د. عماد ادوية 15\4\2018
عدد الاوراق ( 5 ) م\3\موصل lec: 11TETRACYCLINES
Classification:According to source:
Naturally-occurring
Tetracycline
Chlortetracycline
Oxytetracycline
Demeclocycline
Semi-synthetic
Doxycycline
Lymecycline
Meclocycline
Methacycline
Minocycline
Rolitetracycline
Tetracyclines
1) Short-acting (6-8 hours), low lipid solubility
Chlortetracycline, Tetracycline, Oxytetracycline
2) Intermediate-acting (12 hours)
Demeclocycline and Methacycline
3) Long-acting (16-18 hours), high lipid solubility
Doxycycline , Minocycline and Tigecycline
First Generation:(1948 to 1963):
Chlortetracycline
Oxytetracycline
Tetracycline
Demeclocycline
Rolitetracycline
Limecycline
Clomocycline
Second-generation (1965 to 1972):
MethacyclineDoxycycline
Minocycline
Third-generation (glycylcycline) : Tigecycline (2005)
Antimicrobial Activity
Broad-Spectrum Bacteriostatic Antibiotics
Active against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including
Anaerobes
Rickettsiae
Chlamydiae
Mycoplasmas
Protozoa, e.g. amobiasis also effective in acne vulgaris, anthrax,H. pylori,plague, malaria and syphilis if penicillin is C/I
Pharmacodynamics(MOA)
The Tetracyclines bind to the 30S subunit and prevent binding of the incoming charged tRNA unit (Inhibit step 1 in bacterial protein synthesis).Tetracyclines enter microorganisms
↓
Susceptible cells concentrate the drug intracellularly
↓
Tetracyclines bind to 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome
↓
Blocking the binding of tRNA to the acceptor site on the mRNA- ribosome complex
↓
This prevents addition of amino acids to the growing peptide
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorption
60-70% → tetracycline, oxytetracycline, demeclocycline, and methacycline
95-100% → doxycycline and minocycline
Tigecycline is poorly absorbed orally and must be administered intravenously.
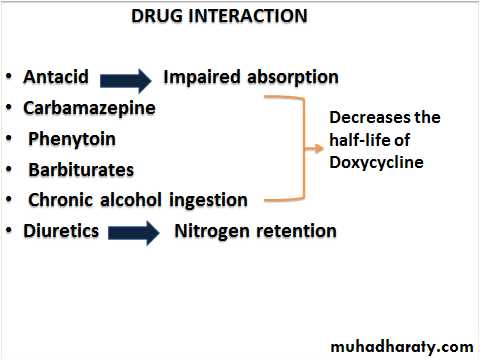
Absorption occurs in upper small intestine and is impaired by
Food (except doxycycline and minocycline)
Divalent cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe2+) or Al3+
Antacids
Minocycline best CSF penetration
PHARMACOKINETICS
40-80% bound by serum proteinsDistributed widely to tissues and body fluids except for CSF(10-25%)
Tetracyclines cross the placenta to reach the fetus and are also excreted in milk Chelation with calcium, damage growing bones and teeth
10 – 50 % excreted into the urine
10 - 40 % excreted in feces
Doxycycline and Tigecycline eliminated by nonrenal mechanisms do not accumulate in renal insufficiency
INDICATIONS ( Clinical uses)
Tetracycline
Drug of choice in infection with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Chlamydiae
Rickettsiae
Some spirochetes
Used in PEPTIC ULCER caused by H.pylori
Vibrio infections( Cholera)
Chlamydial infections, including sexually transmitted diseases
indicated for plague, tularemia, and brucellosis
Treatment of acne
Exacerbations of bronchitis
Community-acquired pneumonia
Lyme disease
Relapsing fever
Leptospirosis
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections (e.g., Mycobacterium marinum)
Minocycline Meningococcal carrier state
Demeclocycline Inhibits the action of ADH So used in inappropriate secretion of ADH
Tigecycline antimicrobial activity
Tetracycline-resistant strains are susceptible to Tigecycline.
Methicillin& Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococci
Penicillin-susceptible and – resistant streptococci
Vancomycin-resistant enterococci
Gram-positive rods
Enterobacteriaceae
Gram-positive and gram-negative anaerobes
Rickettsiae, chlamydia, and legionella
Rapidly growing mycobacteria
Uses
Intra-abdominal Infections
Tigecycline is used for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections
including appendicitis, cholecystitis, diverticulitis, gastric/duodenal perforation, intra-abdominal abscess, intestinal perforation, and peritonitis
Skin and Skin Structure Infections
Complicated deep soft tissue infections, including wound infections and cellulitis (10 cm or larger, requiring surgery or drainage, or with complicated underlying disease), major abscesses, infected ulcers, and burns.ADVERSE EFFECTS
GASTROINTESTINAL ADVERSE EFFECTSNausea, vomiting, anorexia and diarrhea
Anal Pruritus
Vaginal or oral candidiasis
Enterocolitis
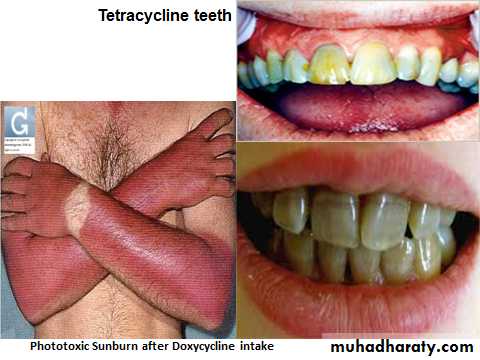
BONE STRUCTURES AND TEETH
When a tetracycline is given during pregnancy
↓
Deposited in the fetal Teeth& Bones
↓
Fluorescence, Discoloration, and Enamel Dysplasia; Bone deformity or Growth inhibition
3) LIVER TOXICITY, rare but fatal occur with high IV doses in pregnant or patient with hepatic or renal dysfunction
Impair hepatic function
Hepatic necrosis (4 g)
4) KIDNEY TOXICITY
Administration of outdated tetracycline
↓
Damage to renal proximal tubule
↓
Renal tubular acidosis
(Fanconi-like syndrome)
Converted to Epitetracycline & Anhydrotetracycline highly toxic compounds to renal tubules
5) LOCAL TISSUE TOXICITY
I/V injection → Venous Thrombosis
I/M injection → Painful local irritation
6) PHOTOSENSITIZATION
Demeclocycline → Sensitivity to sunlight or ultraviolet light
7) VESTIBULAR REACTIONS, especially with minocycline
Dizziness
Vertigo
Nausea
Vomiting
Clindamycin and Lincomycin
Clindamycin is a chlorine-substituted derivative of lincomycin.
Clindamycin has a spectrum similar to that of lincomycin, but it is more active and is well absorbed after oral intake. Therefore clindamycin is preferable.
Clindamycin
It bind to 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes to inhibit bacterial protein synthesis.Its antibacterial spectrum is similar to that of erythromycin. It has the useful additional property of effects against anaerobic bacteria, especially Bacteroid fragilis.
Pharmacokinetics
May be given Orally or parenterallyOrally:
Rapidly absorbed.
Bioavailability is 90%.
Widely concentrated in tissues including bones, and body fluids.
It diffuses across the placenta.
Metabolized in liver
Excretion- urine and bile
Clinical uses of clindamycin:
For Staphylococcal bone and joint infections.Dental infections.
Serious intra-abdominal sepsis and infections originating in the female genital tract e.g. septic abortion and pelvic abscesses, septicaemia caused by Staph. Aureus, Strept. And anaerobic bacteria with other antimicrobial agents.
Clindamycin plus primaquine is an effective treatment for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in AIDS patients.
It is also used in combination with pyrimethamine for AIDS-related toxoplasmosis of the brain.
Pl falciparum malaria
Skin & soft tissue infection including diabetic foot.
Ance 1% topical gel or lotion.
Adverse effects of clidamycin and lincomycin
Diarrhea which is sometime severe.Skin rashes. High doses (both intravenous and oral) may cause a metallic taste.
Impaired liver function and neutropenia sometimes occur.
Antibiotic associated pseudomembraneous colitis, usually due to opportunistic infection of the bowel with Clostridium difficile(fatal complication), treated with metronidazole.
Pain & local abscesses after IM , thrombophlebitis after IV infusion
May enhance the action of N-M blocking agent.