
1
DYSTONIA
Definition
Abnormal sustained posture caused by simultaneous contraction of both
agonist and antagonist muscle causing twisting movement with unintended
spread to adjacent muscles.
Dystonic contractions are usually sustained at the peak of the movement,
differentiating it from contractions seen in chorea or myoclonus.
This contraction may be slow or fast and can be associated with tremor
(dystonic tremor).
Dystonic contraction is typically triggered by action and sometimes it is very
task specific like writing or playing a musical instrument.
One characteristic feature of dystonia is the sensory trick in which a specific
touch to an affected body part can help improve the dystonia.
Epidemiology
Annual prevalence rate of primary dystonia is 150 per million, with focal
dystonia having the highest rate of 120 per million and the most common
focal dystonia is cervical dystonia followed cranial dystonia and lastly
writers cramps.

2
Classification of Dystonia
Dystonia can be classified based on :
1. the age of onset (childhood/adulthood).
2. distribution of affected body regions (focal, segmental, multifocal,
hemidystonia or generalized).
3. etiology (primary/idiopathic or secondary or dystonia plus
syndrome).
4. Genetics.
Classification based on age is clinically useful in predicting progression of
disease. Typically, the earlier the dystonia begins, the more likely it is to be
severe and subsequently generalize.
Classification based on the affected body part is useful in describing the
physical appearance of the dystonia. Examples of classic focal dystonias can
be seen in (Figure 1-2).
Also it can be classified according to etiology into
1. Primary dystonia in which the dystonia is the only clinical finding +_
tremor and abscence of neurodegeneration.
2. Secondary dystonia is associated with neurodegeneration.
3. Dystonia plus syndromes including dopa responsive dystonia and
myoclonus dystonia.

3

4
Childhood-/Adolescent-Onset Primary Dystonia
Early onset primary dystonia “age of onset less than 26 years”
Early-onset dystonia usually begins with symptoms in a limb, most
commonly a leg, during activities such as running or walking. Over time, the
dystonia can become less specific to a certain action and eventually occur
at rest and result in a sustained posture. The dystonia often spreads to
other body regions, including the other leg, trunk, and arms within 5 years.
The average age of onset is around 9 years. When the age of onset is late
childhood or adolescence, the arm is most commonly affected and is less
likely to become generalized.
It is now known that about 70% of patients presenting in this way will carry
mutation in DYT1 gene on chromosome 9. and is more common among
Ashkenazi Jews.
The test for the DYT1 mutation is now commercially available and should be
performed in patients with generalized dystonia with age of onset less than
26 years of age.
Adult-Onset Primary Dystonia
Later onset primary dystonia “age of onset more than 26 years”
The clinical presentation of later onset primary dystonia is quite different
from early onset primary dystonia. It often begins as a focal dystonia in the
upper body, sometimes segmental and rarely generalized.
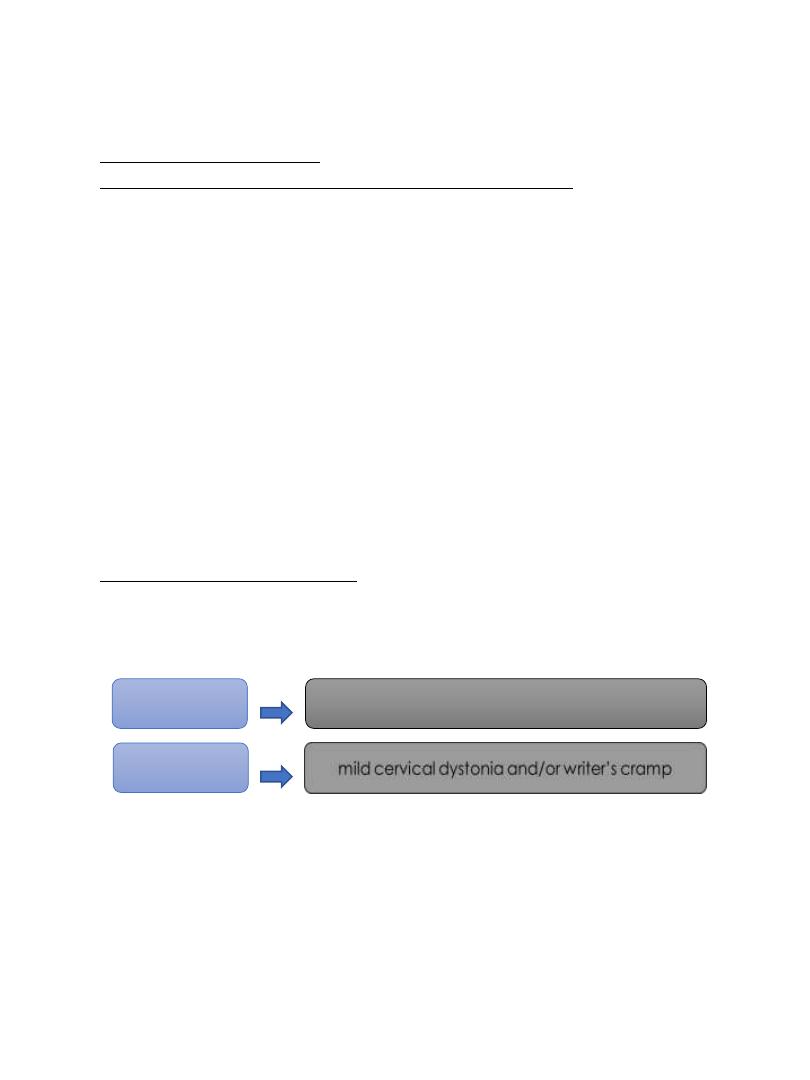
These presentations, in order of descending frequency include cervical
dystonia (spasmodic torticollis), cranial dystonia (e.g. Blepharospasm,
oromandibular dystonia or Meige syndrome [Blepharospasm and
oromandibular dystonia]), writer’s cramp, laryngeal dystonia (sometimes
called spasmodic dysphonia) and other task-specific dystonias.
5
Blepharospasm is the result of
involuntary contraction of the
orbicularis oculi muscles causing
intermittent or sustained bilateral
eyelid closure. Spasms are made
worse by stress, exposure to bright
light, or wind. Patient usually benefit
from wearing dark glasses and
sensory trick touching the upper
eyelid on one side. the dystonia can
spread to the lower face or cervical
area.
Oromandibular
dystonia occurs in the
region of the jaw,
mouth and lower face.
Spasms can result in
jaw closing, opening,
protrusion, or lateral
deviation. Resulting
from contraction of
orbicularis oris muscle
causing difficulty and
pain with chewing,
eating, or speaking.
Laryngeal dystonia, or
spasmodic dystonia, occurs
when dystonic spasms affect
the vocal cords. There are
two types adductor and
abductor spasmodic
dystonia—although mixed
types may also occur. Most
common is adductor
Cervical dystonia, or spasmodic
torticollis affects the muscles of the
neck causing deviation of head in
various directions, including rotation
(torticollis), tilt to the side
(laterocollis), pulling forward
(anterocollis), or pulling backward
(retrocollis).
This is the most common adult-onset
focal dystonia
Focal limb dystonia usually it is
task specific such as writing
called Writer’s cramp
6
Dystonia-plus syndromes
Dopa-responsive dystonia (DRD, DYT5, Segawa disease)
Typically presents in childhood, purely with lower limb dystonia, this
dystonia characterized by A diurnal fluctuation in symptom severity
with a gradual worsening of symptoms throughout the day was said to
be typical of the condition, but is present in only 60% of cases.
This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
it is entirely treatable by small doses of levodopa which lead to
complete resolution of symptoms and the effect is sustained without
causing the long term complication as seen in PD.
therefore all young patients with dystonia should receive adequate
trial of levodopa 100-200 mg daily with Dopa decarboxylase inhibitor
for at least 2 months.
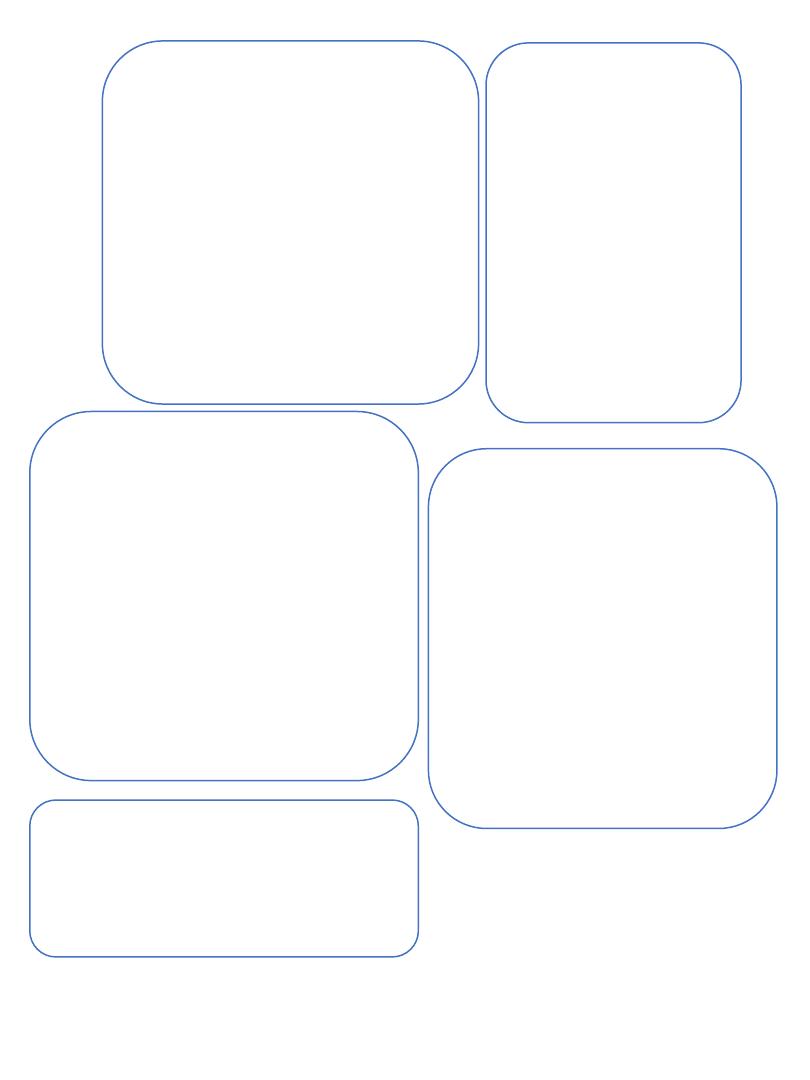
Myoclonus-Dystonia (DYT11)
Myoclonus-dystonia is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion,
with complete paternal inheritance in the epsilon- sarcoglycan gene on
chromosome 7. affect individuals under 20 years of age.
Observing patients during handwriting is critical because this may be
the only task during which myoclonic jerks can appear.
myoclonu
s
dystonia
myoclonus in the upper trunk and
proximal arms
7
It is strikingly alcohol-responsive disorder although it should be
avoided as it cause dependency. Rx Clonazepam, valproate , sodium
oxibate.
Rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism (DYT12)
autosomal dominant condition presented in adolescence with rapid
development of dystonia and parkinsonism, followed by a plateau of
symptoms. Interestingly, it is not associated with nigrostriatal neural
loss or clinical response to levodopa.
Secondary dystonia
Causes
The most common cause of secondary dystonia is perinatal brain
injury.
Secondary dystonia tends to occur more commonly at rest.
Brain imaging is extremely helpful in confirming the diagnoses in these
cases.
Tardive dystonia should be considered in patients with chronic
dystonia and a history of exposure to dopamine blocking medications,
certain anticonvulsants, or antidepressants. Patients with tardive
dystonia typically have prominent oromandibular, lingual, and cervical
dystonia although some will develop generalized dystonia.
Heredodegenerative
Acquired structural
Tardive syndromes

8
Tardive dystonia is difficult to treat and often develops into a chronic
lifelong condition. Withdrawing the offending medication is usually the
first step to prevent worsening of symptoms and if the patient is
psychiatric change to atypical neuroleptics.

9
Features suggestive of secondary dystonia
1. Abnormal birth / perinatal injury
2. Abnormal development.
3. Abnormal neurological examination like pyramidal or cerebellar
signs
4. Unusual distribution of dystonia like bulbar or hemidystonia.
5. Other system involvement (organomegaly).

10
6. Previous history of drug exposure.
Treatment of dystonia
All young patients with dystonia should receive an adequate trial of
levodopa for at least 2 months.
Botulinum toxin has revolutionized the treatment of patients with
focal dystonia “it acts by blocking the release of acetylcholine
irreversibly”, restoration of neuromuscular transmission depend on
formation of new synaptic terminals which requires about 3 months.
Treatment is required every 3-4 months and it expensive but 70-80%
successful particularly those with Blepharospasm and cervical
dystonia.
Side effect of botulinum include weakness of the treated muscles that
may extend to involve the nearby muscles (e.g. paralysis of pharyngeal
muscles following sternomastoid injections). Immune-mediated
resistance to botulinum toxin is seen in a small proportion of
chronically treated patients.
Drug treatment of dystonia is indicated for younger patients with
generalized and/or segmental dystonia for whom botulinum toxin
would be unlikely to control the full extent of the dystonia.
First line treatment is with anticholinergics such as trihexyphenidyl
“artane” Slow introduction of the drug is very important to avoid side
effects but some young patients can tolerate very high doses up to 100
mg per day + Clonazepam can be useful for the treatment of tremor,
jerks and pain associated with dystonia.
Other drugs that are sometimes useful include tetrabenazine”
dopamine depleting drug”, dopamine receptor blocking drugs and
baclofen.

11
Surgery for dystonia
Although the primary treatment for dystonia is medical, a number of
patients, particularly those with generalized dystonia, remain severely
disabled and may benefit from surgery.
Ventrolateral thalamotomies, and to a lesser degree pallidotomies
may produce improvement but carry the risk of dysphagia and
dysarthria especially if bilateral.
Gpi DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION DBS.
