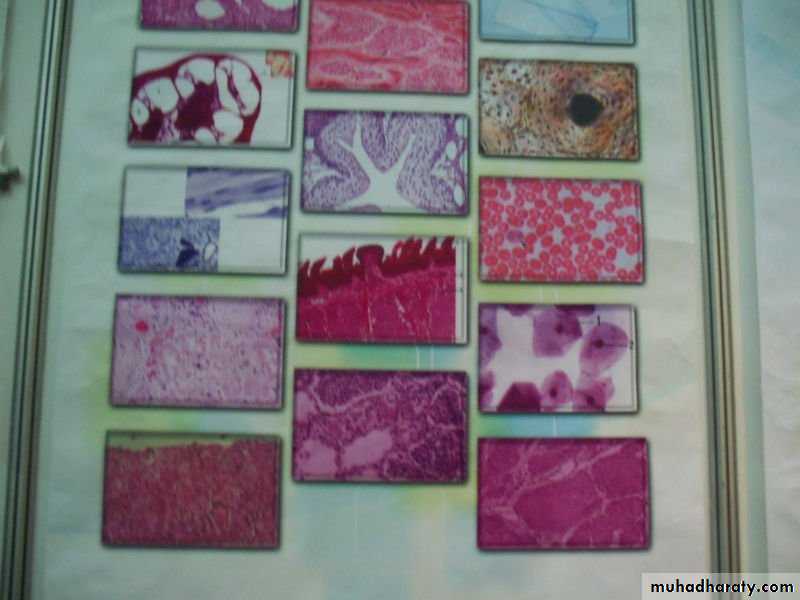
Histology: (Gr. histo, web or tissue, + logos, study) is the study of cell and the extracellular matrix of tissues.
A tissue : is a group of similar cells that perform a particular function.
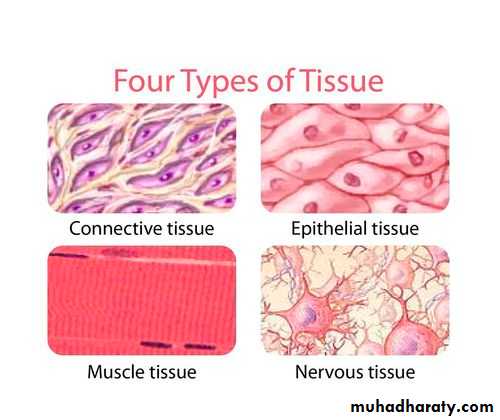
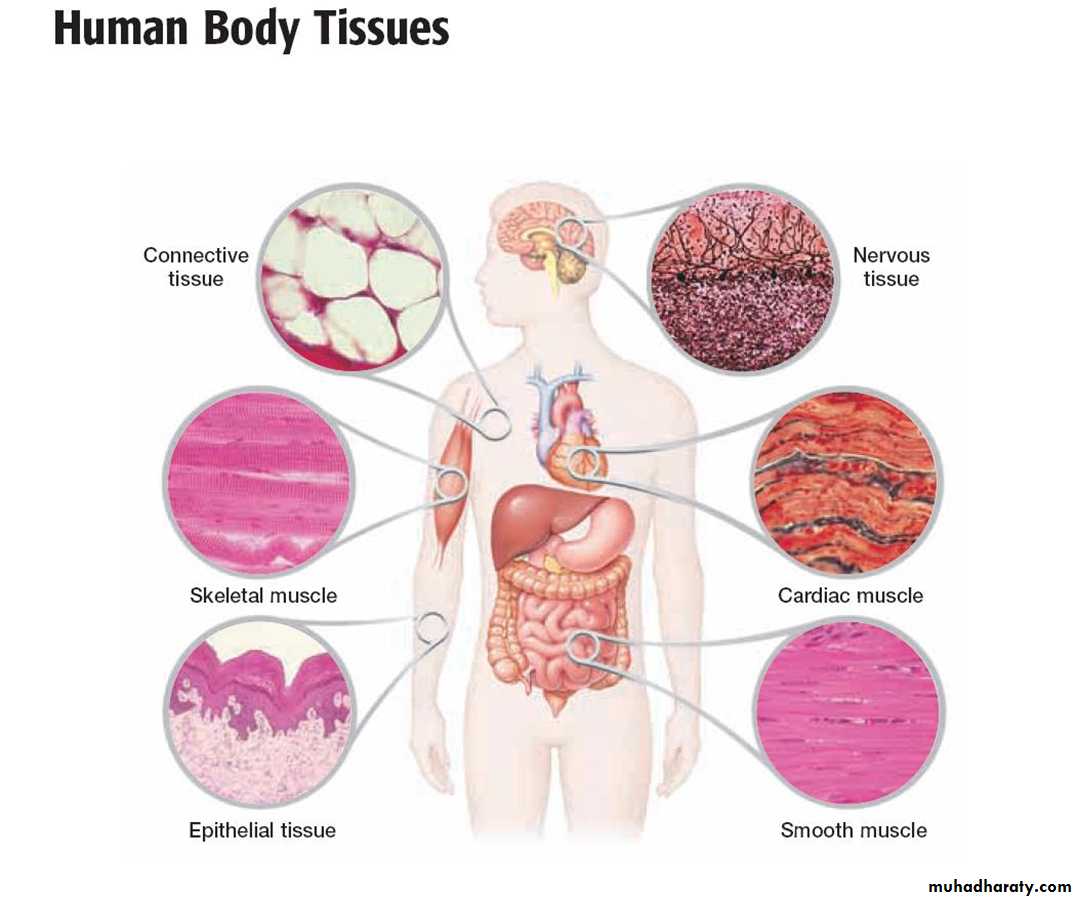
• The human body has four types of tissue:
• Epithelial Tissue.• Connective Tissue.
• Muscular Tissue .
• Nervous Tissue .
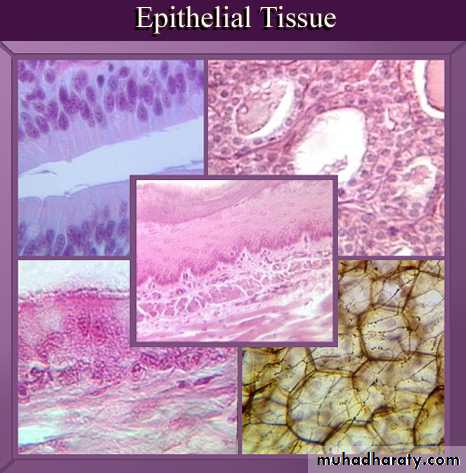
Epithelial tissue is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity. Two forms occur in the human body:
• Covering and lining epithelium– forms the outer layer of the skin; lines open cavities of the digestive and respiratory systems; covers the walls of organs of ventral body cavity.
• Glandular epithelium– surrounds glands within the body.
Characteristics of epithelium :
• Cells are close to each other.• Cells tend to form junctions.
• Little intercellular material.
• Lines surfaces and cavities or form glands.
5. Cells show polarity( apical , lateral , and basal surfaces).
6. Rests on a basement membrane .7.Does not contain blood vessels.
8.Epithelia have the ability to undergo mitosis and replace damaged cells.
Functions of epithelial tissues
(1) To protect the tissues that lie beneath it from radiation, toxins, invasion by pathogens, and physical trauma.
(2) The regulation and exchange of chemicals between the tissues and a body cavity.
(3) The secretion of hormones into the blood vascular system, and/or the secretion of sweat, mucus, enzymes, and other products.(4) To provide sensation.
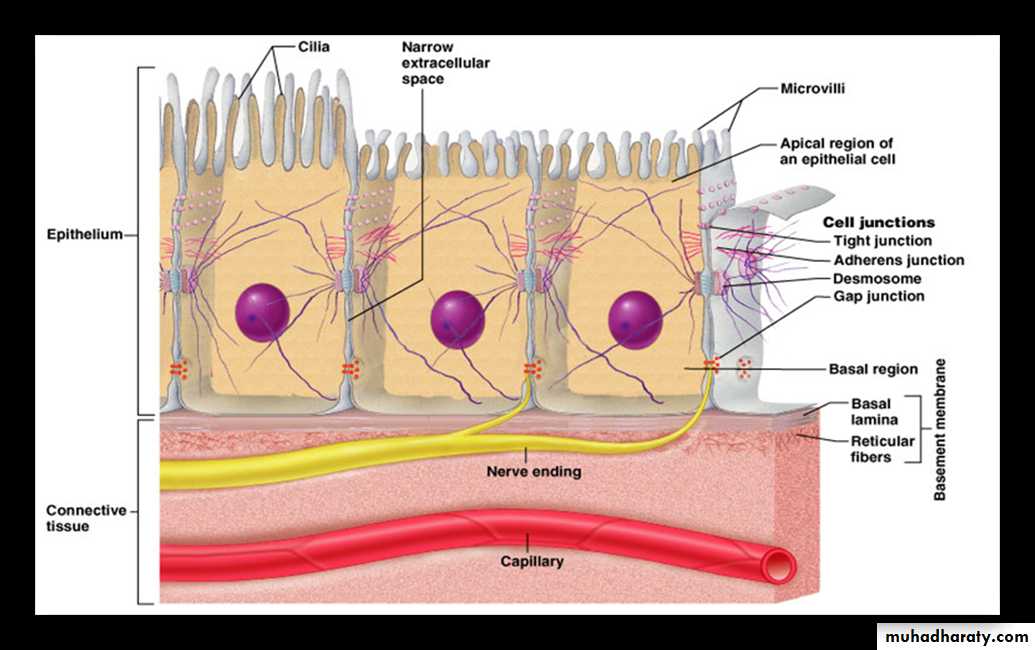
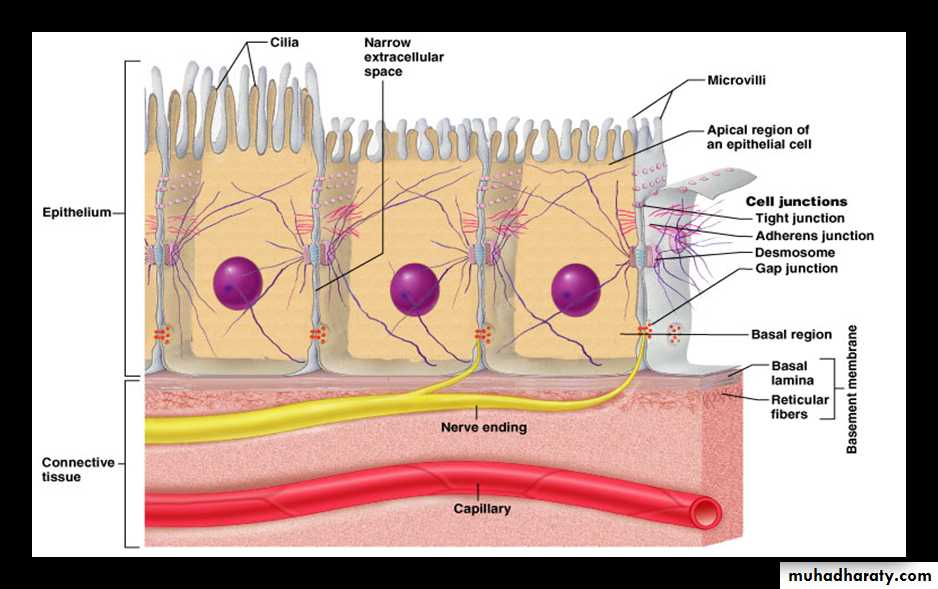
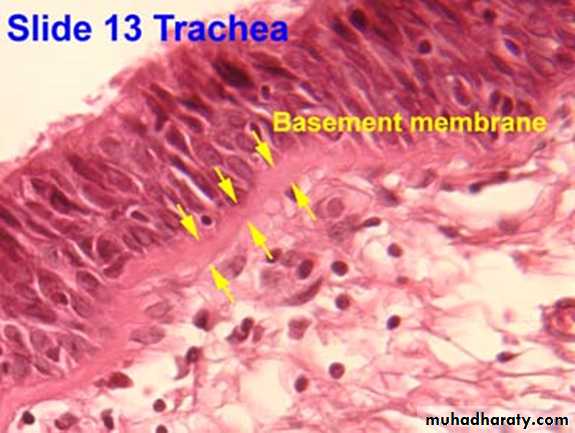
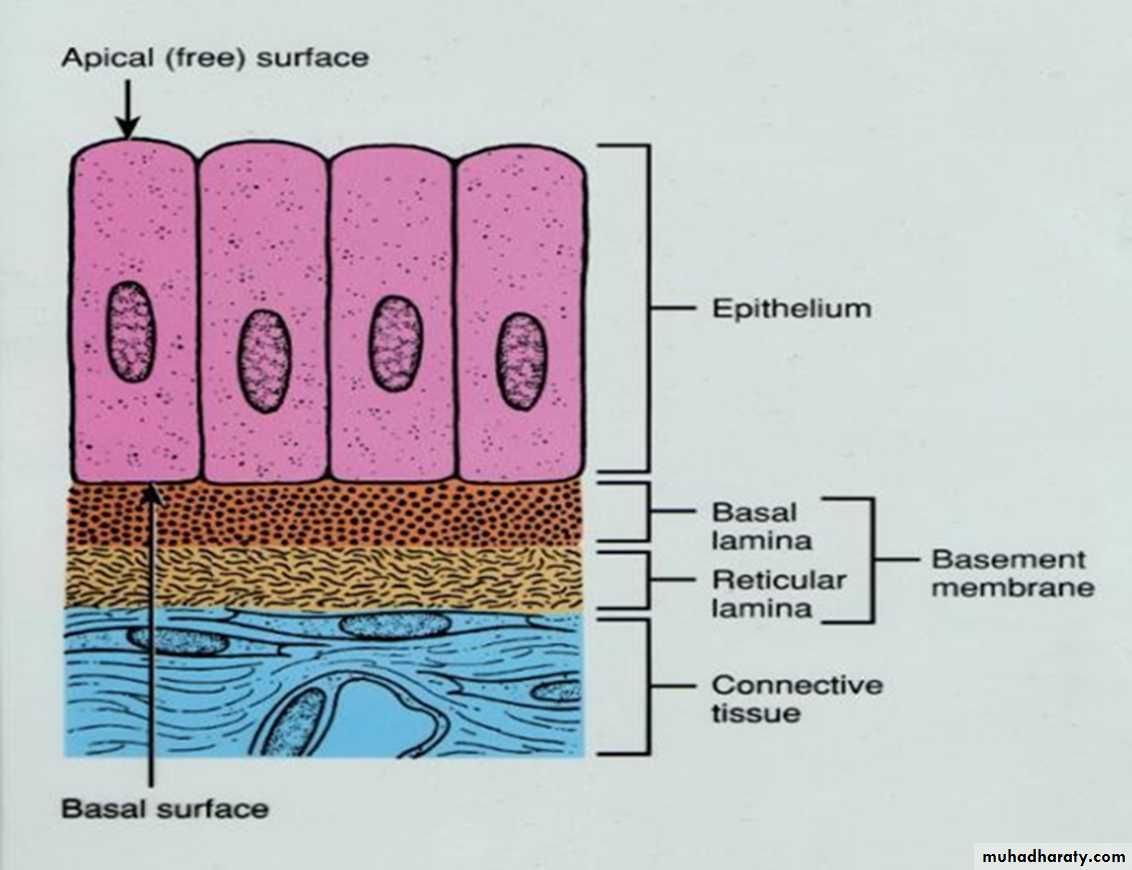
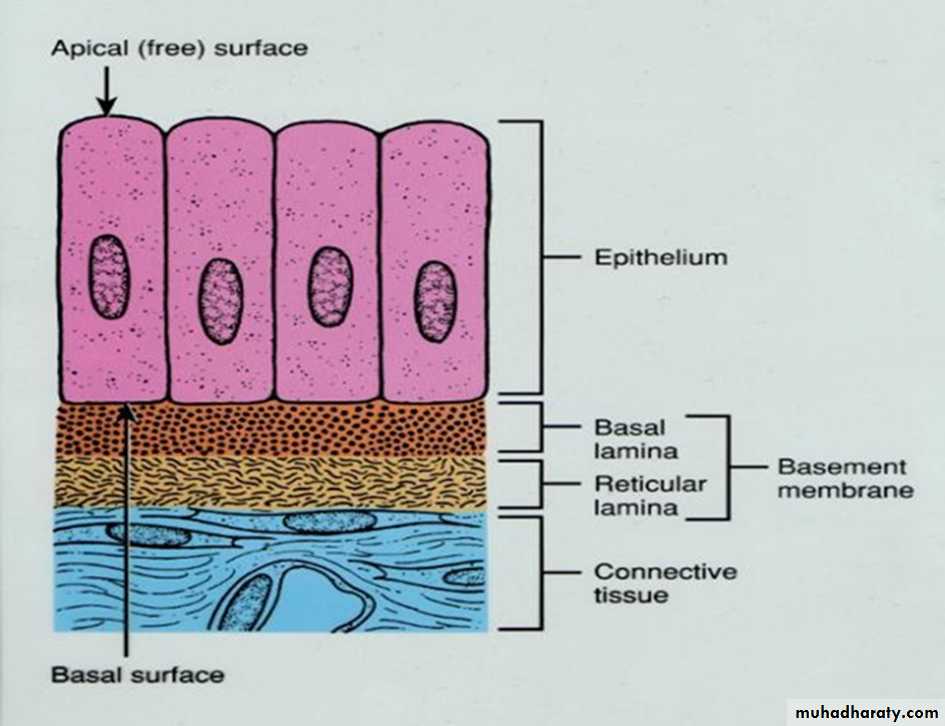
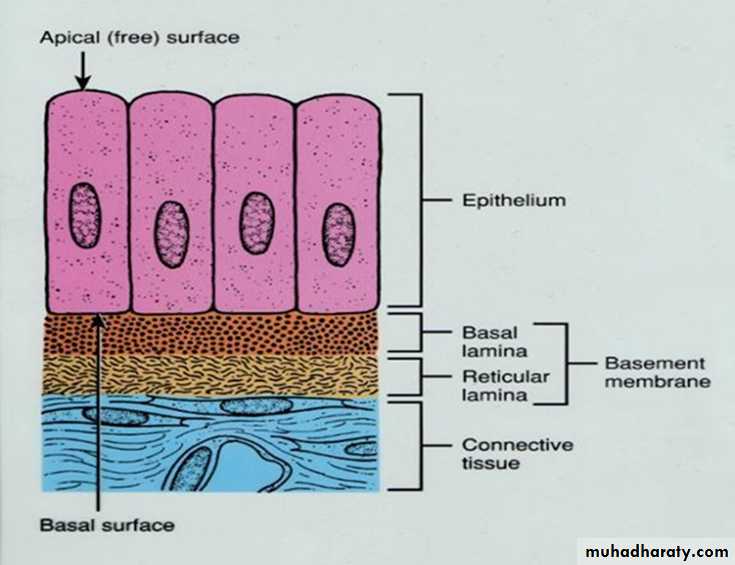
The basement membraneThe basement membrane is a thin sheet of fibers that anchors the epithelium to underlying connective tissue.
basement membrane is composed of two sub layers:
• The basal lamina• The reticular lamina
The two layers (the basal lamina and the reticular lamina) are collectively known as the basement membrane.
1.The basal lamina : The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. The main components of basal lamina are :
• collagen,
• glycoproteins laminin
• and proteoglycan
2.The reticular lamina : The reticular lamina located under the basal lamina of most basement membranes. The reticular lamina consists of:
reticular fibers embedded in ground substance. The components of the reticular lamina are formed by cells of the connective tissue underlying the epithelium.
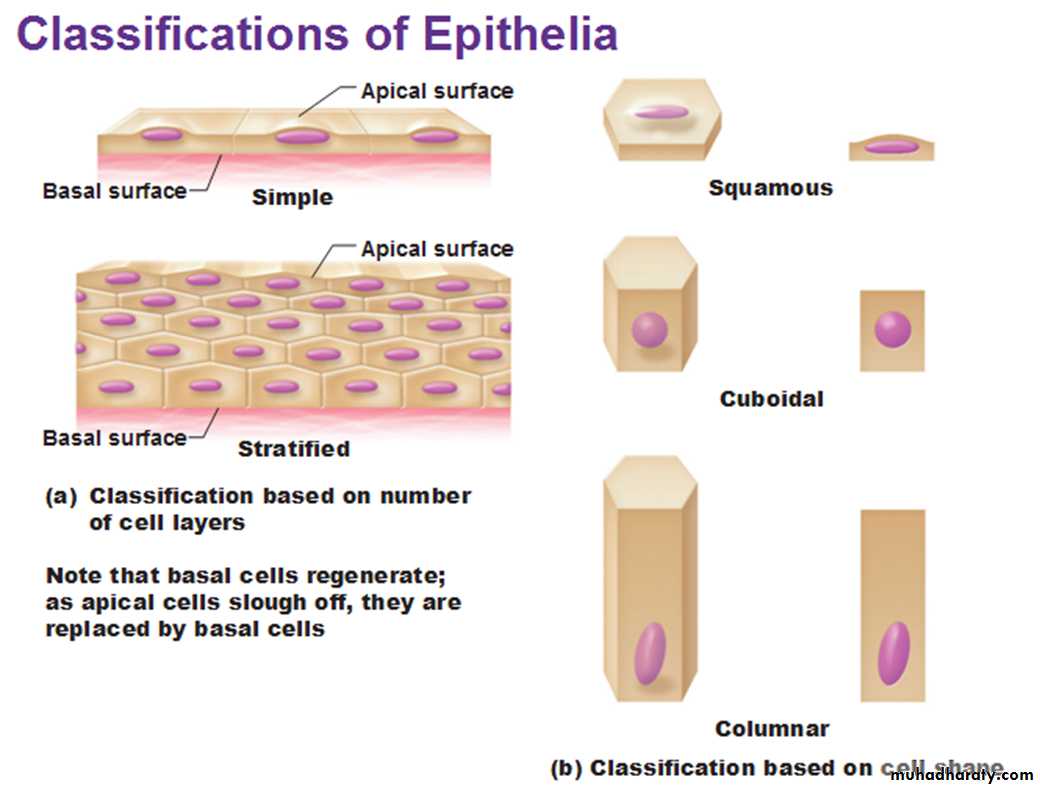
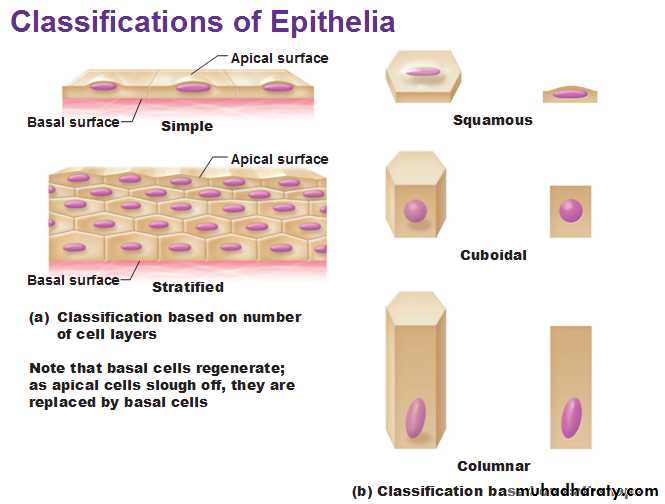
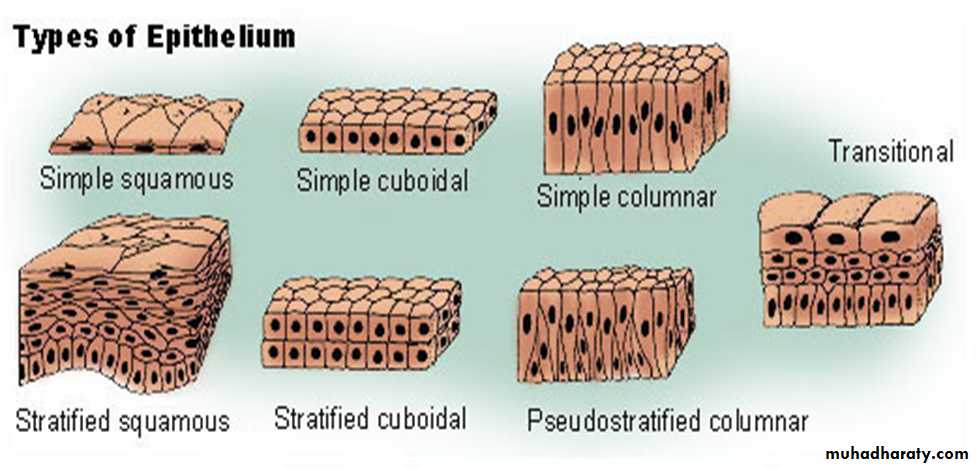
Classification of Epithelia
Epithelium has two names. The first name indicates the number of cell layers, the second describes the shape of its cell.1.Simple epithelia– consist of a single cell layer (found where absorption, secretion, and filtration are needed).
2.Stratified epithelia– are composed of two or more cell layers stacked on top of each other (typically found where protection is needed).
There are three ways to describe the shape of epithelial cells.
1.Squamous cells– are flat and scale-like.2.Cuboidal cells– are box-like.
3.Columnar cells– are tall.Types of epithelium
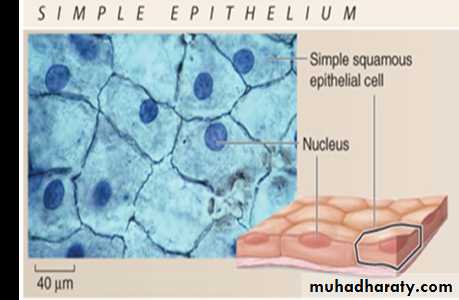
1-Simple squamous epitheliumConsists of a single layer of thin, flattened cells that fit tightly together and have flattened nuclei. It is found where filtration is needed (kidneys, lungs) .
Two simple squamous epithelia in the body :
a.Endothelium– provides a friction-reducing in lymphatic vessels and all organs of the cardiovascular system (heart, blood vessels, capillaries).b.Mesothelium– is the epithelium found in serous membranes (membranes lining the ventral body cavity and covering the organs within it).
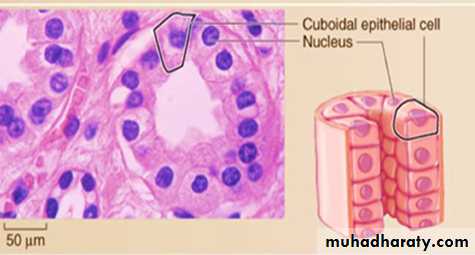
2-Simple cuboidal epithelium
• Consists of a single layer of cube-shaped cells that usually have centrally located, spherical nuclei.• Functions include secretion and absorption (located in small ducts of glands and kidney tubules).
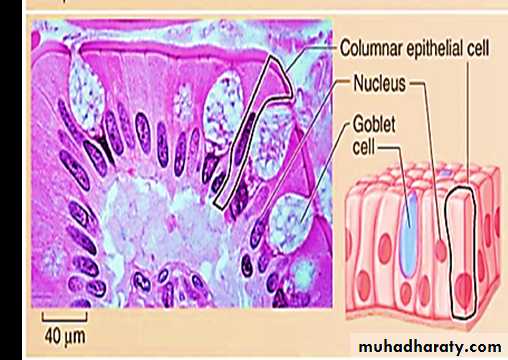
3-Simple columnar epithelium
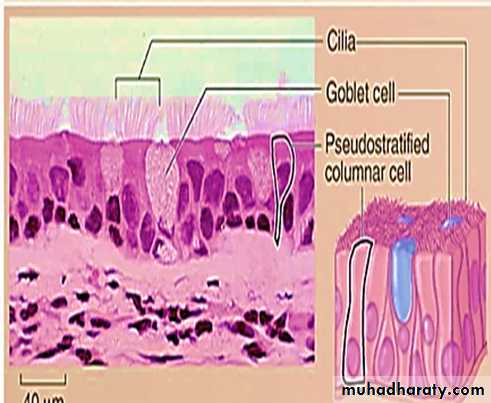
• Consists of a single layer of elongated cells that have oval nuclei usually located near the basement membrane.• Some cells have cilia or microvilli .
• Simple columnar epithelium may contain mucus- secreting unicellular gland (goblet cells).
• Simple columnar epithelia line the digestive tract from the stomach to the rectum. Functions include absorption and secretion
4-Pseudostratified epithelium
• All of their cells rest on the basement membrane and only the tallest reach the apical surface.• When viewing pseudostratified epithelium it may look like there are several layers of cells, but this is not the case. (because the cells have different heights, it gives the illusion of multiple cell layers).
• Most pseudostratified epithelia contain cilia on their apical surface and line the respiratory tract.
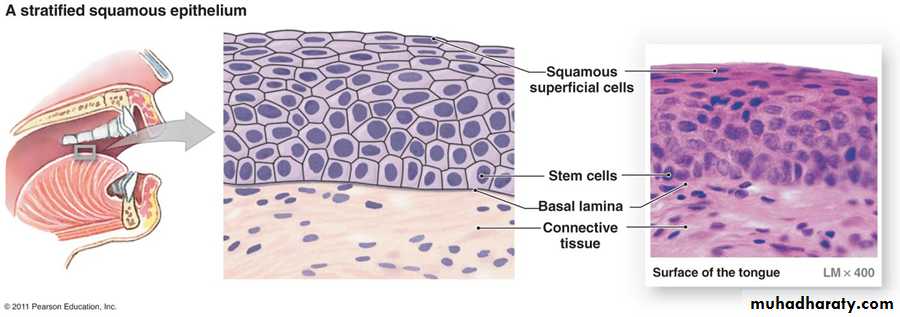
5-Stratified Squamous Epithelium:
a. Stratified Squamous (Non keratinized) Epithelium• Stratified Squamous (Non keratinized) Epithelium tissue is thick, because its composed of several layers of cells, the deepest layer is in contact with the basal lamina.
• The basal cells are cuboidal in shape,
• Cell located in the middle of the epithelium are polymorphous
• The superficial cells of the epithelium are flattened (squamous).
• This tissue is not contain keratin and the surface cells are nucleate. It's found lining the mouth.
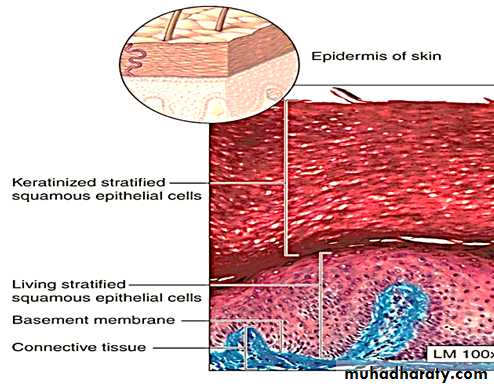
b. Stratified Squamous (keratinized)Epithelium
It is similar to stratified squamous (None keratinized) Epithelium except that the superficial layers are composed of dead cells whose nuclei and cytoplasm have been replaced with keratin, a tough layer that resists friction and is impermeable to water. This epithelium constitutes the epidermis of skin.6-Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Is rare in the human body. It’s mainly found in the ducts of glands (sweat glands, mammary glands) and is typically has two layers of cuboidal cells.7- Stratified columnar epithelium
Is also rare in the human body. Small amounts are found in the pharynx, male urethra, and lining of some glandular ducts.8- Transitional epithelium
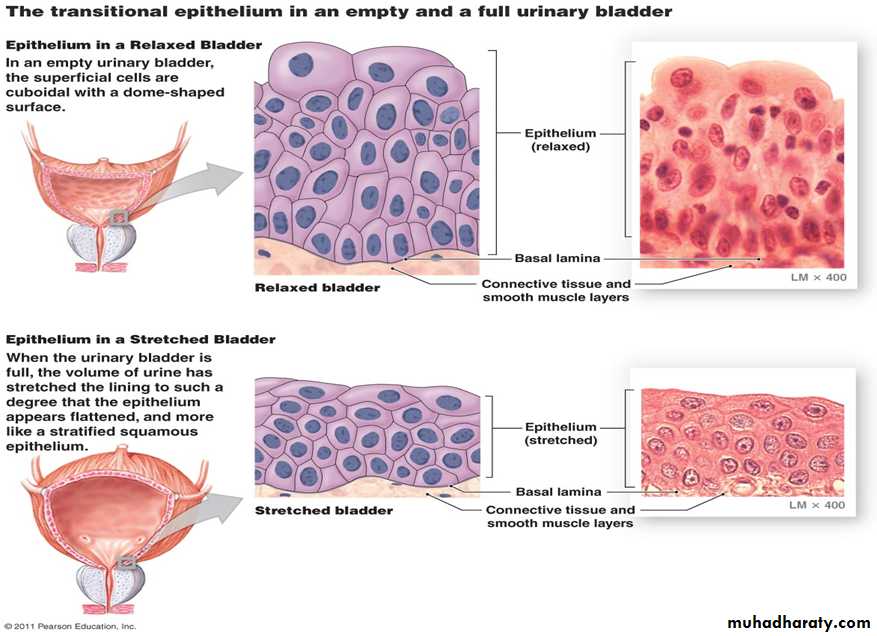
• This epithelium located in the urinary system. Transitional epithelium is composed of many layers of cells
• The basal cells are columnar or cuboidal in shape,
• Cell located in the middle of the epithelium are Polyhedral.
• The superficial cells of the empty bladder are large, bi nucleated and have rounded dome tops . These dome-shaped cells become flattened and the epithelium becomes thinner when the bladder is distended.
.