
Stroke
Presenters
weam Hameed
Dalal Nidhal
Fatima Faris
Abdul-wahed Nafea
Supervised by :
Dr.Bashar Shakir

Acute stroke:
Sudden onset of neurological deficit that results from
either cerebral infarction or bleeding That lasts more
than one hour…
Focal brain dysfunction due to vascular disease…
TIA:
Sudden onset of focal neurological deficit that resolve
completely within minutes ( up to 60 minutes)…
Definition

the third most common cause of death in high-income
countries after cancers and ischemic heart disease…
the most common cause of severe physical disability…
Stroke accounts for 11% of deaths in England and Wales…
About 750 000 new strokes occur…
about 150 000 people die from stroke in the United States
each year…
Around half of all stroke survivors are left dependent on others
for everyday activities: if a patient can return home, the burden
on carers is significant…
One-quarter of all strokes occur in people below the age of 65
years…
Epidemiology
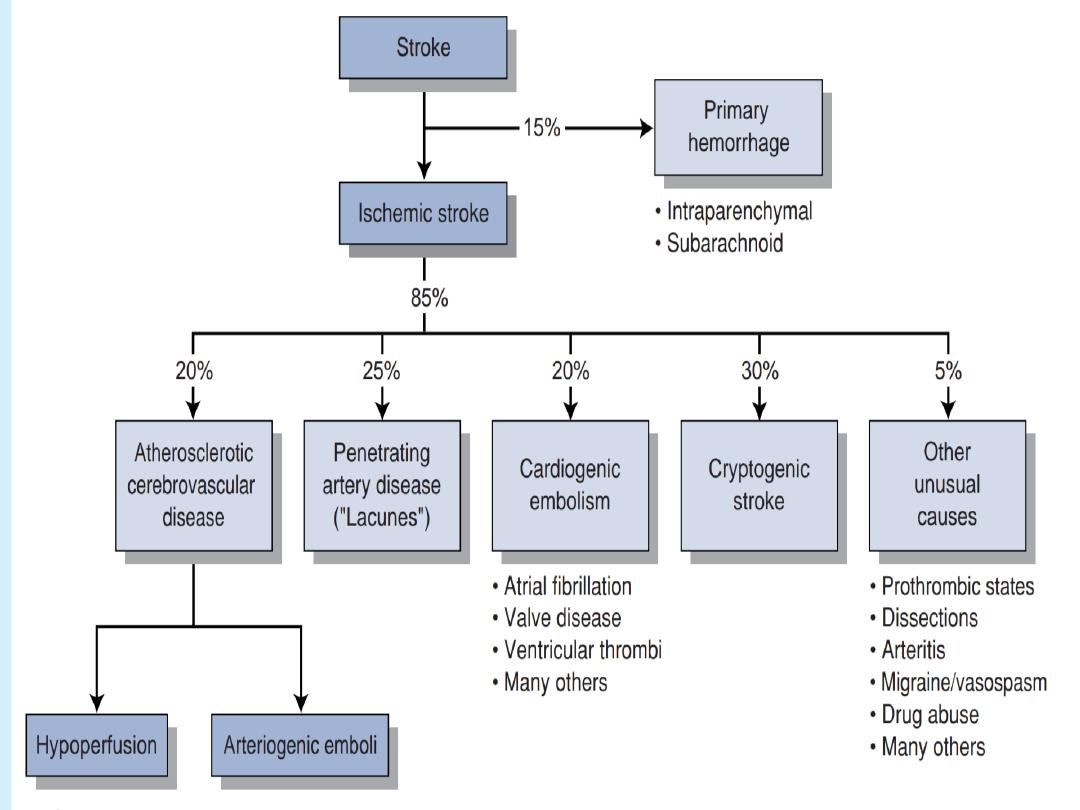

1.
Small vessel occlusion(cerebral microangiopathy).
2.
Cardiac emboli(AF,IE,MI).
3.
Atherothromboemlism (carotid vessels).
4.
CNS bleeds(HTN ,Trauma,repture aneurysm
,Anticoagulation).
Etiology

1.
Premature atherosclerosis.
2.
Arterial dissection.
3.
Thrombophilia.
4.
APS.
5.
Fabry’s disease.
6.
Homocystinuria.
7.
Drug misuse.
8.
Vascular malformation.
9.
Vasculitis.
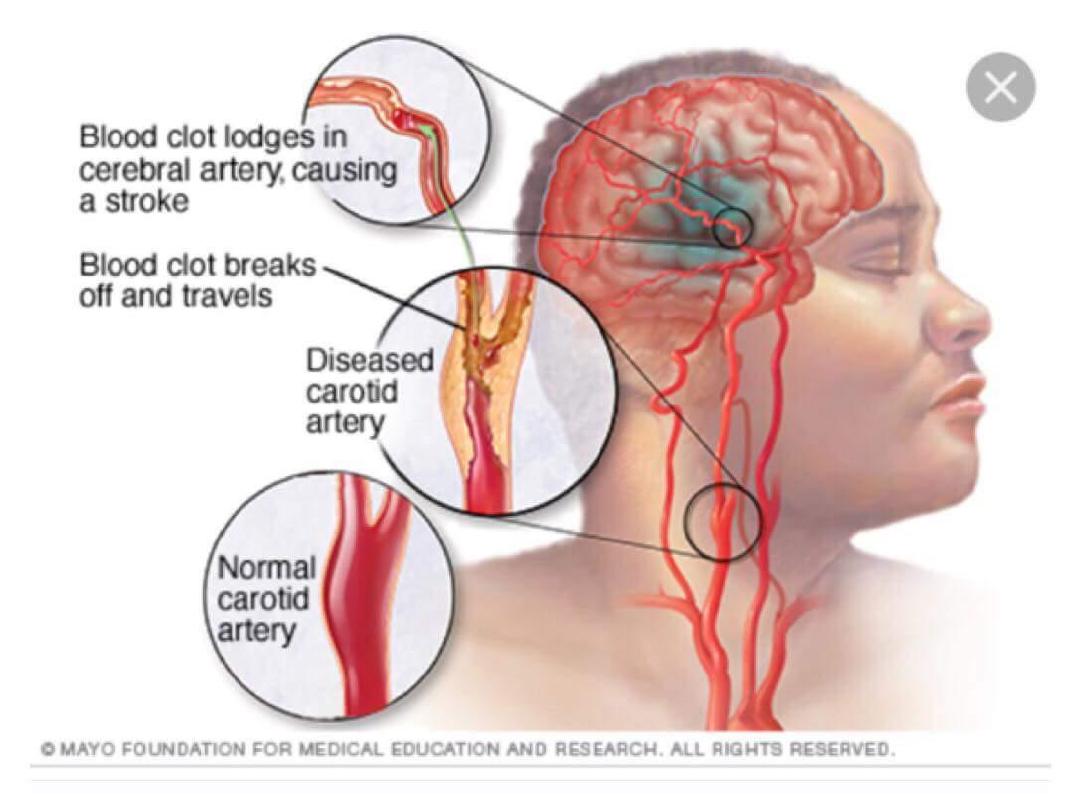
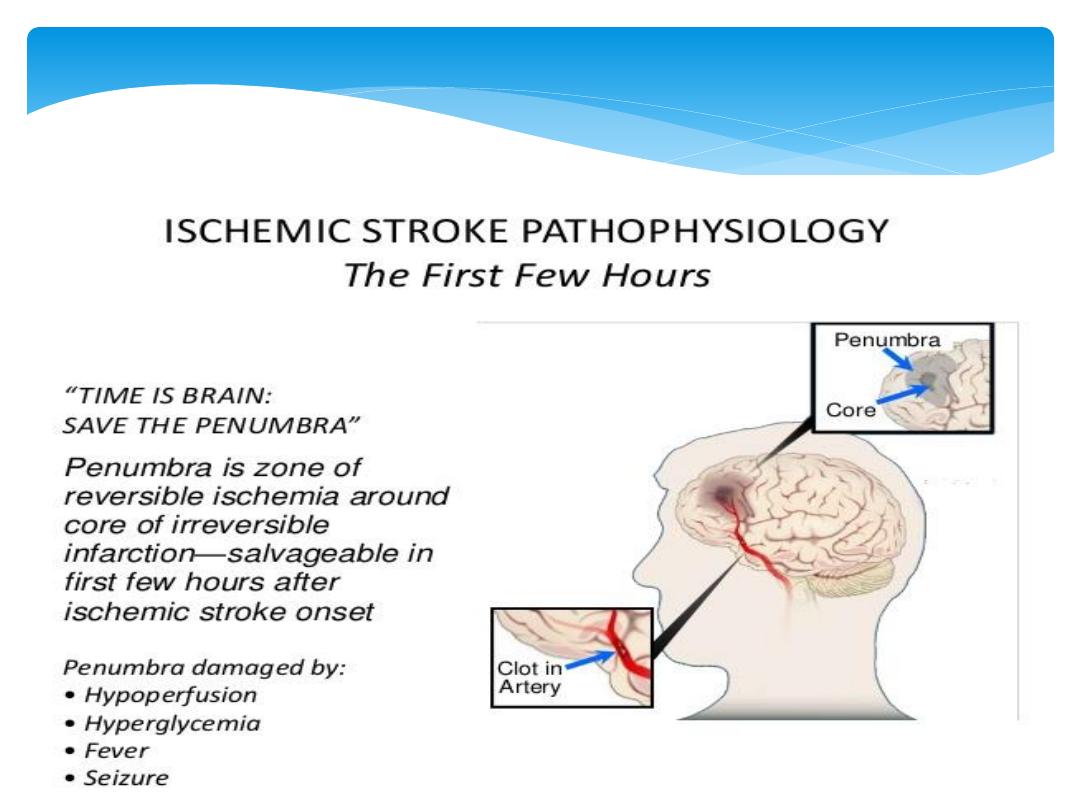
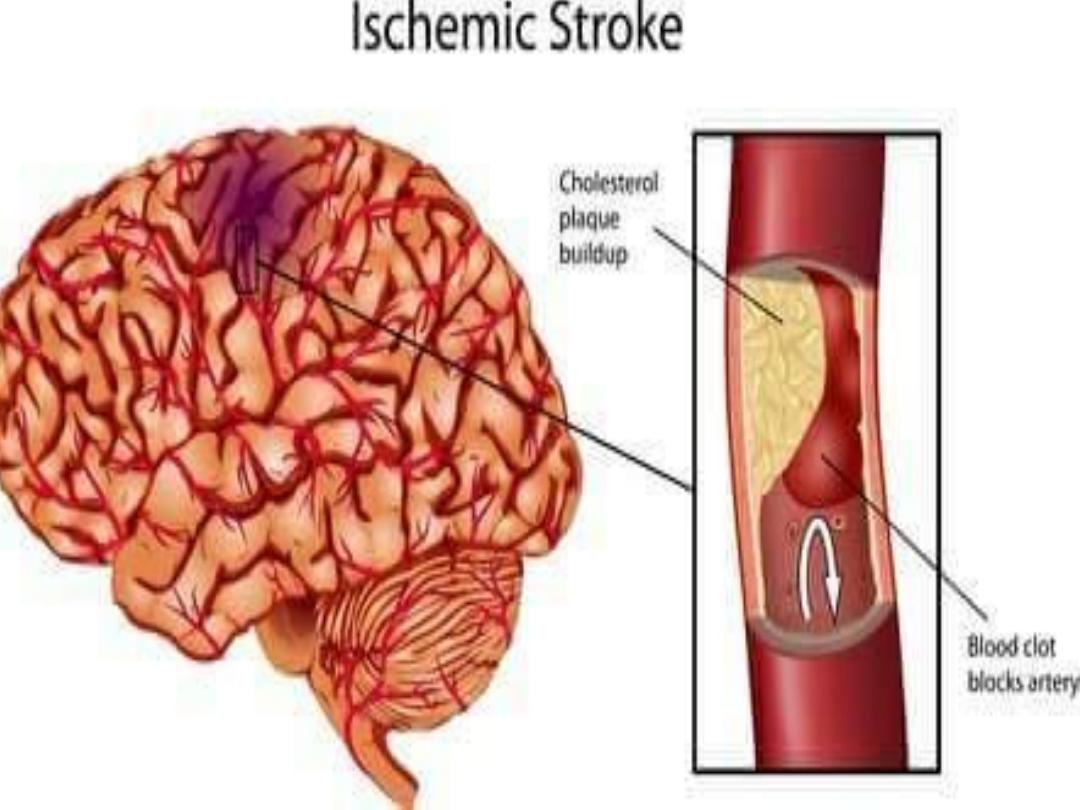
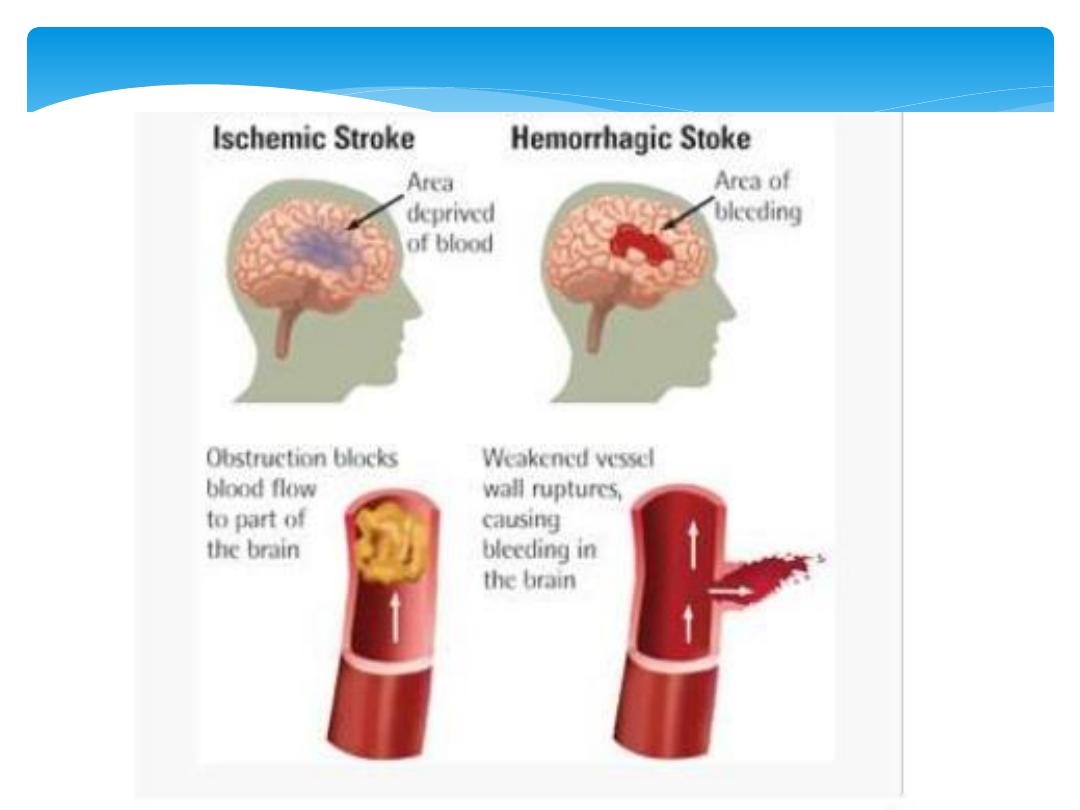
Stroke in younger patients

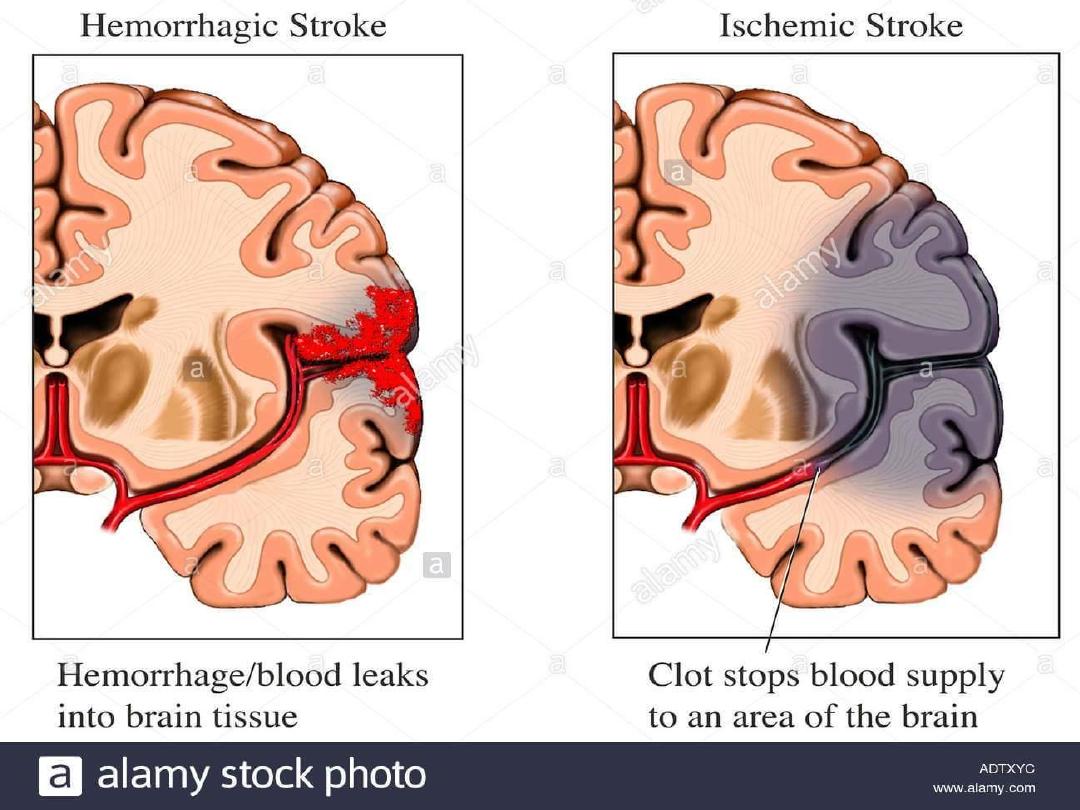
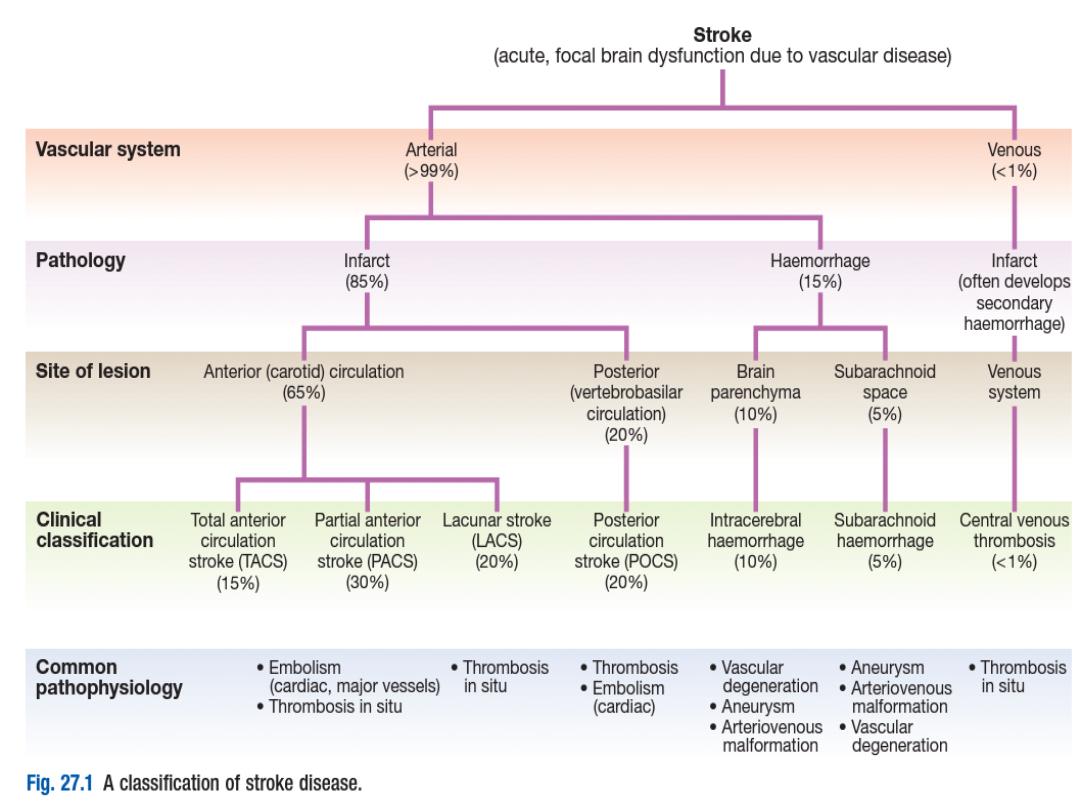
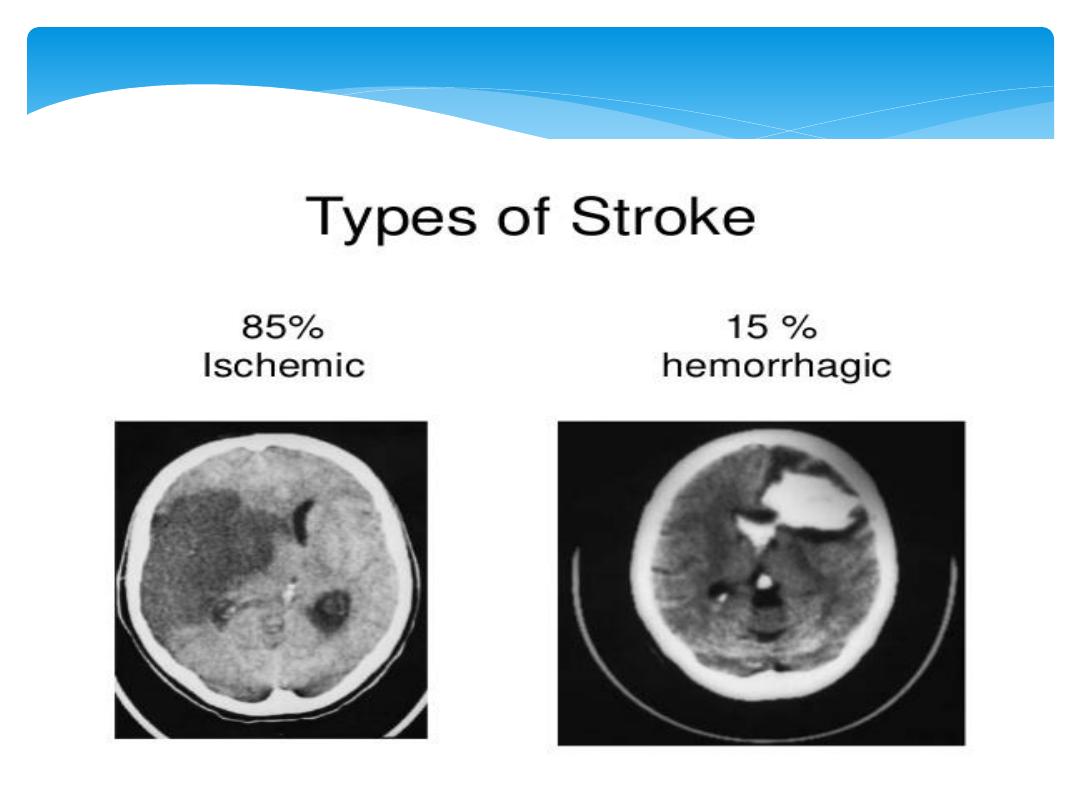
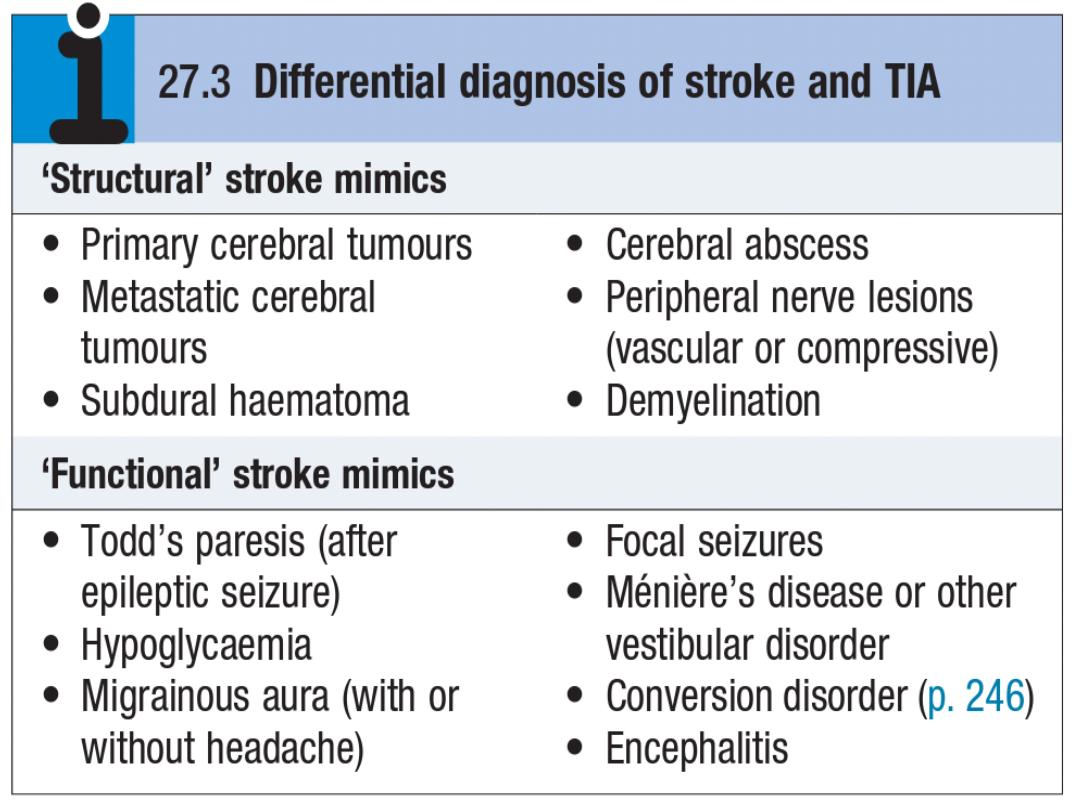
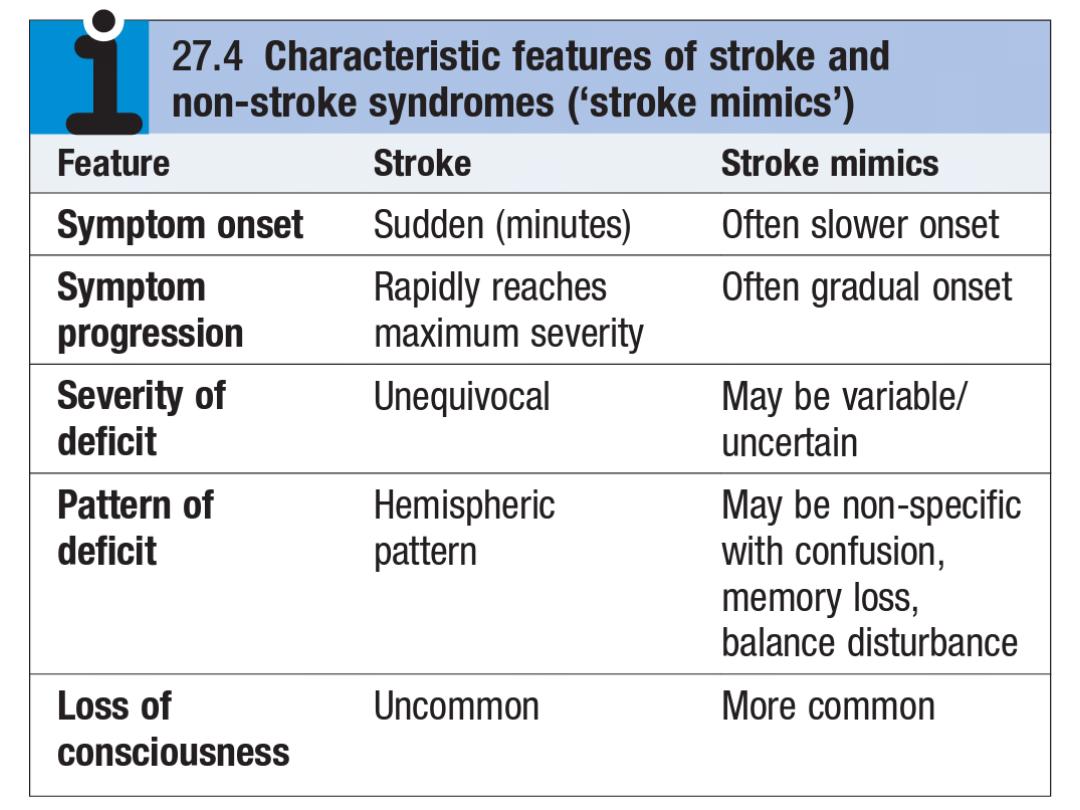
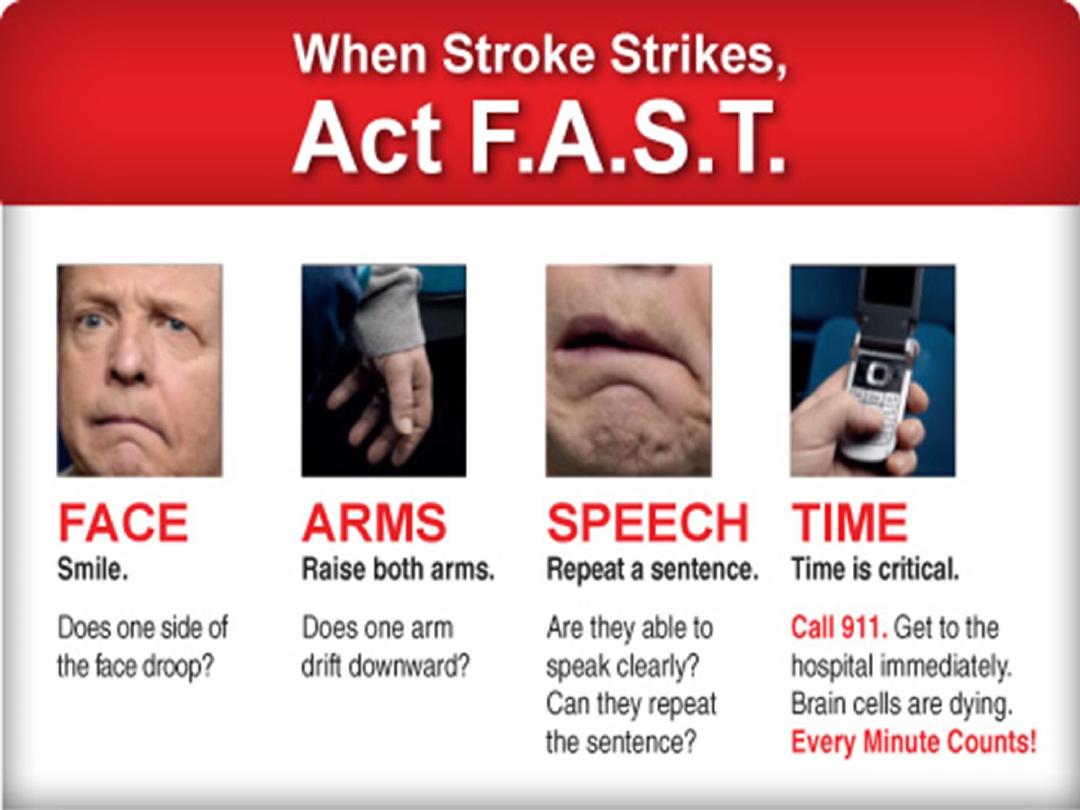
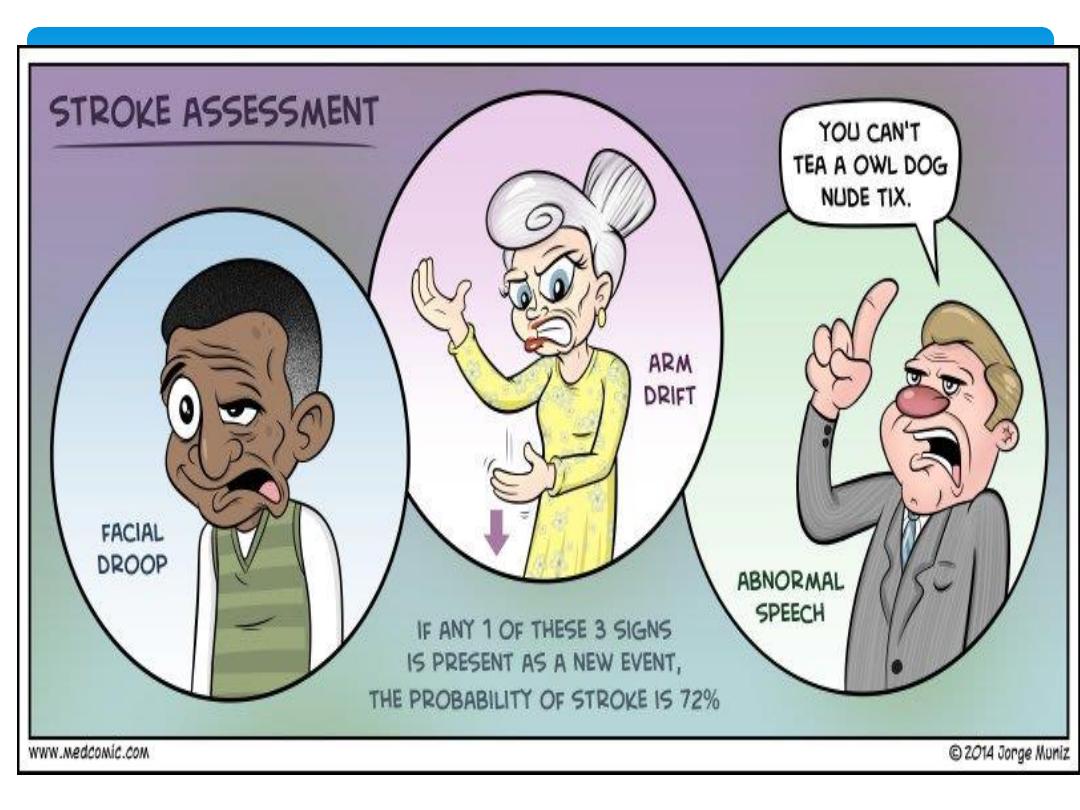
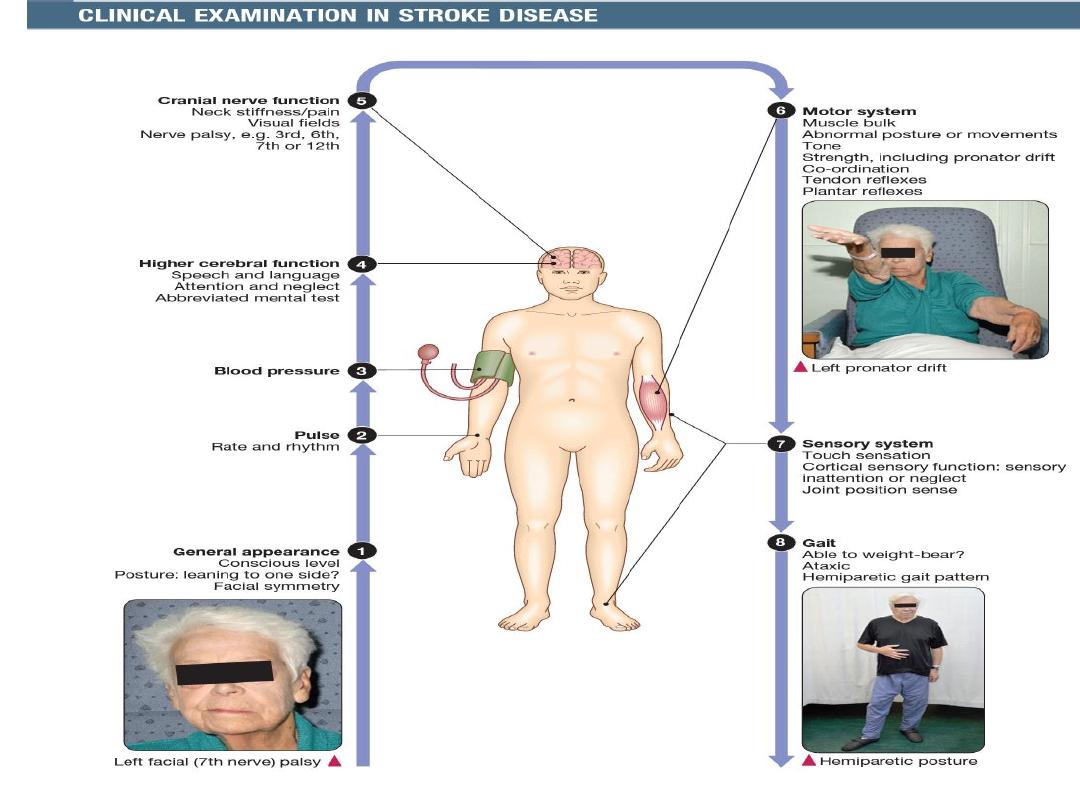
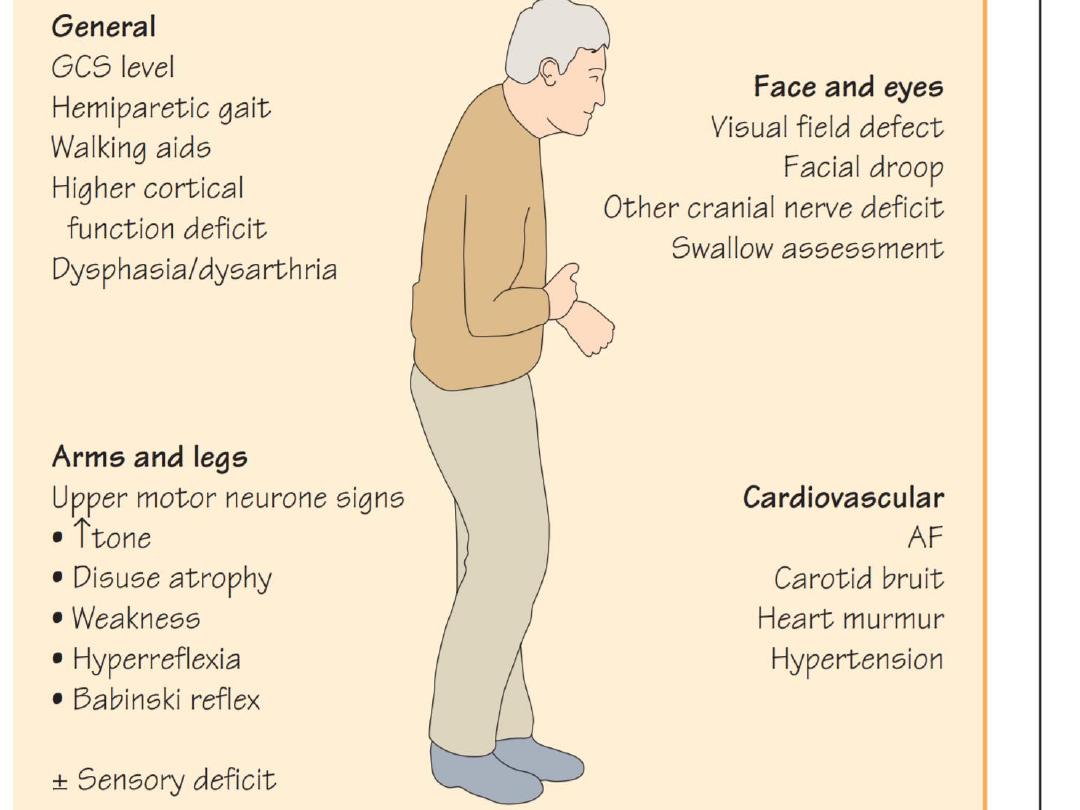
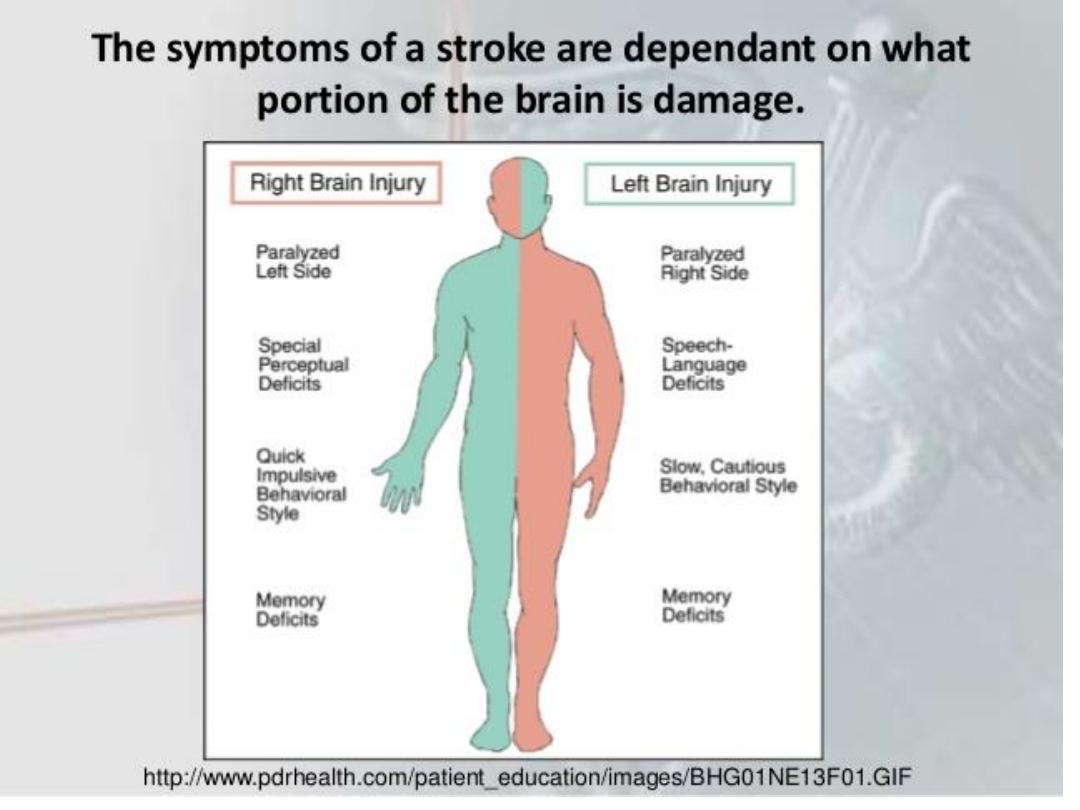
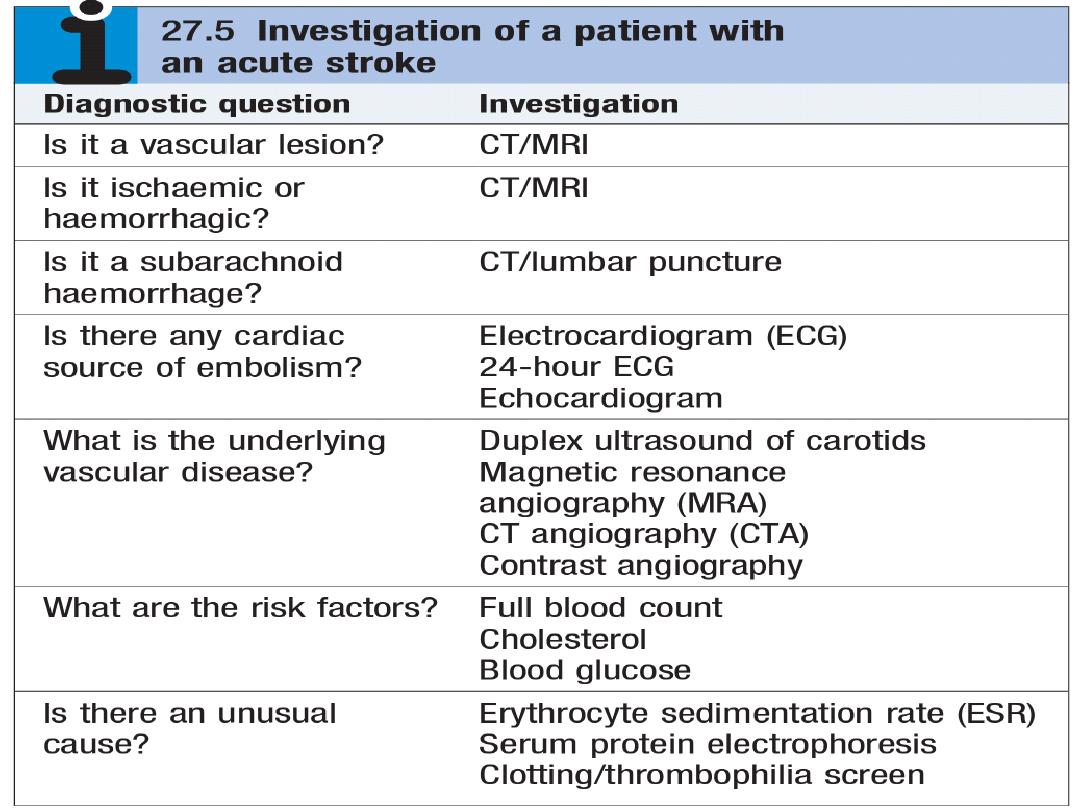
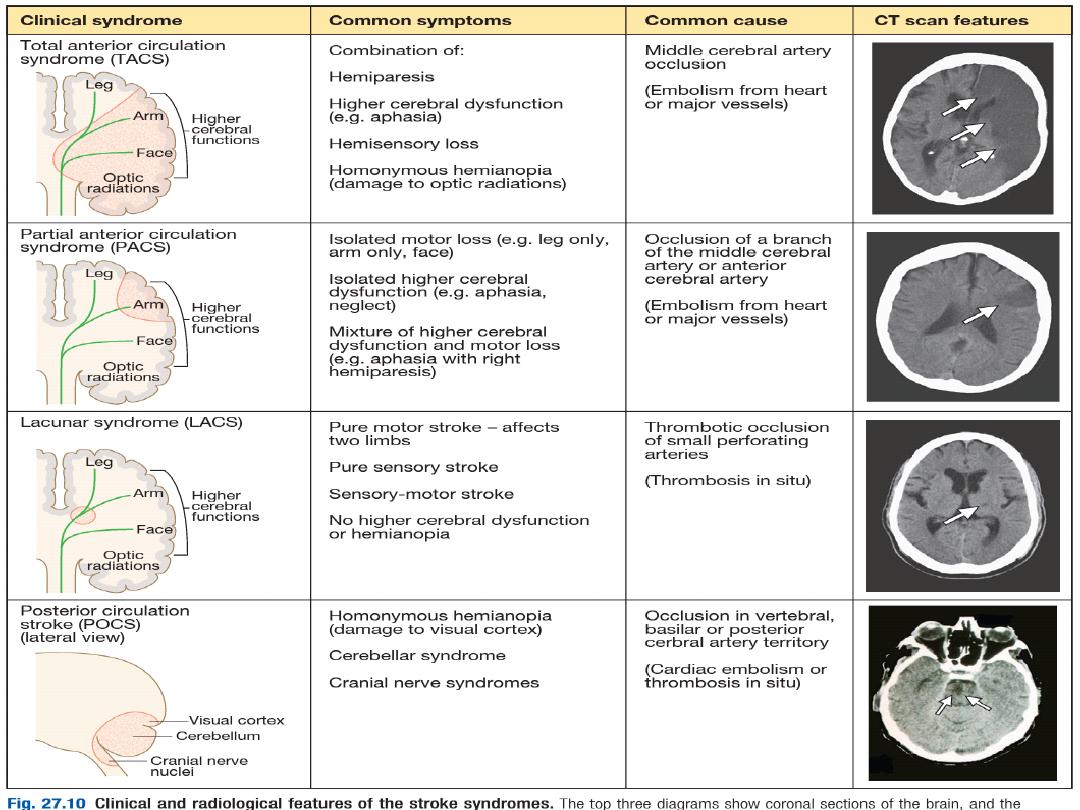

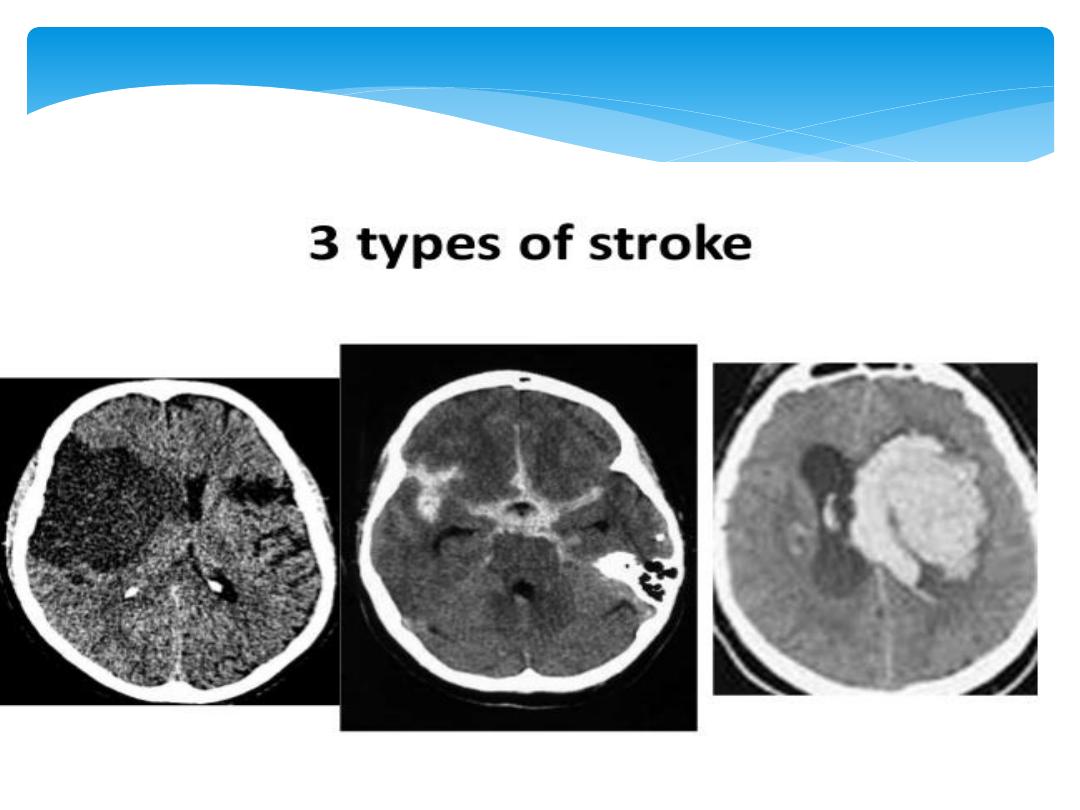
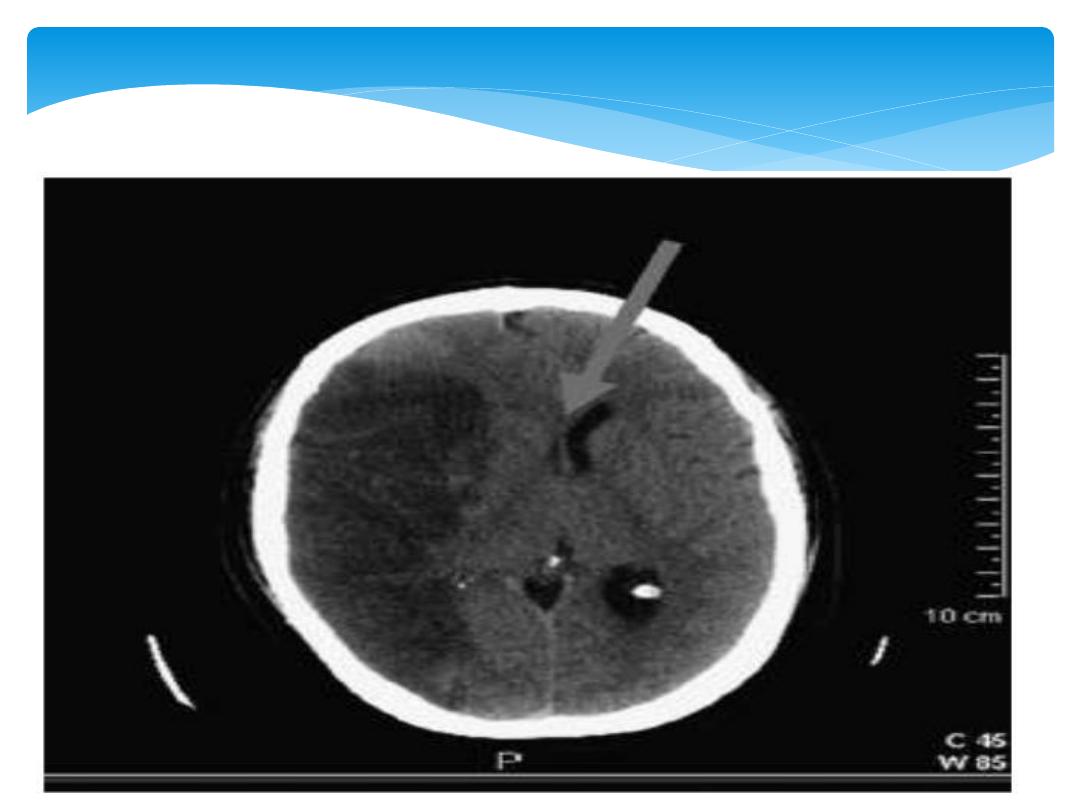
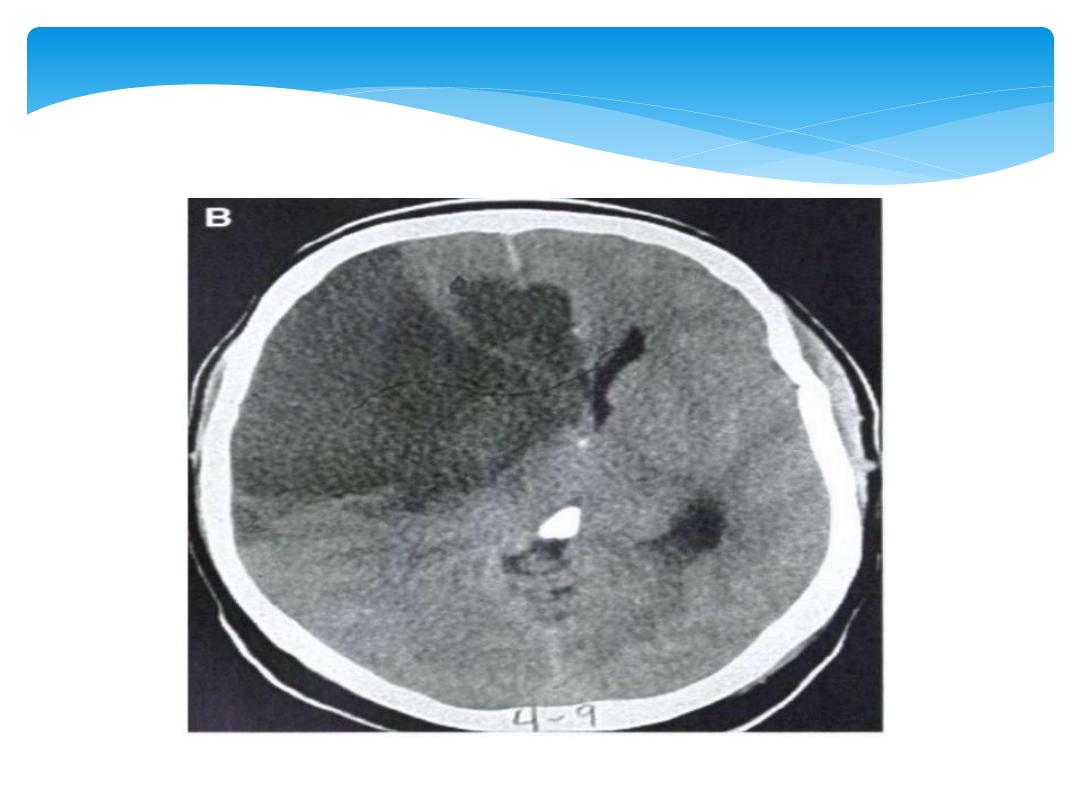
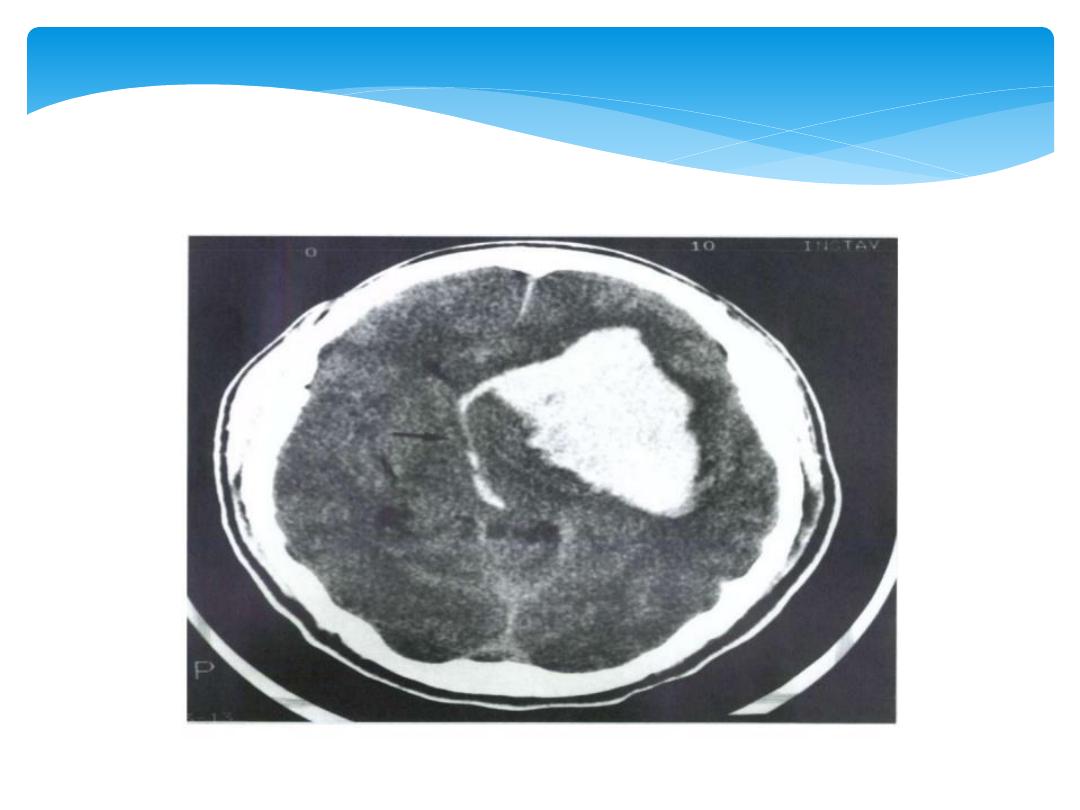



1.
a. The patient’s BP is very high (systolic >220, diastolic >120,
or mean arterial pressure >130 mm Hg).
2.
The patient has a significant medical indication for
antihypertensive therapy. Examples :
Acute
MI • Aortic dissection • Severe heart
failure • Hypertensive encephalopathy.
3. The patient is receiving t-PA—aggressive blood pressure
control is necessary to reduce the likelihood of bleeding.
When to lower BP in stroke



It is often difficult to distinguish ischemic stroke from an
ICH on clinical grounds.
The emergent treatment is initially the same until the
diagnosis is certain.
CT scan is the test that identifies ICH in the initial period.
Treatment of strokes is prophylactic.
Once a stroke has occurred, there is nothing that can be
done to salvage the dead brain tissue.
The goal is to prevent ischemic events in the future.
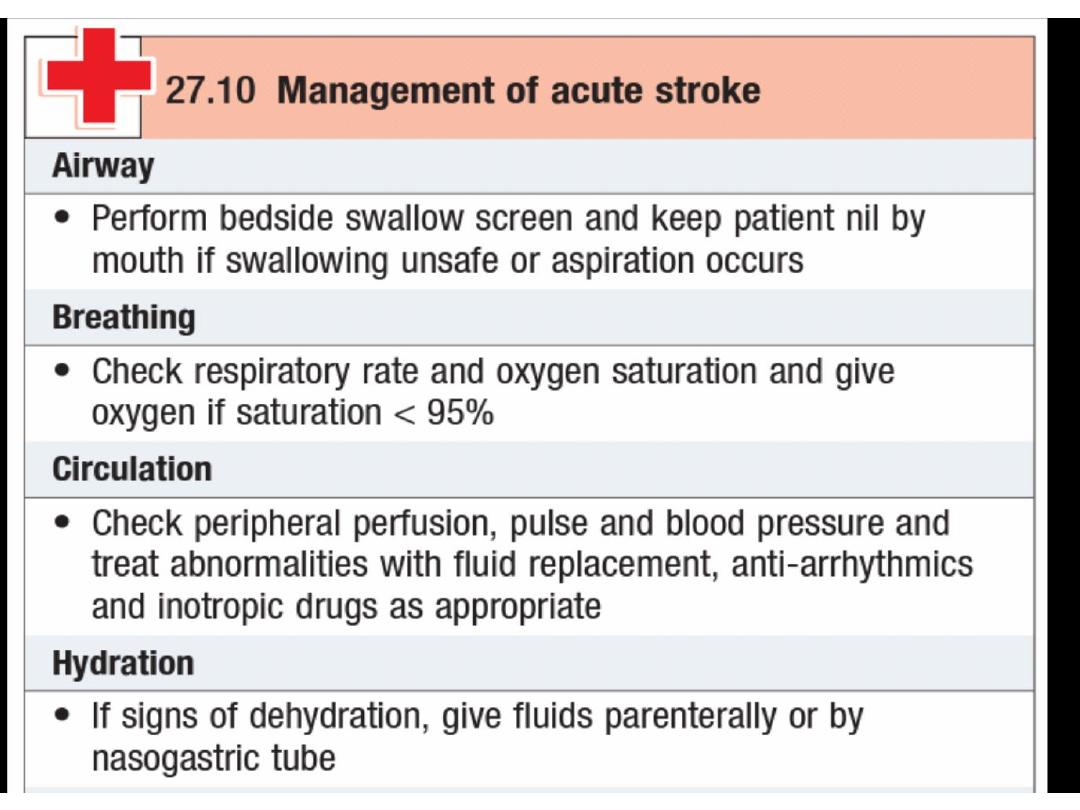
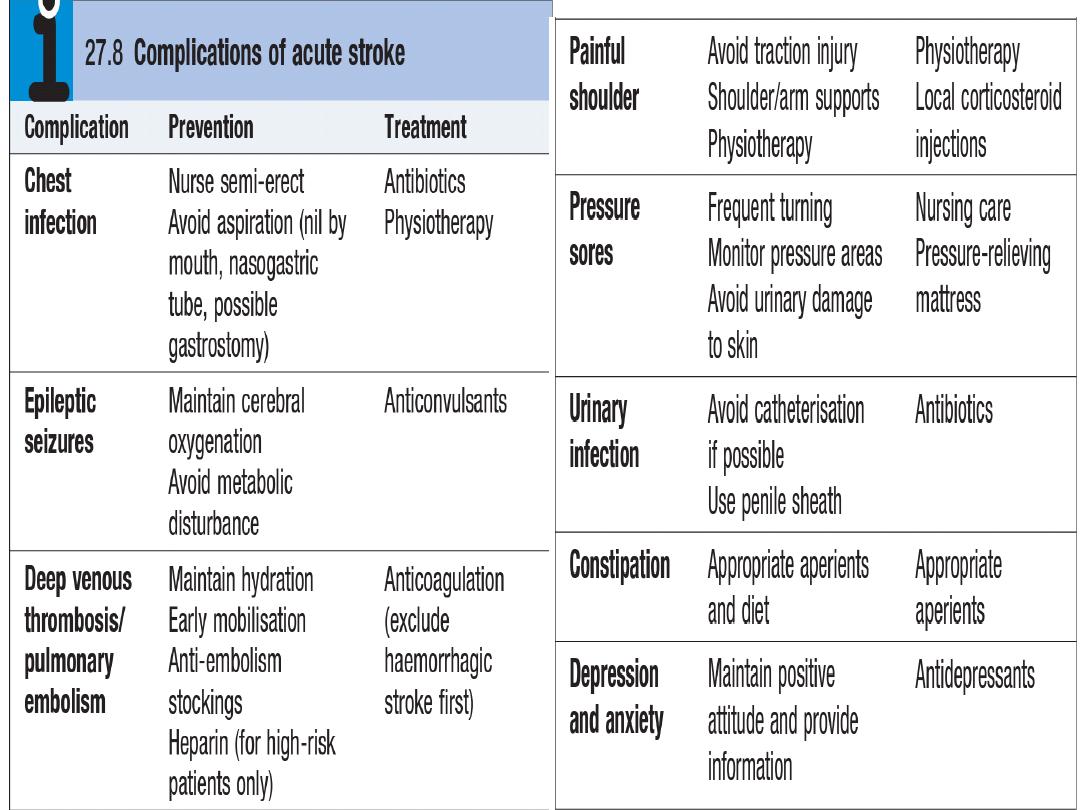
Clinical pearls

Treatment of intraparenchymal hemorrhagic stroke is
supportive, Generally there is no specific therapy.
Pupillary findings in ICH and corresponding level of
involvement.
Pinpoint pupils pons
• Poorly reactive pupils thalamus
• Dilated pupils putamen
Clinical pearls

Cocaine is one of the main causes of stroke in young patients…
ICH, ischemic stroke and
SAH are all associated with cocaine
use…
If stroke is caused by emboli from a cardiac source,
anticoagulation is the treatment of choice…
Two most important poor prognostic factors in stroke old age
and prolonged neuronal shock…
Rapidly worsening stroke indicate either hemorrhagic
transformation or expanding brain edema around the lesion…
Two types of stroke generally carry poor prognosis : massive
hemispheric stroke and stroke that affect brain stem…
Clinical pearls

Thank you
