Eyelids and Lacrimal System
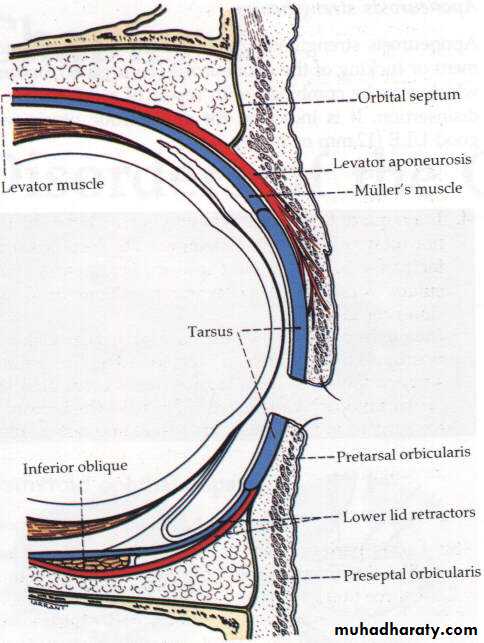
Anatomy of the eyelidThe eyelid is the protective cover or the curtain o f the eye-ball
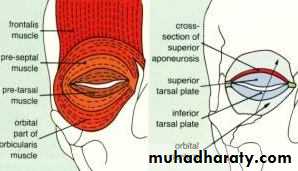
Composed of five layer
1- Skin
2- Muscles; Orbicularis oculi, and Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
3- Sub-muscular layer
4- Tarsal plate forms the fibrous backbone of the lid
5- Conjunctiva; mucous membrane forms the inner lining layer
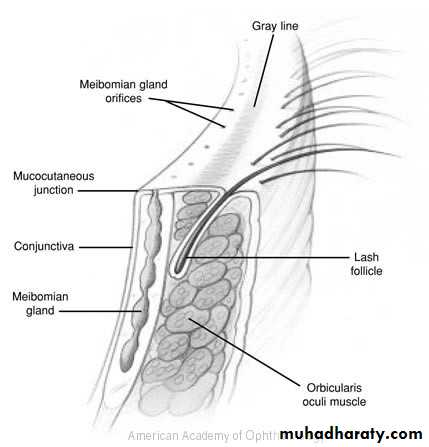
The margin of the lid
is 2mm muco-cutaneous junction,contains :Posteriorly the opening of meibomian glands and the upper and lower lacrimal puncti.
Anteriorly the eye lashes about 50-100 in each eyelid.
Eyelids Margin
• The lashes (Cilia).• Grey line
• Orifices of Meibomian glands.
• Mucocutaneous junction.
• Superior and inferior puncti of Naso- lacrimal system.
Muscles of the eyelids
• 1- Orbicularis oculi muscle:• 2- Levator palpebrae superioris muscle:
• 3- Superior palpebral muscle (Müller's muscle or superior tarsal muscle):
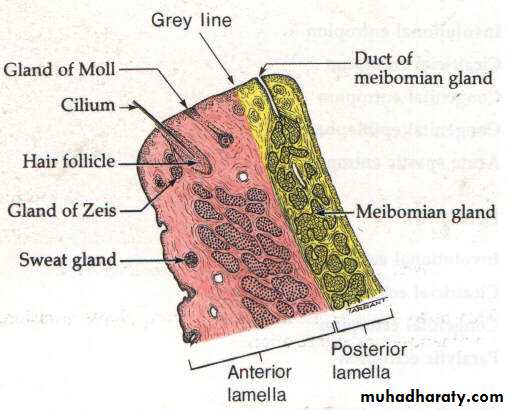
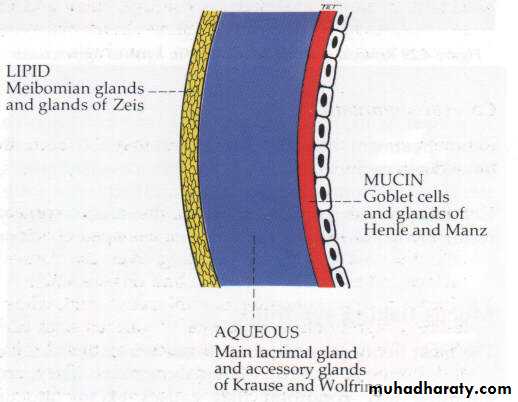
Glands in the eyelids:
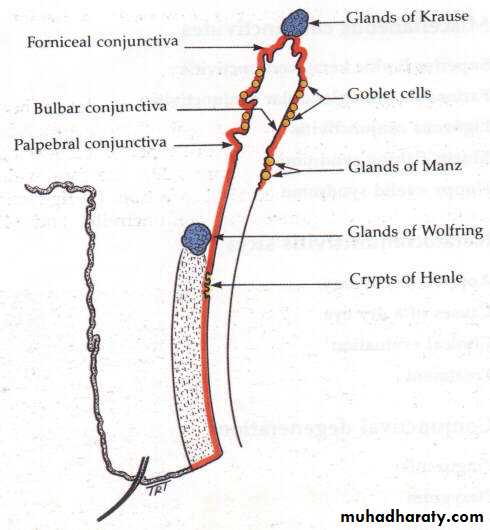
Accessory lacrimal glands
Goblet glands: are unicellular glands
Meibomian glands are modified sebaceous glands
Closure of the lids
is by contraction the Orbicularis oculi muscle which is innervated by facial nerve .Damage to the muscle or its nerve supply cause inability to close the eye and exposure keratitis .
Elevating the upper lid
is by Levator palpebral muscle which is innervated by oculomotor nerve.Damage to the muscle or its nerve supply cause dropping of the upper lid (Ptosis).
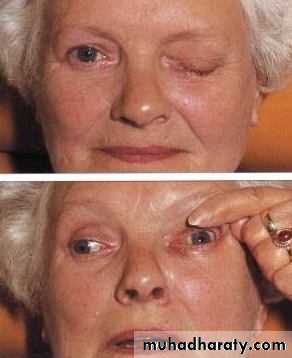
Muller’s muscle : a thin smooth muscle, supplied by sympathetic nerve, contributes in elevation of the upper lid. Interruption of nerve supply to this muscle cause mild ptosis (Horner syndrome).
Functions
Protection to the eye globe by blinking reflex.Prevent dryness of the eye from continuous exposure.
Contributes in tear secretion; secrets oily layer of the tear film
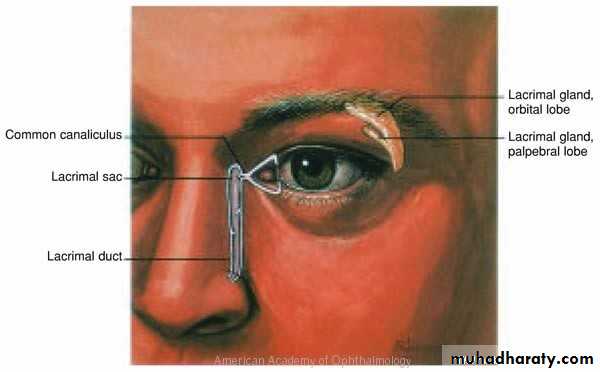
Drainage of tear through the upper and lower puncti and canaliculi.
Spread tears over the anterior surface of the eye
Abnormalities in shape and position:
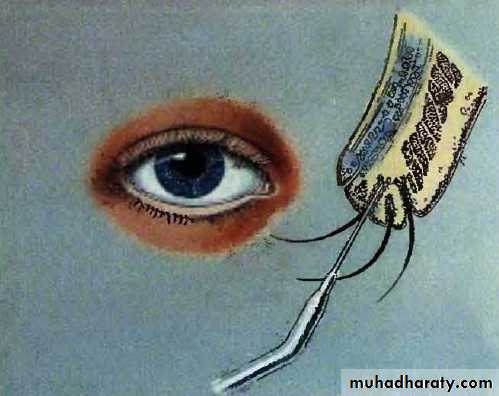
• TrichiasisMisdirection of the eyelashes which may cause irritation and ulceration of the cornea.
Causes : scarring to the lid margin e.g. trachoma, trauma, chronic blepharitis.
Treatment :
Destroy the abnormal lash follicles by :Epilation
Electrolysis
Laser
Cryotherapy
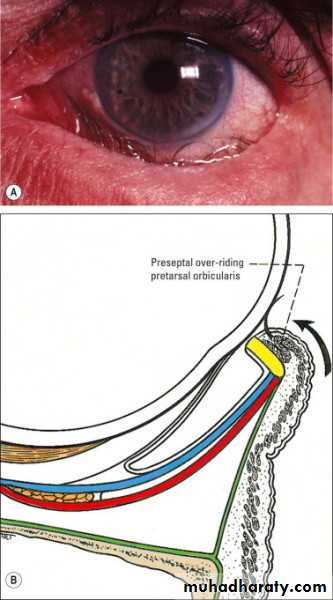
Entropion
Inward inversion of the lid . Eyelashes cause rubbing and ulceration of the cornea.Causes
CongenitalCicatricial conjunctivitis secondary to scarring of palpebral conjunctiva e.g. trachoma, chemical burn.
Senile; Due to weakness of Orbicularis oculi muscle .
Spastic
Treatment : surgical
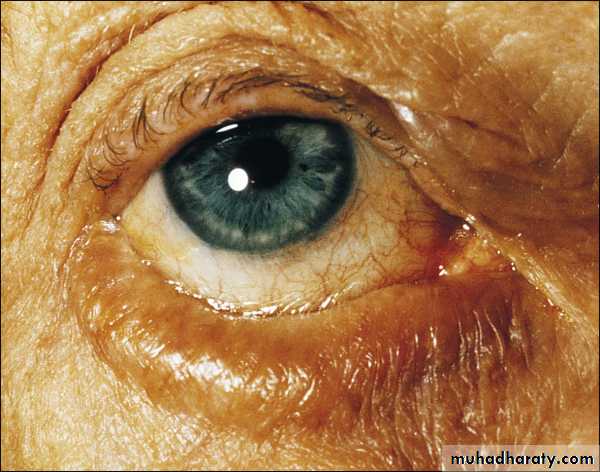
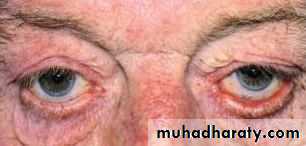
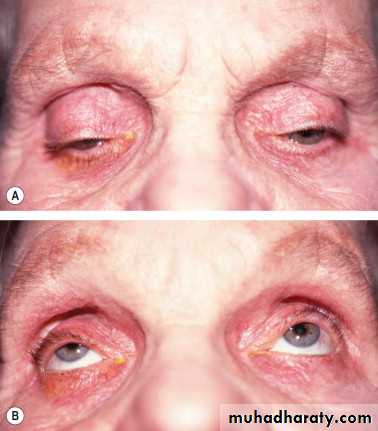
Ectropion
Outward eversion of the lid.Misdirection of the lacrimal puncti cause
Tearing (epiphora)
Exposure conjunctivitis and keratitis
Causes
CongenitalCicatricial; secondary to scarring of skin e.g. post-traumatic
Paralytic; facial nerve palsy
Senile; Due to laxity of lower lid tendons
Treatment : surgical
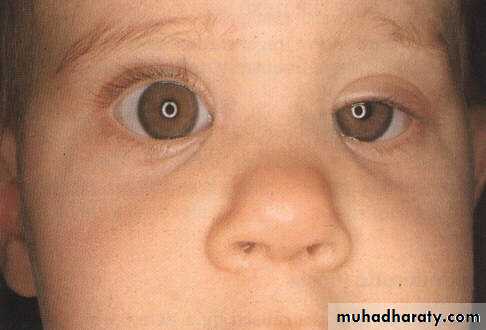
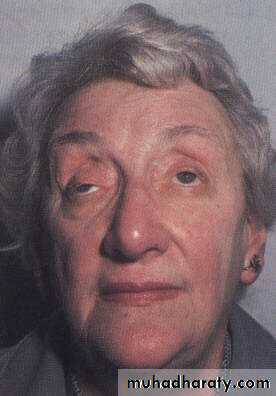
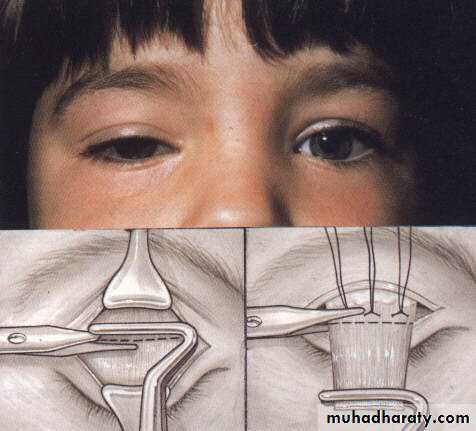
Ptosis
Drooping of the upper lidCauses:
1-Congenital, present at birth, may be unilateral or bilateral.
Treatment : surgery .
2-Neurogenic :
Oculomotor nerve palsyCauses complete ptosis, with impairment of eye movement
Sympathetic palsy (Horner syndrome)Causes mild ptosis about 2-3mm dropping of the upper lid
3-Muscular :
Myasthenia gravis, impairment of transmission at the neuromuscular junction .Myotonic dystrophy
4- Aponeurotic blepharoptosis:
Weakness of the Levator palpebral aponeurosis (tendon)i- Involutional (senile).
ii- Post operative.
5- Mechanical blepharoptosis:
DermatochalasisLarge tumour
Severe oedema
Heavy scar tissue
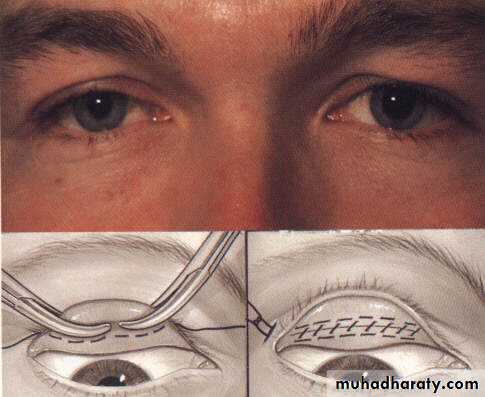
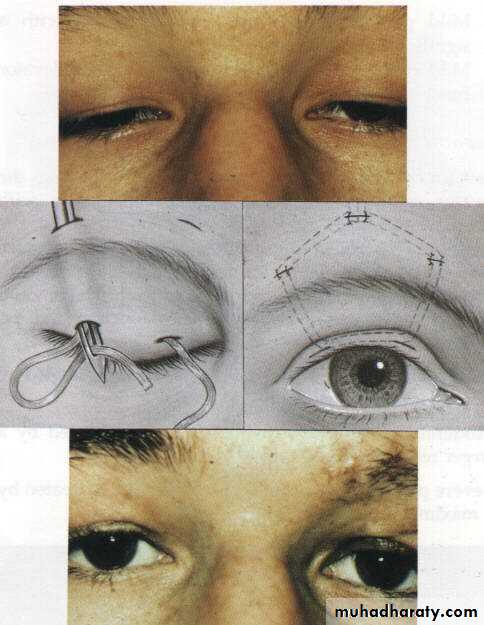
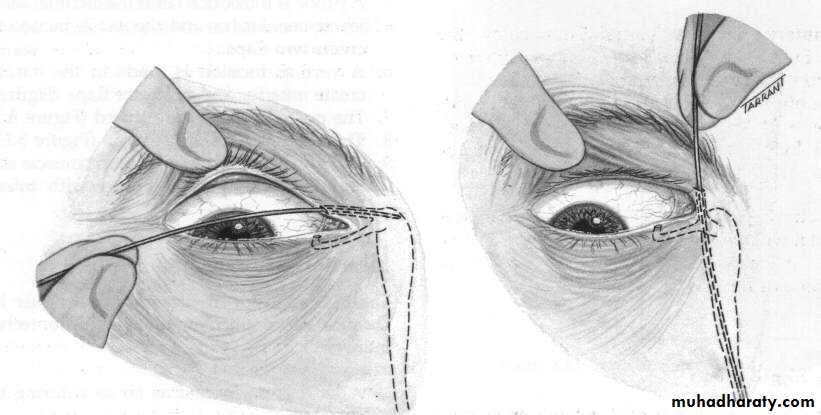
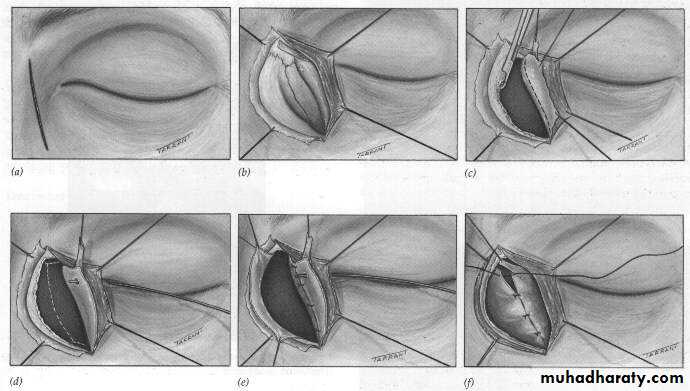
Treatment of ptosis :
Medical
Surgical :
a- Levator resection.
b- Frontalis brow suspension (Sling operation).c- Mullerectomy (resection of Muller muscle).
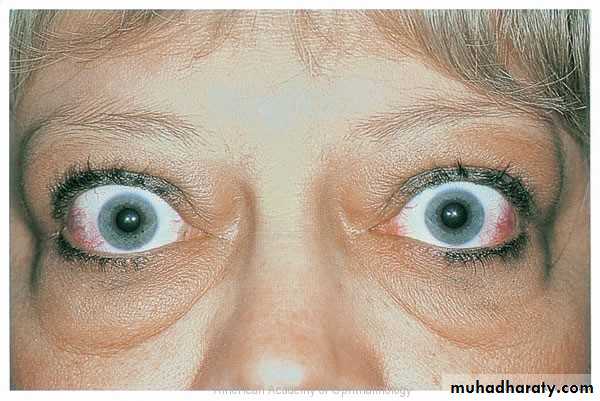
Lid retraction
In Dysthyroid OphthalmopathyOver-exposure of the eye, the sclera is exposed at the upper and lower limbus.
Inflammation of the lid
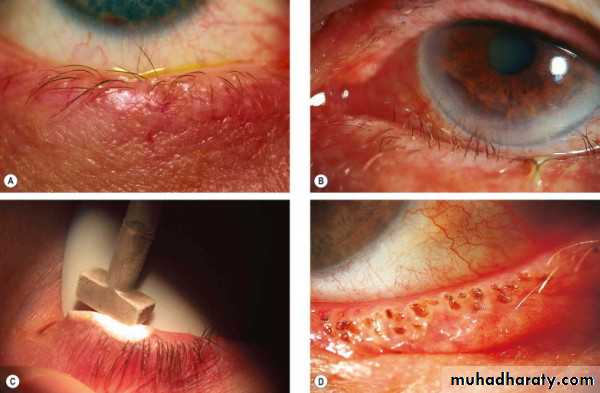
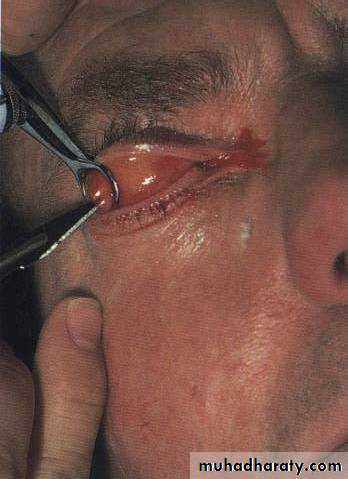
Stye (External hordeolum) :Acute Staphylococcus infection of a eyelash hair follicle or one of the associated glands.
Clinical features; small tender swelling in the lid margin
Treatment; application of an antibiotic ointment
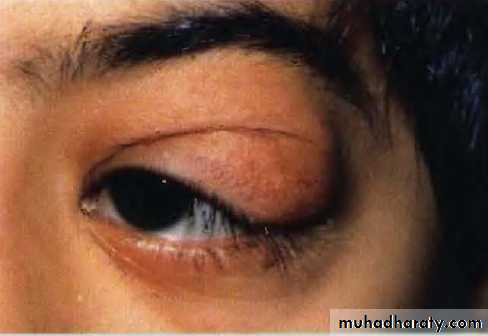
Internal hordeolum;
Acute Staphylococcus infection of a meibomian glandClinical features; tender hyperemic, swelling within the lid .
Treatment; surgical drainage
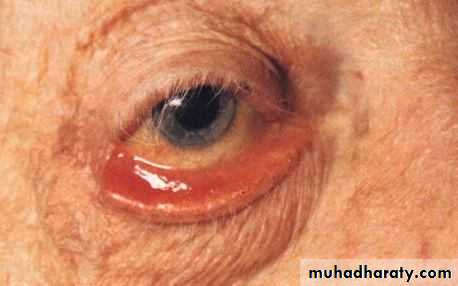
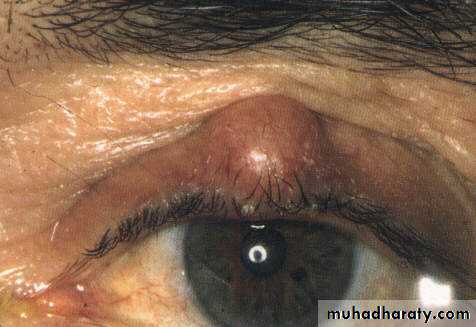
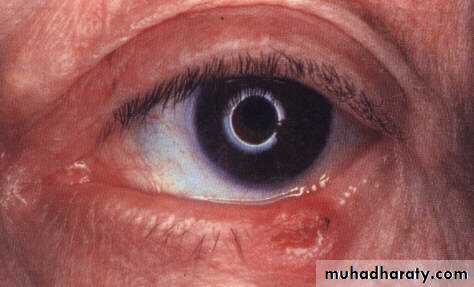
Chalazion
Chronic lipogranulomatous inflammation of a meibomian secondary to retention of sebum .Clinical features; painless swelling within the lid .
Treatment surgical
Lid Tumors
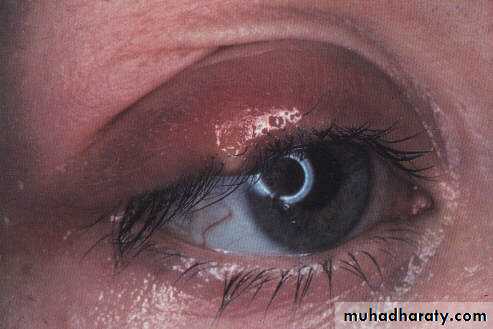
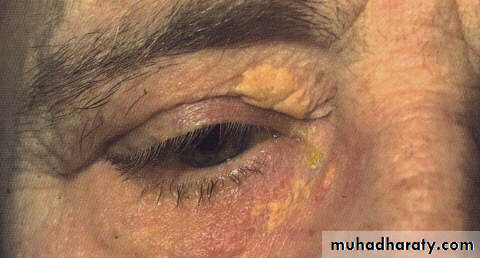
BenignXanthelasma; yellowish slightly elevated plaque of lipid deposits
located medial aspects of both lids
Malignant
Basal cell carcinoma; elderly people, starts as well defined nodule, then the center becomes ulcerated and crusted
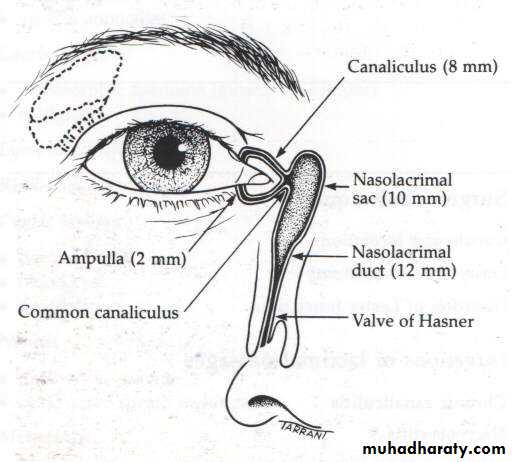
Lacrimal System
1- Secretory portion:2- Drainage portion:
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca Dry eye
Clinical featuresChronic irritation, foreign body sensation and recurrent conjunctivitis
Causes:
1-Sjogren’s syndrome; is an autoimmune disease (antinuclear antibody positive in 80%). Middle age female. Sometimes associated with dry mouth and connective tissue disorders2-Damage to the lacrimal gland by inflammation (e.g. sarcodosis), trauma or tumor
3- Congenital absent of lacrimal gland
4- Blockage of secretary ducts in cicatricial conjunctivitis e.g. trachoma, chemical burn.
5-Mucin deficiency due to goblet gland destruction in hypovitaminosis A
Watering eye
1- Lacrimation due to excessive secretion of tears (e.g. crying).
2- Epiphora is watering eye due to mechanical obstruction of the lacrimal drainage system.
Epiphora
Causes• Punctal stenosis
• Canalicular obstruction
• Acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction
• Congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Causes:a- idiopathic stenosis (most common cause).
b- Naso-orbital trauma.
c- Irradiation.
d- Wegener's granulomatosis.
e- Nasopharyngeal tumor.
Congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Present since birth
Treatment
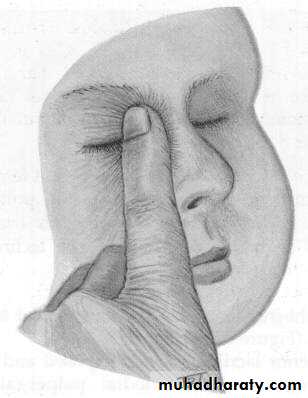
- Age 1-12 months : Hydrostatic massage .
-After age of 12 months; Probing of naso-lacrimal duct under G.A.-Surgery (Dacryocystorhinostomy) after age 2 years.
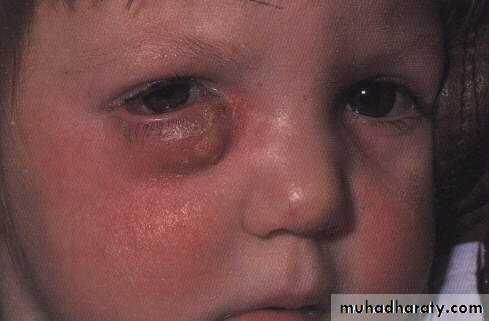
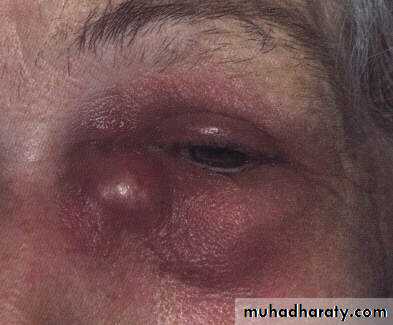
Dacryocystitis
Infection of the lacrimal sac.Causative agents Staphylococci and Streptococci
Clinical features :
Painful tender swelling inner canthus
Treatment :
Systemic antibiotics.
Surgical drainage if abscess is present .
Differential diagnosis of watery in neonates
a- Nasolacrimal duct obstructionb- ophthalmia neonatorum.
c- Congenital glaucoma.
d- F.B.