Lipogenesis. Metabolism of cholesterol.
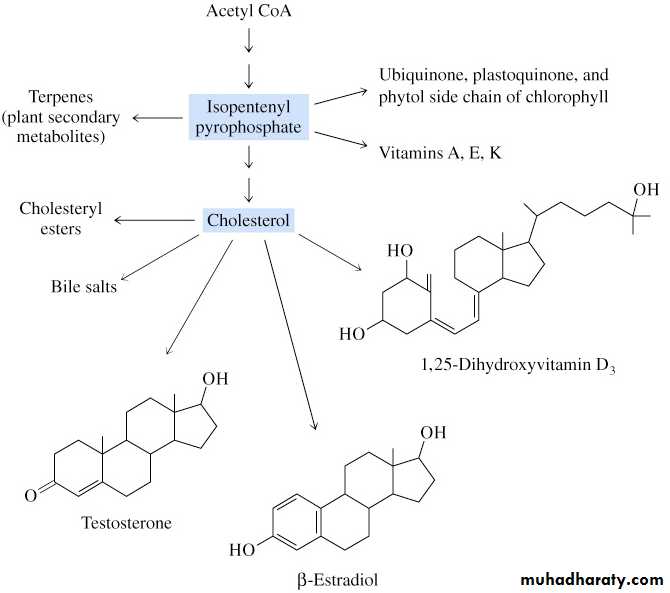
Functions of Cholesterola precursor of steroid hormones (progesterone, testosterone, estradiol, cortisol, etc.)
a precursor of bile acids
a precursor of vitamin D
important component of many mammalian membranes (modulates the fluidity)
Sources of Cholesterol• from the diet
• can be synthesized de novo (about 800 mg of cholesterol per day) - in the liver (major site) - in the intestine
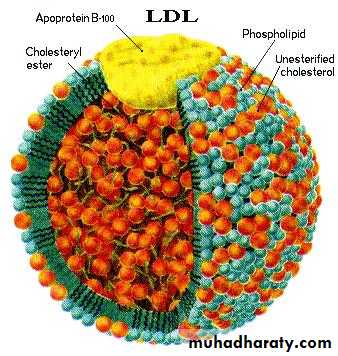
Liver-derived and dietary cholesterol are both delivered to body cells by lipoproteins
Synthesis of Cholesterol
Three stages of cholesterol biosynthesisAcetyl CoA (C2) Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (C5)
Squalene (C30) Cholesterol (C27)
1. Synthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate, that is the key building block of cholesterol, from acetyl CoA
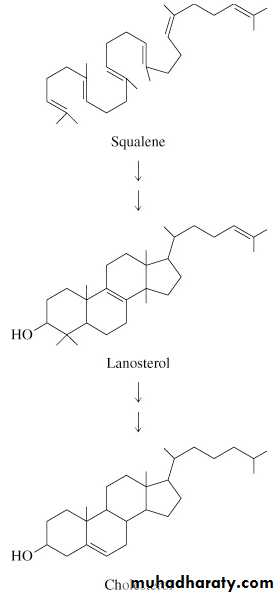
2. Condensation of six molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form squalene
3. Squalene cyclizes and the tetracyclic product is converted into cholesterol
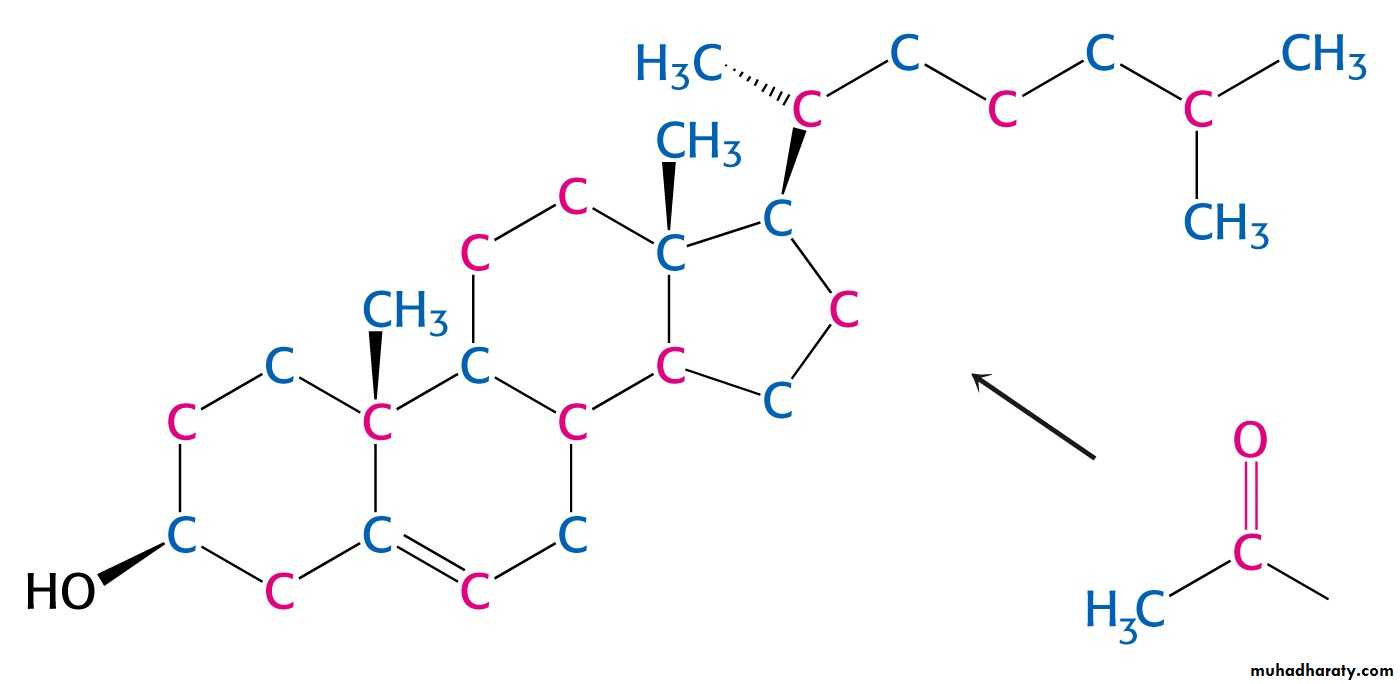
All carbons of cholesterol come from cytosolic acetyl CoA (transported from mitochondria via citrate transport system)A. Stage 1: Acetyl CoA to Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate
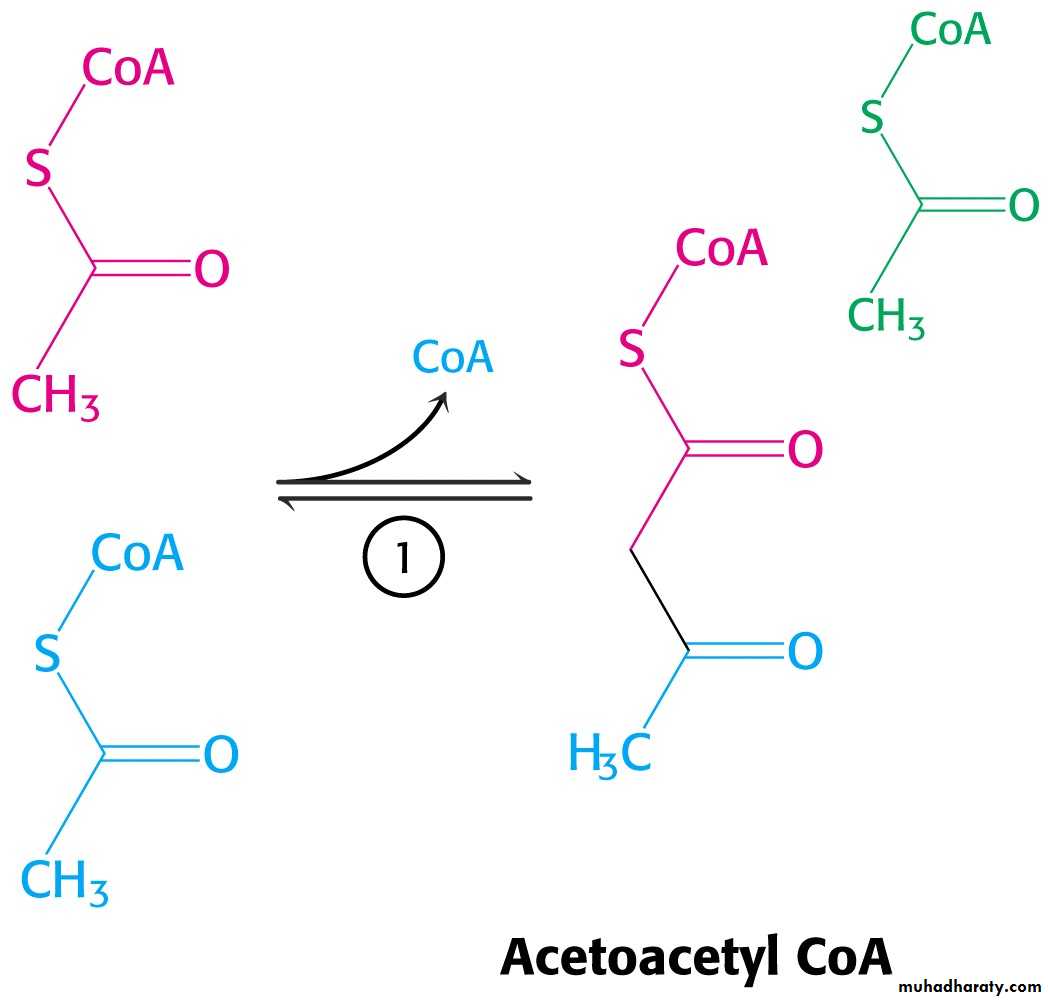
• Sequential condensation of three molecules of acetyl CoATwo molecules of acetyl CoA condense to form acetoacetyl CoA.
Enzyme – thiolase.
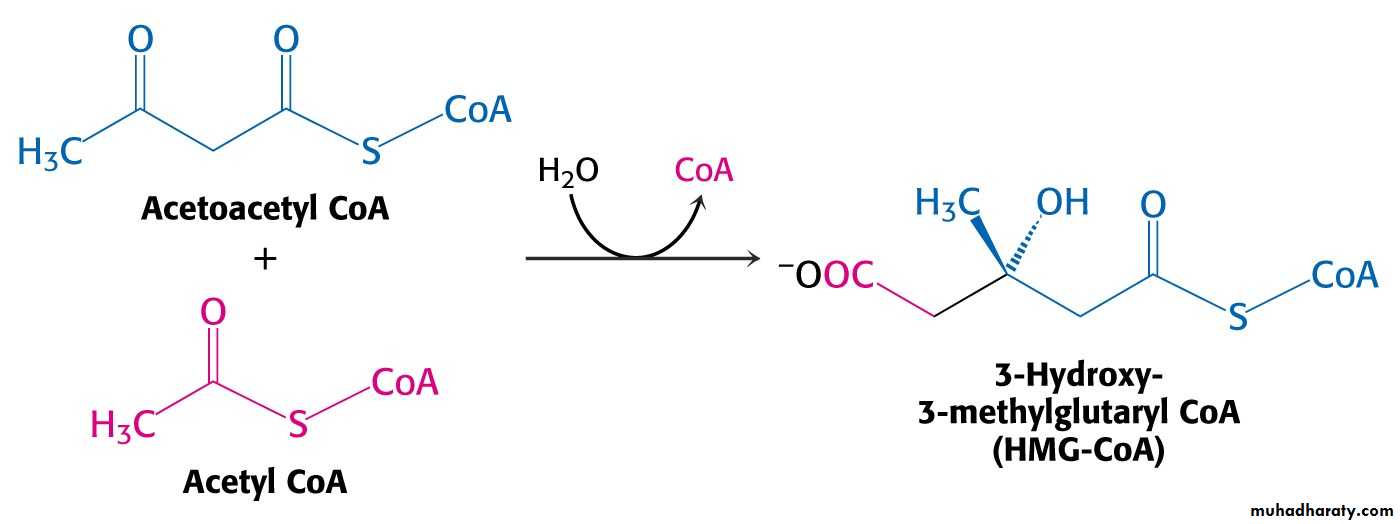
Acetoacetyl CoA reacts with acetyl CoA and water to give 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA) and CoA.
Enzyme: HMG-CoA synthase
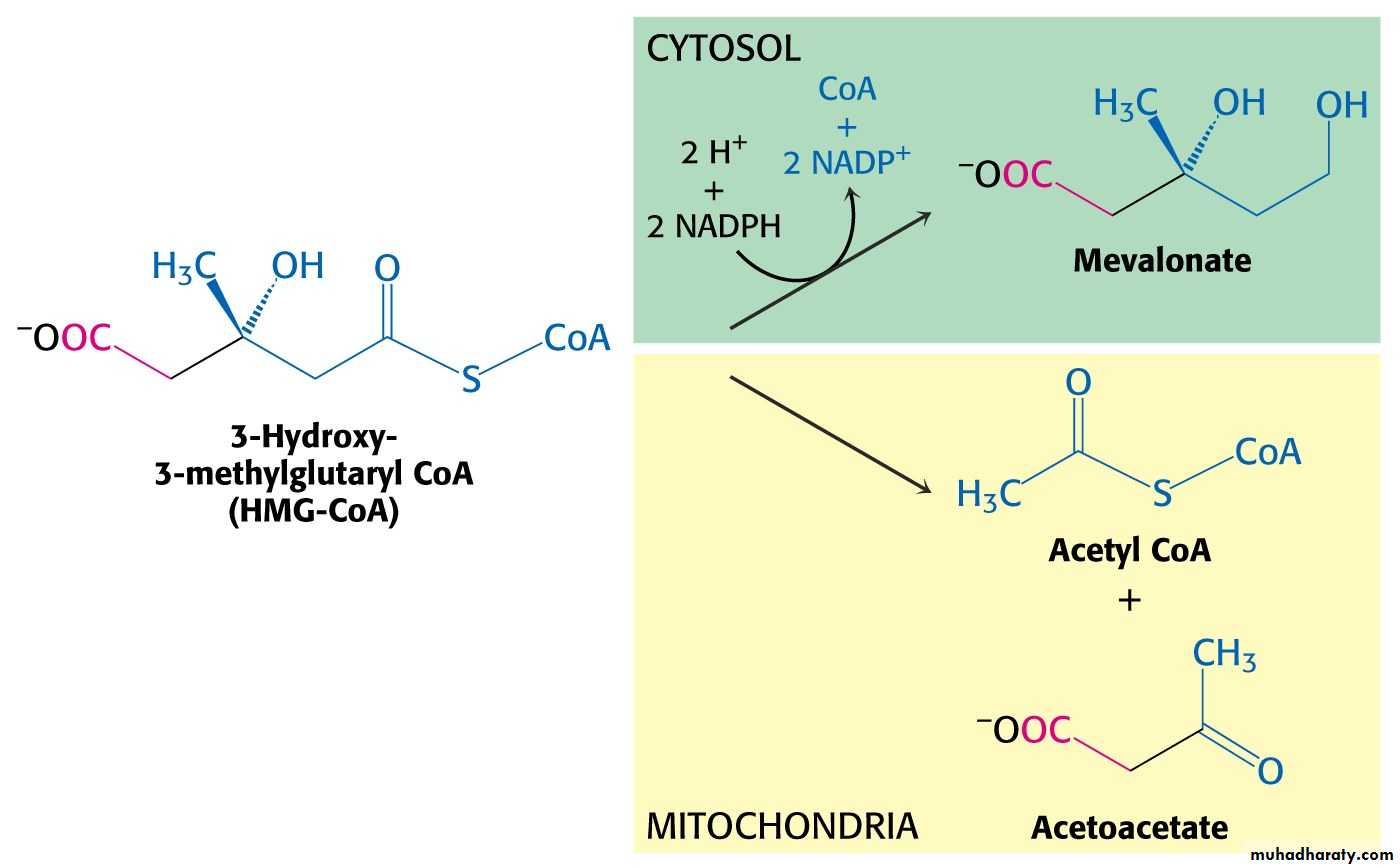
In cytoplasm 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA is reduced to mevalonate.
In mitochondria 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA is cleaved to acetyl CoA and acetoacetate.Enzyme: HMG-CoA lyase.
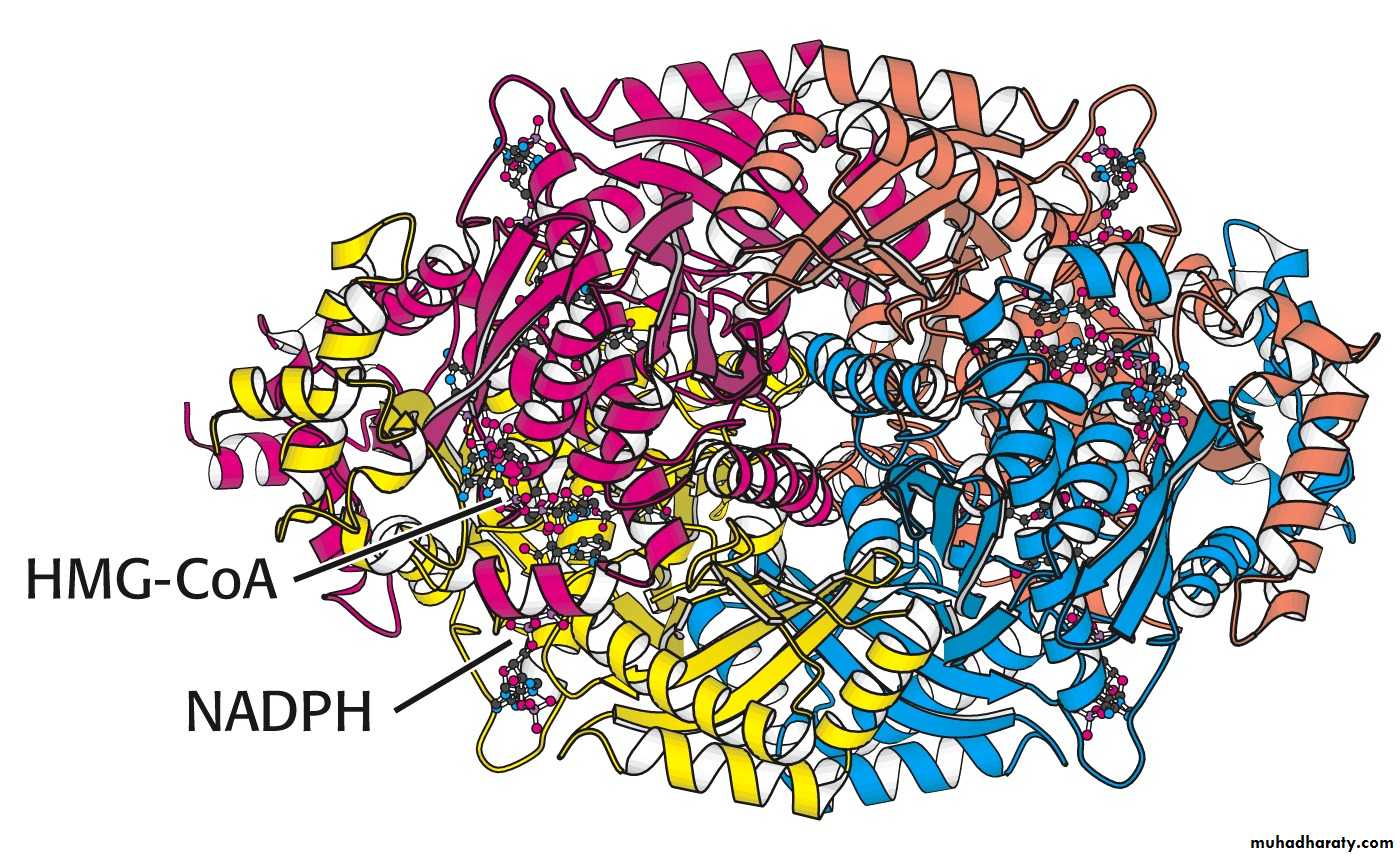
Enzyme: HMG-CoA reductase• HMG-CoA reductase is an integral membrane protein in the endoplasmic reticulum
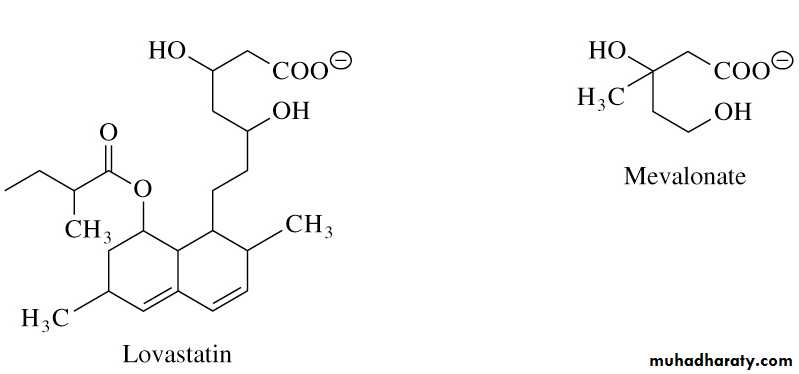
• Primary site for regulating cholesterol synthesis• Cholesterol-lowering statin drugs (e.g. Lovastatin) inhibit HMG-CoA reductase
HMG-CoA reductase
Lovastatin resembles mevalonate
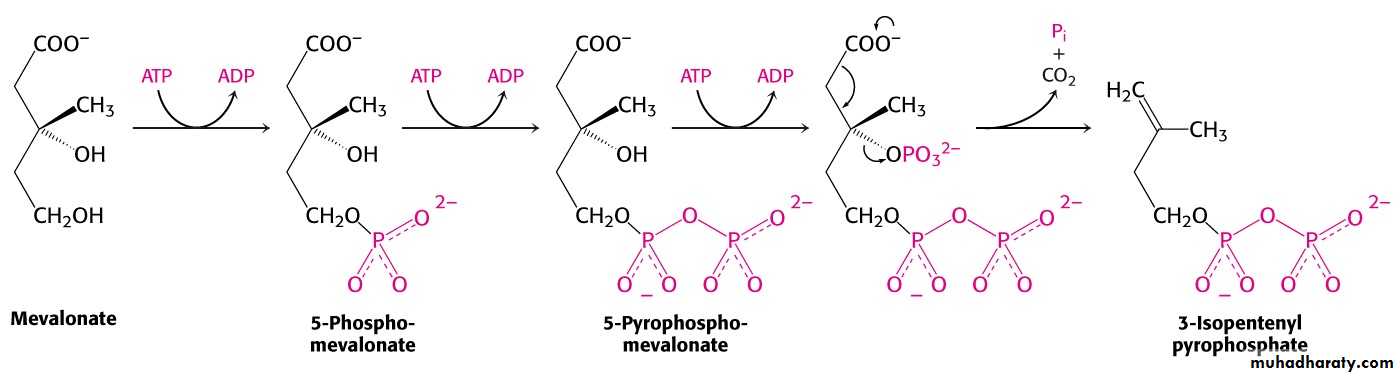
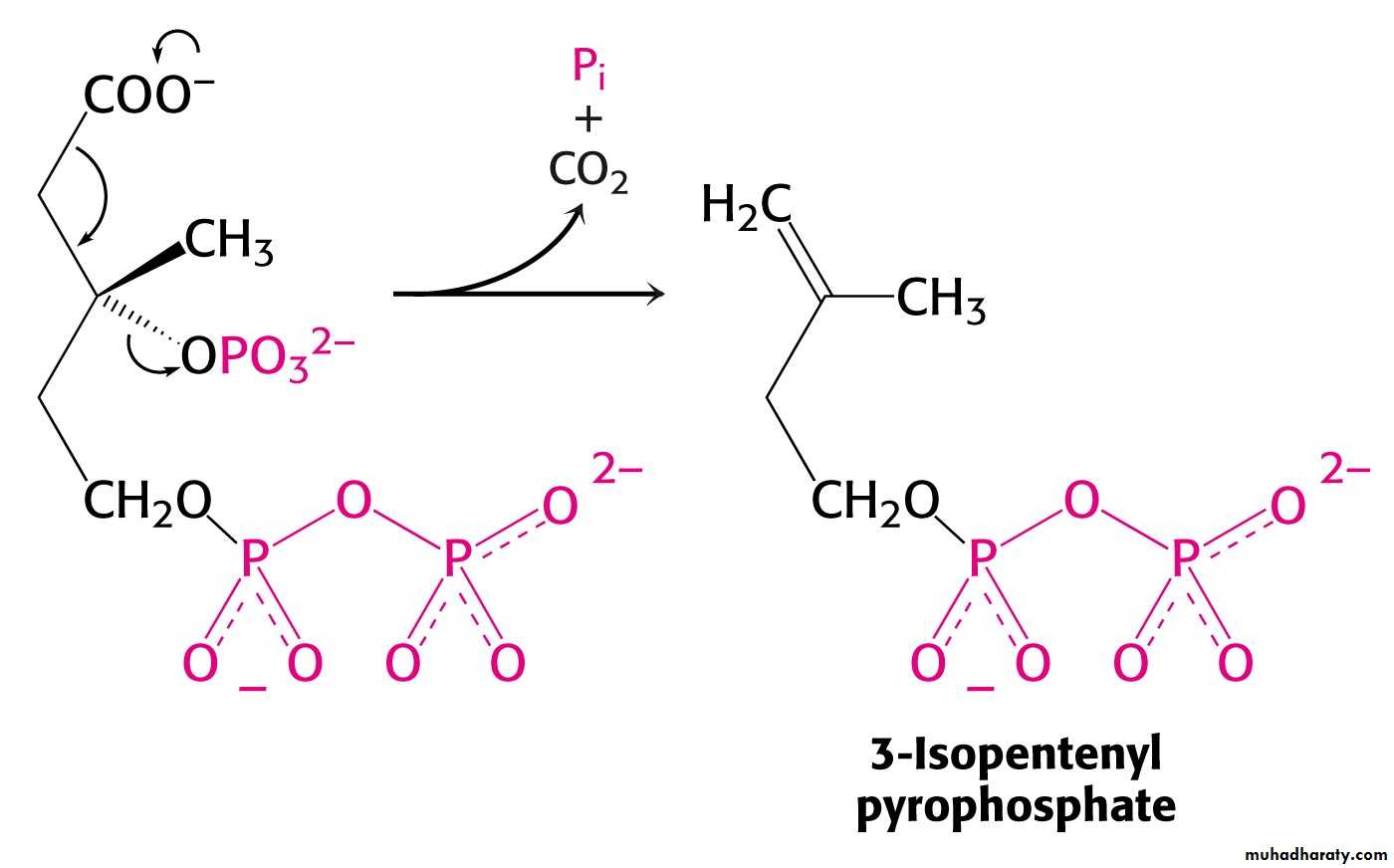
Mevalonate is converted into 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate in three consecutive reactions requiring ATP and decarboxylation.
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate is a key building block for cholesterol and many other important biomolecules.
• Stage 2:
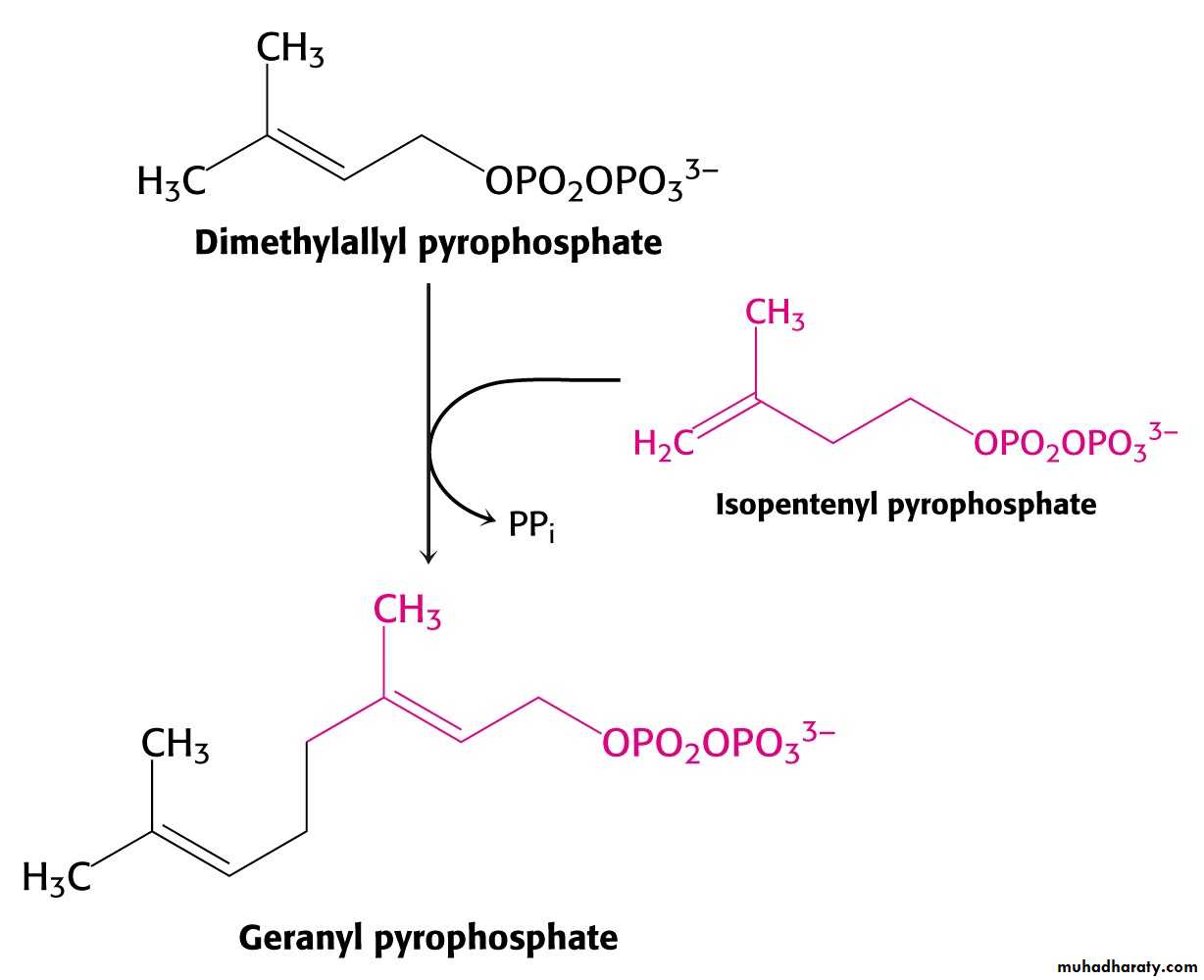
Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate to SqualeneIsopentenyl pyrophosphate is isomerized to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate.
C5 units isopentenyl pyrophosphate react with C5 units dimethylallyl pyrophosphate to yield C10 compound geranyl pyrophosphate
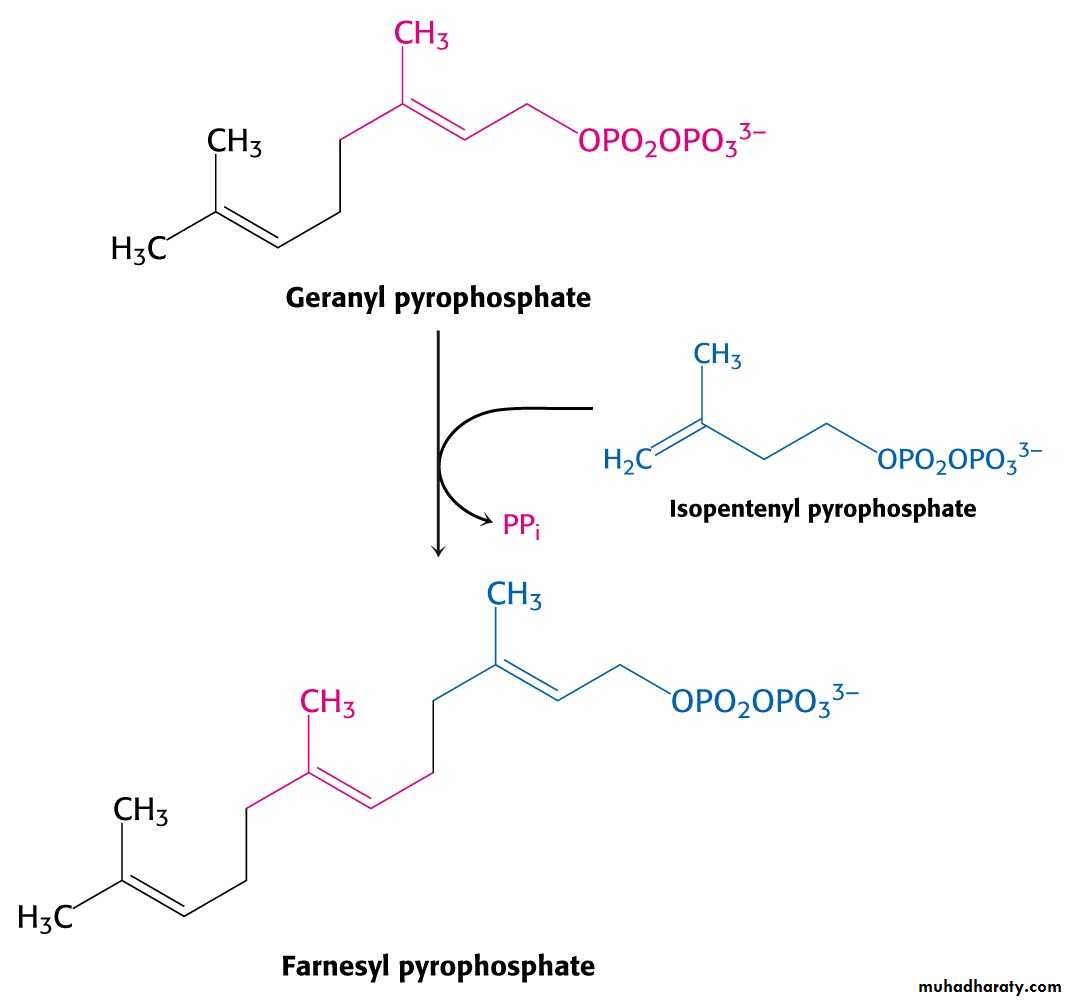
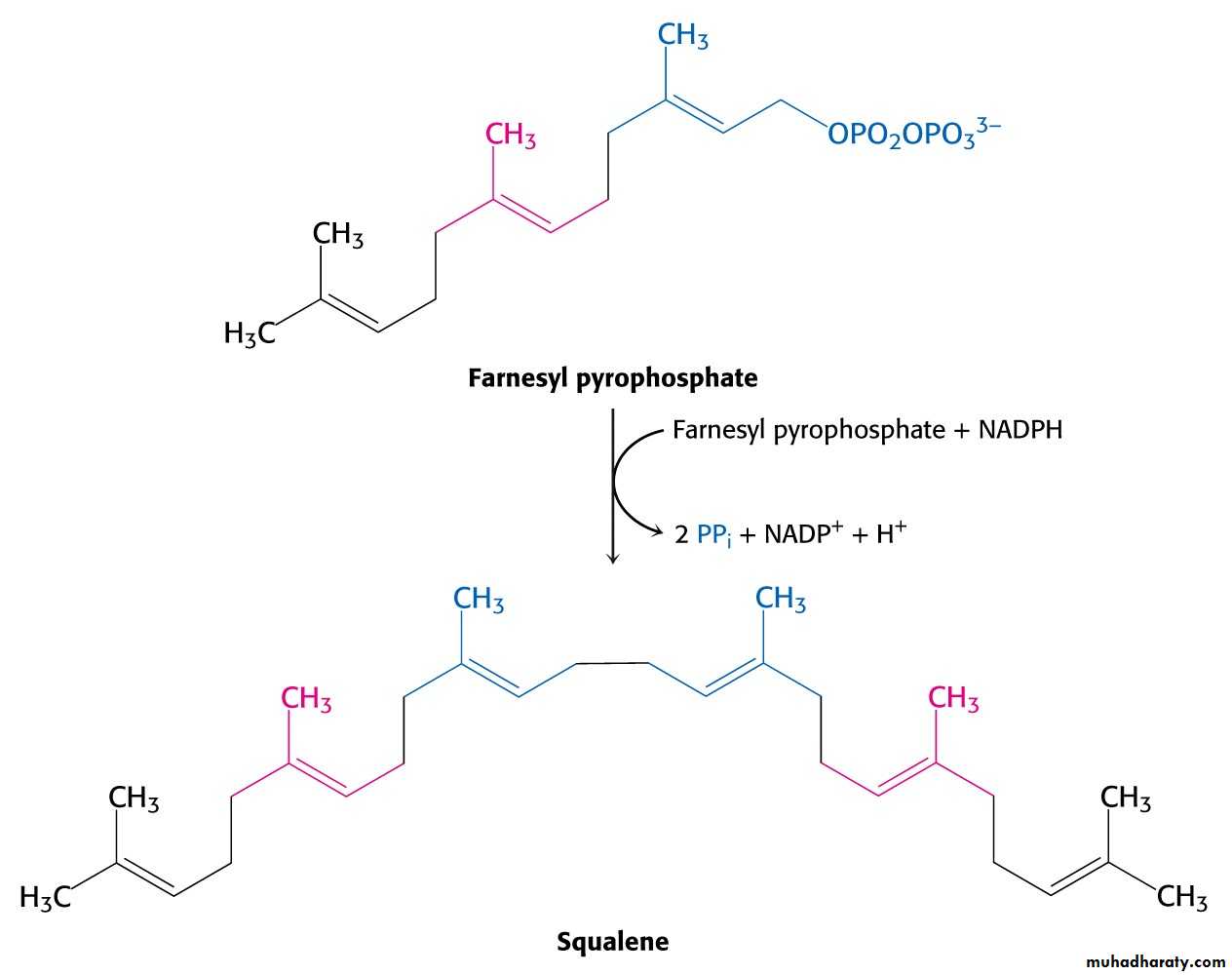
C10 compound geranyl pyrophosphate reacts with C5 units isopentenyl pyrophosphate and C15 compound is formed - farnesyl pyrophosphate.
Reductive tail-to-tail condensation of two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate results in the formation of C30 compound squalene
C. Stage 3:
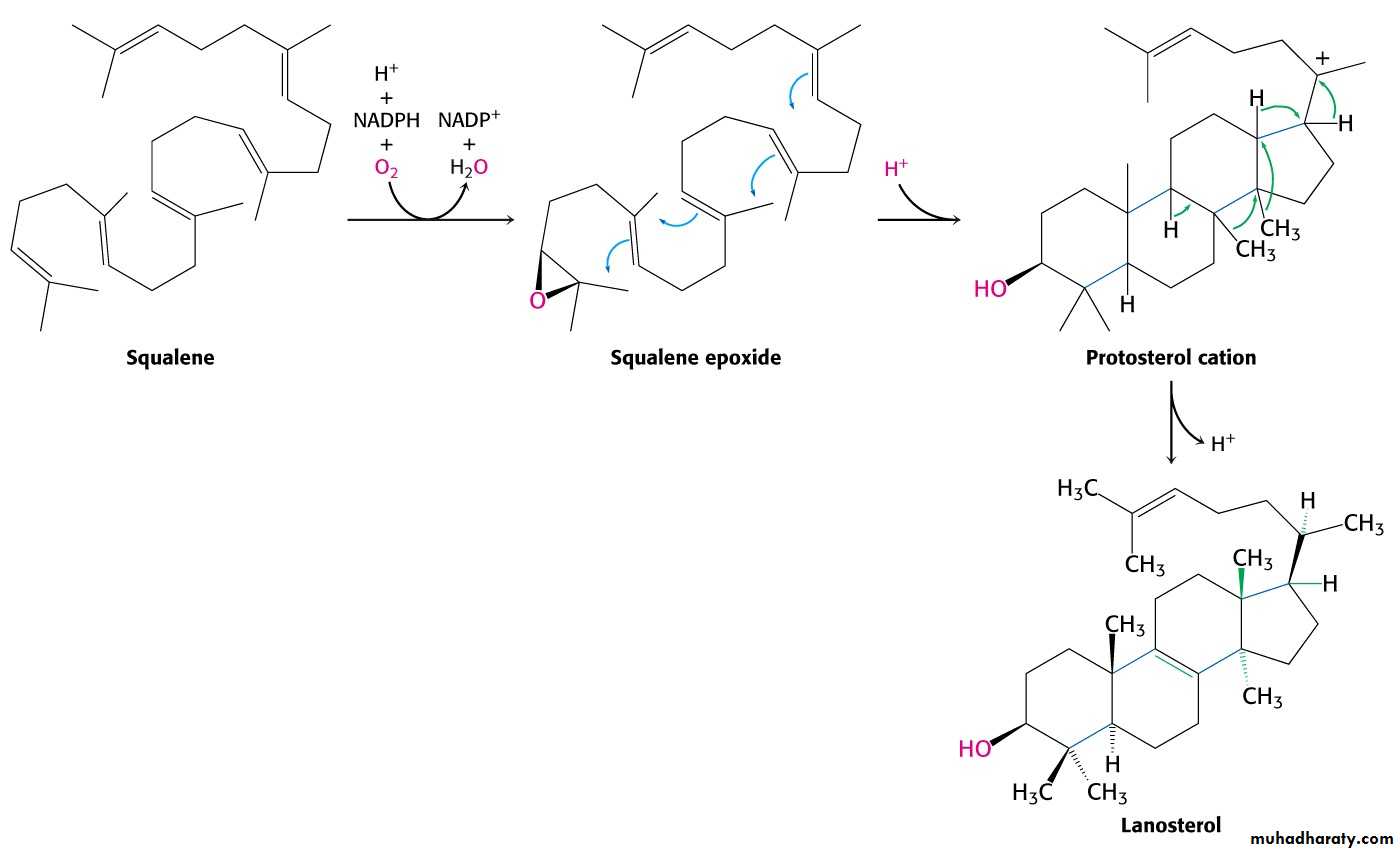
Squalene to CholesterolSqualene activated by conversion into squalene epoxide.
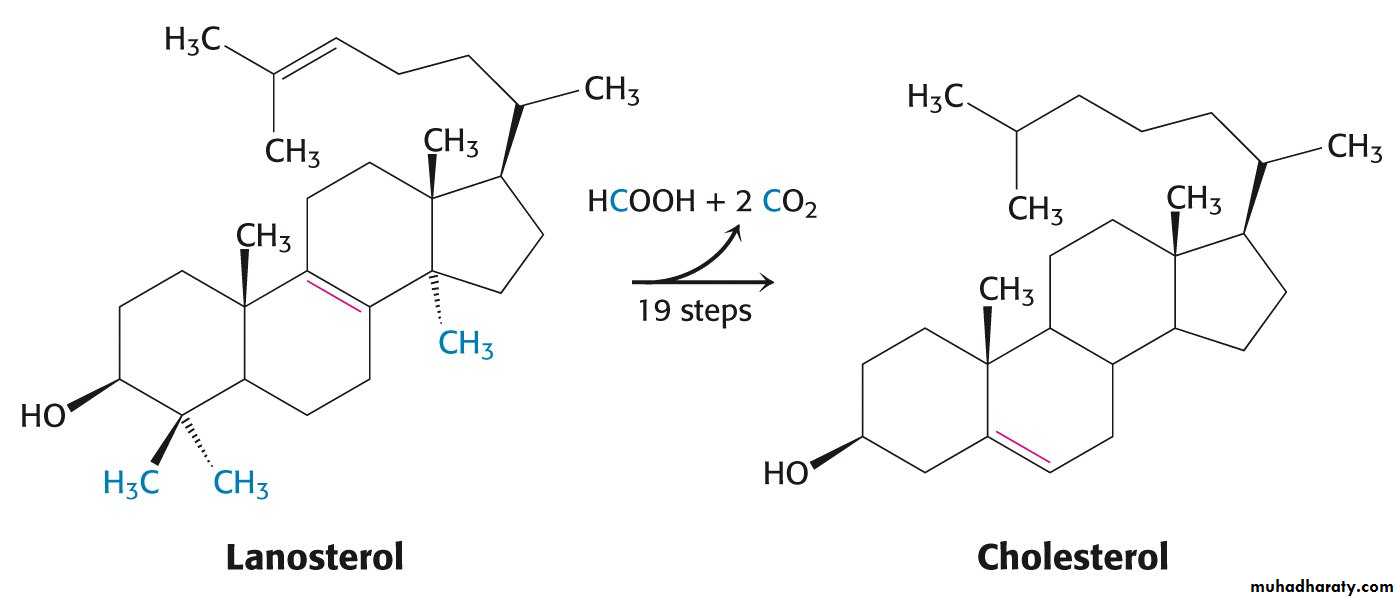
Squalene epoxide is cyclized to lanosterol.Lanosterol is converted into cholesterol in a multistep process.
THE REGULATION OF CHOLESTEROL BIOSYNTHESIS
Regulatory enzyme - 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase.