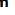IDUCTION OF LABOUR 18
تسلسل 13المرحلة الرابعة
نسائية
د.شيماء
العدد 110
3\4\2018
Induction of Labour IOL
Is the planned initiation of labour prior to its spontaneous onset .Indications of IOL
Post datesFetal growth restriction
placental insufficiency e.g. oligohydramnios
Pre-eclampsia& other maternal hypertensive disorders
Deteriorating maternal illness
Prolonged prelabour rupture of membranes
Unexplained antepartum hemorrhage
Diabetes mellitus
Twin pregnancy beyond 38 weeks
Rhesus iso immunization
Social reasons
Contraindicatios
Any contraindications to vaginal delivery, or indication for cesarean delivery
Uterine hypercontractility
tachysystole (more than five contractions per ten minutes for at least 20 minutes)uterine hypersystole/hypertonus
(a contraction lasting at least two minutes).Modified Bishop Score
As the time for spontaneous labor approaches , the cervix becomes softer, shortened, moves forward and start to dilate.Bishope score used to quantify how far this process had progressed prior to IOL
The total score is in the range of 0-13,
(favourable /unfavourable cervix)
Modified Bishop score
• >=5• 3-4
• 1-2
• 0
• Dilatation of cervix (cm)
• Soft
• Medium
• Firm
• Consistency of cervix
• <1
• 1
• 2
• 3
• Length of cervical canal (cm)
• Soft Anterior
• Moderate Central
• Firm Posterior
• Position of cervix
• +1
• -1or 0
• -2
• -3
• Station (cm above ischial spines)
0
1
2
3
Methods of induction
A.mechanical methods
hygroscopic dilators (laminaria,lamicel, or dilapan);
balloon (e.g. Foley); and balloon with extra-amniotic saline infusion (EASI).
membrane stripping
amniotomy
2.Membrane stripping (or sweeping)
.
In most of the cases with favourable cervix ,labour commenced in 24 hours
.
3. Placement of an extra-amniotic balloon catheter such as a Foley.
It causes stretching of the cervix with release of endogenous PG as result of stimulation of the cervix & lower uterine segment4-Extra-amniotic saline infusion
The stimulatory effect of the extra-amniotic balloon catheter may be enhanced by infusion of normal saline into the extra-amniotic space at 50 ml/h.5-Amniotomy
Amniotomy alone results in delivery within 24 hours in about two-thirds of cases..
This method has the advantage that the risk of uterine hyperstimulation, is avoided, and the amniotic fluid may be observed.
Methods:
Forewater (low) amniotomy: Stripping of the membranes is done first, then the forewater is ruptured by amnihook, toothed forceps or Kocher's forceps.Hindwater (high) amniotomy: The Drew-Smythe catheter is introduced between the membranes and uterine wall to a point above the presenting part.
Disadvantages:
Less efficient in inducing labour.
More incidence of uterine trauma.
Separation of a posteriorly situated placenta.
Higher incidence of infection as ascending infection &the procedure itself might place the fetus at increased risk of HIV if the skin of presenting part is scratched
B.Prostaglandine PG
PGs are naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids present in different body fluids and tissues as the seminal fluid, endometrium, amniotic fluid, lungs and brain. PGs are resulted from the action of PG synthetase enzyme on arachidonic acid.PG
Labour induction with prostaglandin F2 alpha was introduced in the 1960s. Subsequently, formulations of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2, dinoprostone) were developed which largely replaced the use of F2 alpha. within 24 h than dinoprostone. The greater efficiency of misoprostol has been related to more rapid cervical Ripening
Obstetric Actions
Ripening of the cervix: Natural and synthetic PGs can ripen the cervix at any stage in pregnancy by inducing collagen breakdown and tissue hydration.Initiation and/or stimulation of uterine contractions: at any stage of pregnancy.
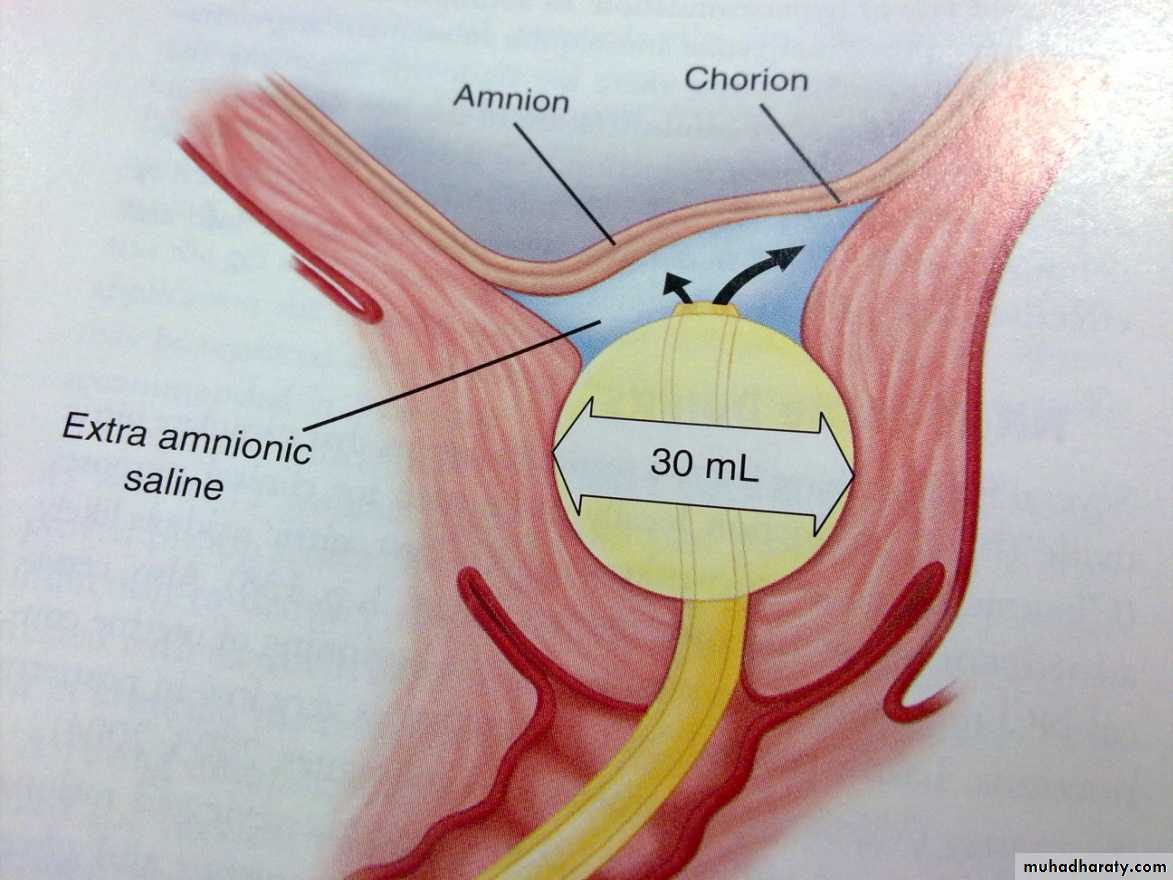
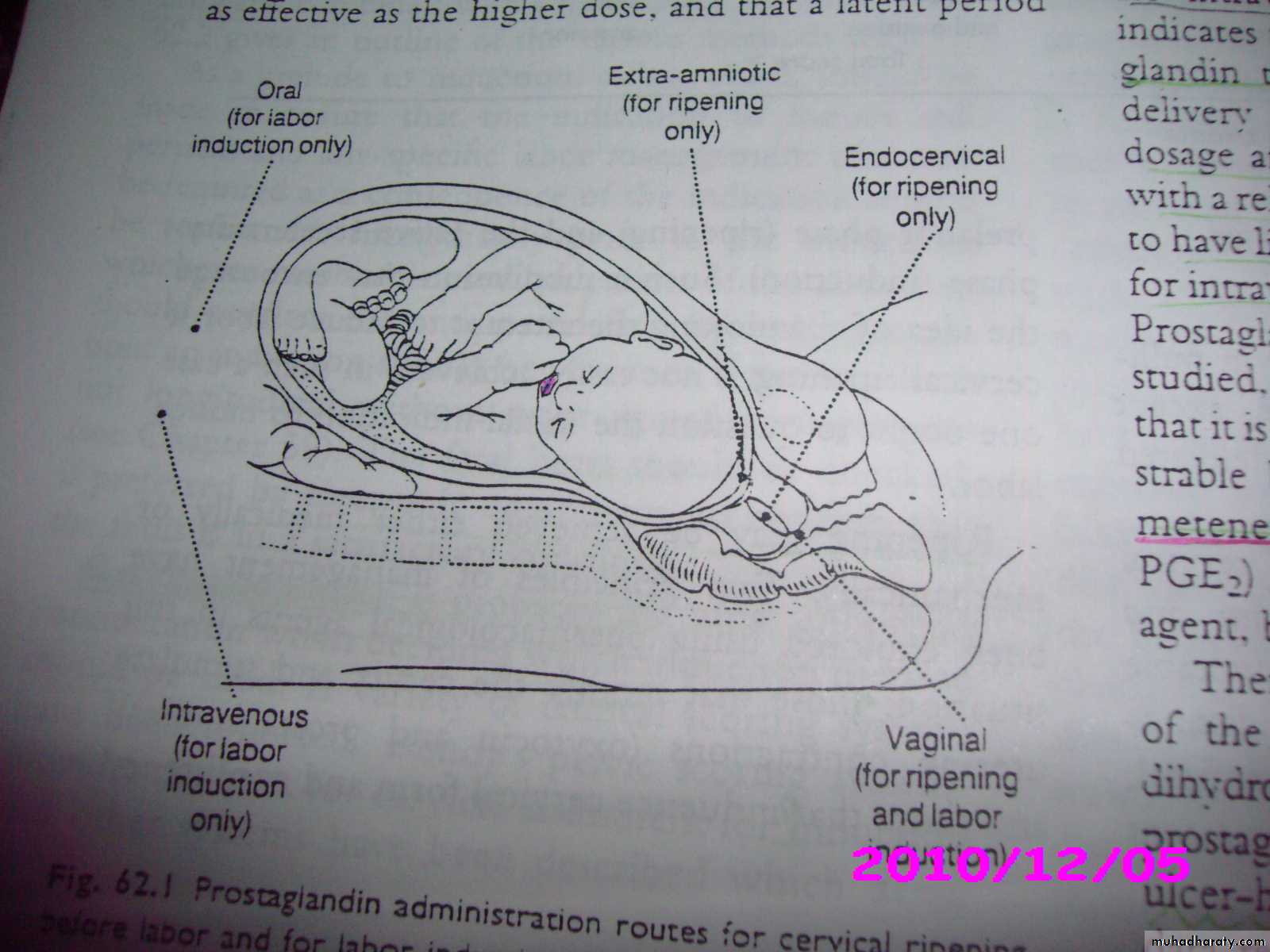
Routes of Administration
Intramuscular: PGF2α 15-methyl (Prostin 15 M) 250m g/2 hours.Intravenous: PGF2α 0.25m g / minute.
Oral: PGF2α (Prostin tablets 0.5 mg) 0.5-1 mg/ hour.
Vaginal tablets: PGE2 3 mg.
Vaginal gel: PGE2 1-2 mg.
Endocervical gel: PGE2 0.5 mg.
Extra-amniotic gel: PGE2 400-500m g.
Intramyometrial: PGF2α 1 mg.
Intra-amniotic and extra-amniotic PGF2α.
Buccal or subligual
Rectal misoprostol
Complications
Nausea.Vomiting.
Diarrhoea.
Flushing.
Tachycardia.
Pyrexia.
Contraindications
Cardiac disease.Hypertension.
Oxytocin
Mode of action: It depolarises cell membrane potential and alter permeability to sodium.The maximal sensitivity to oxytocin is achieved by 34-36 weeks’ gestation.
Mode of Action
Oxytocics act on the pregnant uterus within 1 minute if injected IV, within 2 minutes if injected IM and its action lasts for 30 minutes. These cause initiation and increase in frequency, strength and duration of uterine contractions. These are more effective with the advancement of pregnancy.Indications
Inevitable, incomplete and missed abortions.
Induction of labour.
Augmentation of labour.
Evacuation of vesicular mole.
Prophylaxis and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage.
Oxytocin challenge test.
Routes of Administration
• IV drip is the most common use.• IV pump using an electronic pump: is the most accurate for calculation of the infused dosage.
• IM and IV bolus may be given postpartum.
• Direct intramyometrial
• Nasal spray: to help evacuation of the engorged breasts.
Contraindications
Previous uterine scar as C.S, hysterotomy or open uterus metroplasty.Some malpresentations as shoulder and brow presentations.
Foetal distress and placental insufficiency.
Contracted pelvis.
Grand multipara.
Complications
Rupture uterus.Foetal distress and asphyxia.
Constriction ring and hypertonic inertia.
Amniotic fluid embolism.
Water intoxication due to its antidiuretic effect and the large amount of IV fluids when given as a drip.
Coronary spasm if the crude posterior pituitary extract was used.
Because of the considerable variability in sensitivity of the myometrium to oxytocin, oxytocin is administered as a variable dose infusion, titrated against uterine contractions.
The dose 1 mU/min, doubling the rate of infusion every 20–30min until adequate uterine contractions are achieved or a rate of 32 mU/min is reached. Once labour is
. Once labour is established the infusion rate may be progressively reduced, as the myometrial sensitivity increases, to a rate of about 7 mU/min.
Complications of IOL
1. hyponatremia2.failed induction
3.uterine hyperstimulation
4.Fetal distress /hypoxia
5.cord prolapse
6.abruptio placenta
7.uterine rupture
8.inadvertant preterm labor
9.hypotonic uterine post partum hemorrhage
10.hyperbilirubinemia.
Key points
When administering oxytocin, the target is to stimulate uterine activity that is sufficient to effect cervical change as well as fetal descent without compromising the fetus.Minimally effective uterine activity is usually defined as 3 contractions per 10 minutes averaging greater than 25 mmHg above baseline, with 5 contractions in 10 minutes considered adequate for the progression of labor. The Montevideo unit was created in 1957 to describe the summation of the amplitudes of all contractions in a 10-minute
.
Key point
. Uterine tachysystole is usually defined as > 5contractions in 10 minutes, or contractions occurring within 1 minute of one another . Some clinicians define hyperstimulation as ≥ 6 contractions in 10 minutes.
Key point
Castor oil, bath, and/or enemaCastor oil, bath and enema were a time-honoured method
of inducing labour. Only one randomized trial has evaluated
castor oil with inconclusive results. There is an association between castor oil, a cathartic, and meconium passage possibly by a direct effect on the fetal bowel.
Other methods
For the following methods of labour induction, there
is insufficient evidence either of effectiveness or of benefits over the methods outlined above: extraamniotic
prostaglandins, intravenous prostaglandins, oral
prostaglandins, mifepristone, oestrogens, corticosteroids,
relaxin, hyaluronidase, acupuncture, breast stimulation,
sexual intercourse, and homoeopathic methods.
Other drugs that stimulate uterine contraction
BUT DO NOT USED IN LABOUR INDUCTION OR ACCELERATION
ERGOT ALKALOID
Ergometrine = MetherginAction
It induces sustained uterine contraction lasts for 3-4 hours.Routes of Administration
• Onset of action• Dose
• Route
• 7 minutes
• 1mg
• Oral
• 4 minutes
• 0.5 mg
• IM
• 1 minute
• 0.25 mg
• IV
Indications
Inevitable and incomplete abortions.
Prophylaxis and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage.
Subinvolution of the uterus.
Contraindications
Before delivery of the foetus as it will cause foetal asphyxia and rupture uterus.Cardiac disease.
Hypertension.