Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Abdullah Alyouzbaki, MD
University of Mosul, Faculty of Medicine
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Liver Enzymes
– Aminotransferases
• AST (SGOT)
• ALT (SGPT)
– Alkaline phosphatase
– Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase
• Synthetic function
– Albumin
– Prothrombin time
– Bilirubin
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• The use of or exposure to any chemical or medication
(including prescription and over-the-counter medications
as well as herbal therapies)
• The duration of LFT abnormalities
• The presence of any accompanying symptoms such as
jaundice, arthralgias, myalgias, rash, anorexia, weight
loss, abdominal pain, fever, pruritus, and changes in the
urine and stool
• Parenteral exposures including transfusions, intravenous
and intranasal drug use, tattoos, and sexual activity.
• Recent travel history, exposure to people with jaundice,
exposure to possibly contaminated foods, occupational
exposure to hepatotoxins, and alcohol consumption.
History
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
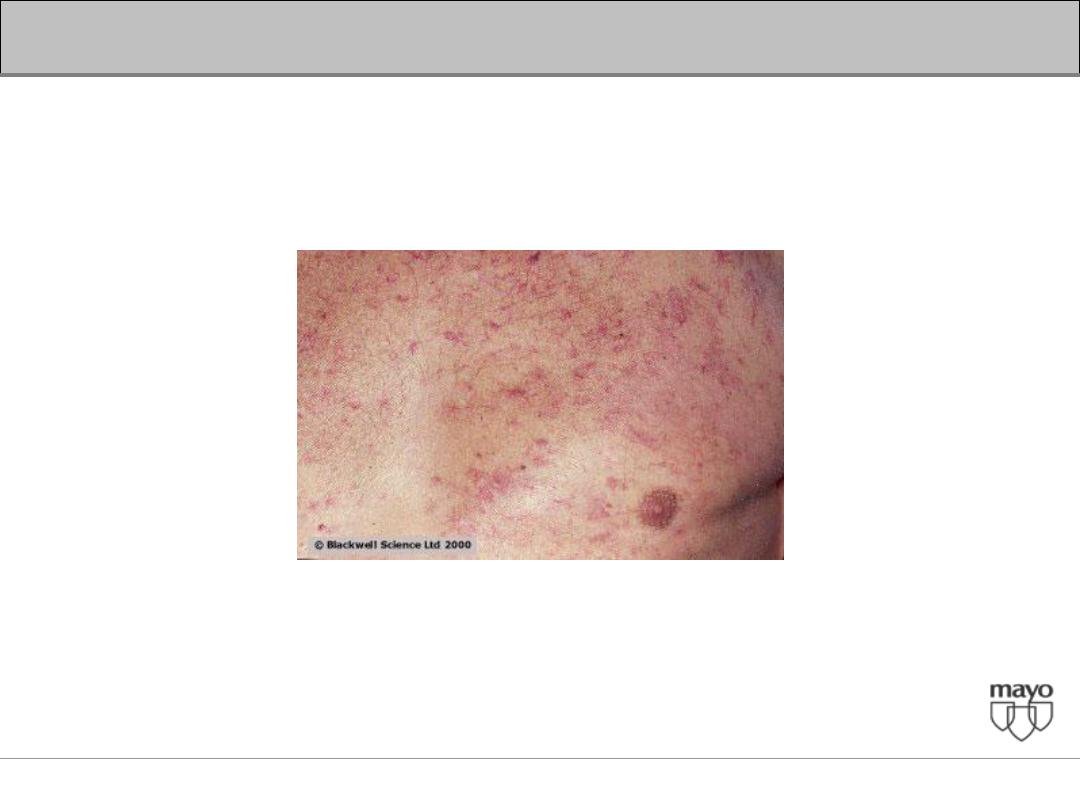
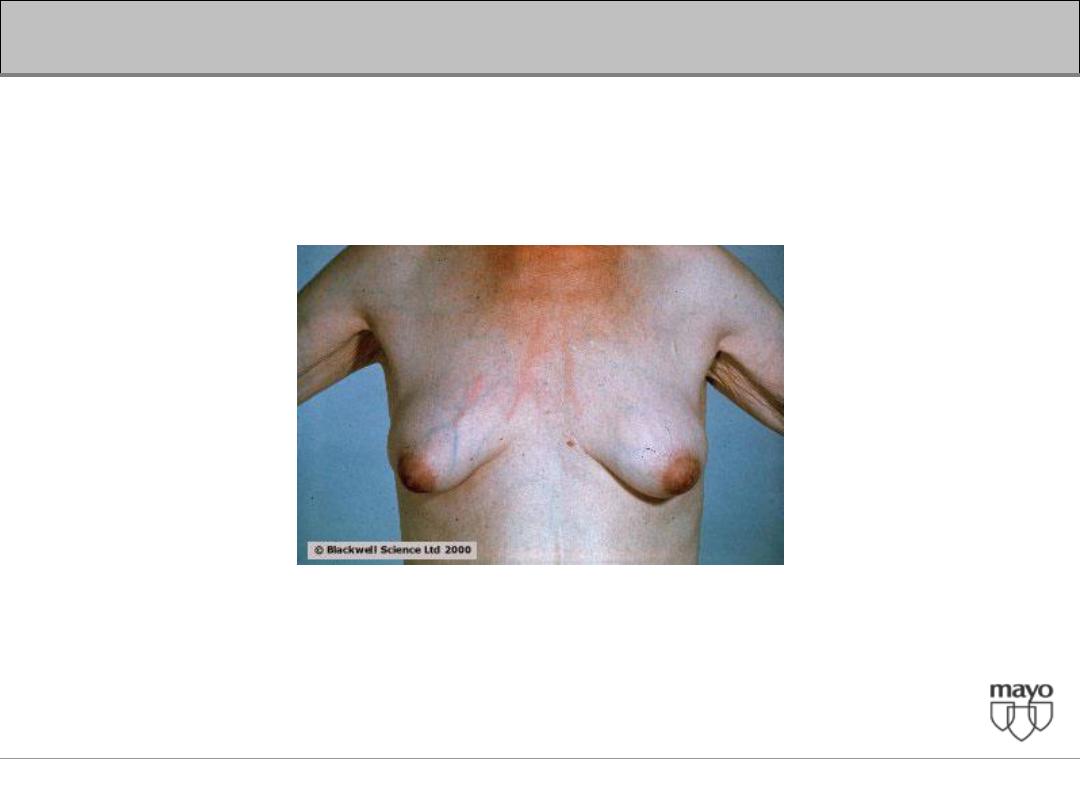
• Temporal and proximal muscle wasting suggest
longstanding diseases
• Stigmata of chronic liver disease include spider nevi,
palmar erythema, gynecomastia, caput medusae
Dupuytren's contractures, parotid gland enlargement, and
testicular atrophy
• Enlarged left supraclavicular node (Virchow's node) or
periumbilical nodule (Sister Mary Joseph's nodule)
suggest an abdominal malignancy
• Jugular venous distension, a sign of right sided heart
failure, suggests hepatic congestion
Physical Examination
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Patterns predominantly reflecting hepatocellular
injury
• Patterns predominantly reflecting cholestasis
Laboratory testing

Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
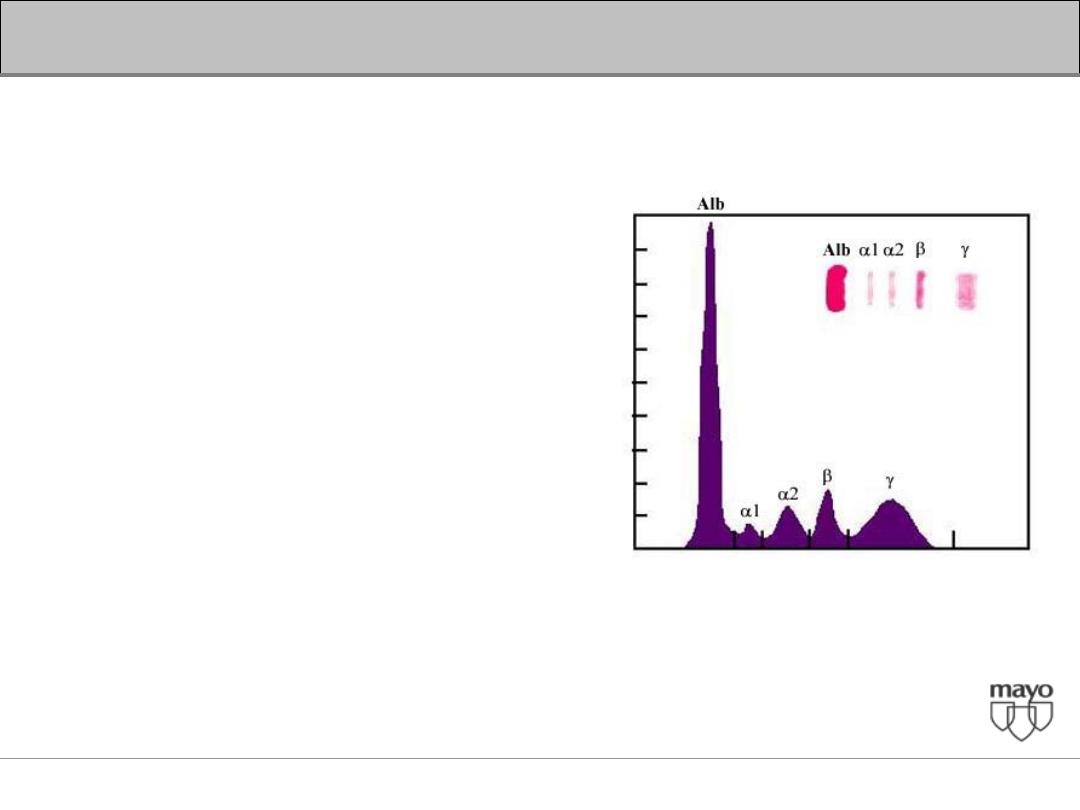
Serum Proteins
•
The liver is the major site at which serum
proteins are synthesized.
• These include albumin and the coagulation
factors
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Albumin
• Average adult liver synthesizes
approximately 15 g per day
(200 mg/kg per day).
• The serum albumin reflects the
– Rate of synthesis
– Rate of degradation
– Volume of distribution.
• Albumin synthesis is regulated
by a variety of influences
including
– nutritional status
– Serum oncotic pressure
– Cytokines, and hormones
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Hypoalbuminemia
– Systemic inflammation
– Nephrotic syndrome
– Malnutrition
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Coagulation factors
• The liver is the major site of synthesis of 11
blood coagulation proteins.
– Factor I (fibrinogen)
– Factor II (prothrombin)
– Factor V
– Factor VII
– Factor IX
– Factor X
– Factors XII
– Factor XIII
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Coagulation factors
• Prolonged Prothrombin time (PT)
• Congenital or Acquired
– Consumption of clotting factors (such as
disseminated intravascular coagulation or severe
gastrointestinal bleeding)
– Certain drugs ( Warfarin)
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Coagulation factors
•
Vitamin K deficiency
– Inadequate dietary intake,
– Prolonged obstructive jaundice,
– Malabsorption
– Administration of antibiotics that alter the gut flora.
– (PT typically returns to normal within 24 hours after
a single parenteral injection of vitamin K).
– Poor utilization of vitamin K due to advanced
parenchymal liver disease (Vitamin K
supplementation is generally ineffective)
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Serum Aminotransferases
• Sensitive indicators of liver cell injury.
• ALT and AST < 30 - 40 IU/L
• ALT levels are normally higher in
– Men
– Vary directly with body mass index
– Serum lipid levels.
– Elderly
– Infants
– ? Race
• ALT levels are normally lower in
– Consumption of coffee and especially caffeine
– Renal Failure
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Serum Aminotransferases
• Correlate poorly with the magnitude of liver injury
• Elevated in most liver diseases.
• Extensive hepatocellular injury
– Acute viral hepatitis
– Shock liver (ischemic hepatitis)
– Acute drug- / toxin-induced liver injury
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Alkaline Phosphatase
• Found in many locations throughout the body
• Its precise function is not yet known
• Derived from three sources: liver, bone, and the
intestinal tract.
• Retained bile acids appear to play a central role
leading to increase synthesis in the liver followed
by direct release into the circulation.
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Alkaline Phosphatase
• Level varies with age and gender
– Higher in men than in women
– Children elevated in both sexes, correlates well with
the rate of bone growth
– Adolescent males may reach mean values three times
greater than in normal adults
– Enzyme activity in serum may double late in normal
pregnancy, primarily because of influx from the
placenta
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Gamma-Glutamyl TransPeptidase
• Present in cell membranes in many tissues,
including the kidneys, pancreas, liver, spleen,
heart, brain, and seminal vesicles.
• Serum GGT and alkaline phosphatase correlate
reasonably well.
• Elevation in GGT is not completely specific for
hepatobiliary disease.
• High GGT values are found in people who take
medicines such as barbiturates or phenytoin or
ingest large quantities of alcohol
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Patterns predominantly reflecting hepatocellular
injury
• Patterns predominantly reflecting cholestasis
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Patterns predominantly reflecting hepatocellular
injury
– Increase in AST and ALT
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Patterns predominantly reflecting cholestasis
– Increase in Alkaline phosphatase and GGTP
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
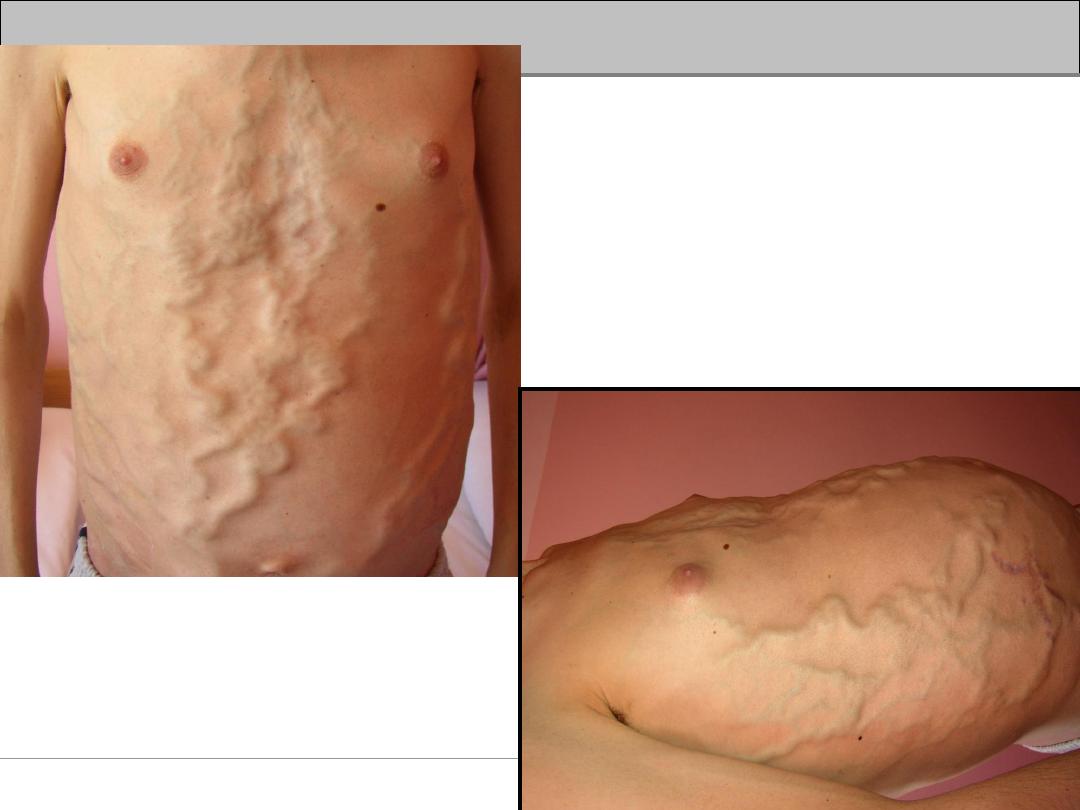
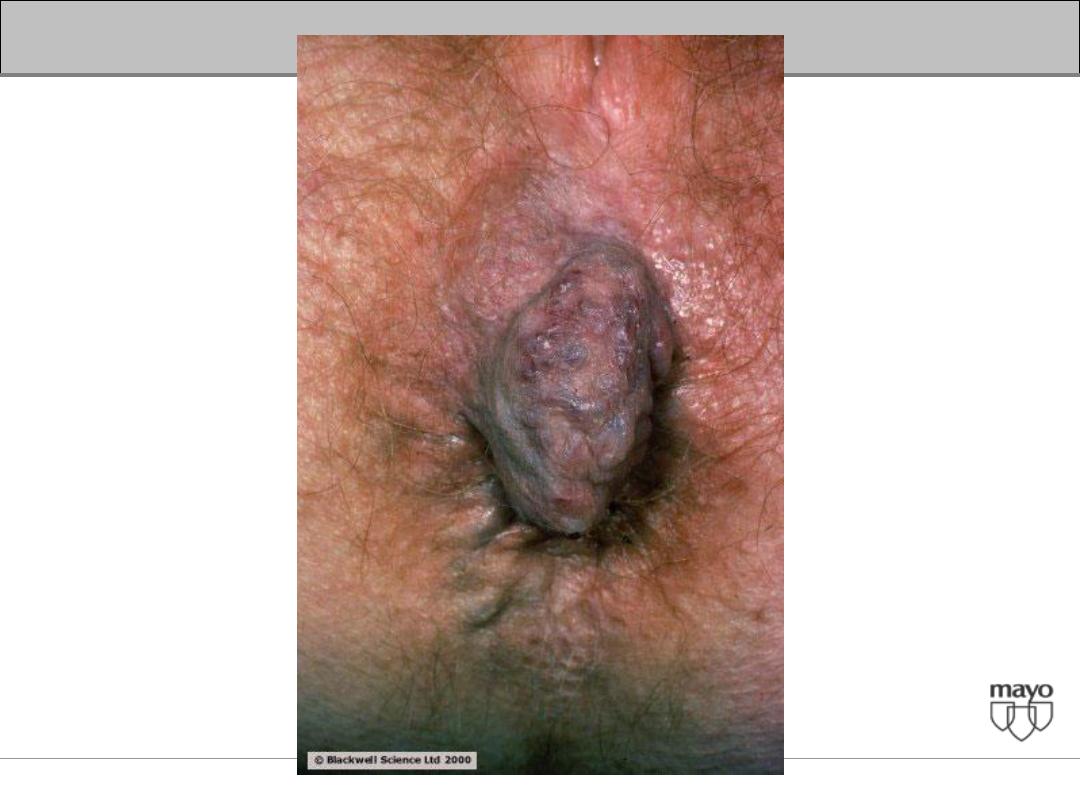
Describes the appearance of
distended and engorged
umbilical veins which are seen
radiating from the umbilicus
across the abdomen to join
systemic veins.
Caput Medusae
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Case 1
• Abnormal liver enzymes for > 6 months
– AST
80
– ALT
110
– Alkaline phosphatase, GGTP and Bilirubin WNL
Mild chronic elevation of serum transaminases
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 1
– Viral Hepatitis Screen
– Medications and Herbs
– Alcohol abuse
– Steatosis and steatohepatitis
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 1
– Viral Hepatitis Screen
– Medications and Herbs
– Alcohol abuse
– Steatosis and steatohepatitis
Careful history and risk factors
HBsAg
HCV antibodies
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 1
– Viral Hepatitis Screen
– Medications and Herbs
– Alcohol abuse
– Steatosis and steatohepatitis
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Predictable
Acetaminophen
Ethanol
Idiosyncratic
Methyldopa
Aspirin
Phenytoin
Halothane
Isoniazid
Chlordiazepoxide
Methotrexate
Nitrofurantoin
Phenothiazines
Phenylbutazone
Sulindac
Sulfonamides
Valproic
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 1
– Viral Hepatitis Screen
– Medications and Herbs
– Alcohol abuse
– Steatosis and steatohepatitis

Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• CAGE questionnaire
– Have you ever felt the need to
c
ut down on
drinking?
– Have you ever felt
a
nnoyed by criticism of your
drinking?
– Have you ever had
g
uilty feelings about your
drinking?
– Have you ever taken a morning
e
ye opener?

Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 1
– Viral Hepatitis Screen
– Medications and Herbs
– Alcohol abuse
– Steatosis and steatohepatitis
Obese / Overweight
Type 2 Diabetes
Hyperlipidemia
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 2
– Autoimmune hepatitis
– Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
– Wilson's disease
ANA
ASMA
Anti LKM
γ- Globulins
A1AT level and phenotype
Ceruloplasmin level
24 hour urine Cu collection
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 3
– Muscle disorders
– Thyroid disorders
– Celiac disease
– Adrenal insufficiency
– Anorexia nervosa
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Step 4
– Liver Biopsy
When transaminases more than double
Negative ultrasound and other tests
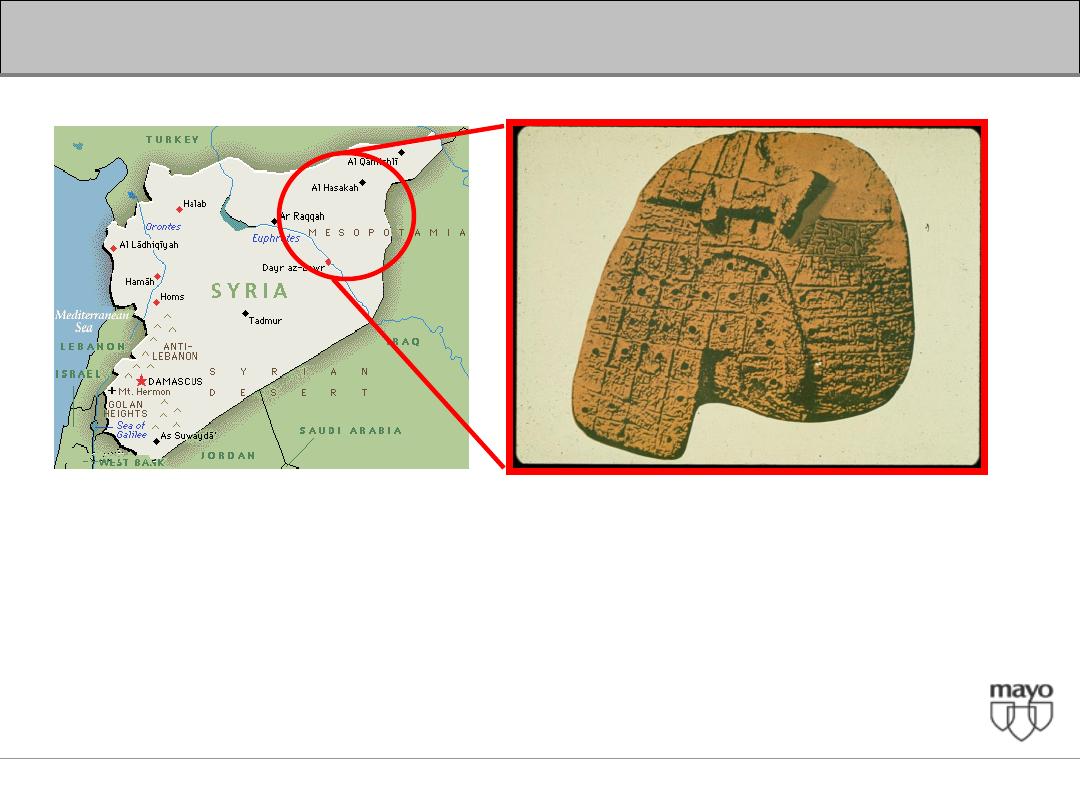
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
The Origins of Liver Anatomy
The earliest representation of a LIVER
Clay Model (Assyro-Babylonia civilization 3000-2000 B.C.)
British Museum at London
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Case 2
• Asymptomatic adult with intermittent jaundice
and normal liver enzymes except for
T. bilirubin 3.5 mg/dl (direct 2.5 mg/dl)
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Increased bilirubin production
– Extravascular hemolysis
– Extravasation of blood into tissues
– Intravascular hemolysis
– Dyserythropoiesis
• Impaired hepatic bilirubin uptake
– Congestive heart failure
– Portosystemic shunts
– Certain drugs - rifampin, probenecid flavaspadic acid,
bunamiodyl
• Impaired bilirubin conjugation
– Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I and II
– Gilbert's syndrome
– Hyperthyroidism
– Liver diseases - chronic persistent hepatitis, advanced
cirrhosis, Wilson's disease
Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Case 2
• Asymptomatic adult with intermittent jaundice
and normal liver enzymes except for
T. bilirubin 3.5 mg/dl (direct 2.5 mg/dl)
Family history
Drug history
Hgh / Hct
LDH
Haptoglobulin
TSH
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Crigler Najjar
• Crigler Najjar type I
– Exceptionally rare condition found in neonates
– Characterized by severe jaundice (bilirubin >20 mg/dL)
– Neurologic impairment due to kernicterus.
• Crigler-Najjar type II
– More common than Type I and can live into adulthood
– Bilirubin levels that range from 6 to 25 mg/dL.
– Bilirubin UDP glucuronosyl transferase activity is
typically reduced.
– Bilirubin UDP glucuronosyl transferase activity can be
induced by the administration of phenobarbital, which
can reduce serum bilirubin levels in these patients.
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Gilbert's syndrome
• Affects approximately 3 - 7 % of the
population with
• Males > females (2 : 7)
• Reduced bilirubin UDP glucuronosyl
transferase activity.
• Mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia with
serum levels almost always less than 6
mg/dL.
• The serum levels may fluctuate and jaundice
is often identified only during periods of
illness or fasting.
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Suggested that jaundice is originated from
obstruction of bile passage.
Rhazes (860-932 A.D.):

Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Avicenna (980-1037 B.C.):
• Differentiated obstructive jaundice from jaundice due
to other causes.
• Noted meat intolerance of cirrhotic patients
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Case 3
• AST
1200
• ALT
1450
• Bilirubin 9.5 mg/dl (direct 6 mg/dl)
• Alkaline phosphatase 230 mg/dl
Predominantly hepatocellular pattern with jaundice
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Viral hepatitis
– Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E
– Epstein-Barr virus
– Cytomegalovirus
• Drugs
– Predictable, dose-dependent (eg, acetaminophen)
– Unpredictable, idosyncratic (many drugs)
• Environmental toxins
– Vinyl chloride
– Jamaica bush tea - pyrrolizidine alkaloids
– Wild mushrooms - Amanita phalloides or verna
• Autoimmune hepatitis
• Wilson's disease
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Case 4
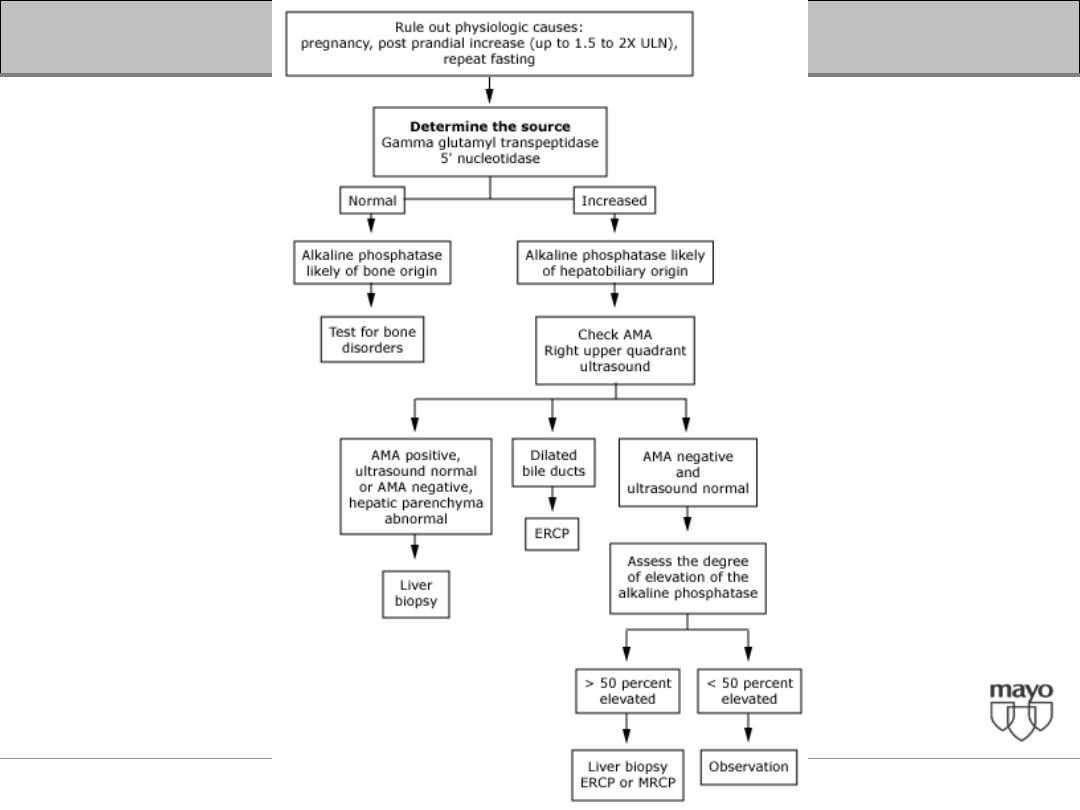
Isolated elevation of the alkaline phosphatase and/
or GGTP
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
• Partial bile duct obstruction
• Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
• Primary sclerosing cholangitis,
• Drugs such as androgenic steroids and
phenytoin.
• Infiltrative diseases include sarcoidosis, other
granulomatous diseases
• Unsuspected cancer metastatic to the liver.
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
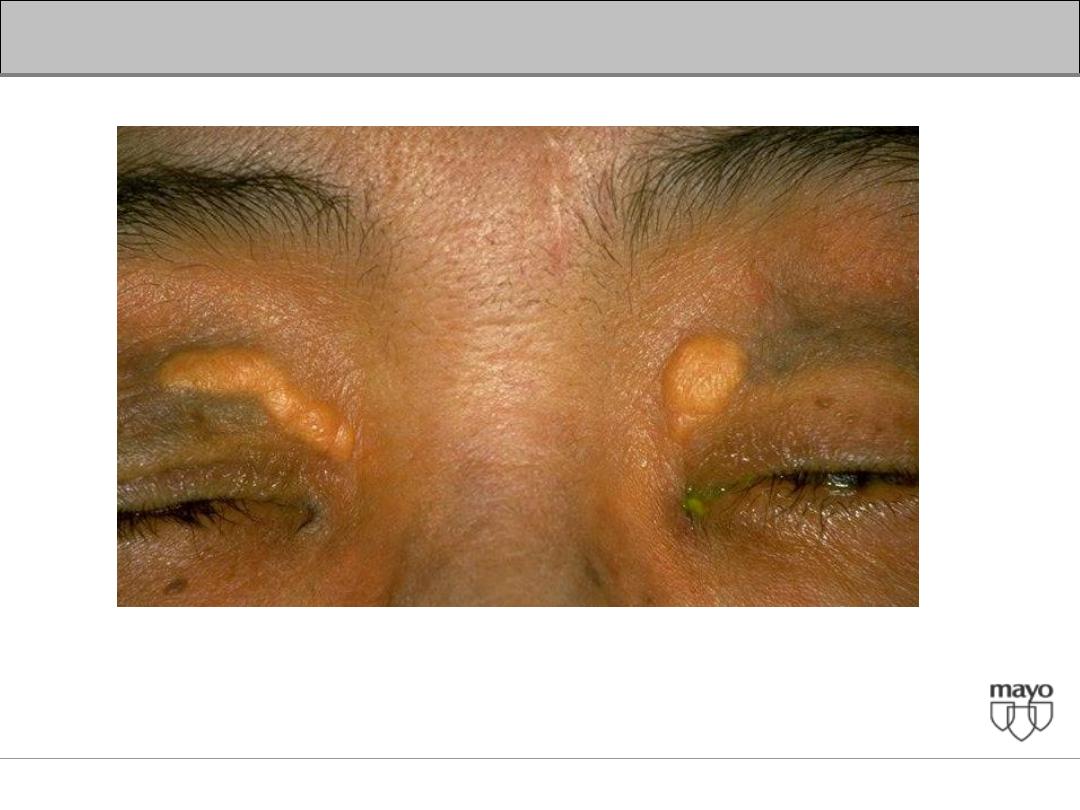
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
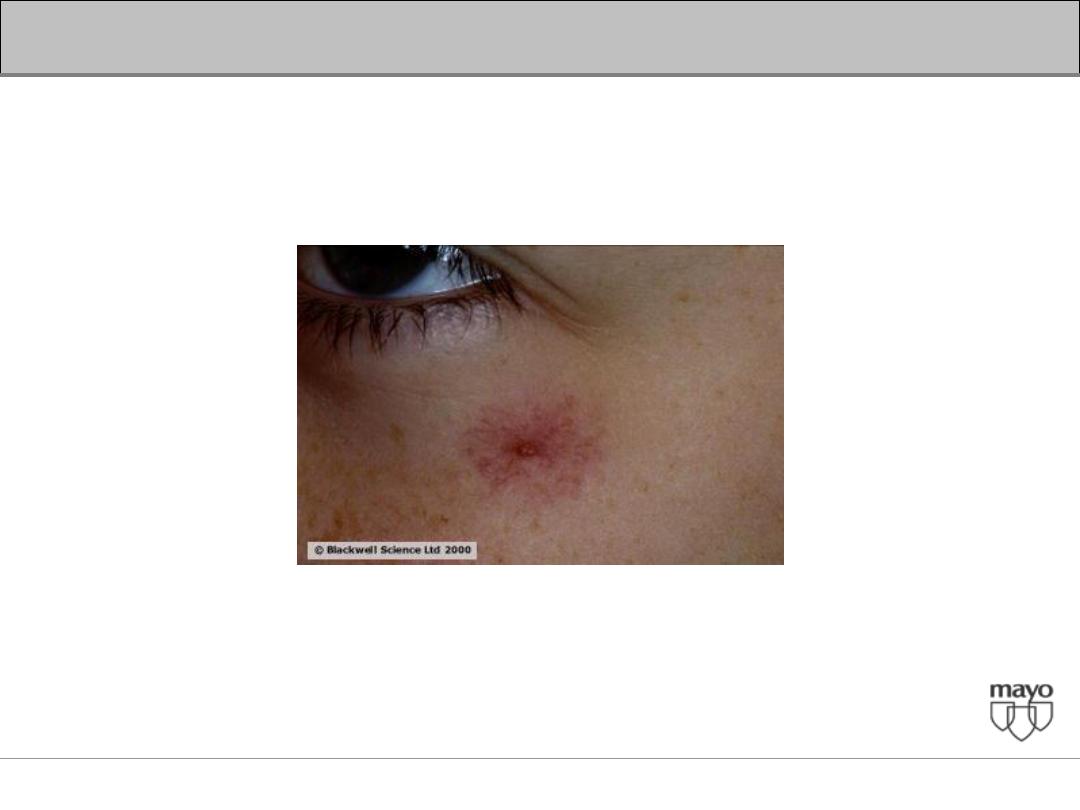
Xanthelasma
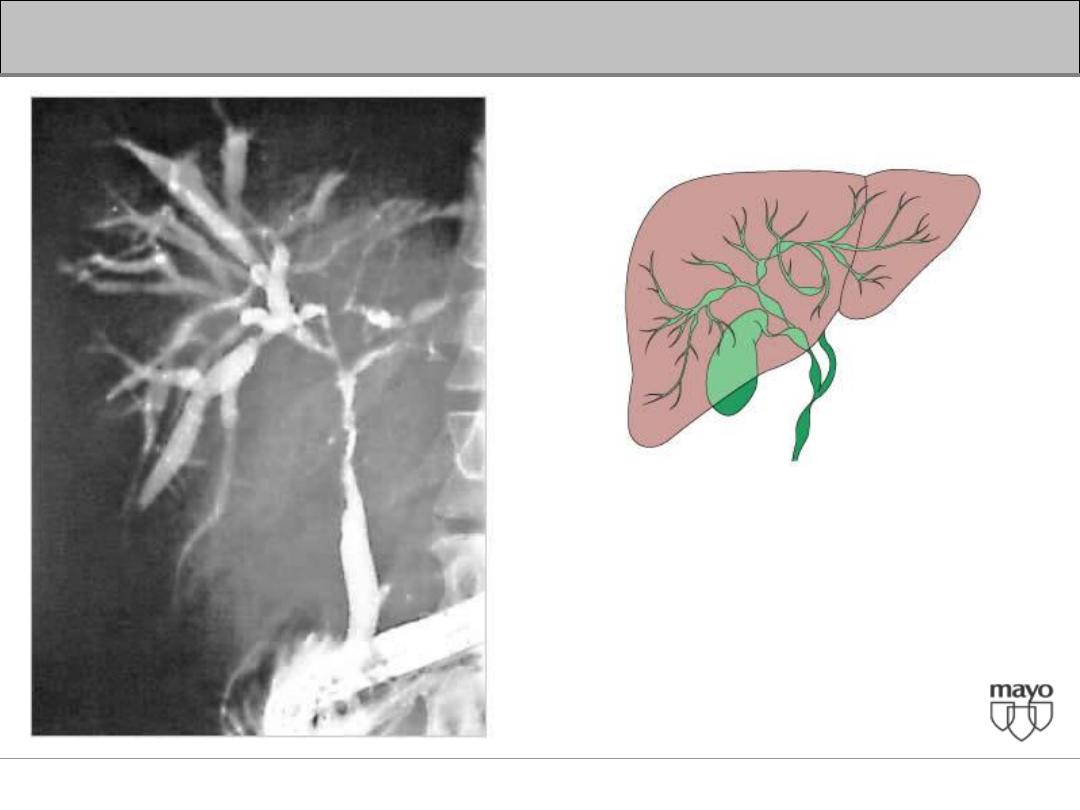
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
(PSC)
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
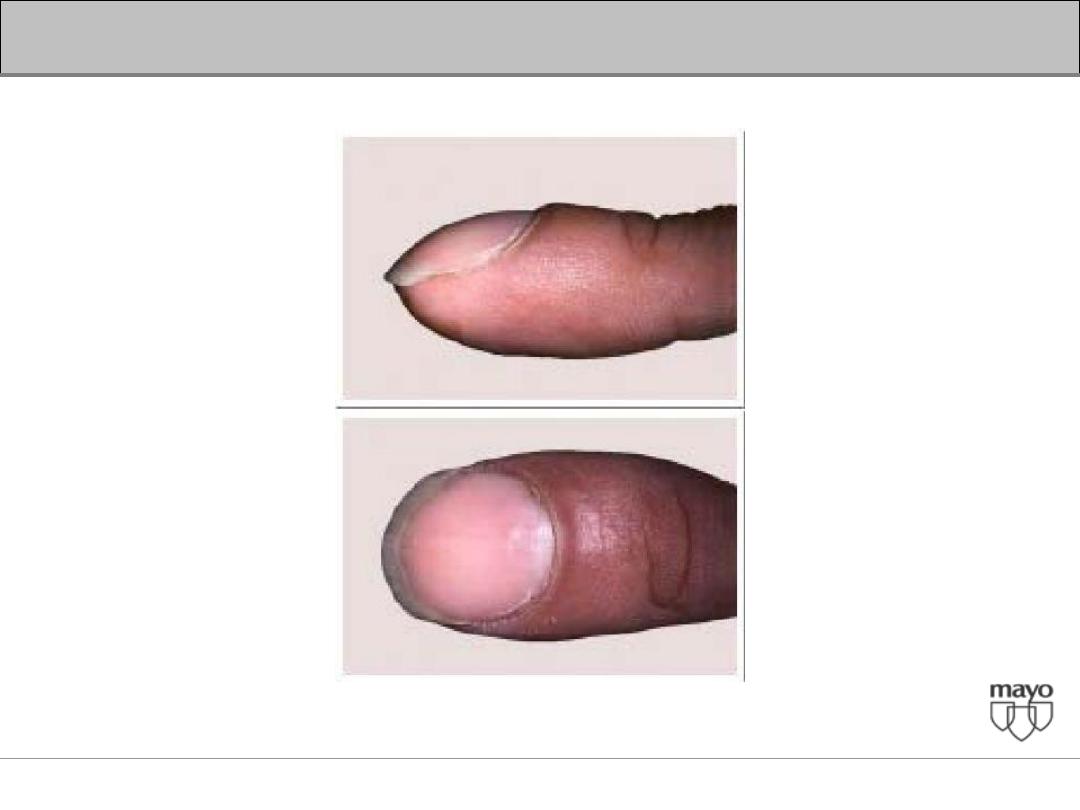
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
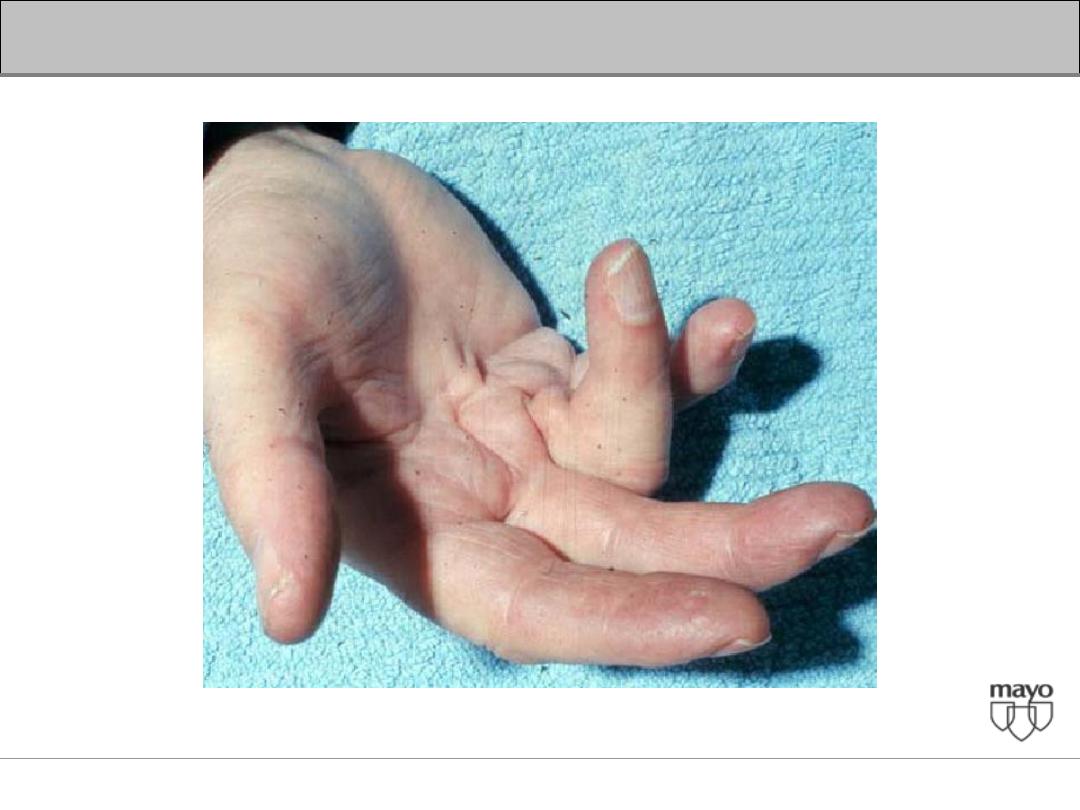
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
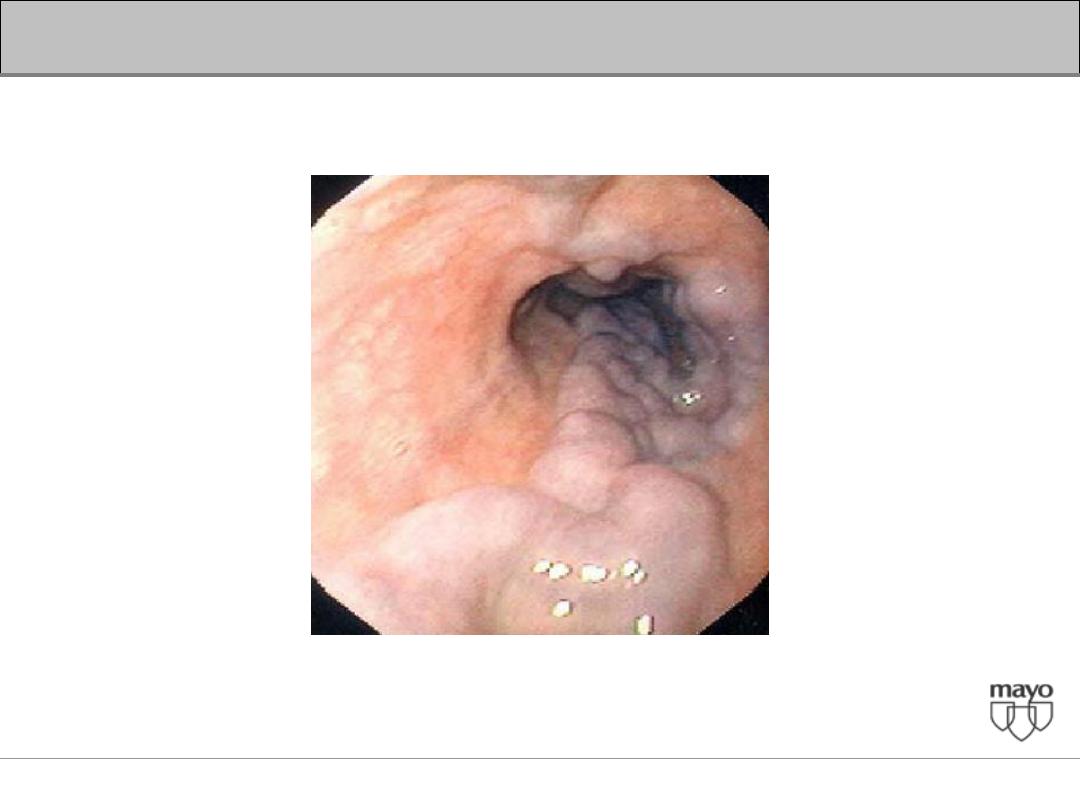
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
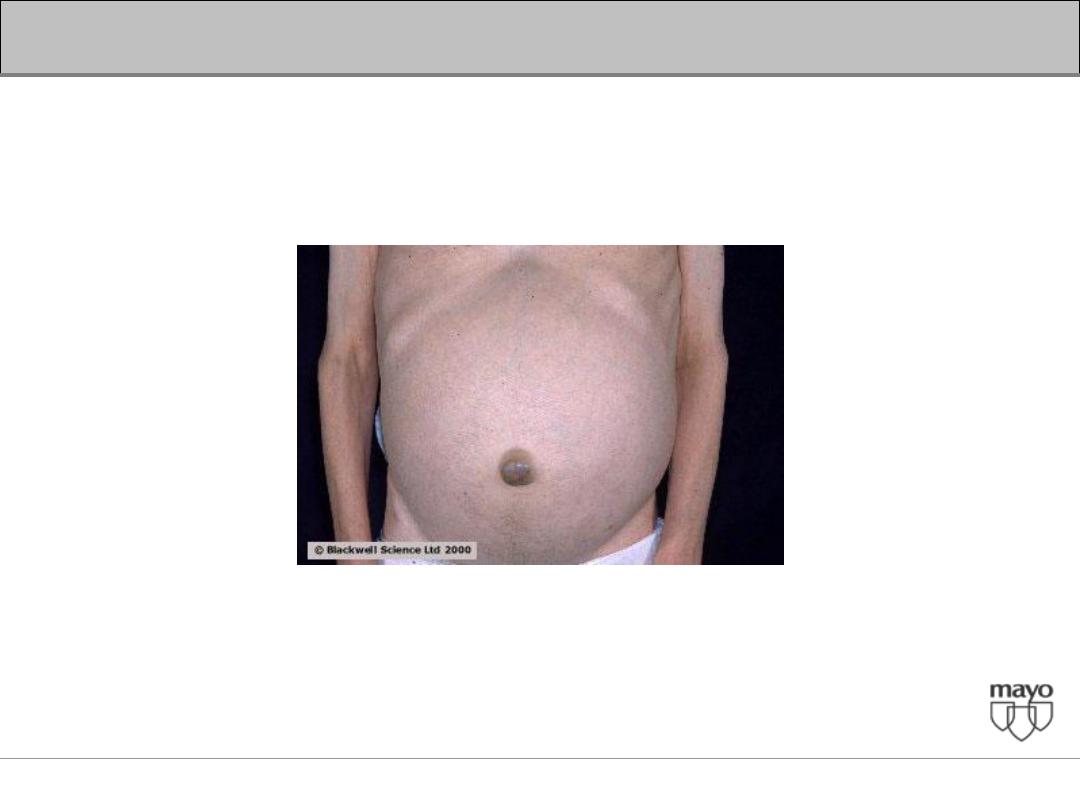
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
Interpretation of abnormal liver enzymes
