Respiratory
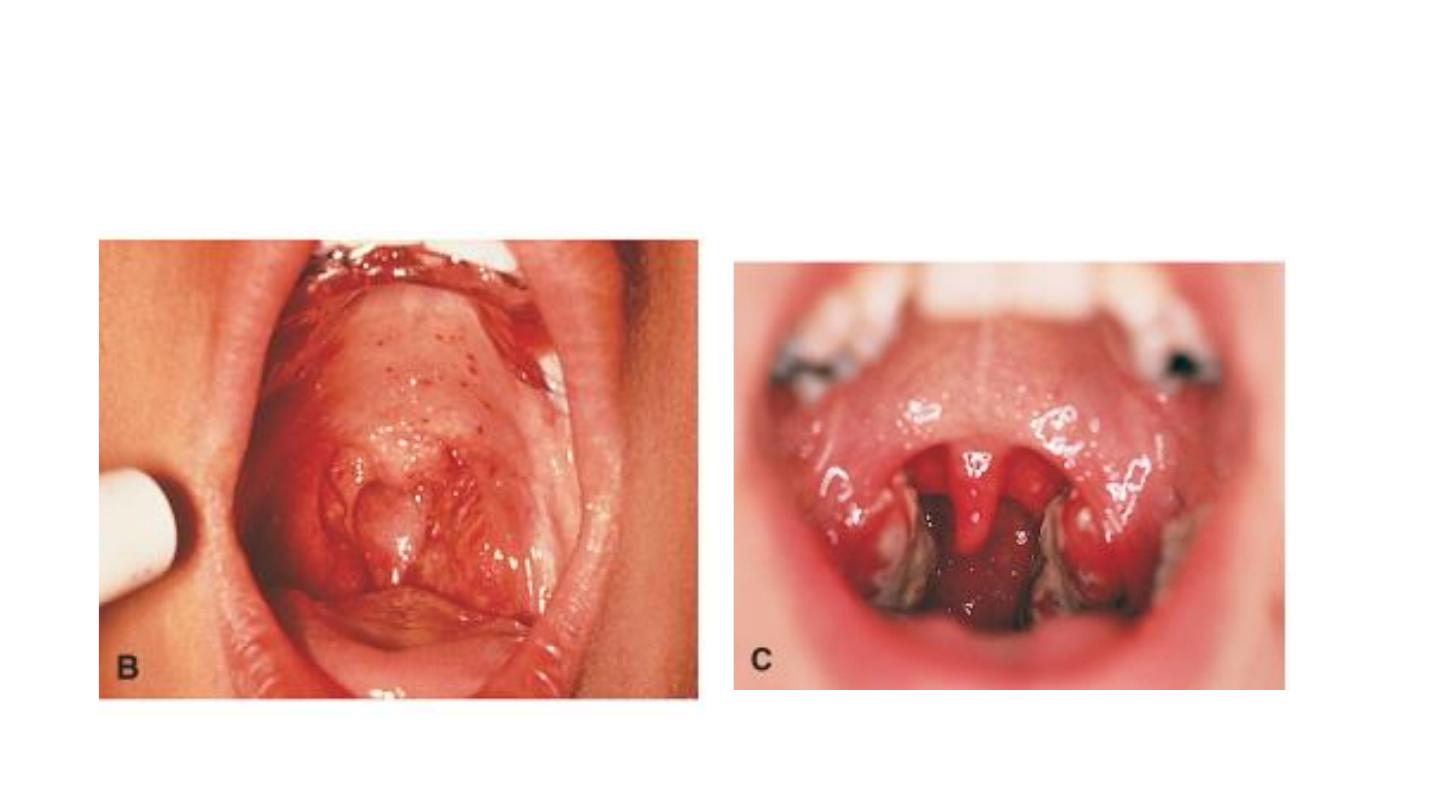
Streptococus pharyngitis
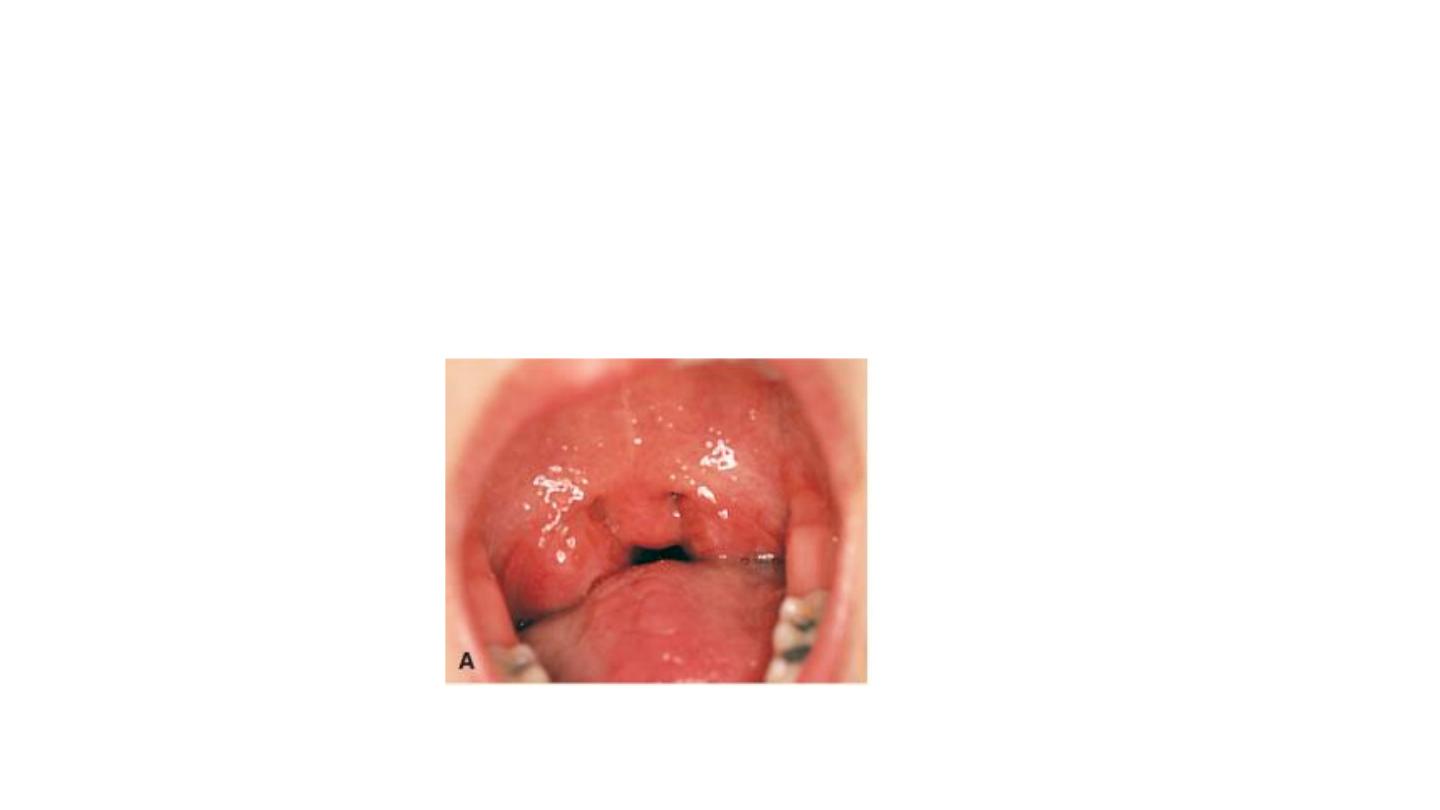
Viral pharyngitis
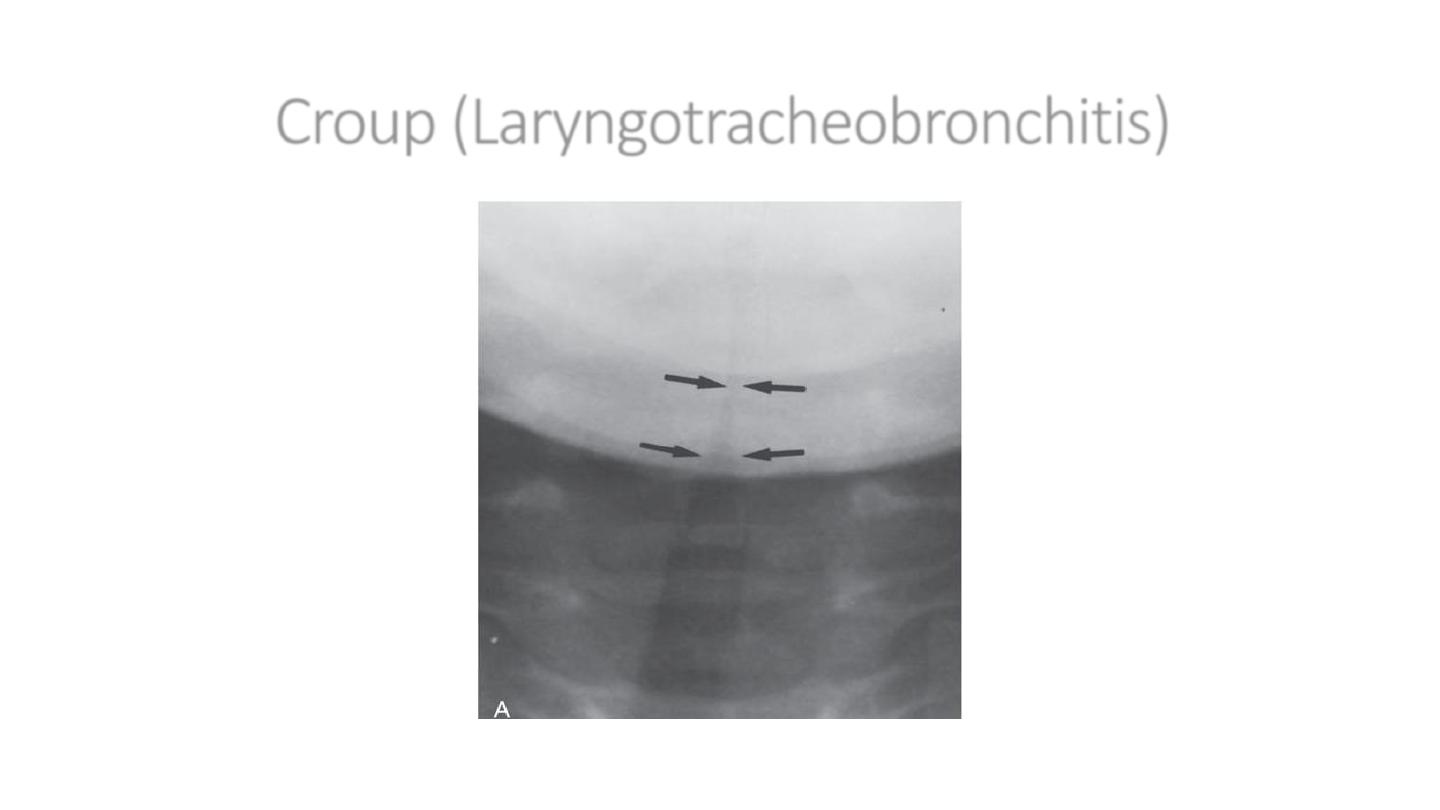
Croup (Laryngotracheobronchitis)
Steeple sign

Asthmatic pt
Tripod position
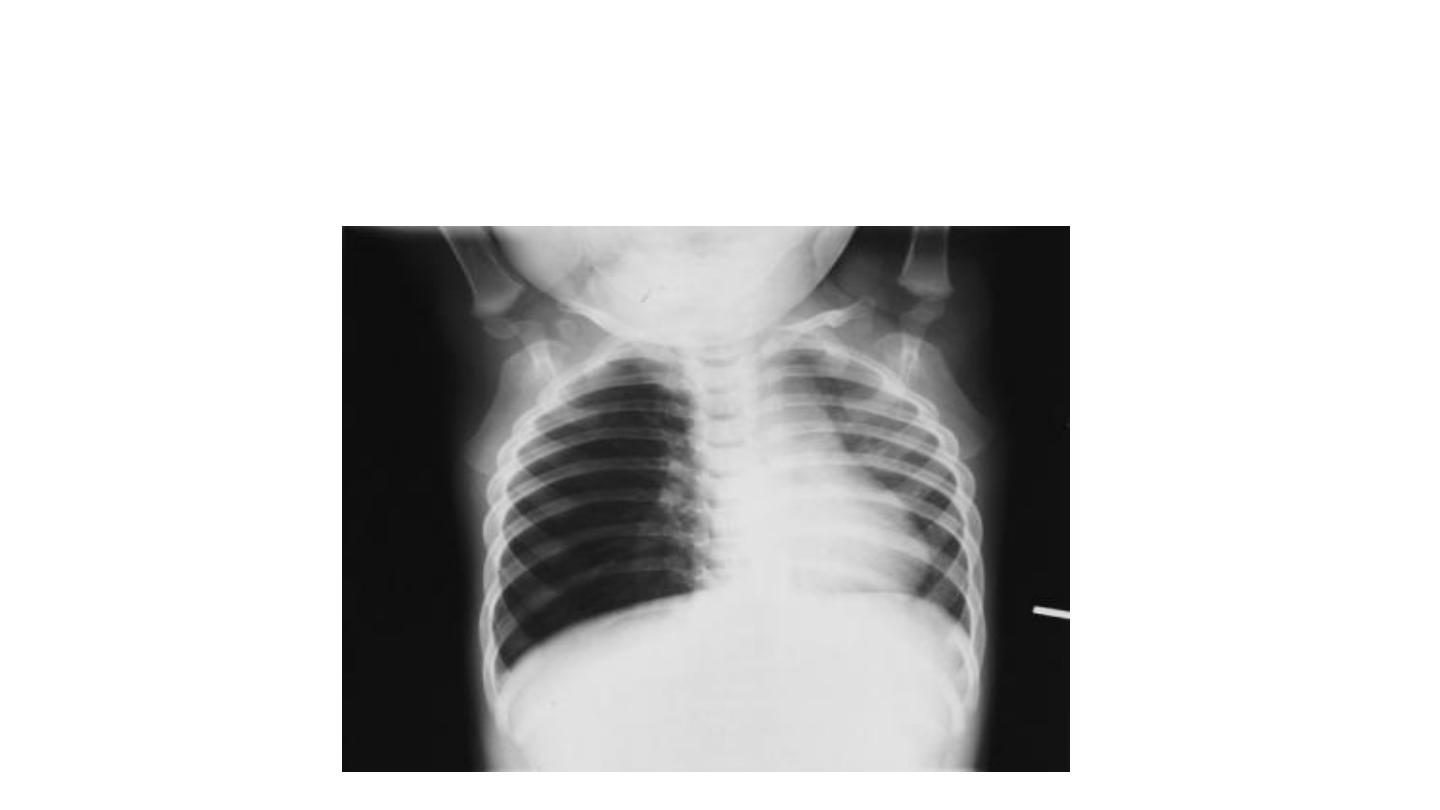
Expiratory chest radiograph in a 12-month-old boy with a 2-month history of wheezing
demonstrates continued hyperlucency and hyperexpansion of the right hemithorax.
Foreign body
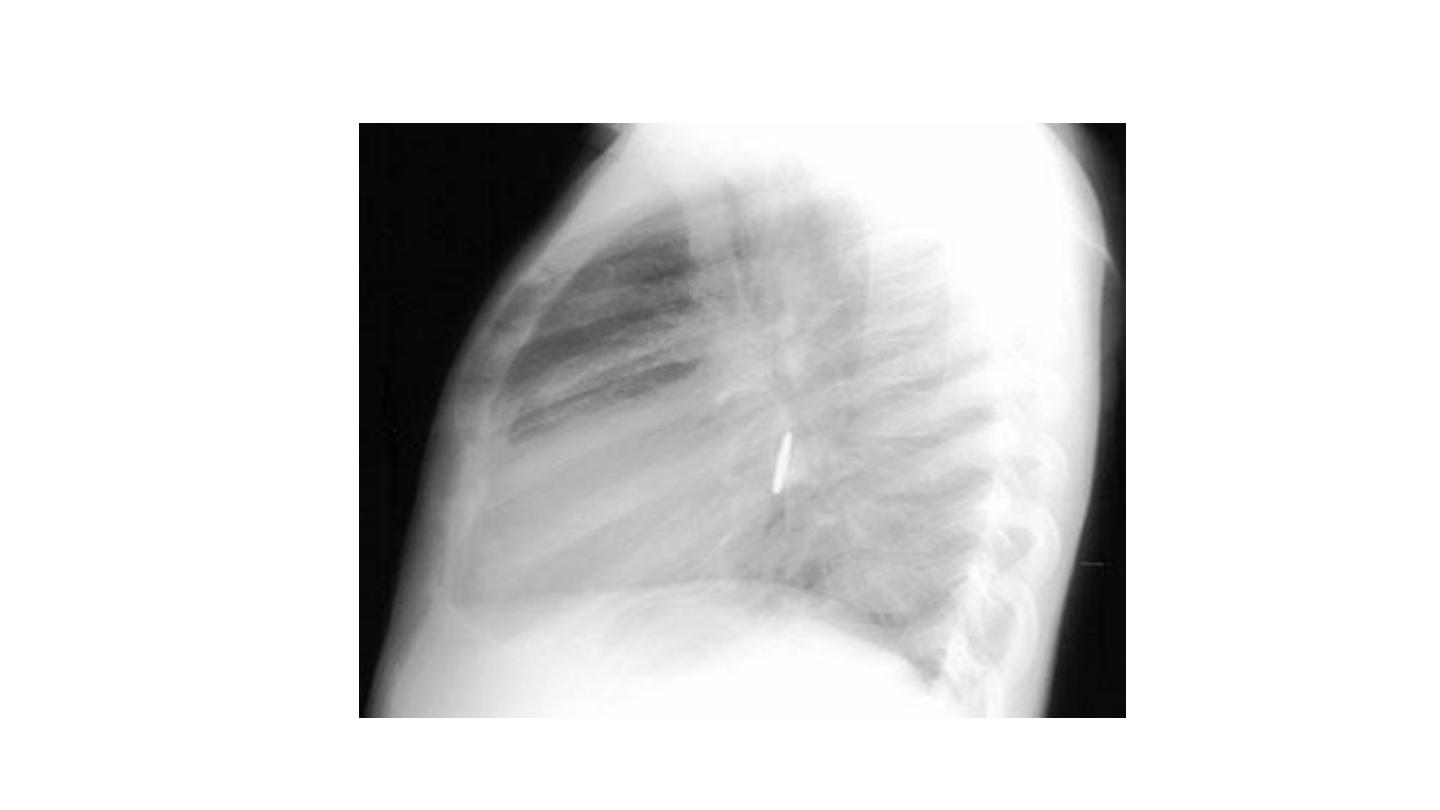
Foreign body
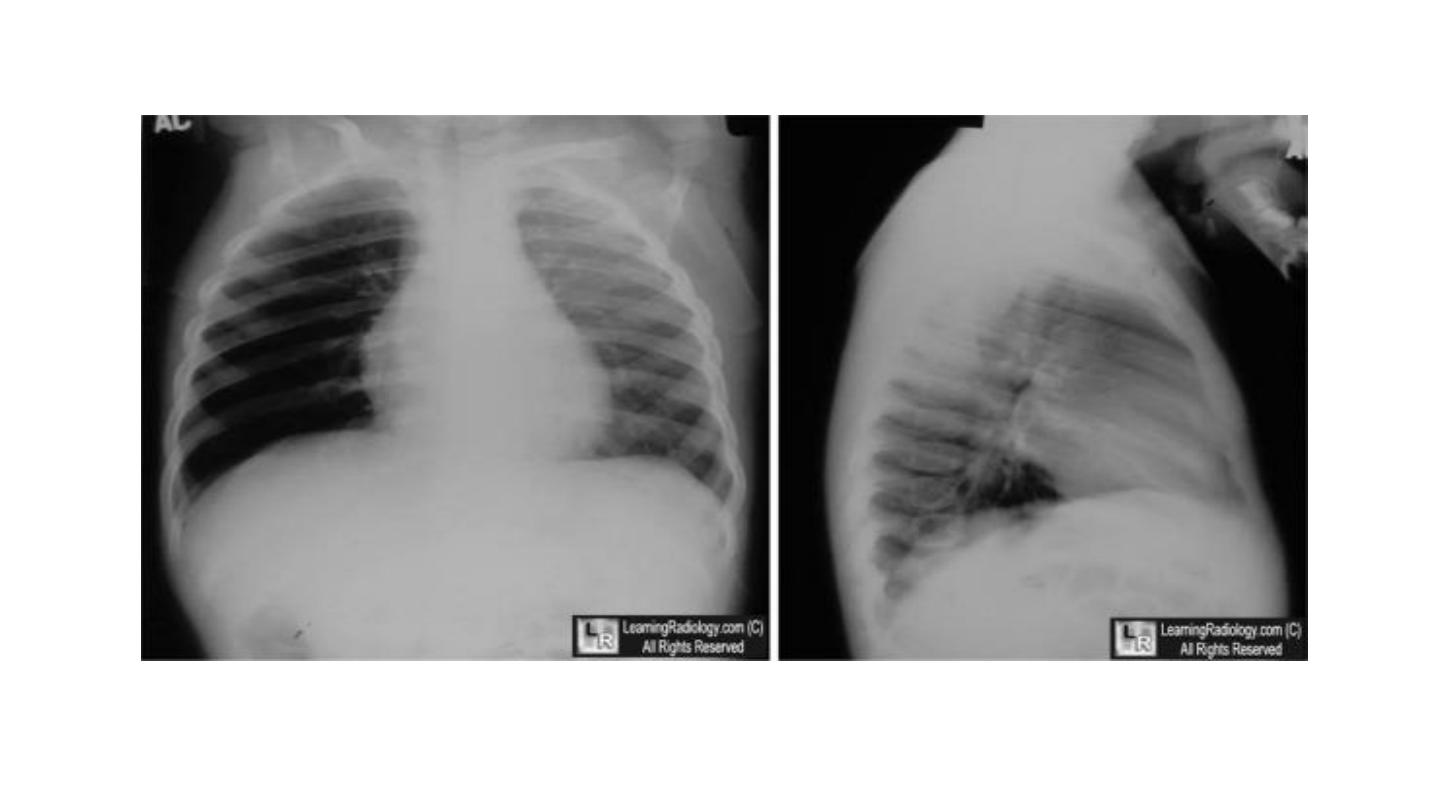
Foreign body
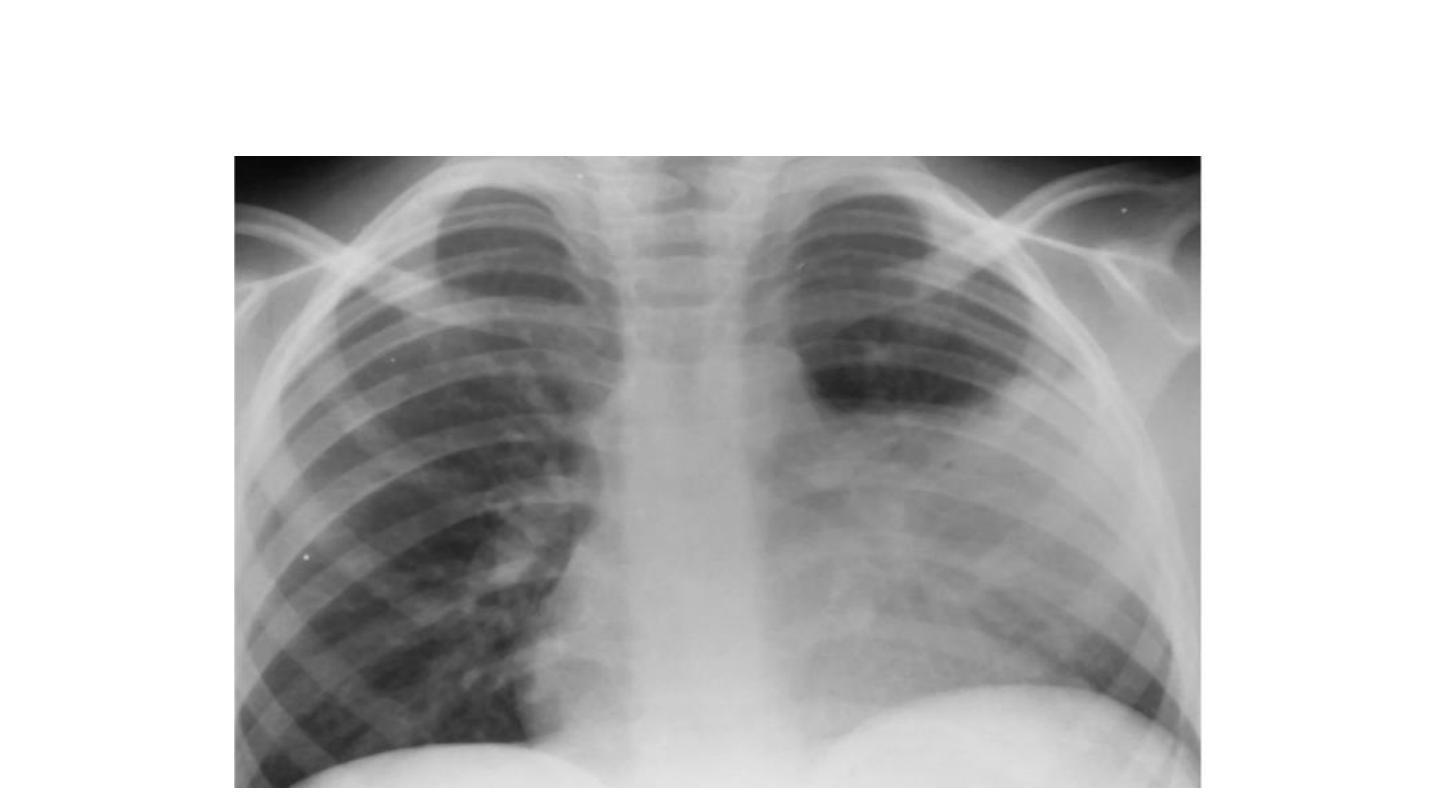
Lobar Pneumonia
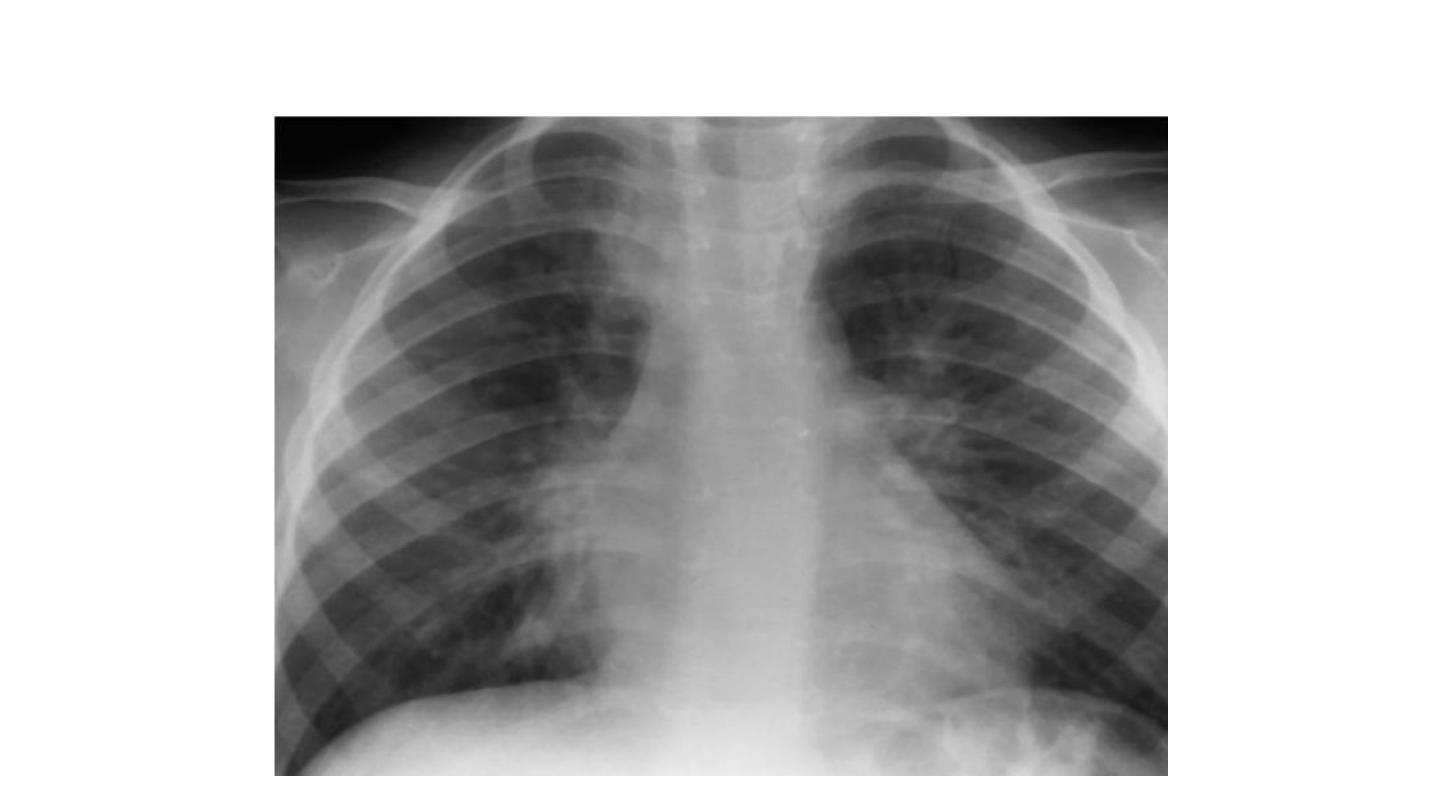
Bronchopneumonia
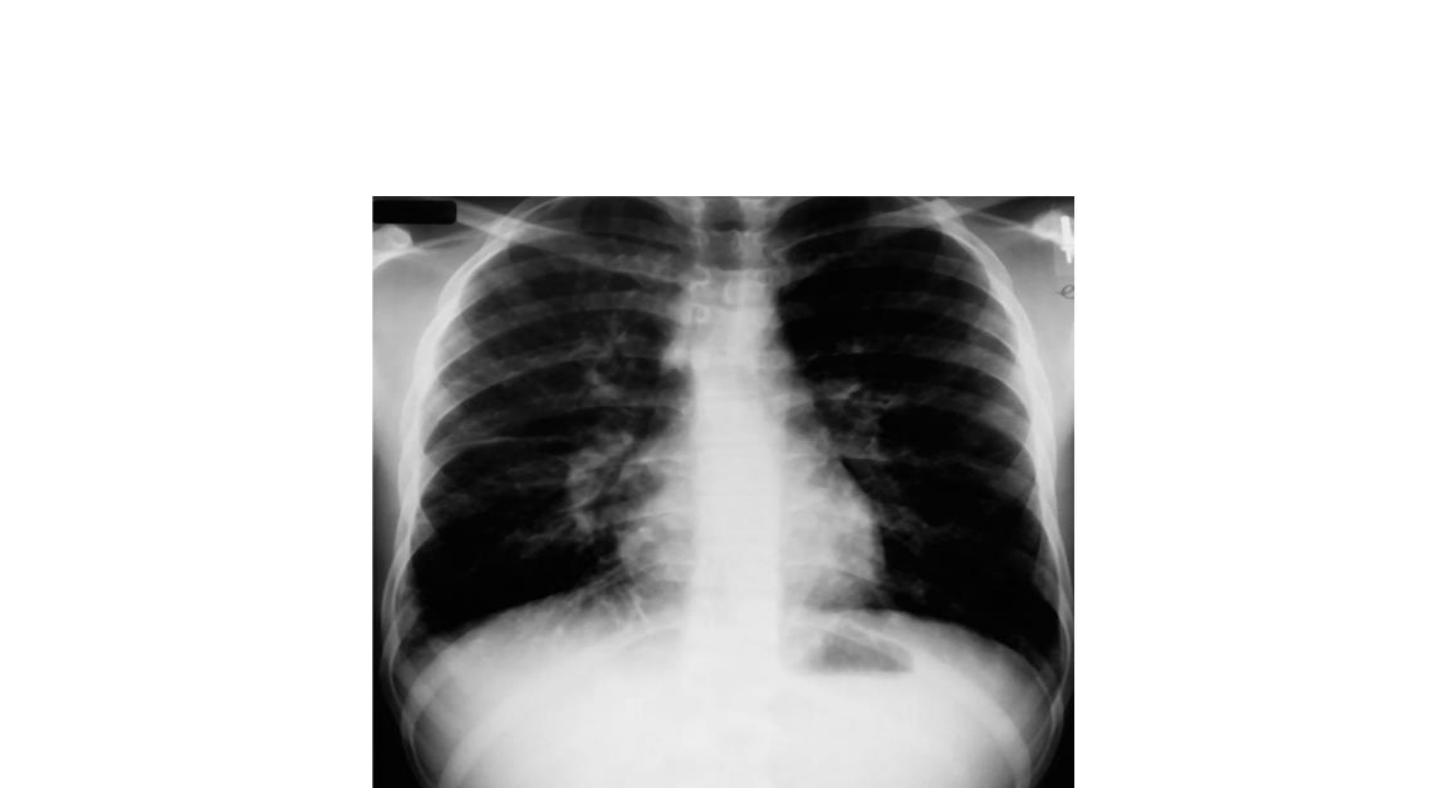
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection (atypical
pneumonia)
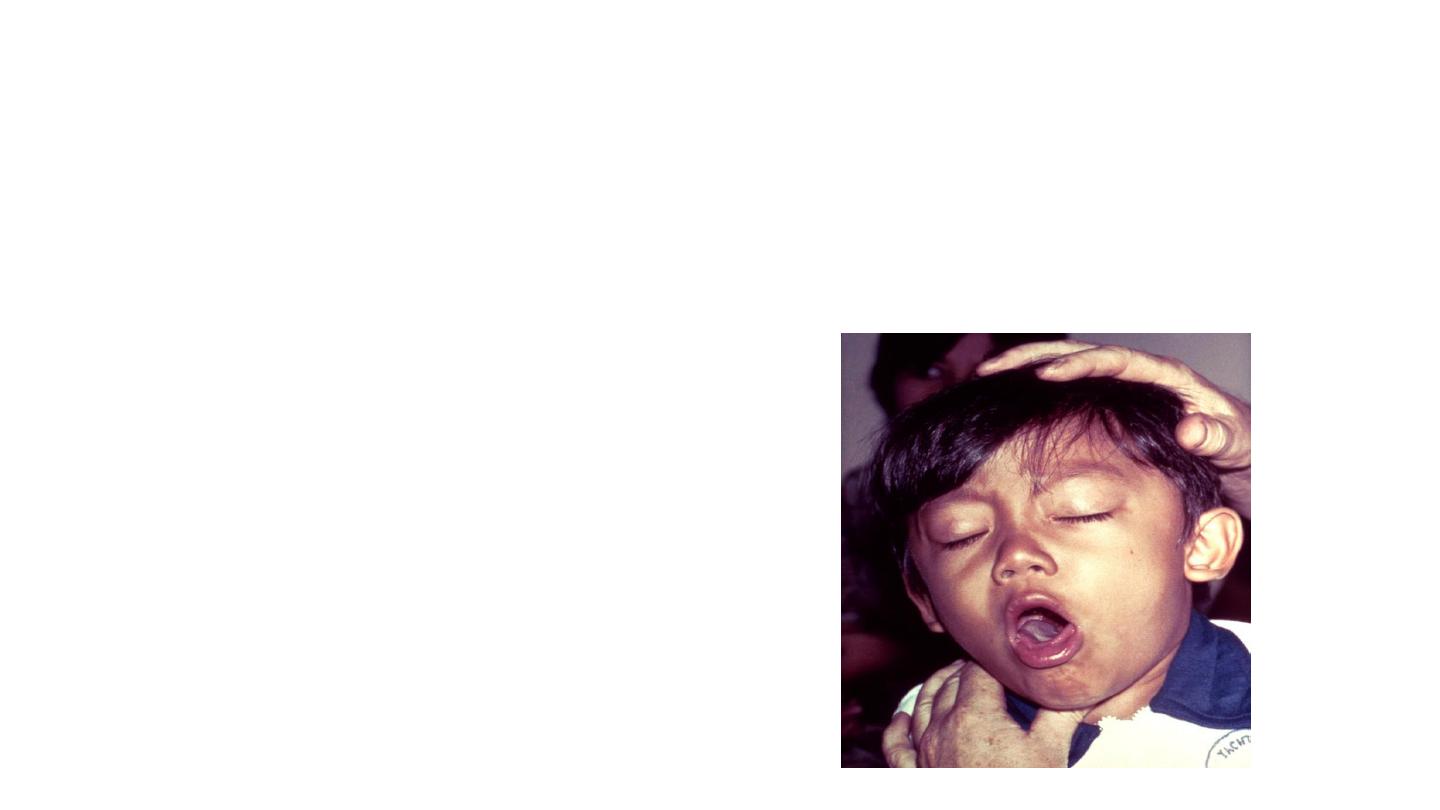
• Whooping cough
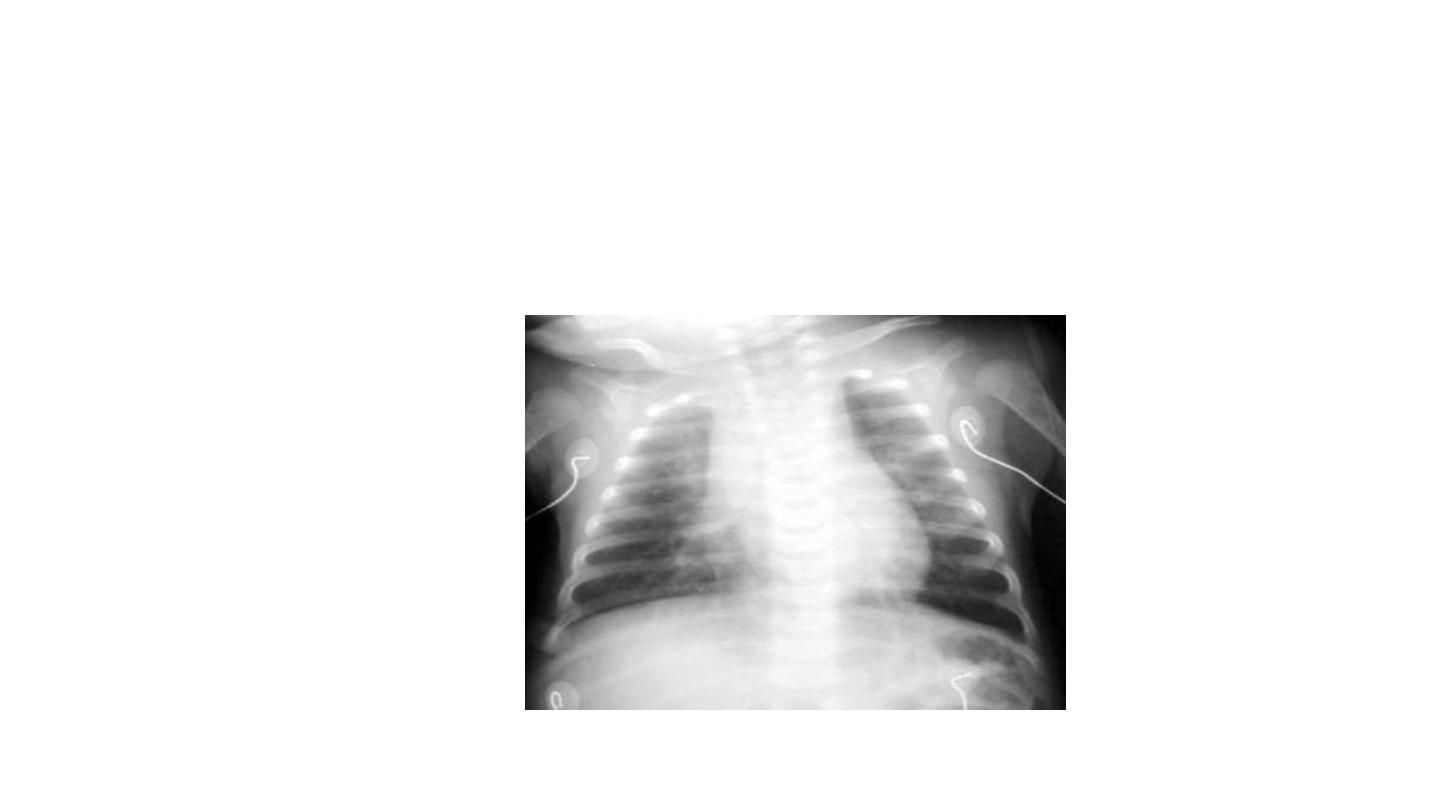
"shaggy heart" on CXR in a patient with
Bordetella pertussis pneumonia.
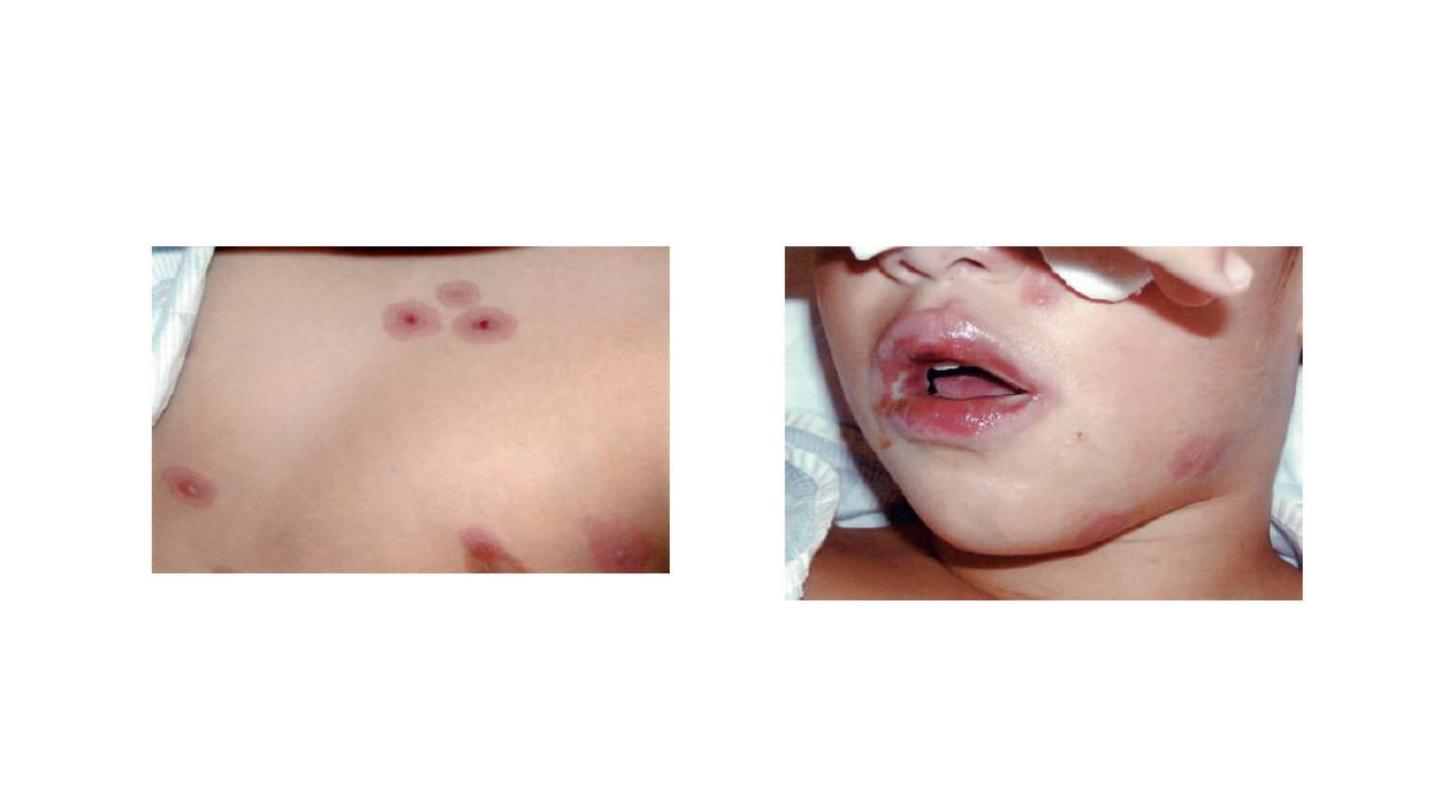
Stevens-Johnson-like syndrome
associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
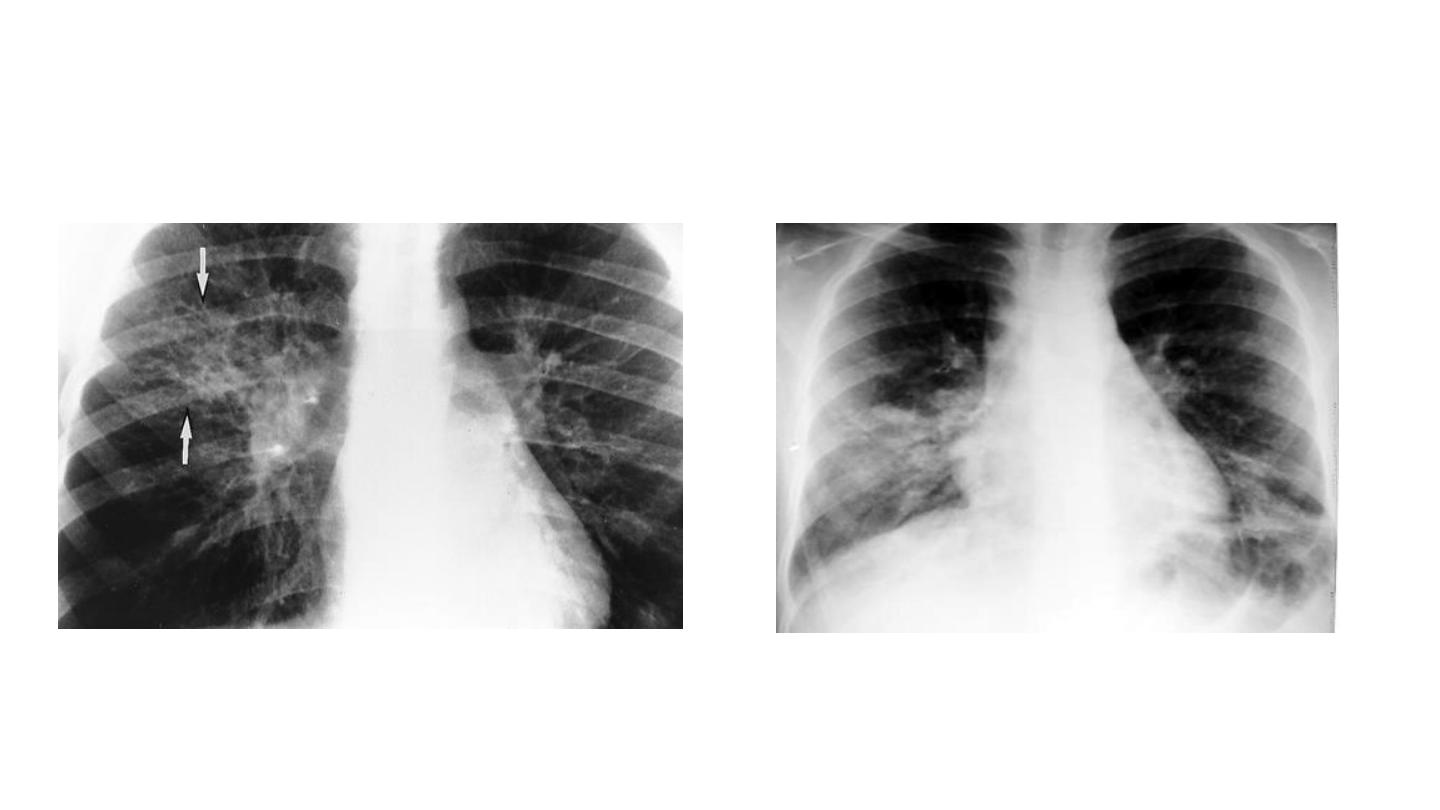
Lower lobe pn
Hilar involvement

Neonatology
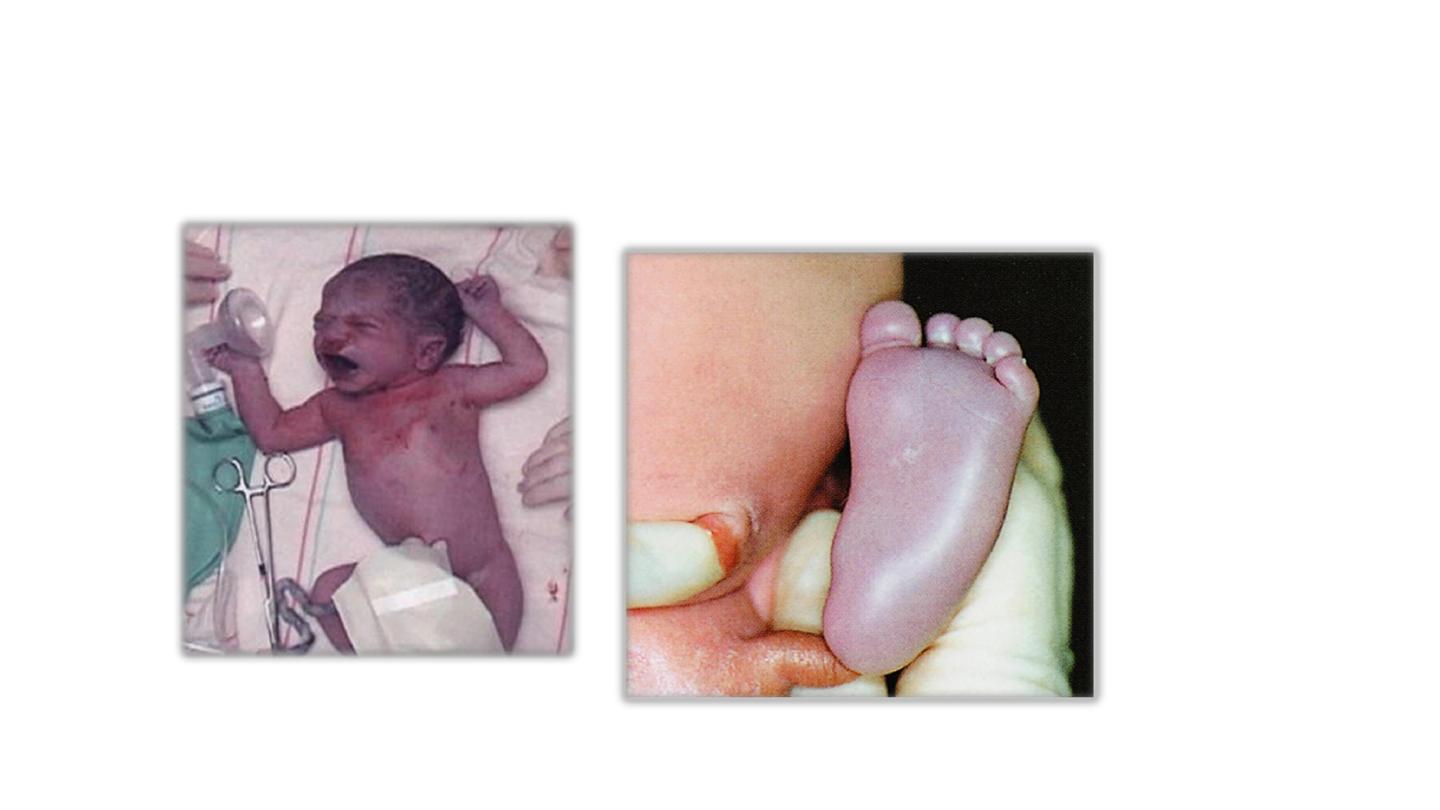
Acrocyanosis
Central cyanosis
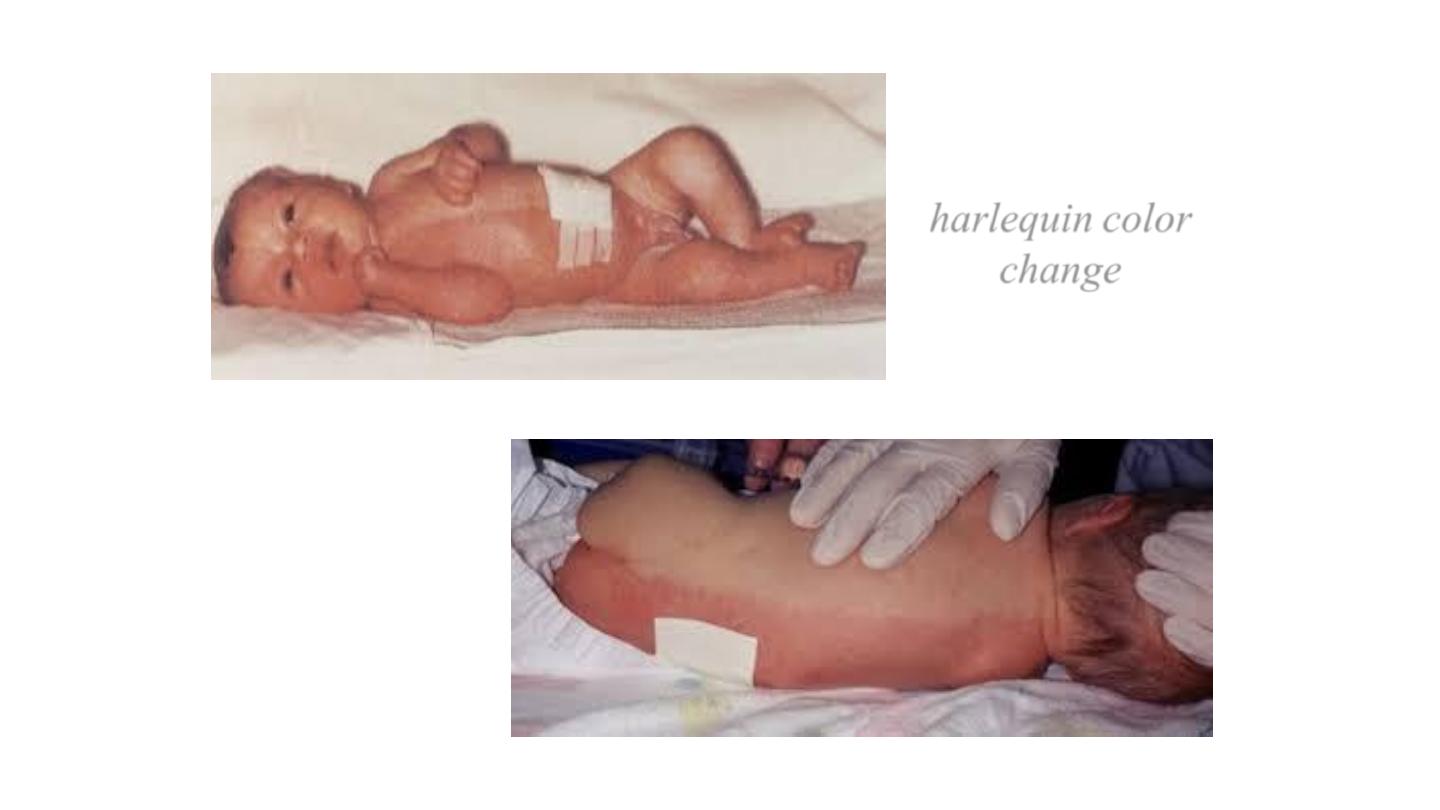
harlequin color
change
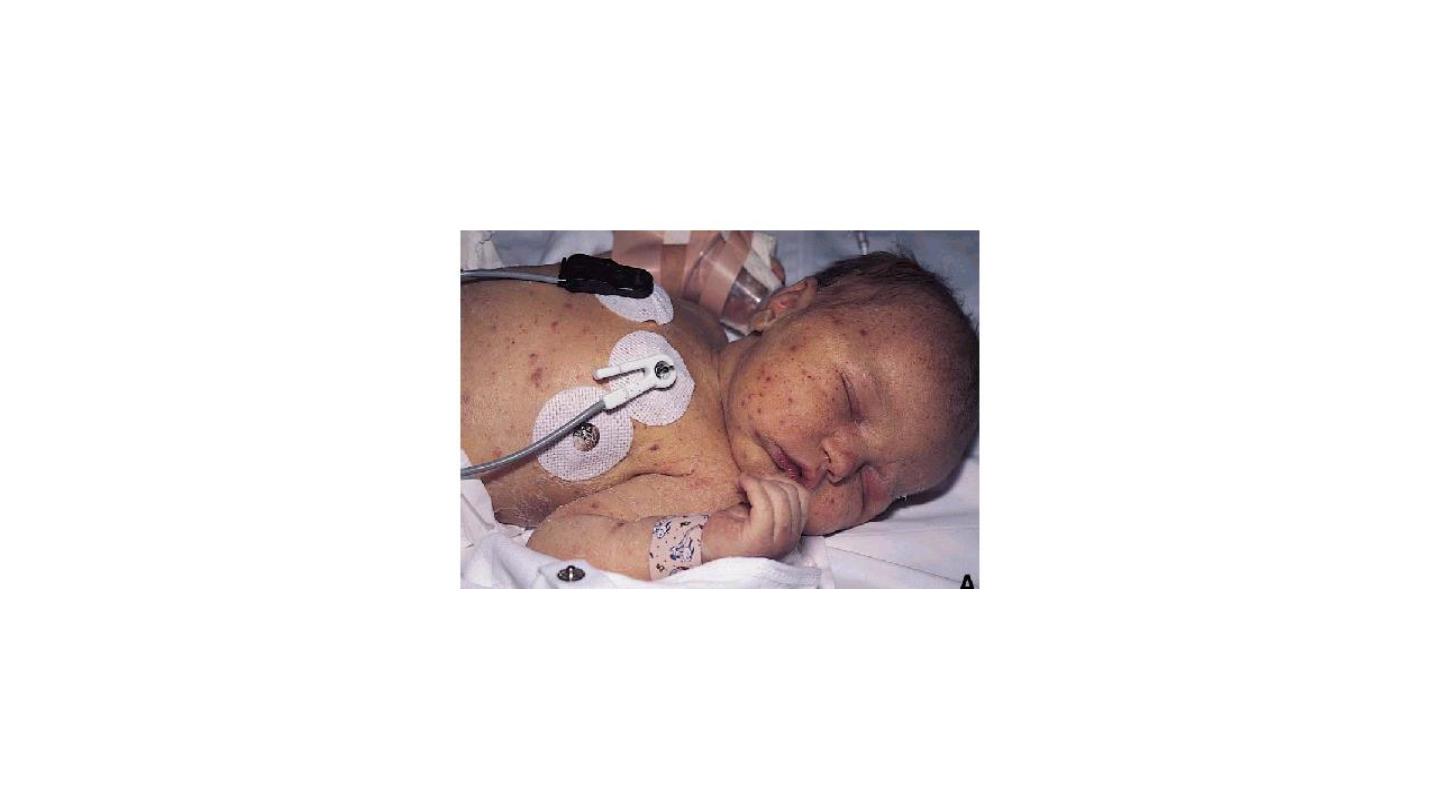
Petechiae
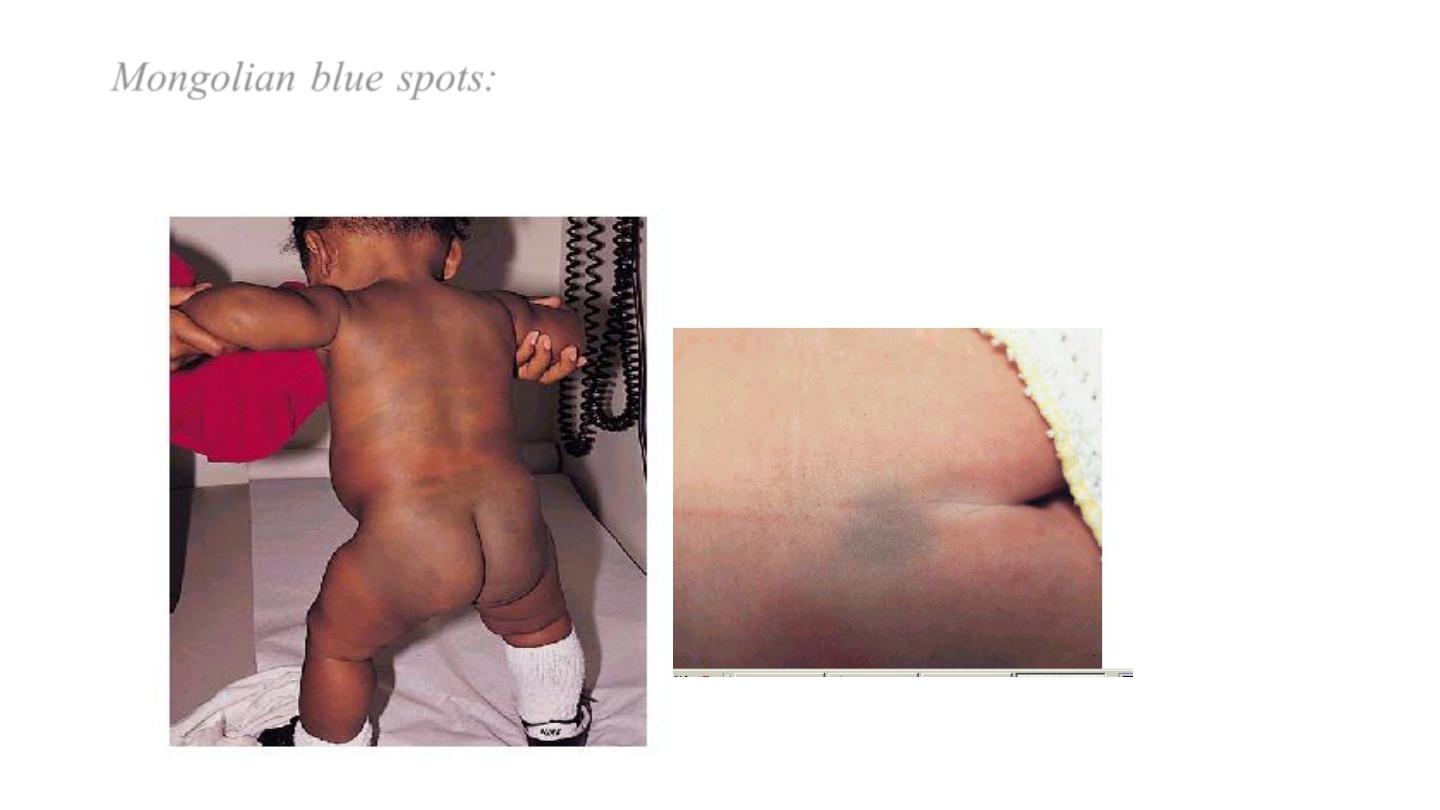
Mongolian blue spots:
are blue well demarcated areas of pigmentation
are seen over the buttocks, back and sometimes other parts of the body,
they tends to disappear within the first year of life.
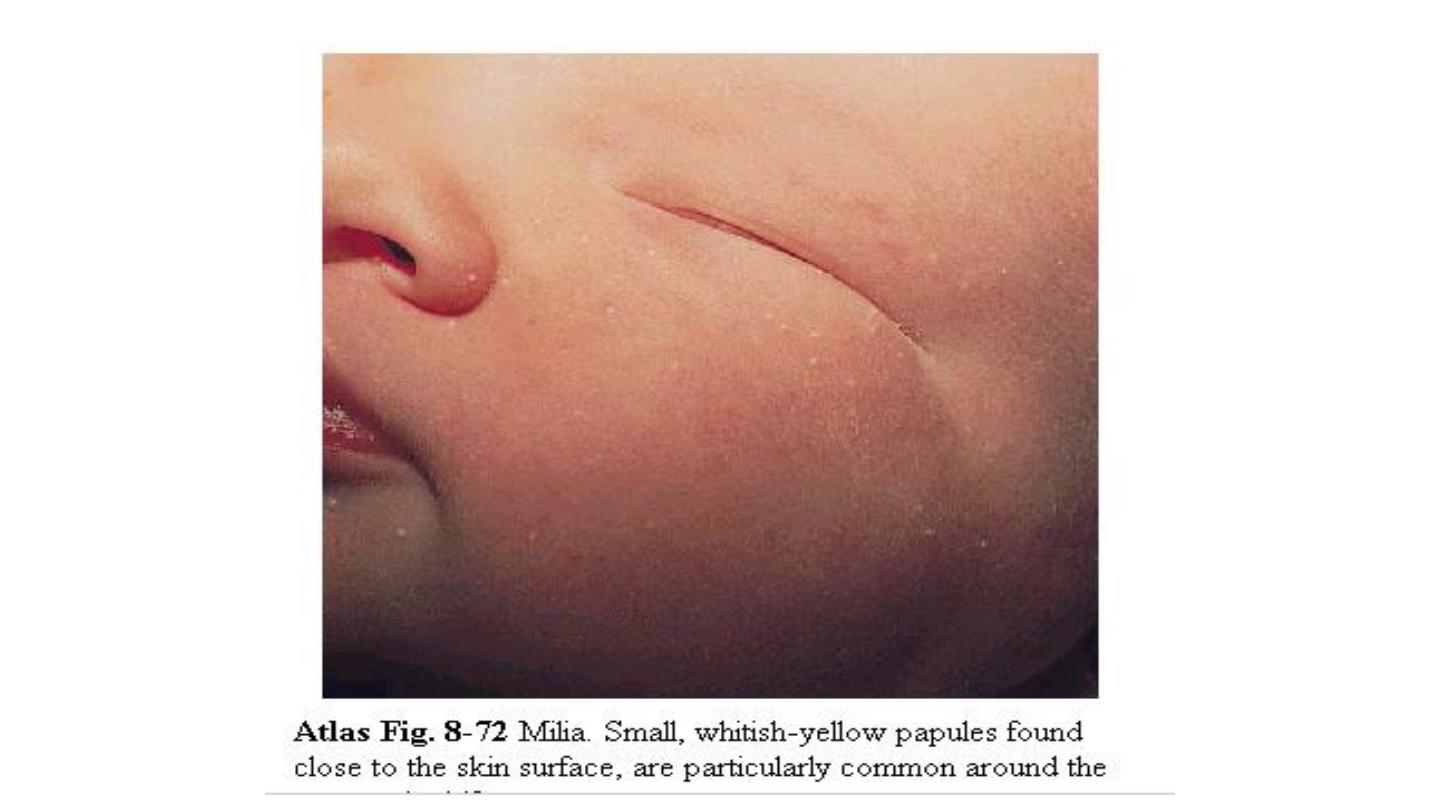
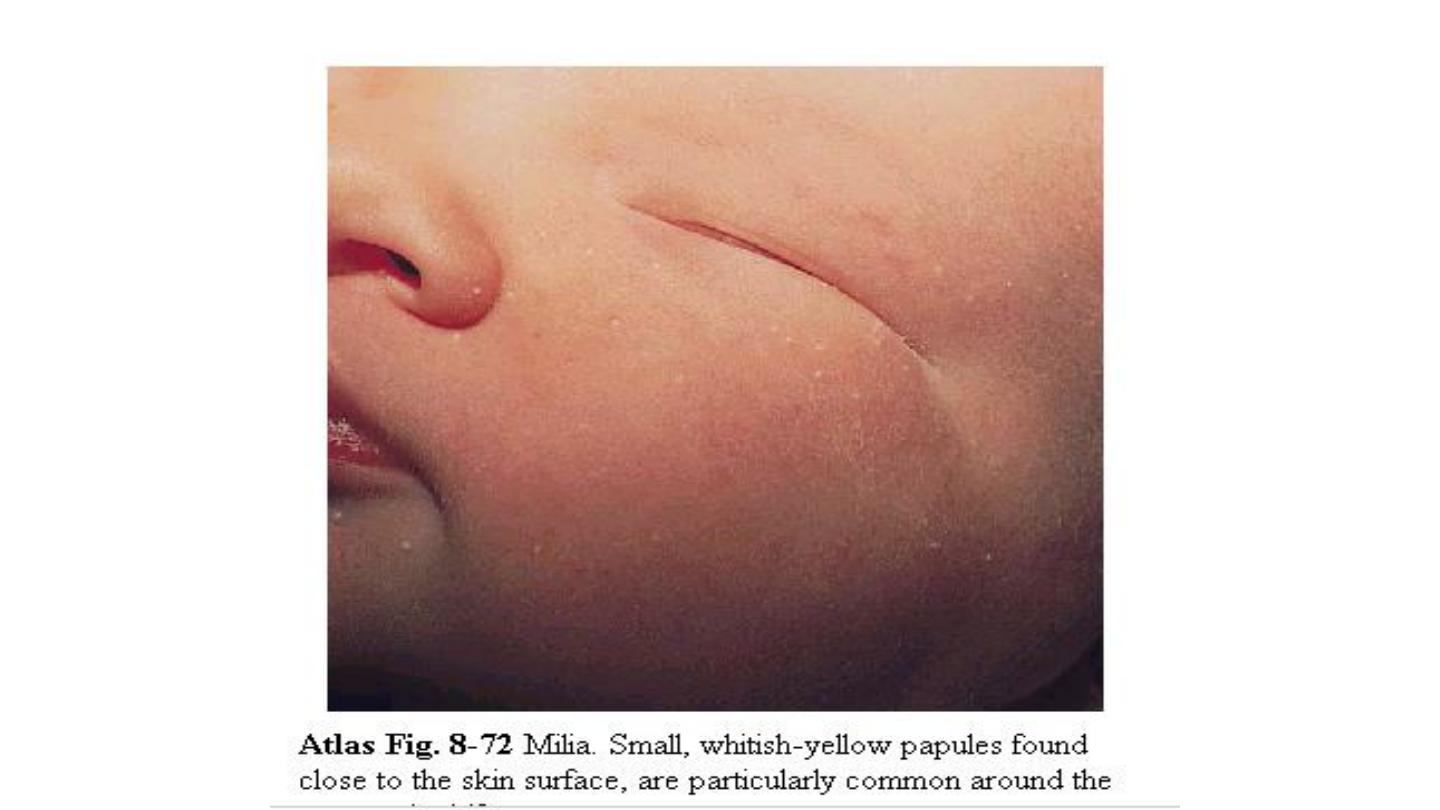
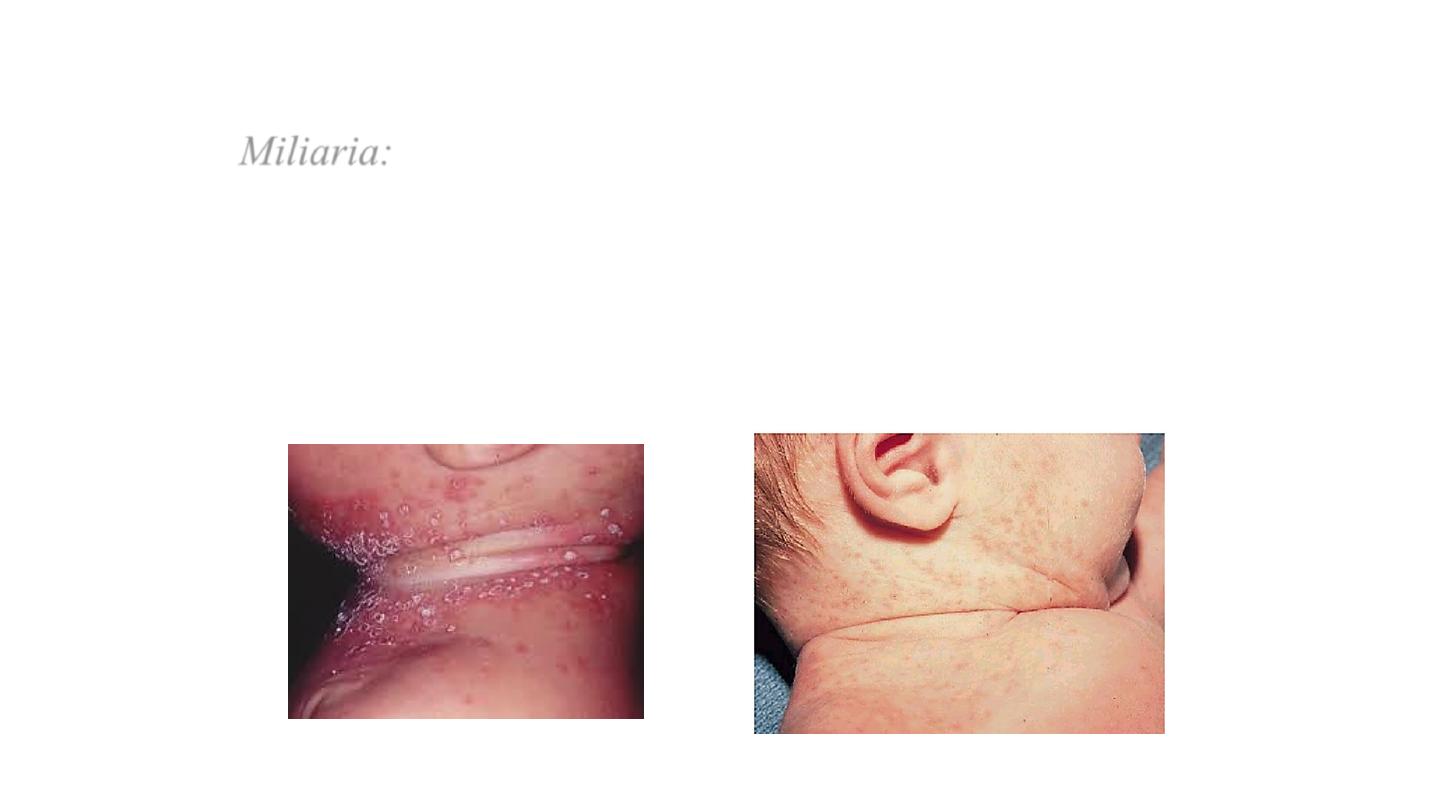
Miliaria:
erythematous minute papulovesic-ular lesions
may impact a prickly sensation the lesions are usually
located to sites of occlusion or to flexural areas such as
the neck, groin, and axilla. It is due to retention of
sweat in occluded sweat ducts.
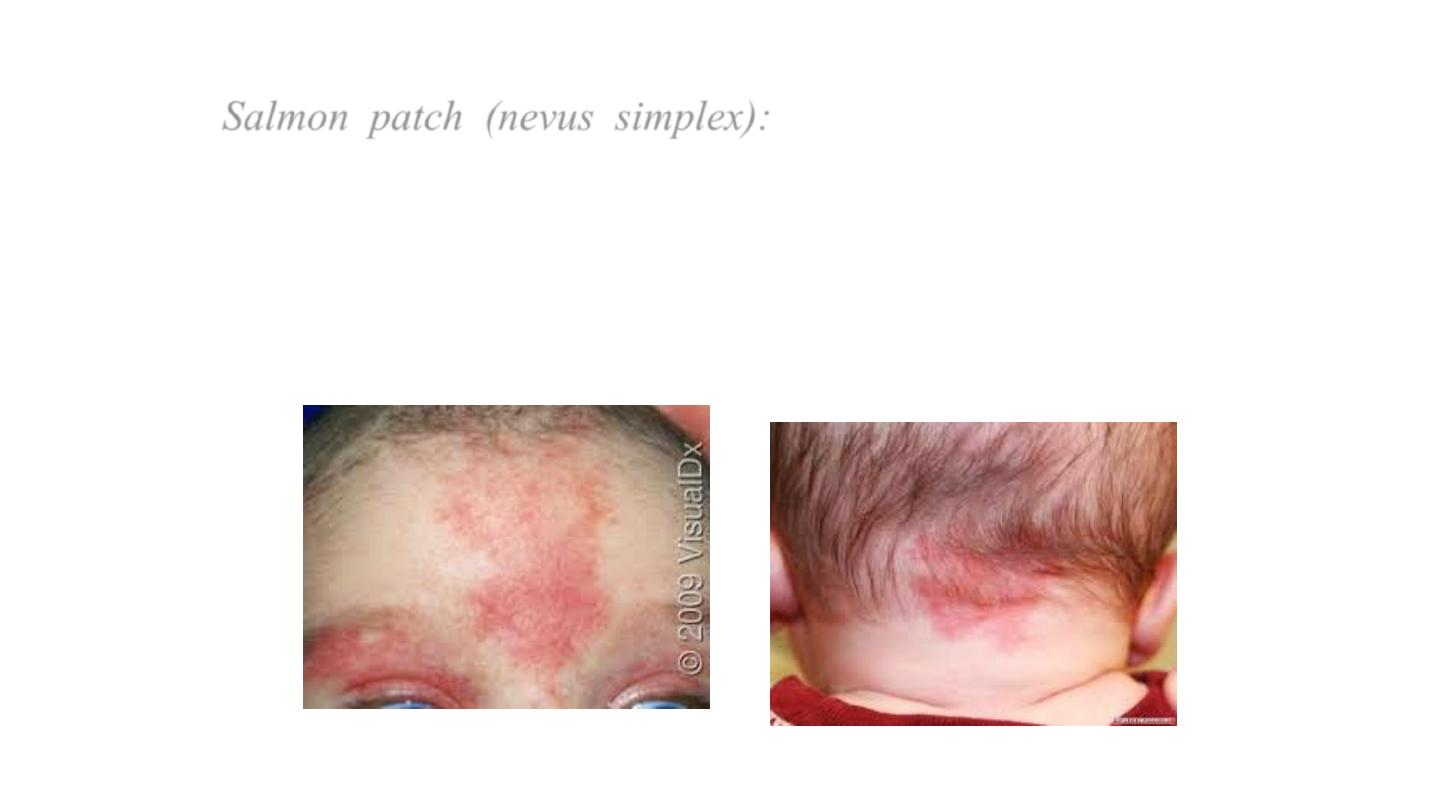
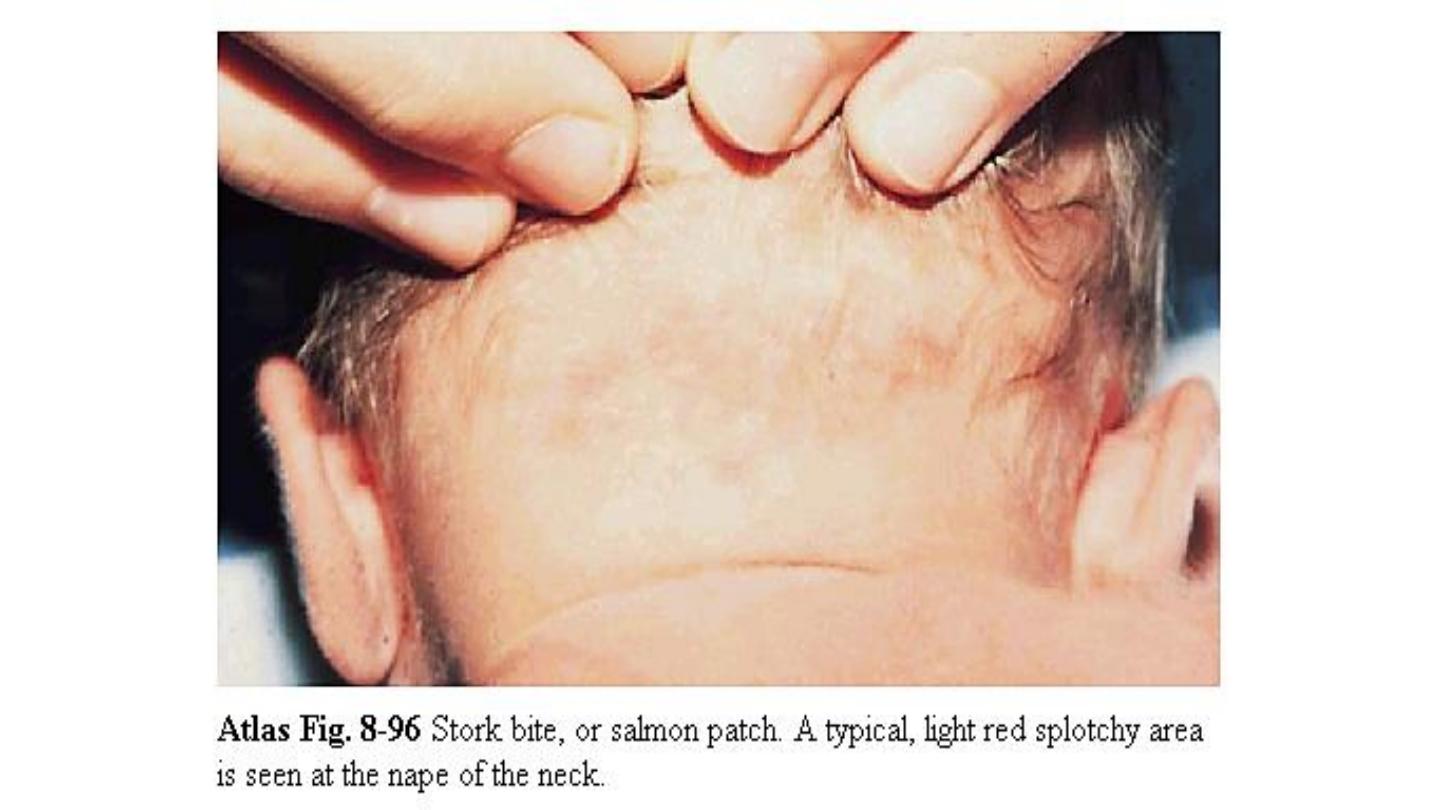
Salmon patch (nevus simplex):
are small
pale pink ill
defined flat vascular lesions that occur mostly on the
glabella, eye lid, upper lip & nuchal area of normal NBB,
they may persist for several months & become more
visible with crying

See neonatal examination lecture plz
Caput succedaneum
cephalhematoma
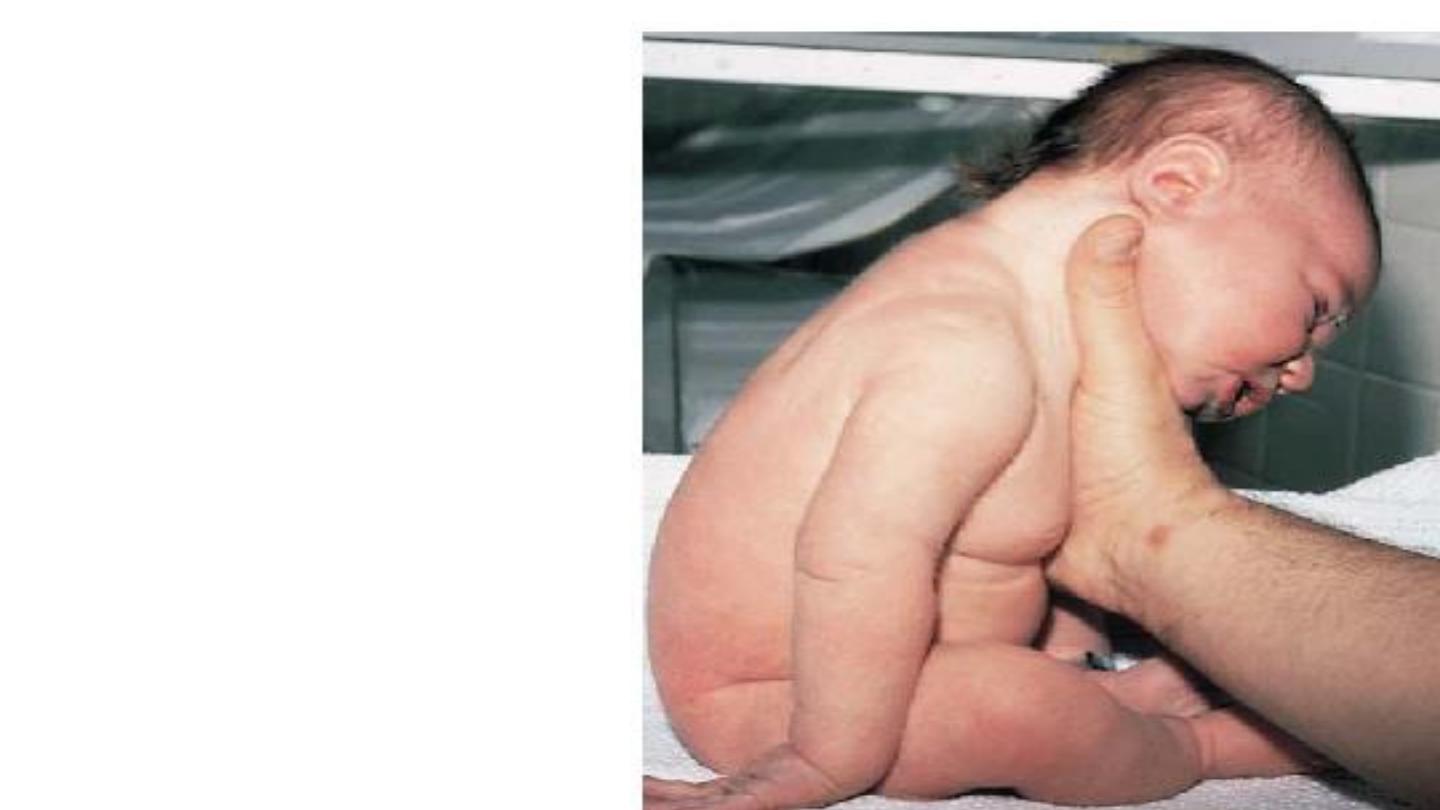
Erb’s palsy
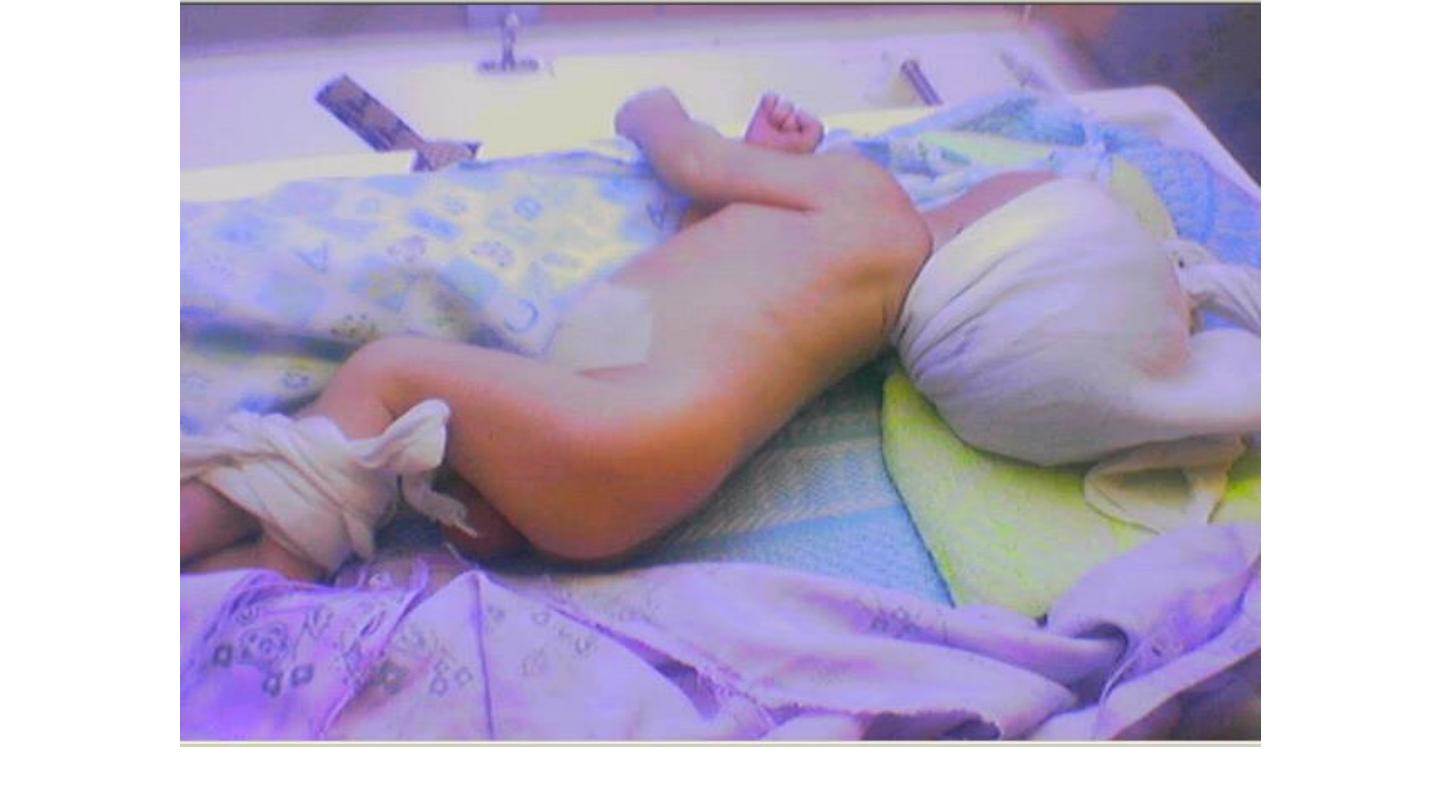
opisthotonos
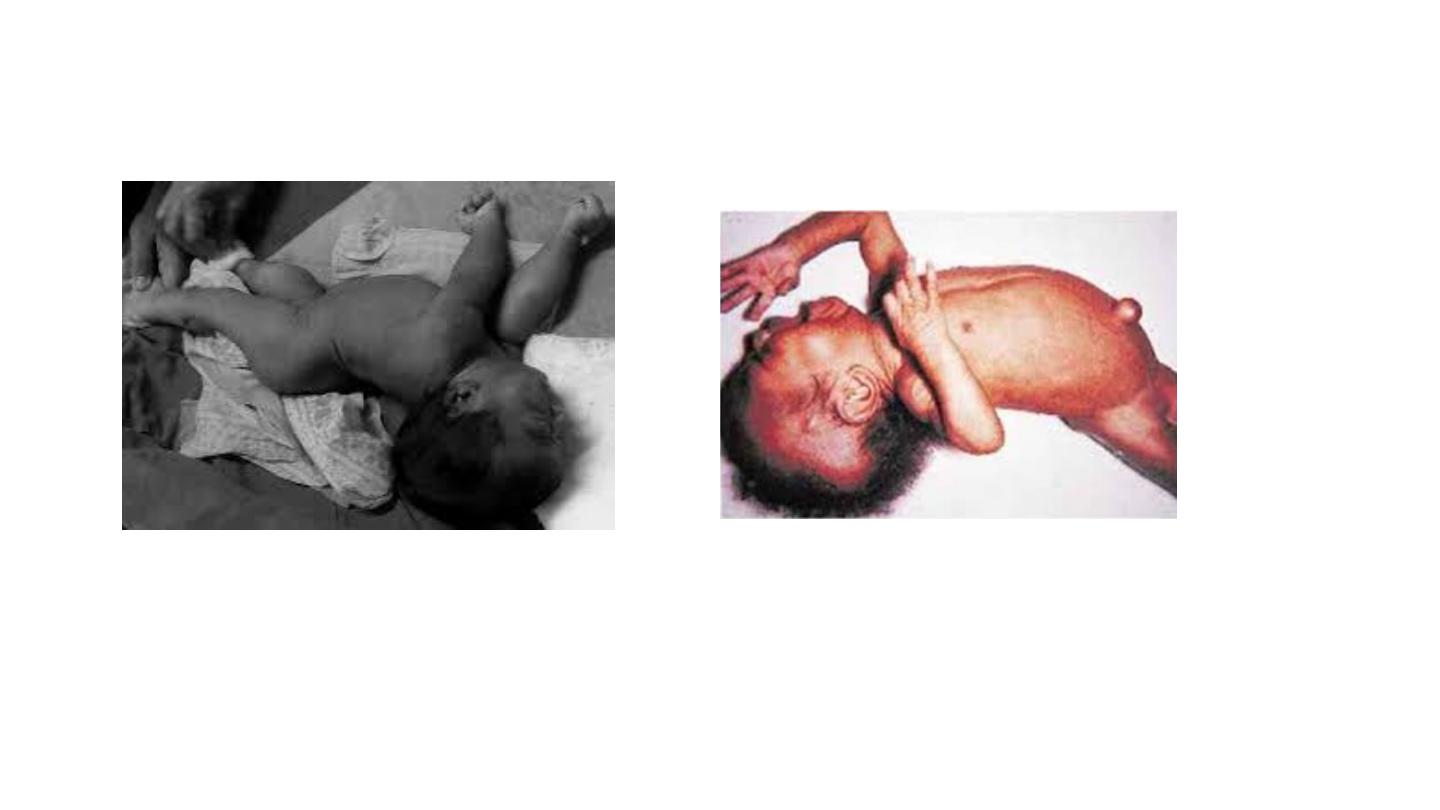
opisthotonos

Cardiology
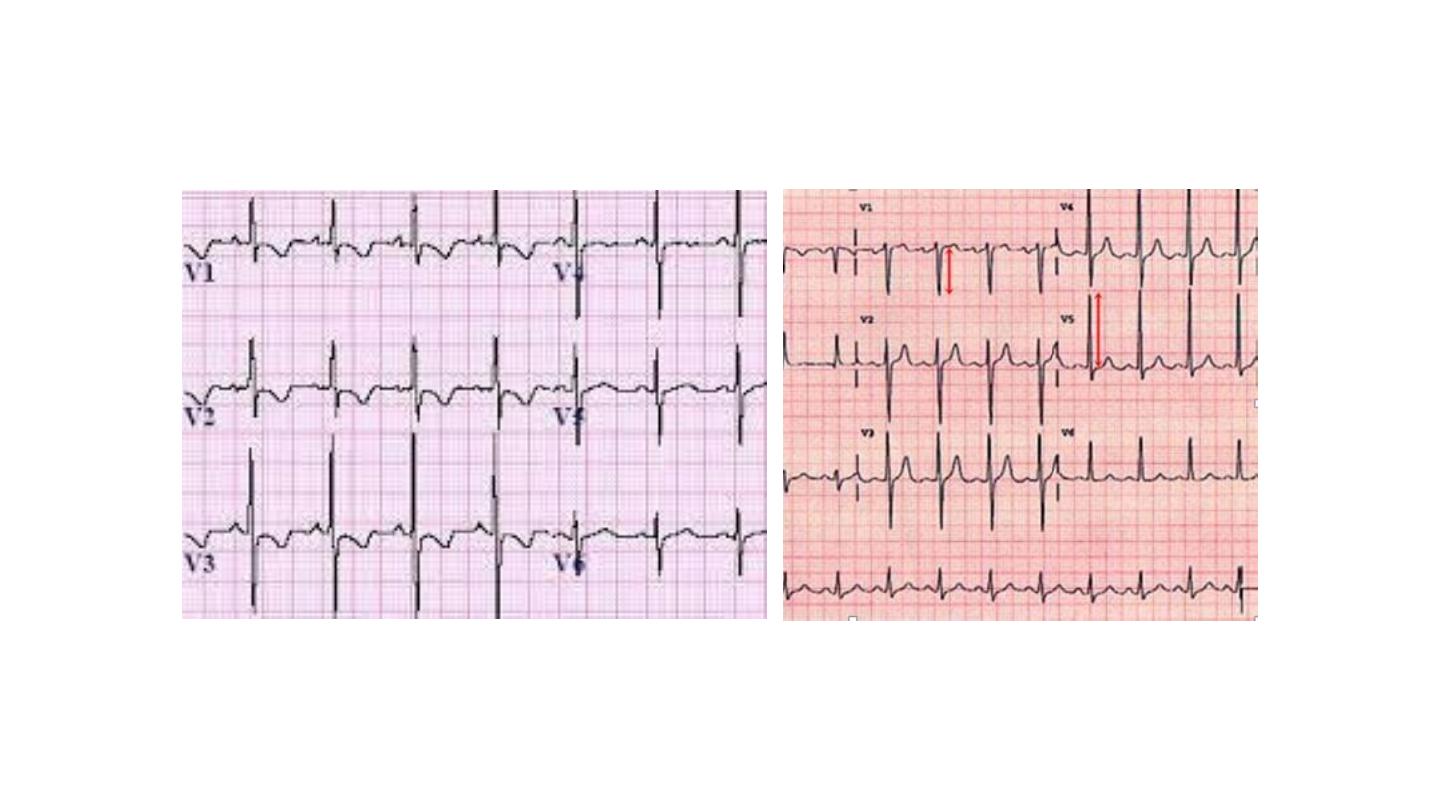
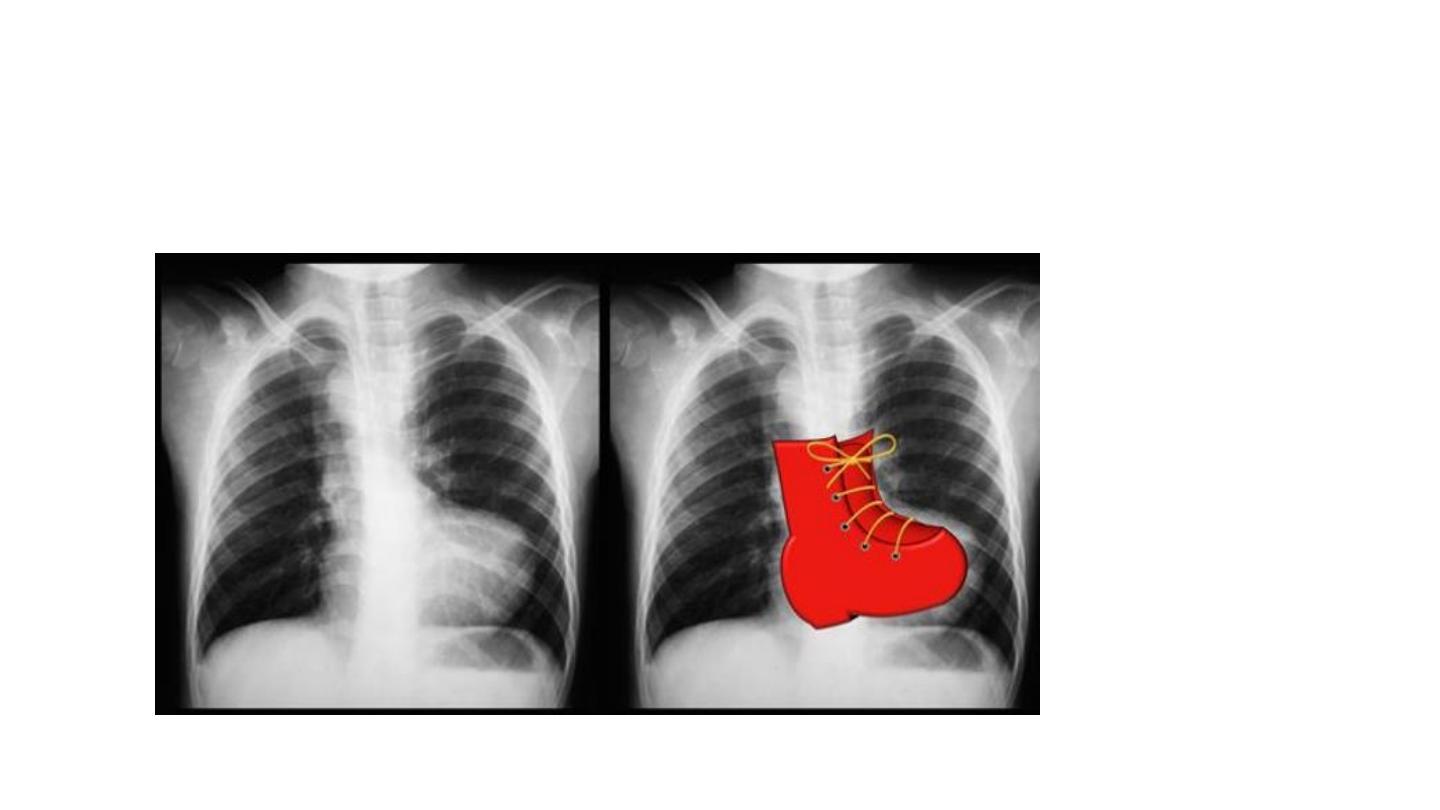
RVH LVH
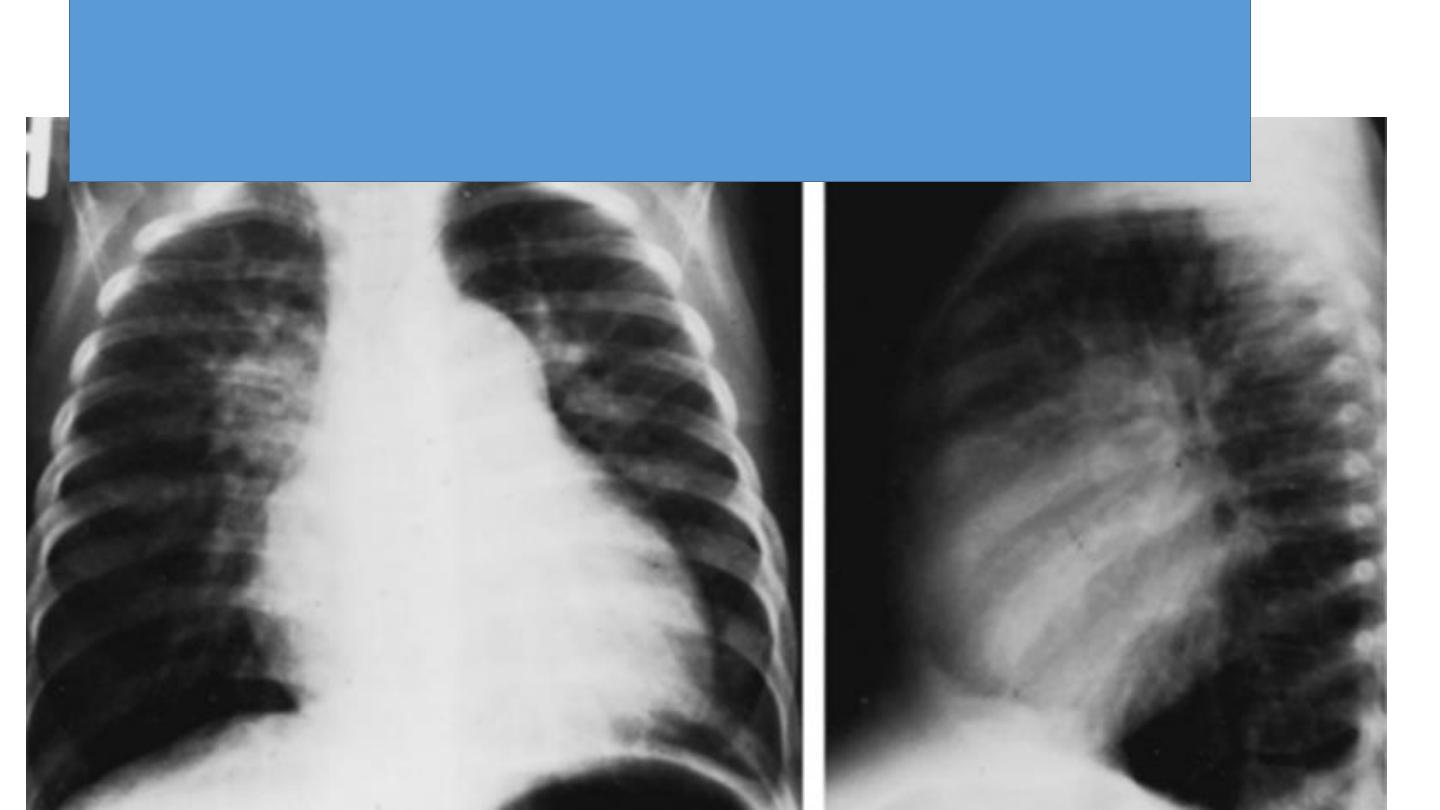
CXR of 6 years old child PA and lateral views showing
cardiac enlargement and increased pulmonary markings
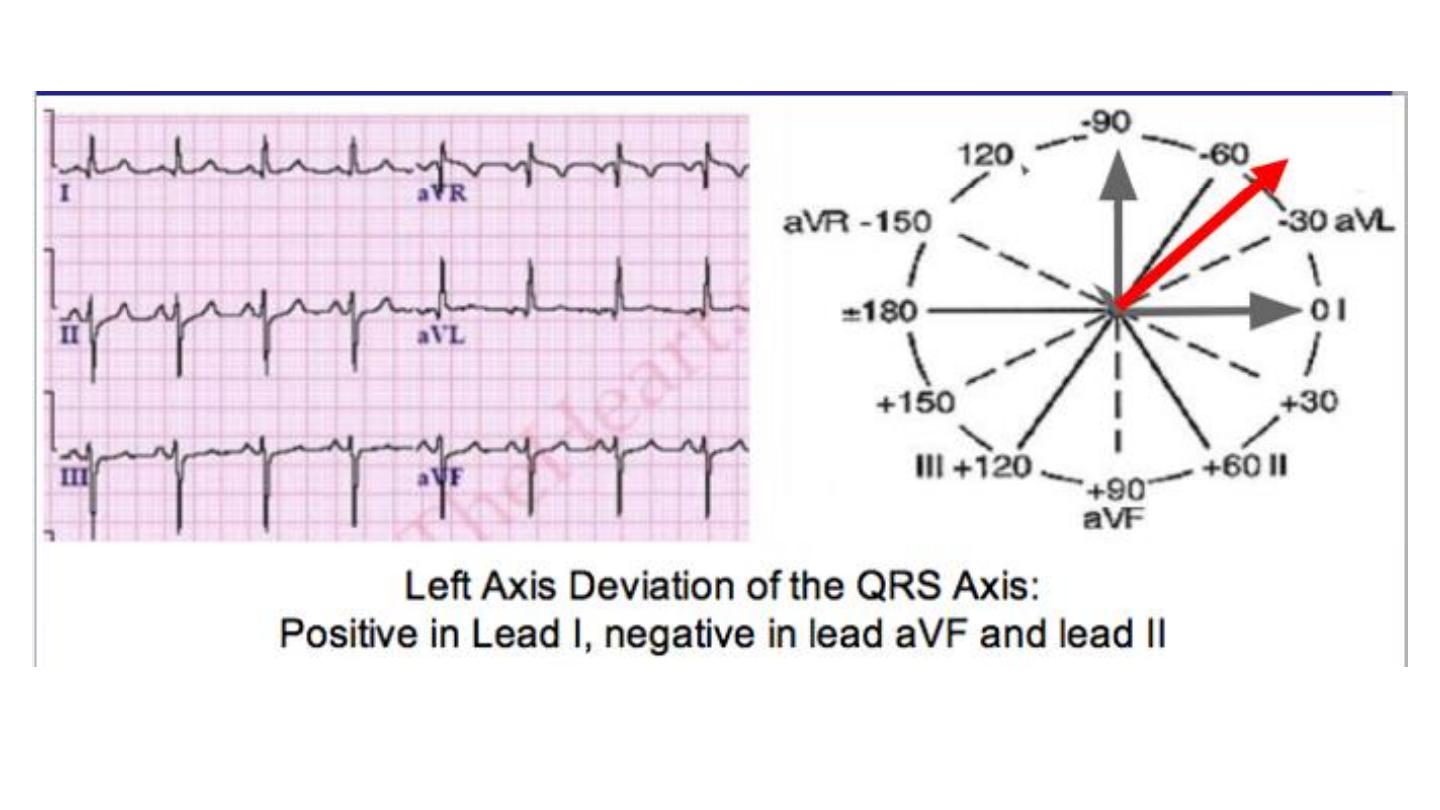
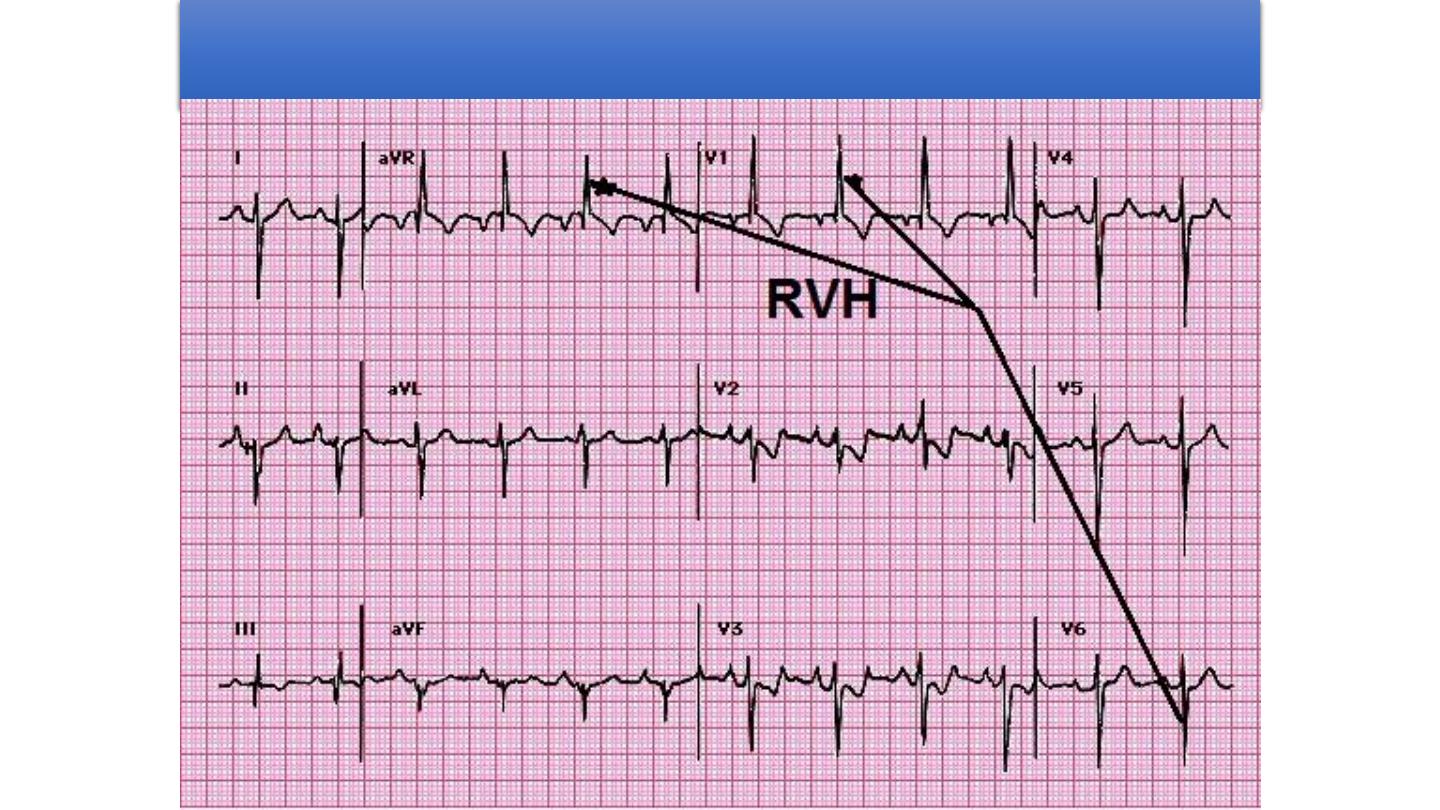
2-The ECG usually has right axis deviation and right
ventricular hypertrophy.
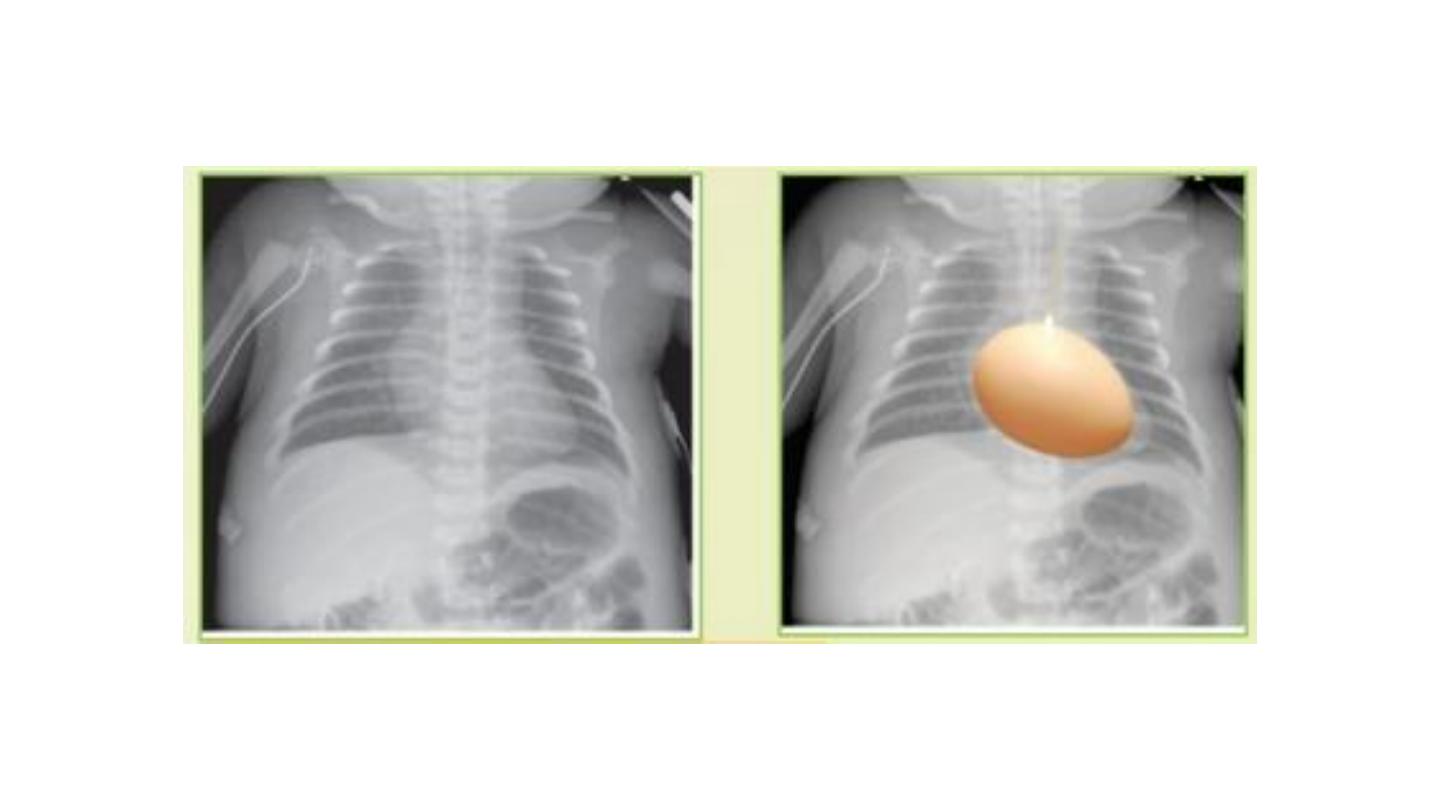
TGA

CNS
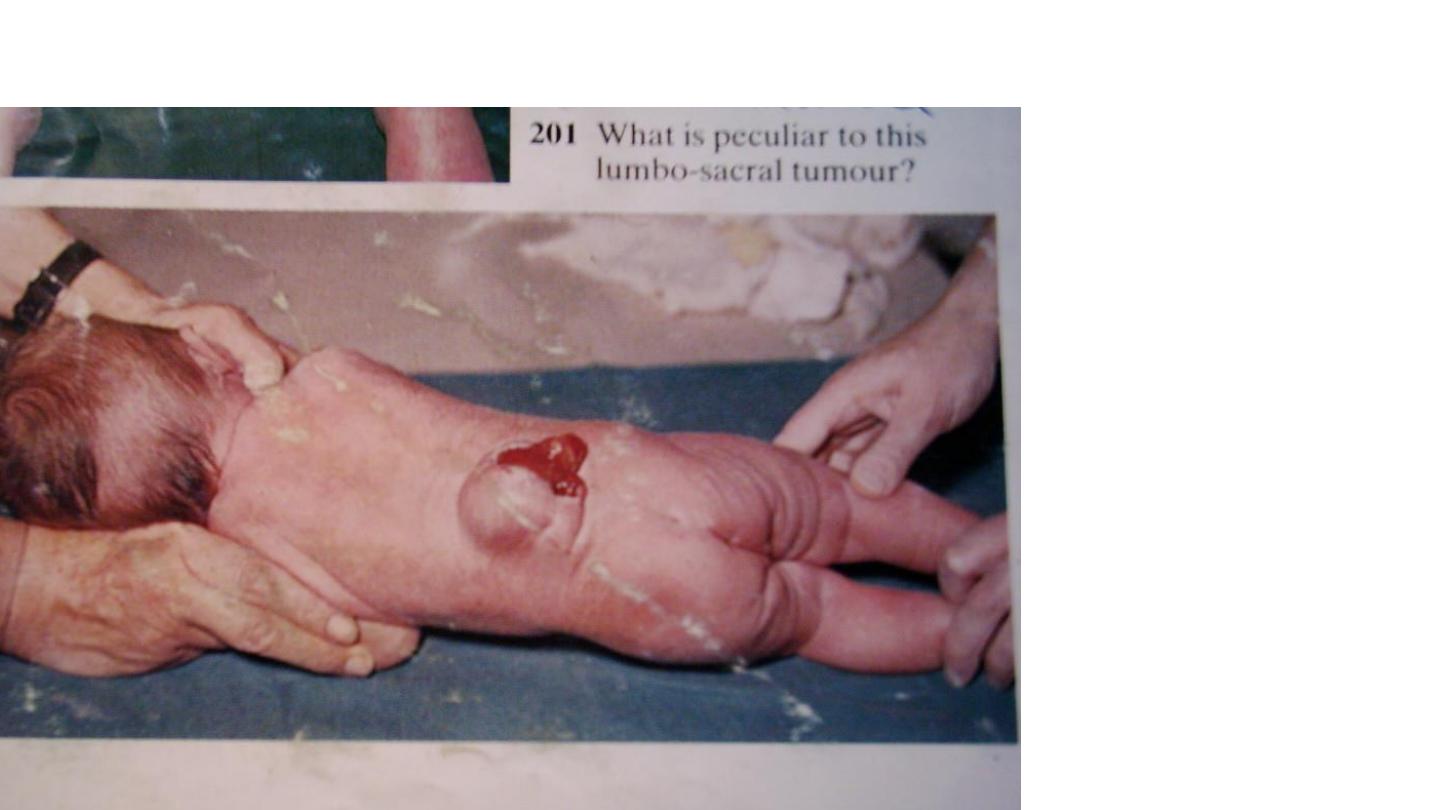
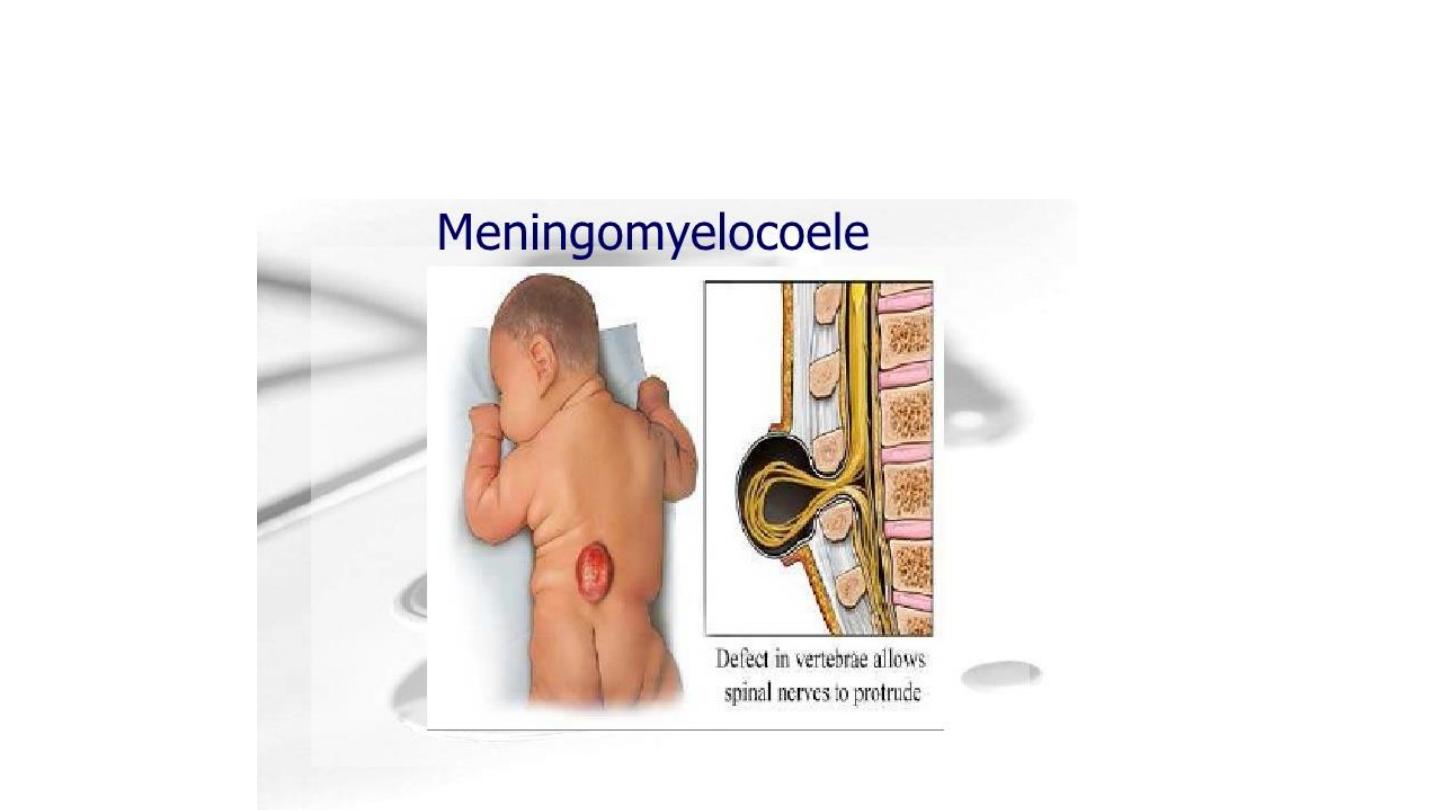
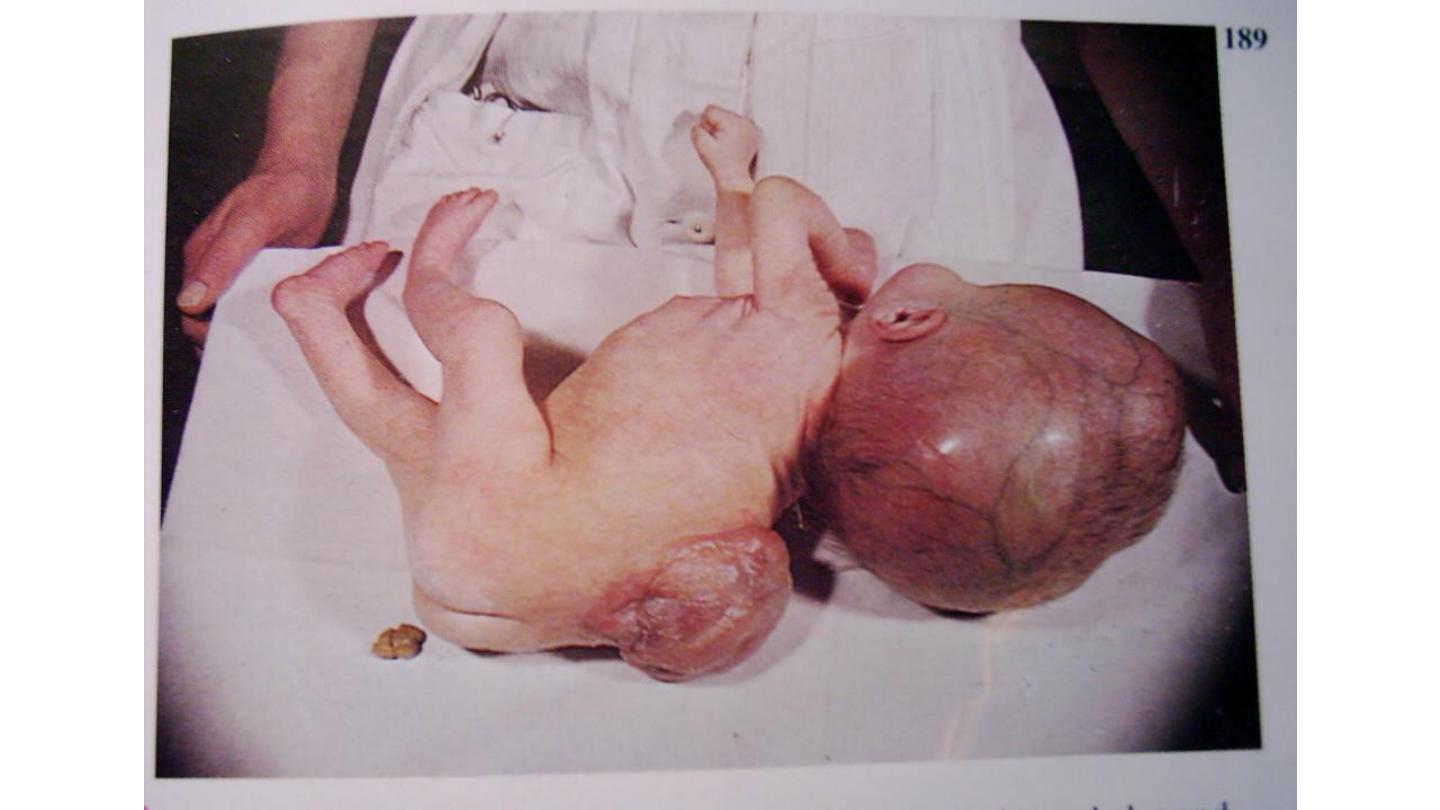
Myleomengiocele (spina bifida)
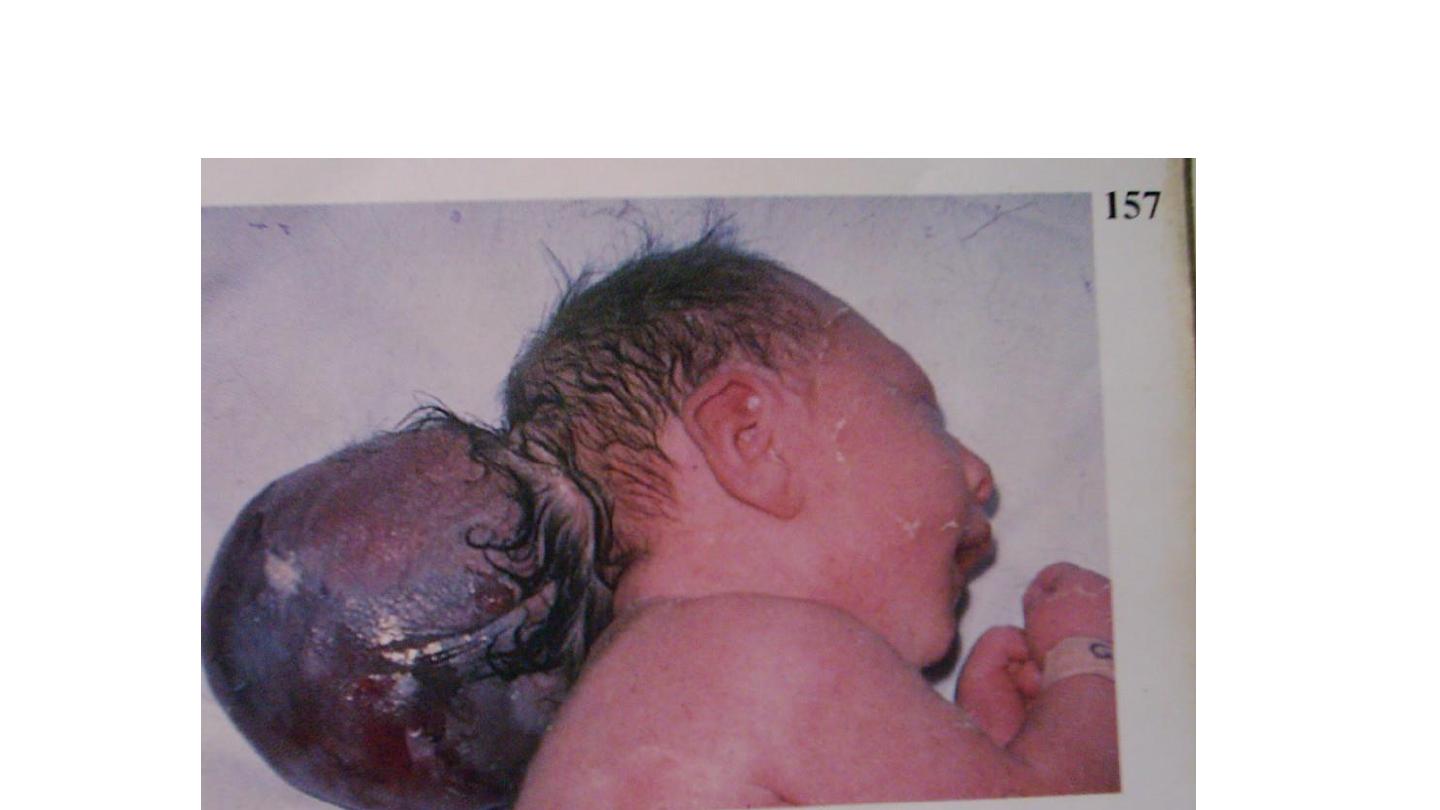
encephalocele
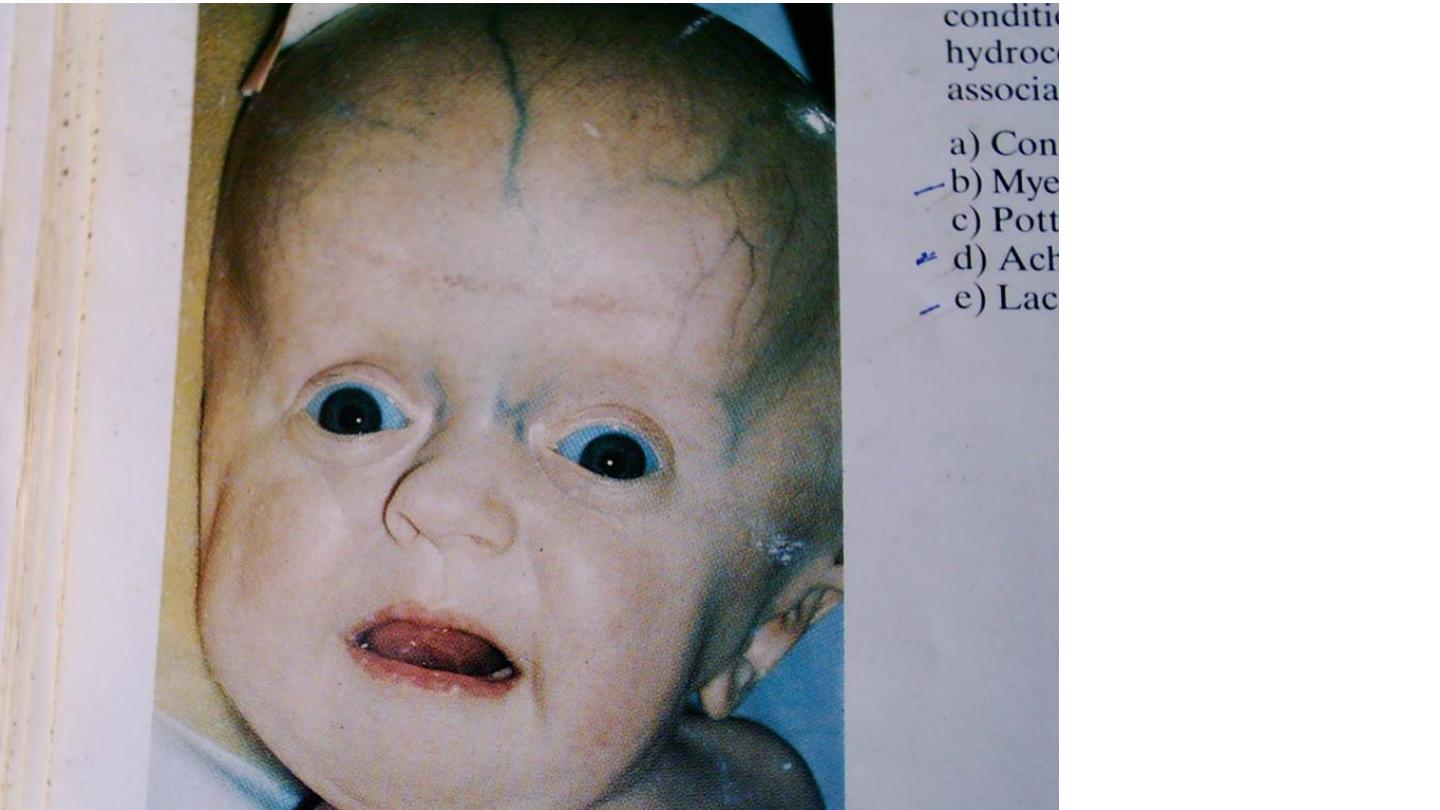
hydrocephaly
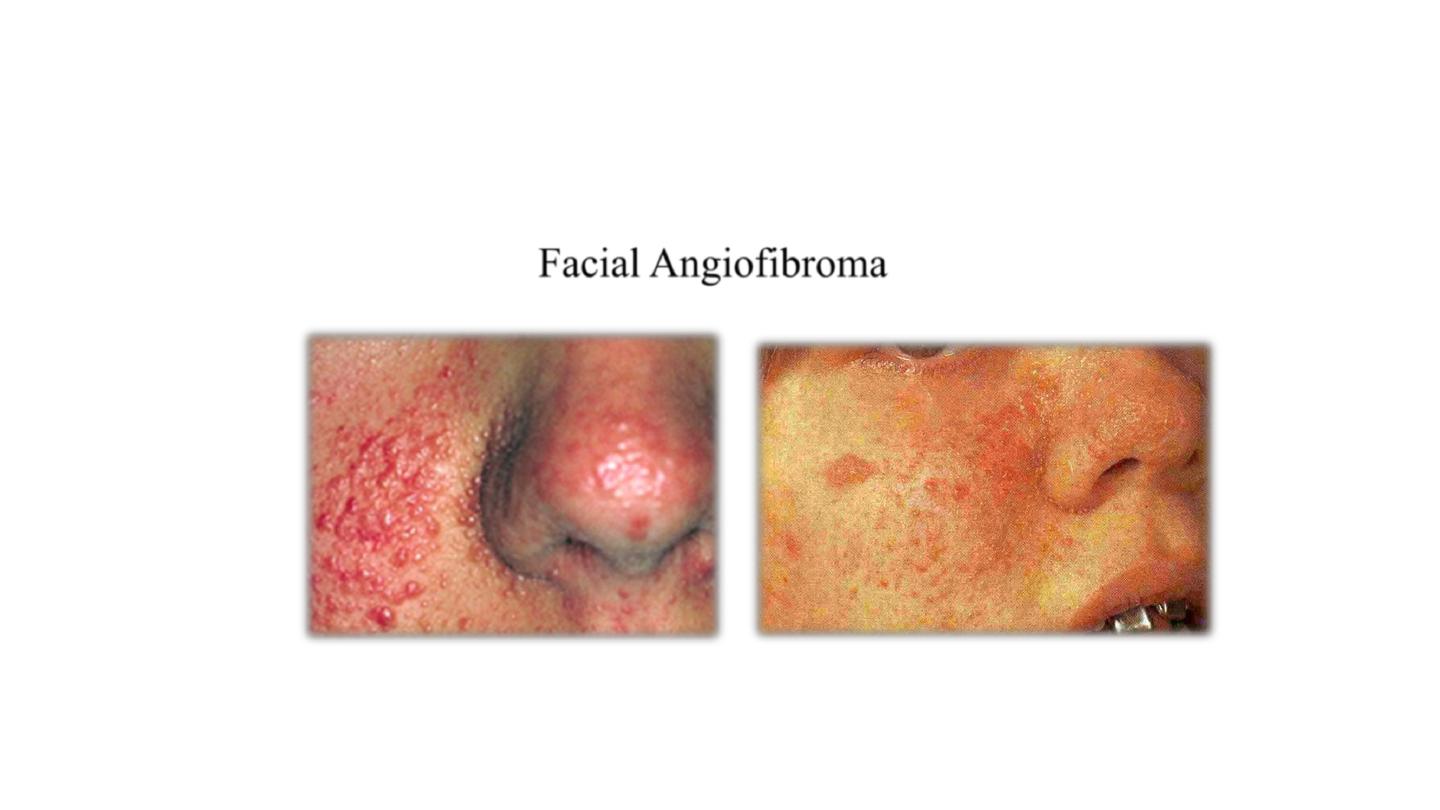
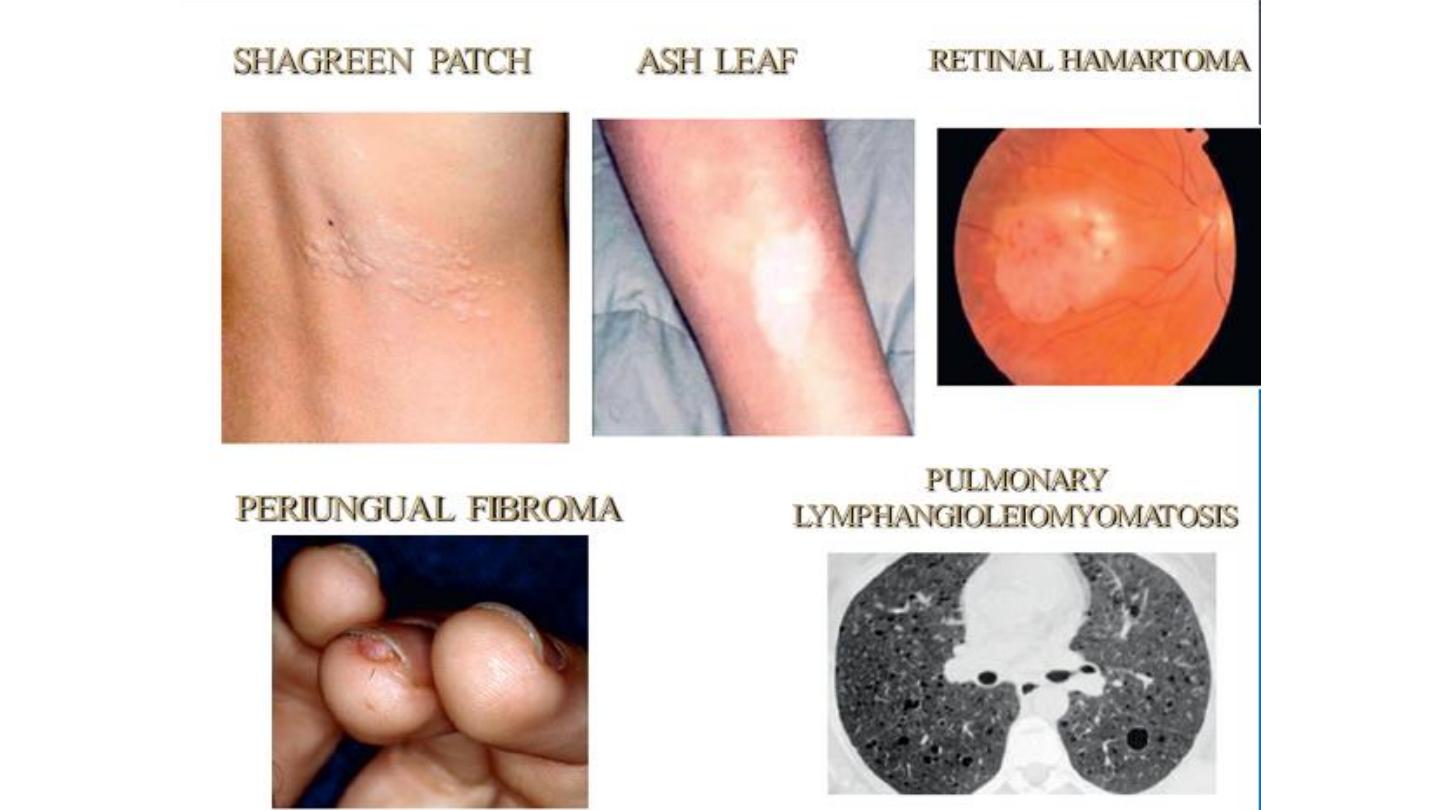
neurofibromatosis
Facial Angiofibroma
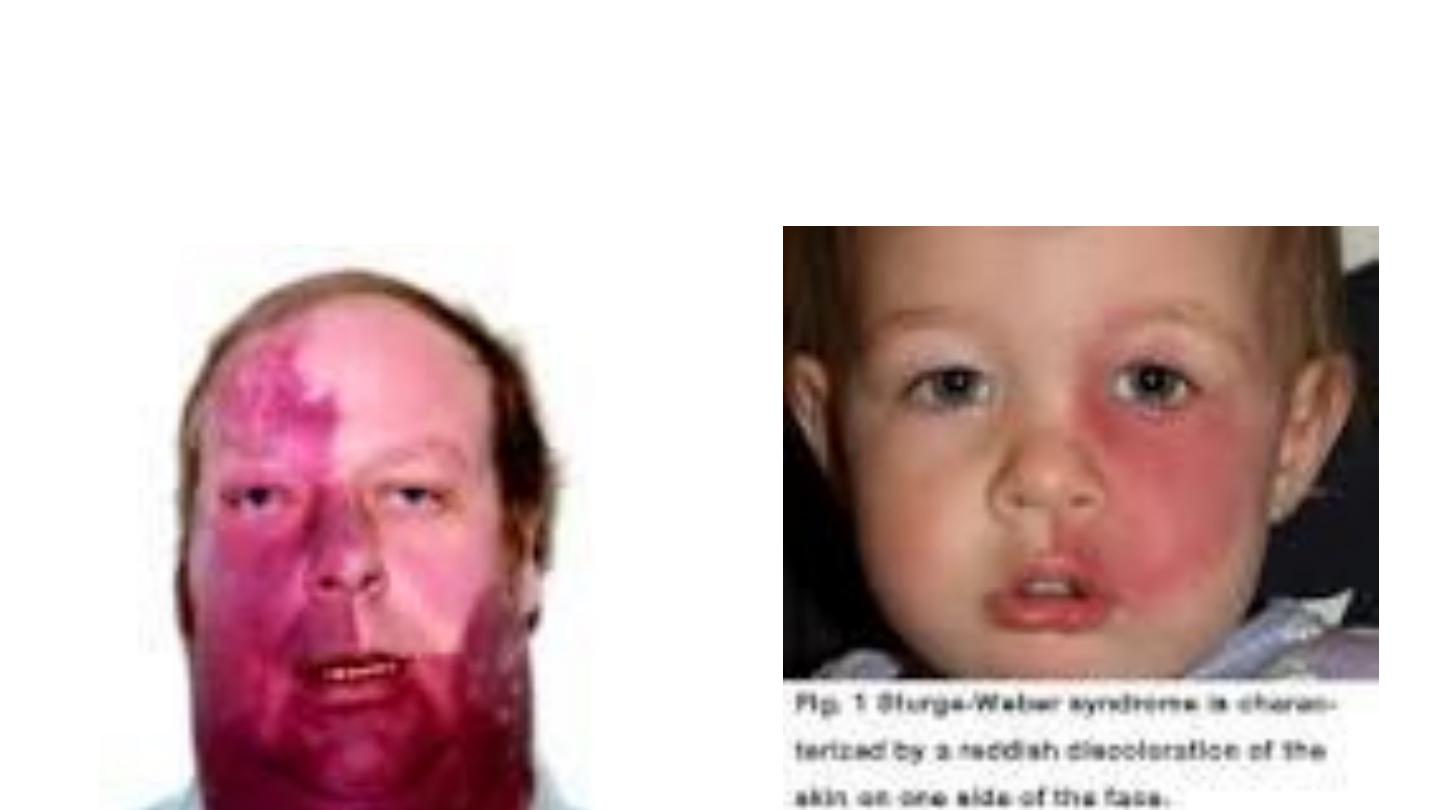
Sturge weber syndrome
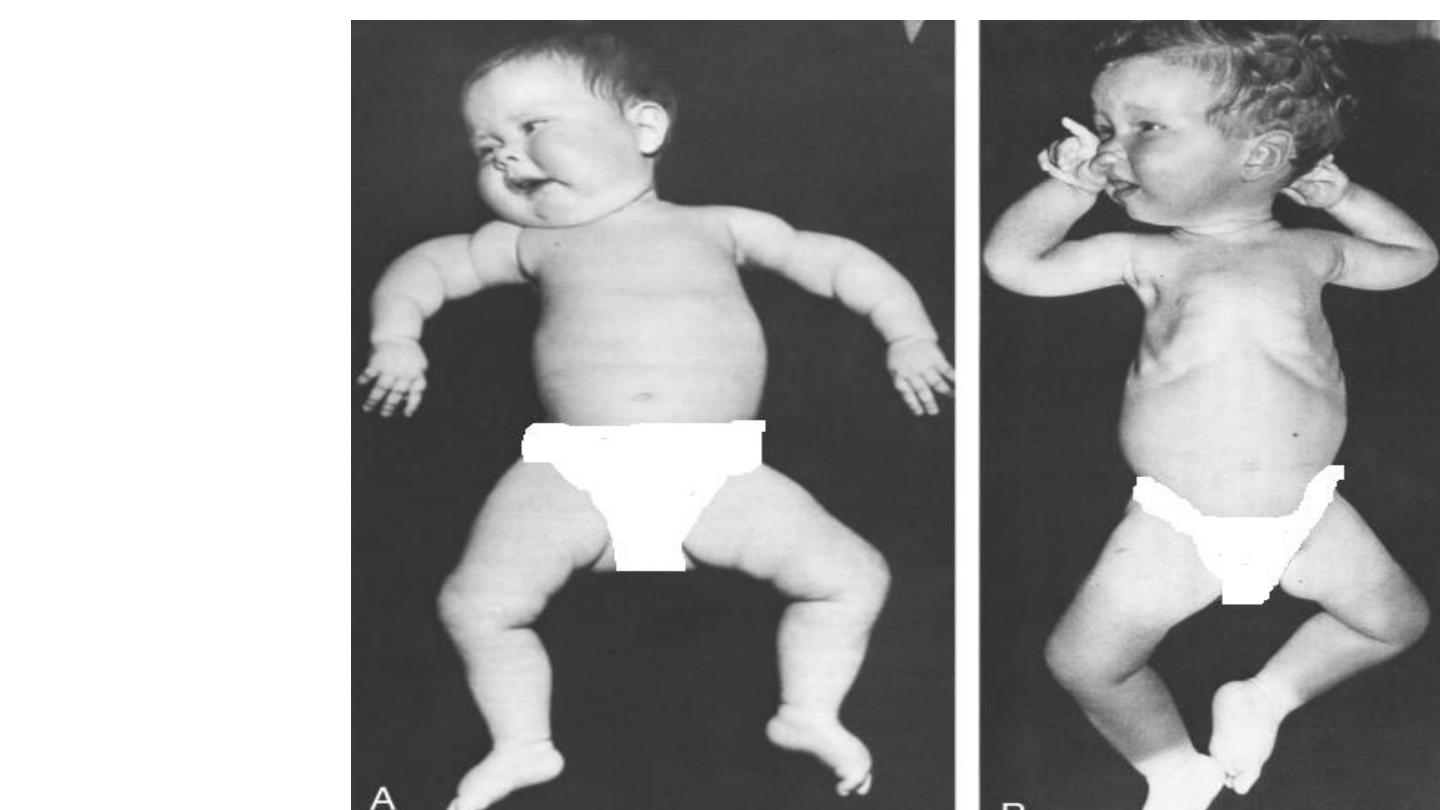
• Weding hofman

Duchen muscle dystrophy

infections
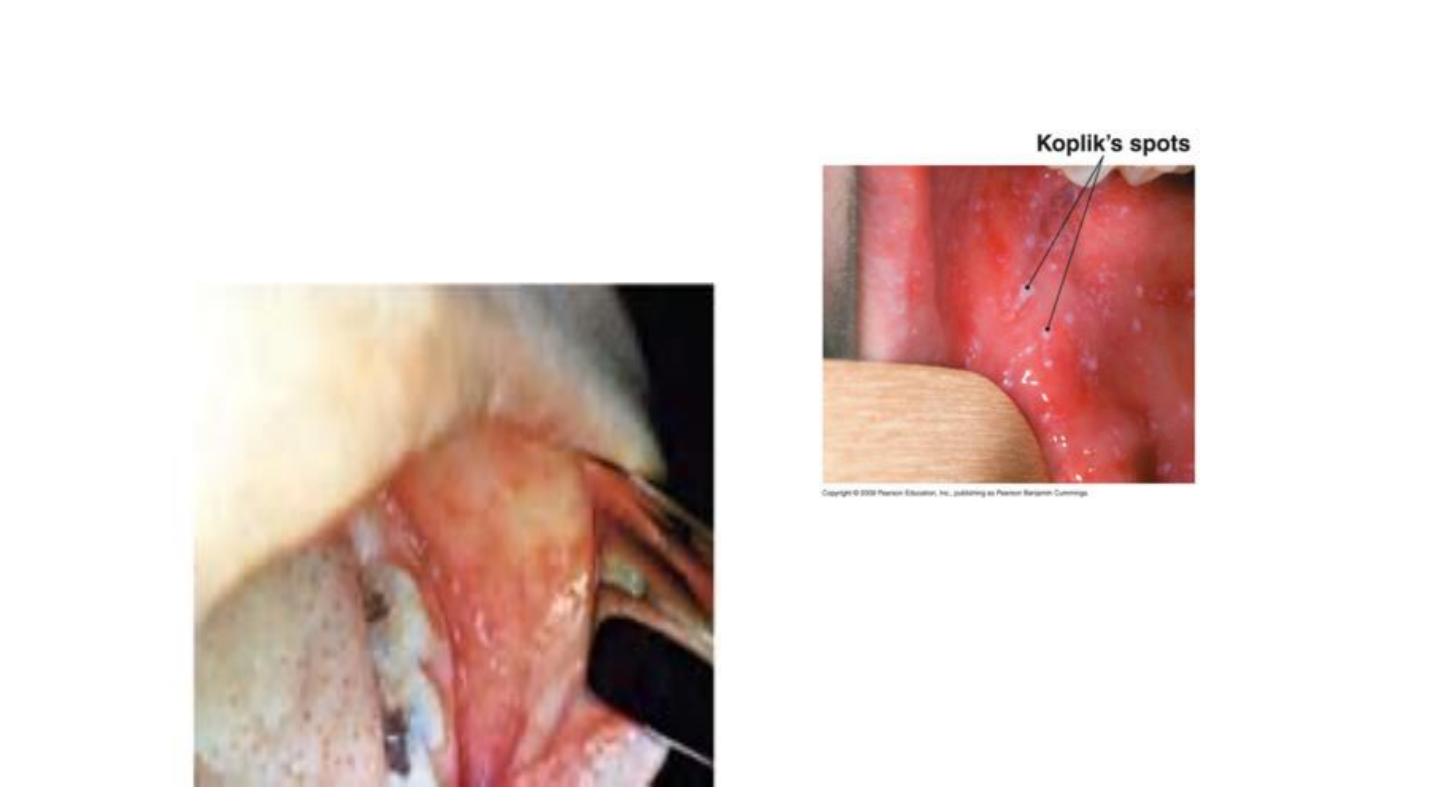
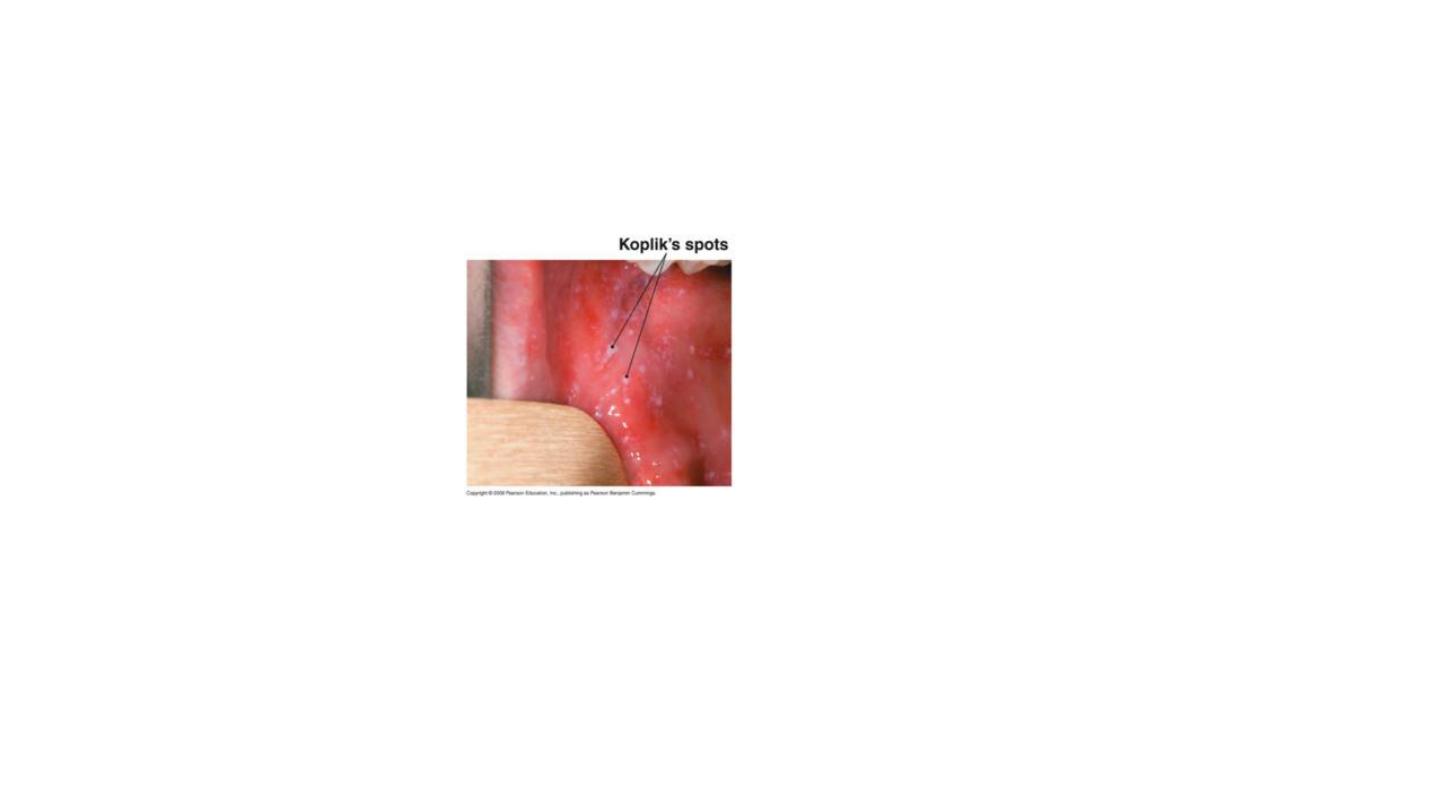
KOPLIK SPOTS
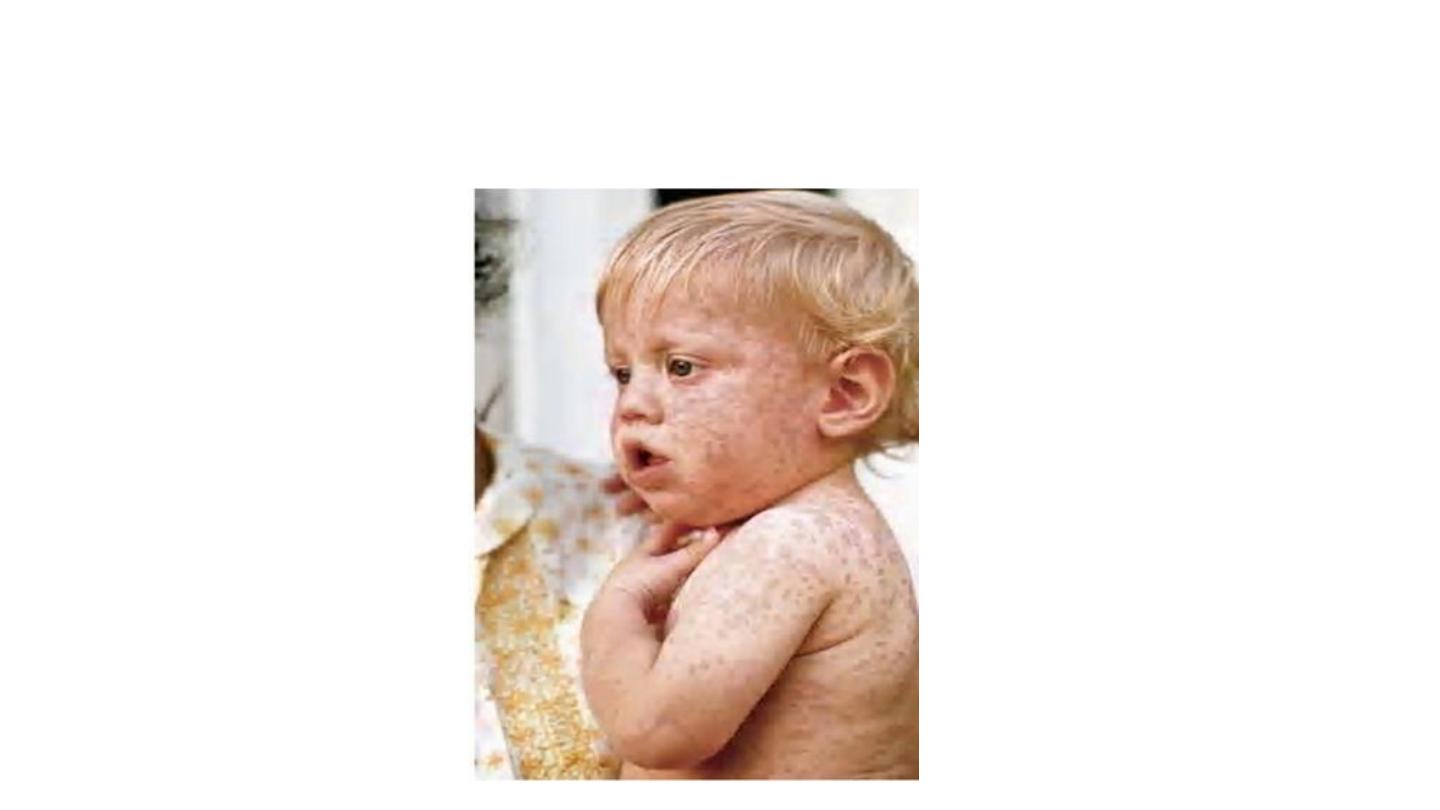
MEEASLES
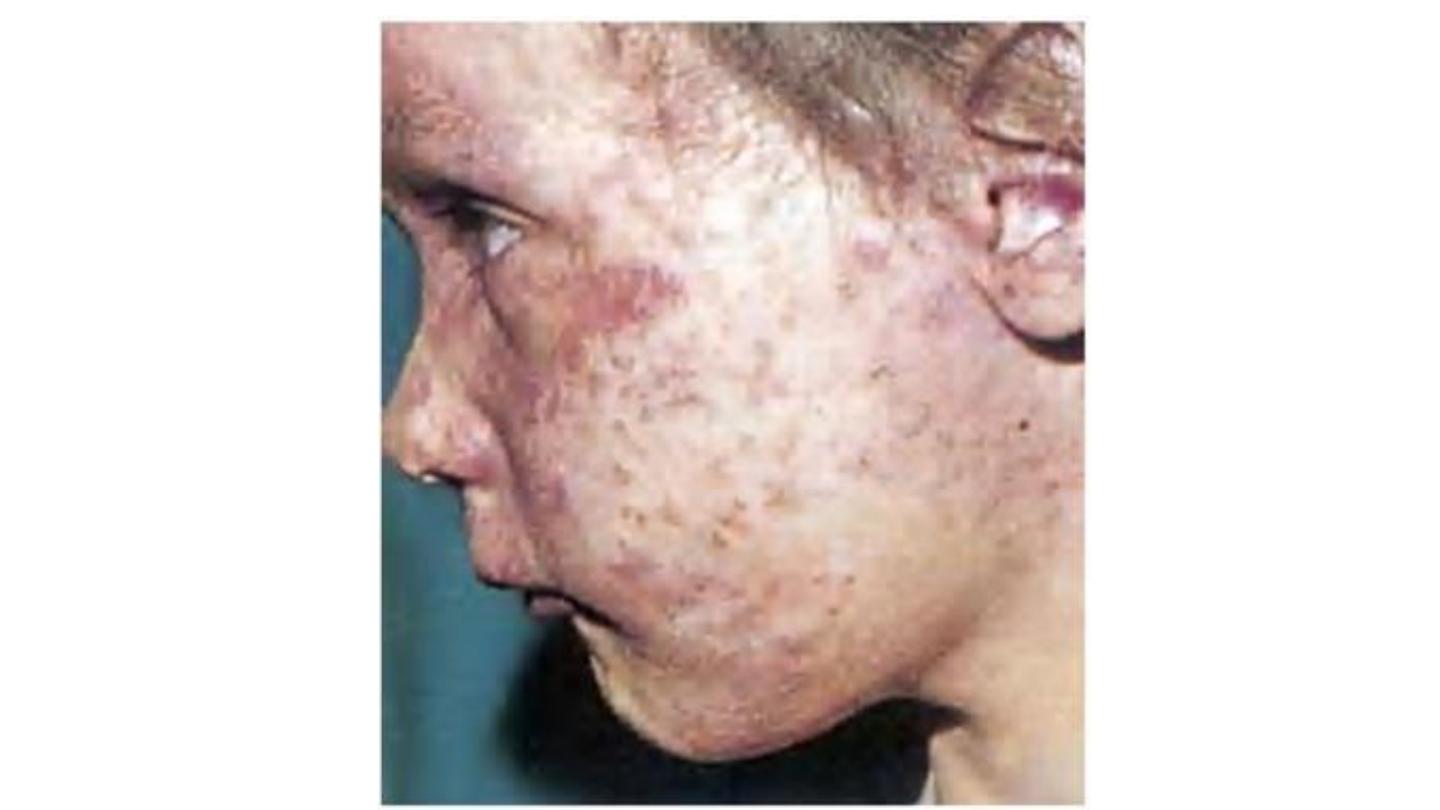
Rubella’
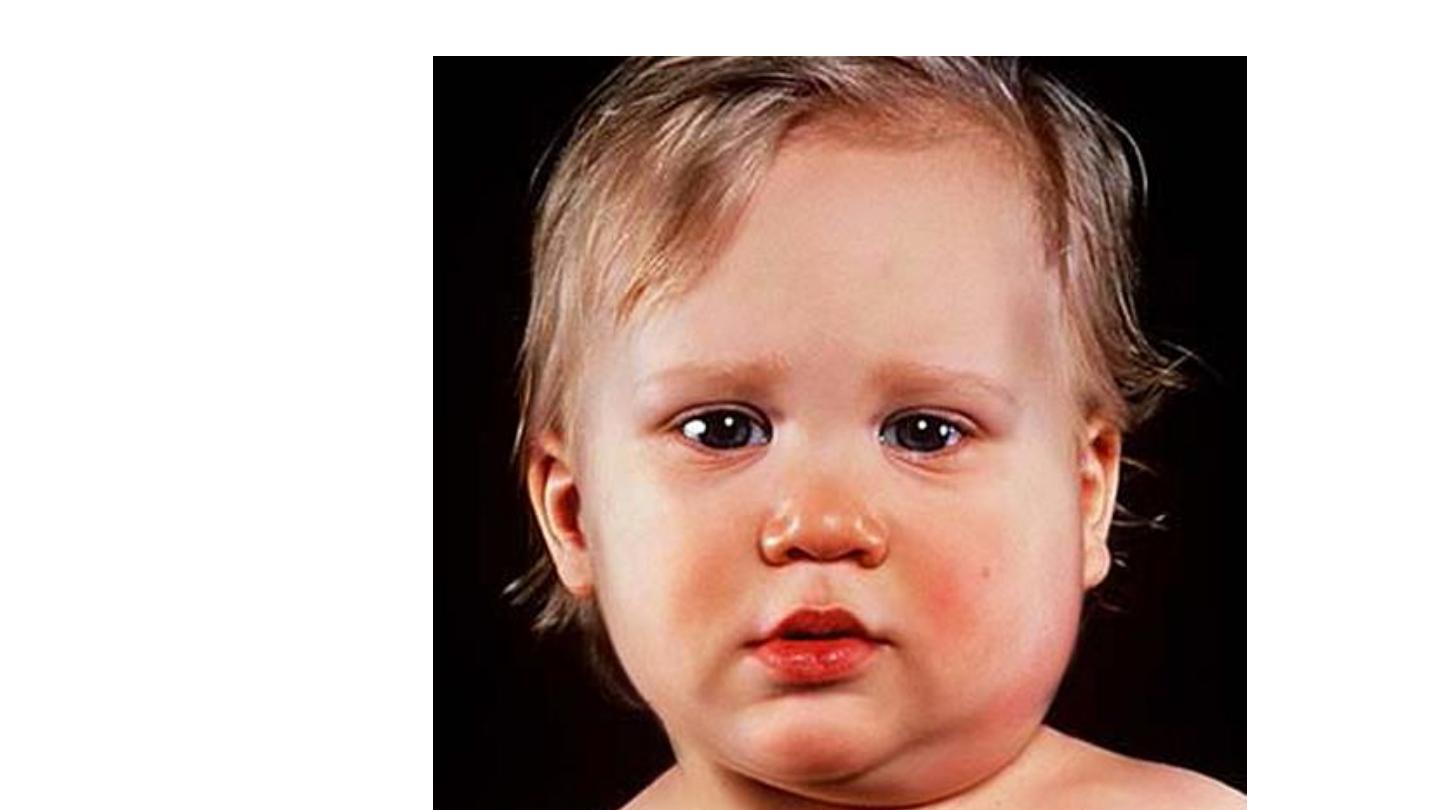
mumps
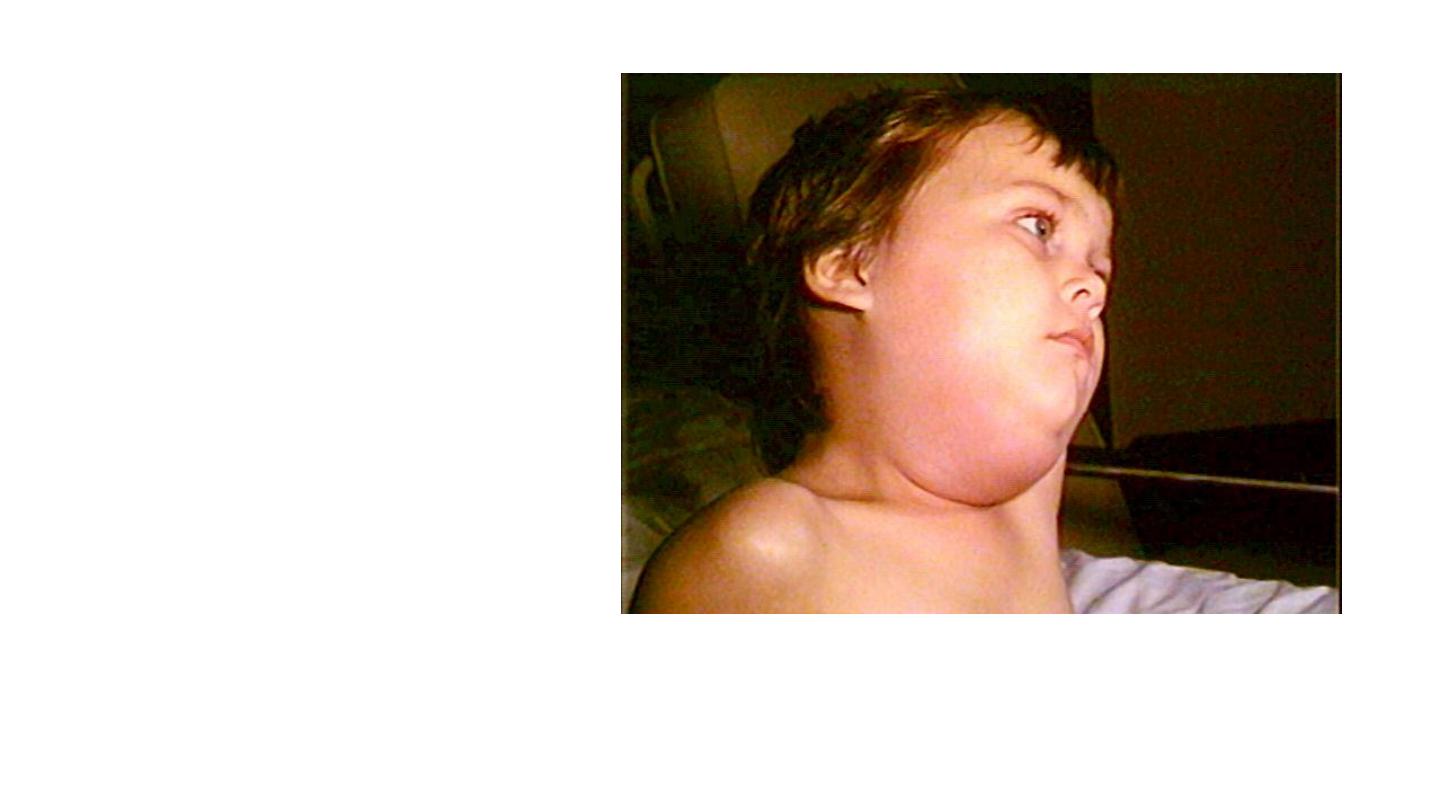
mumps
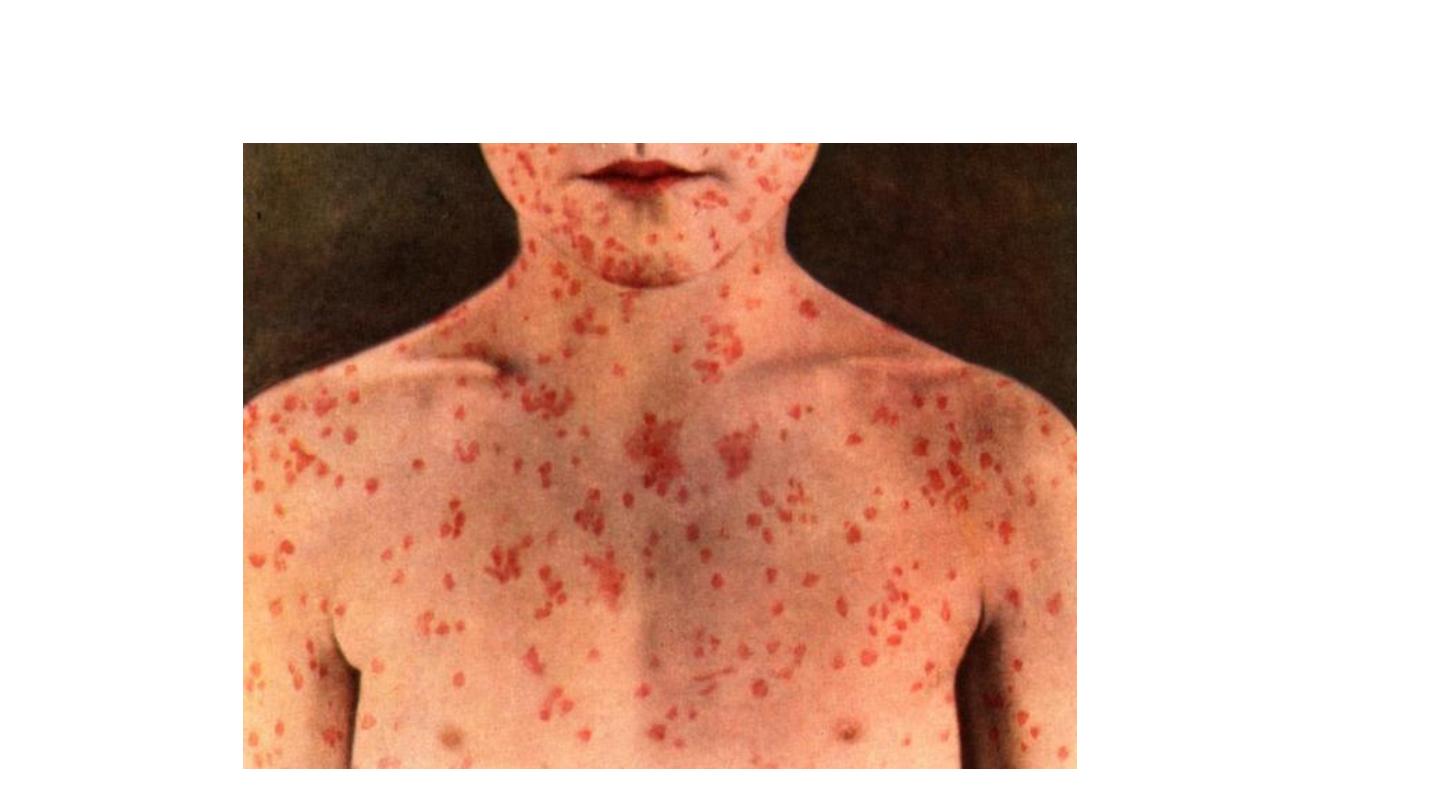
measles
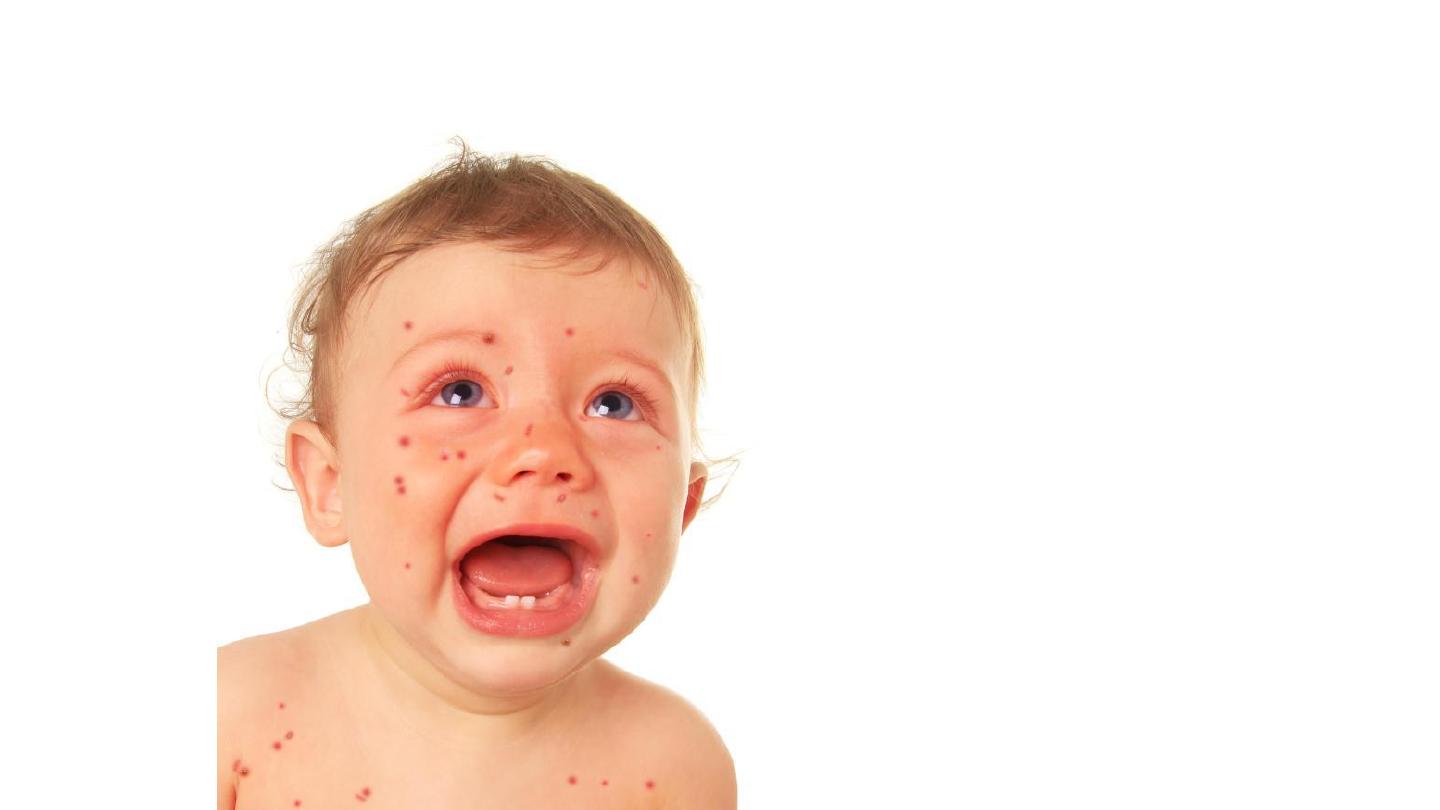

measles
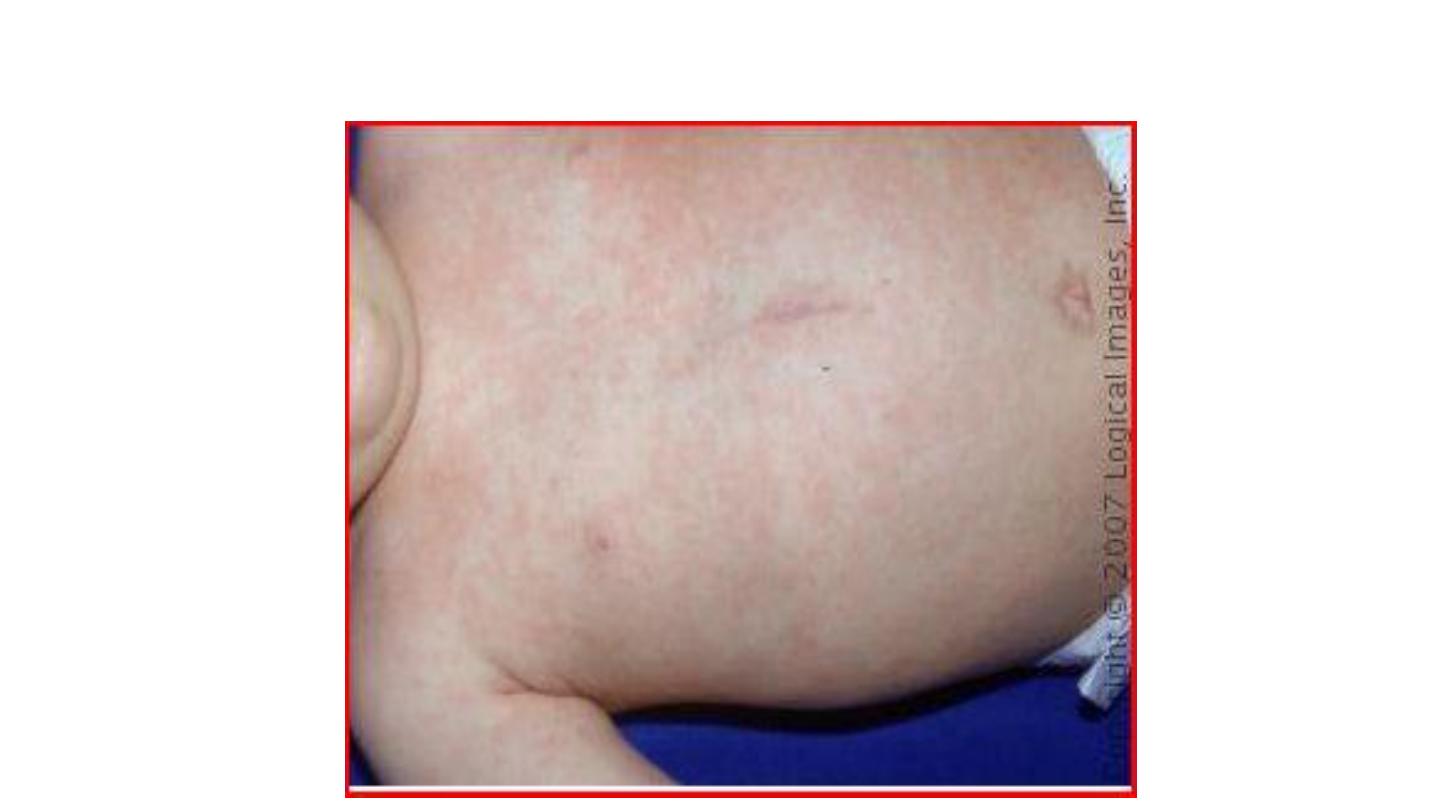
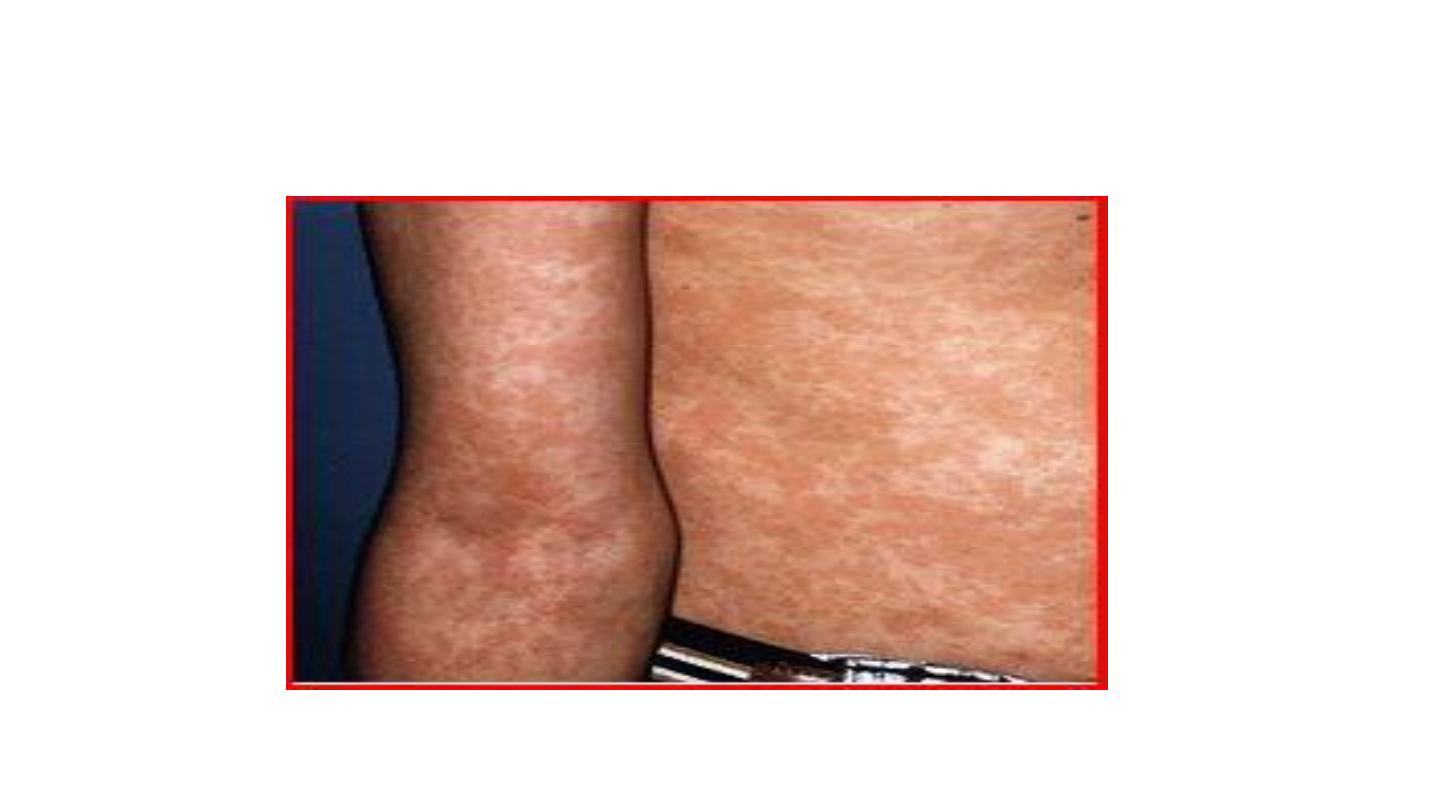
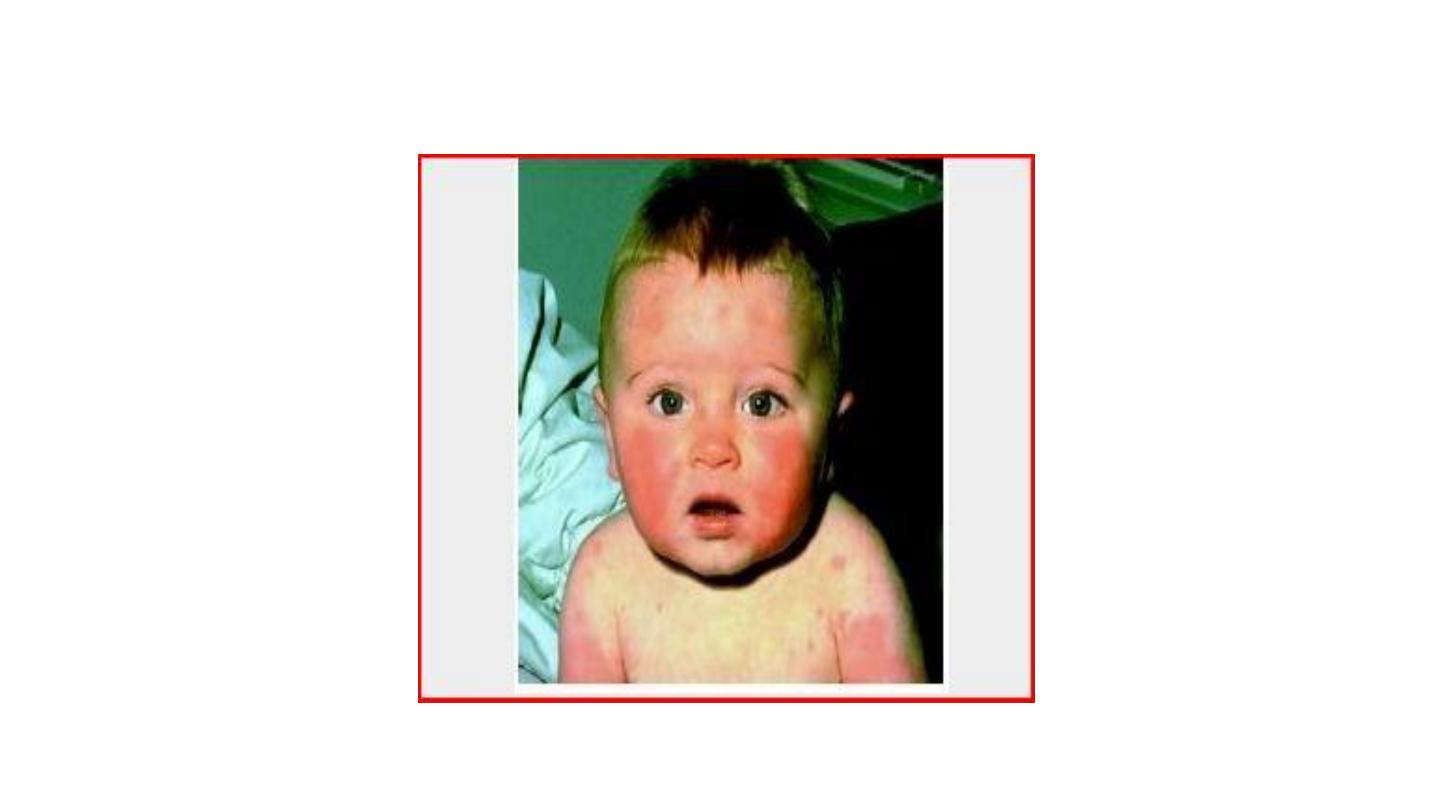
Rosella infantum
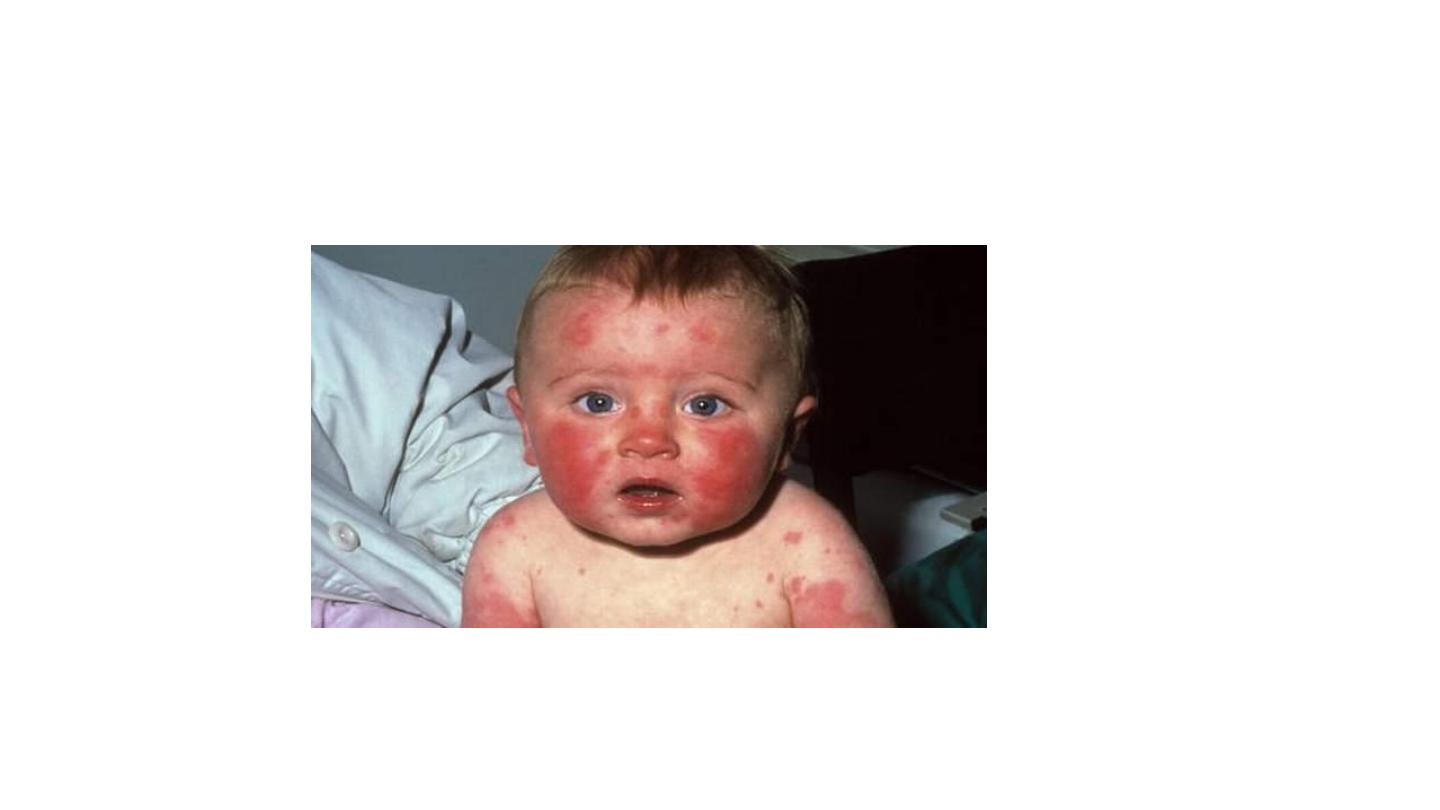
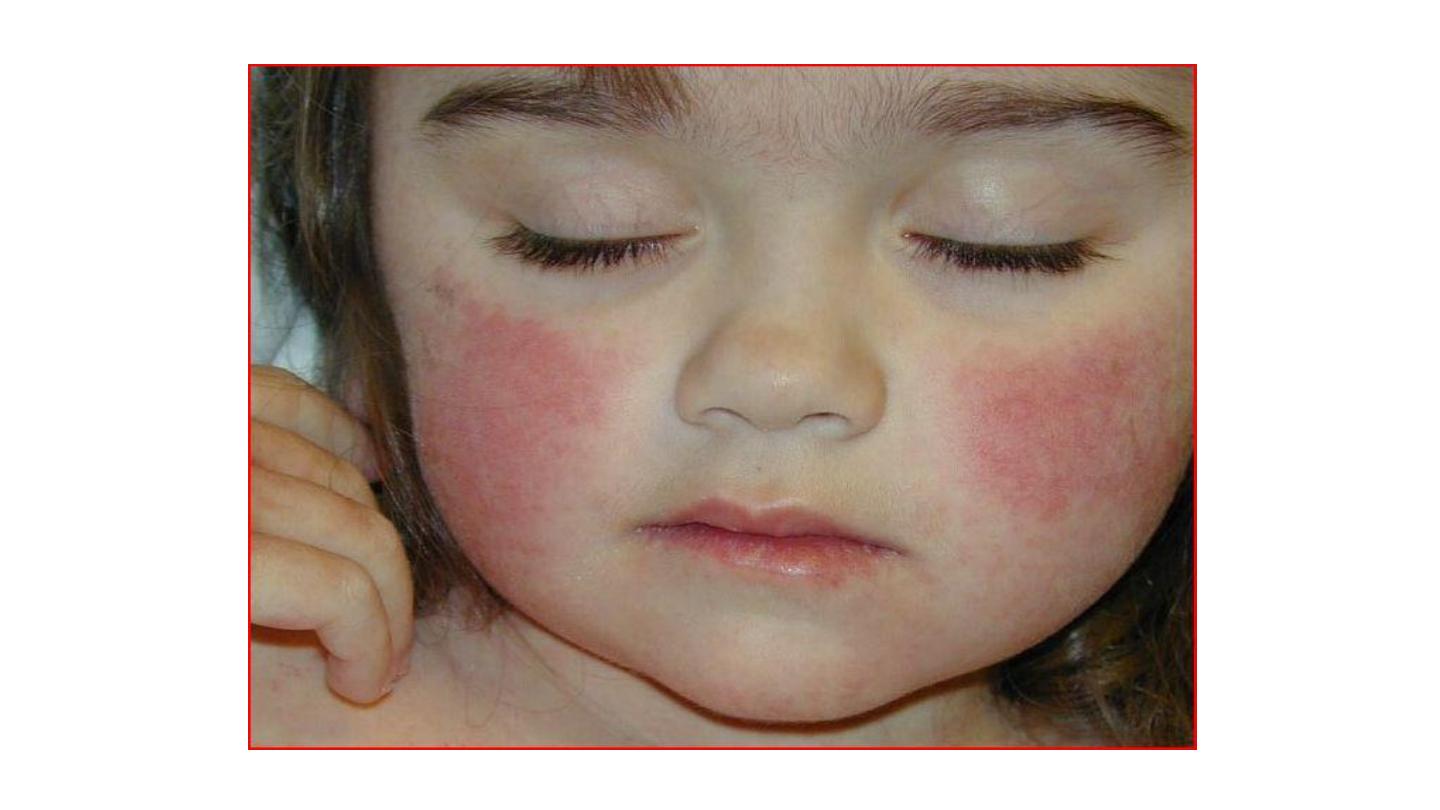
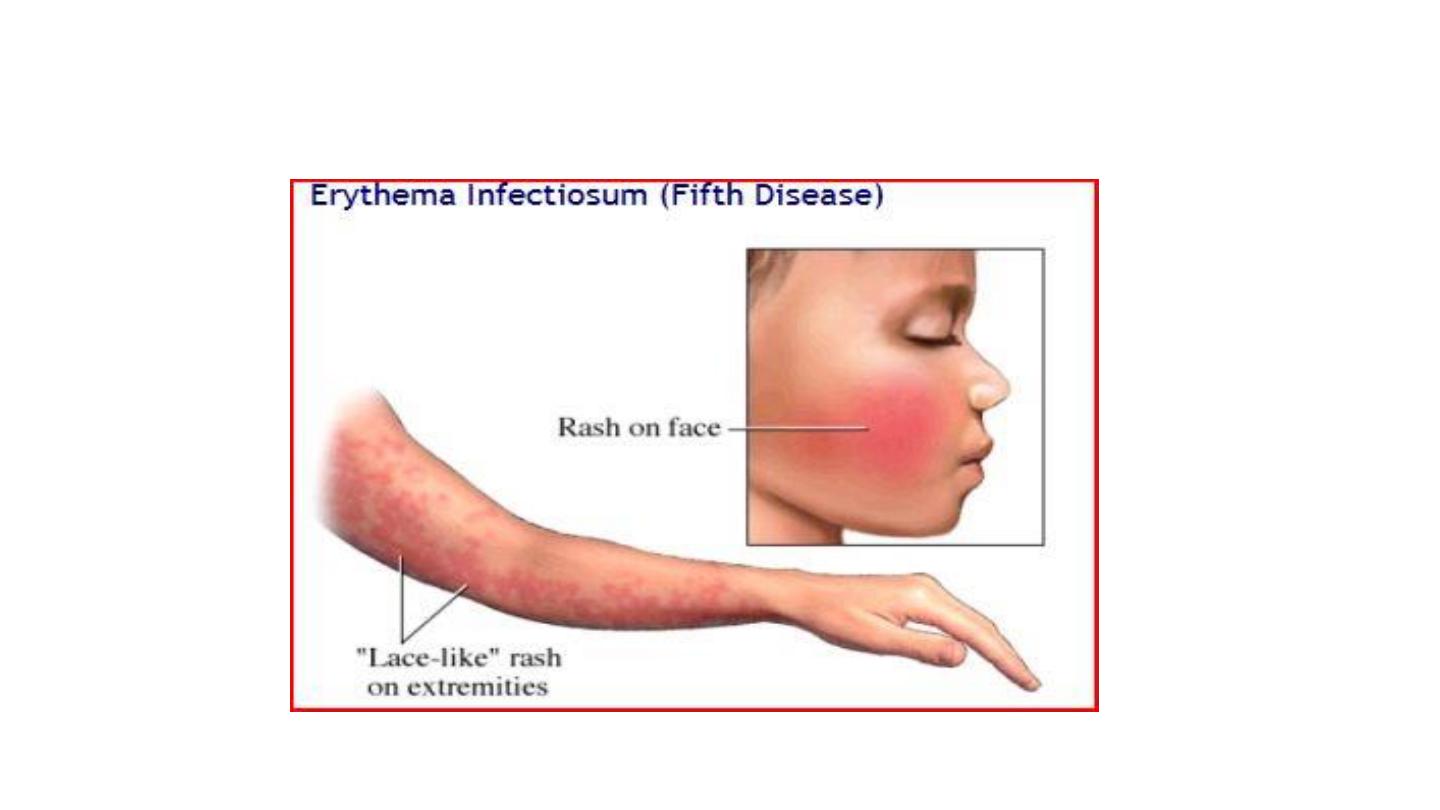
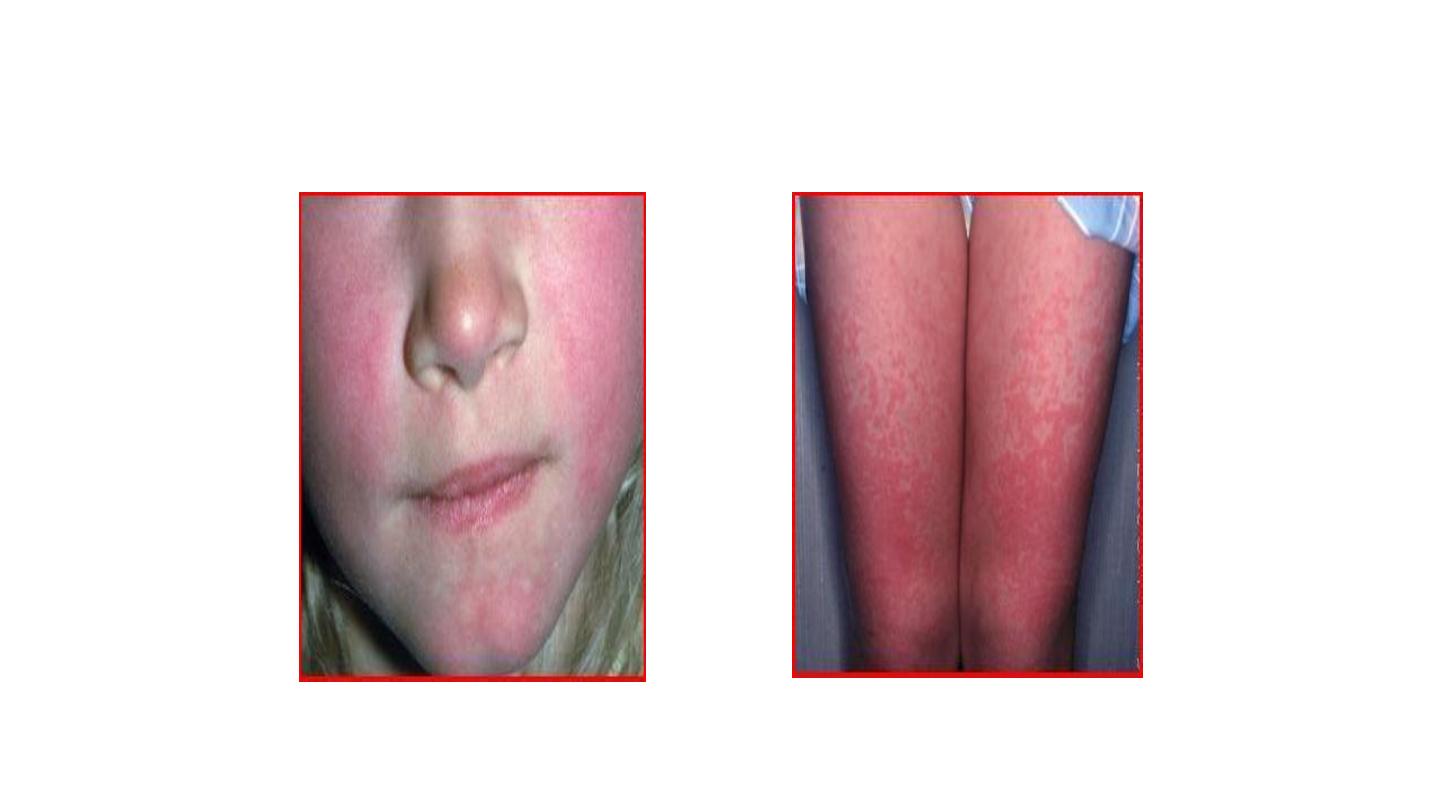
Erythema infectiosum
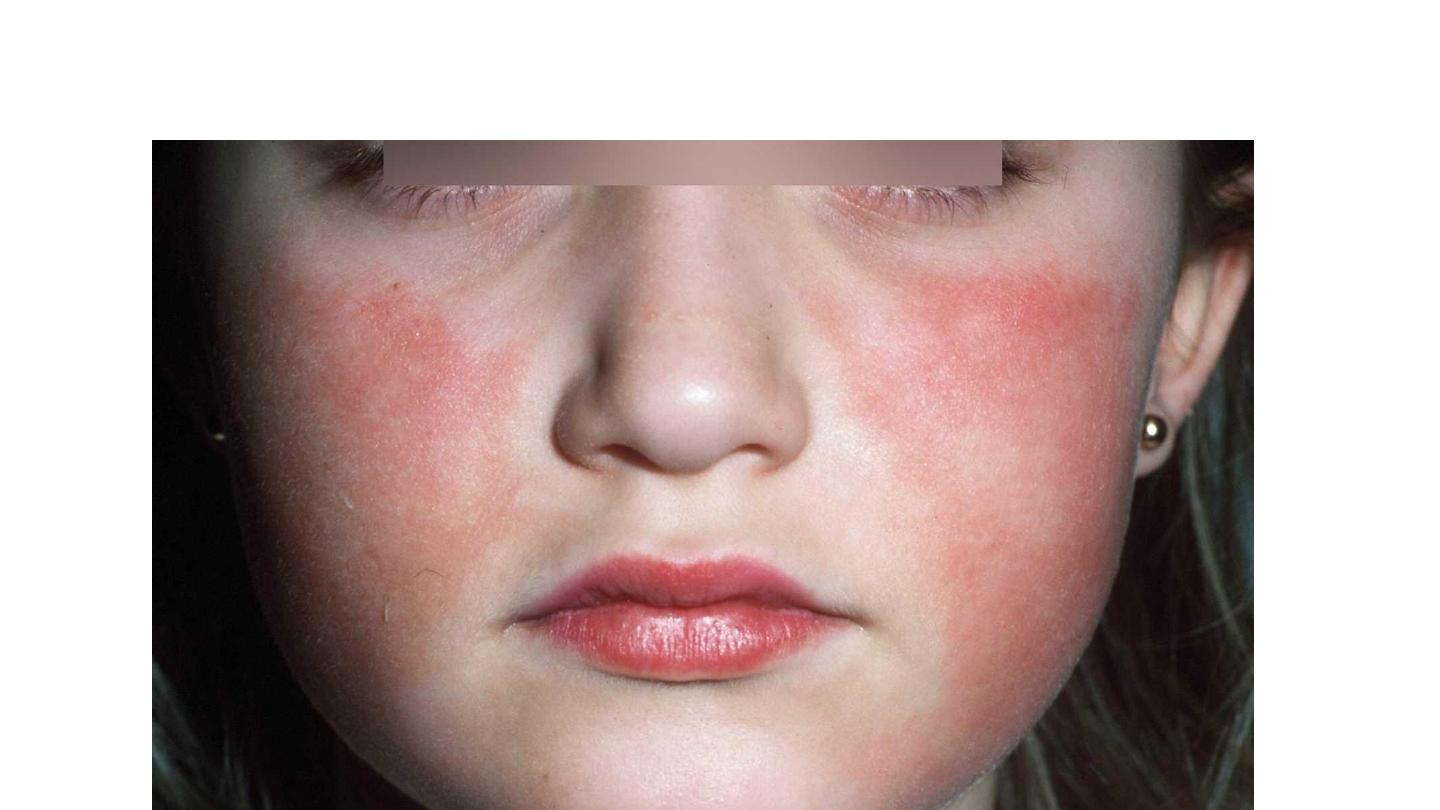
Erythema infectiosum
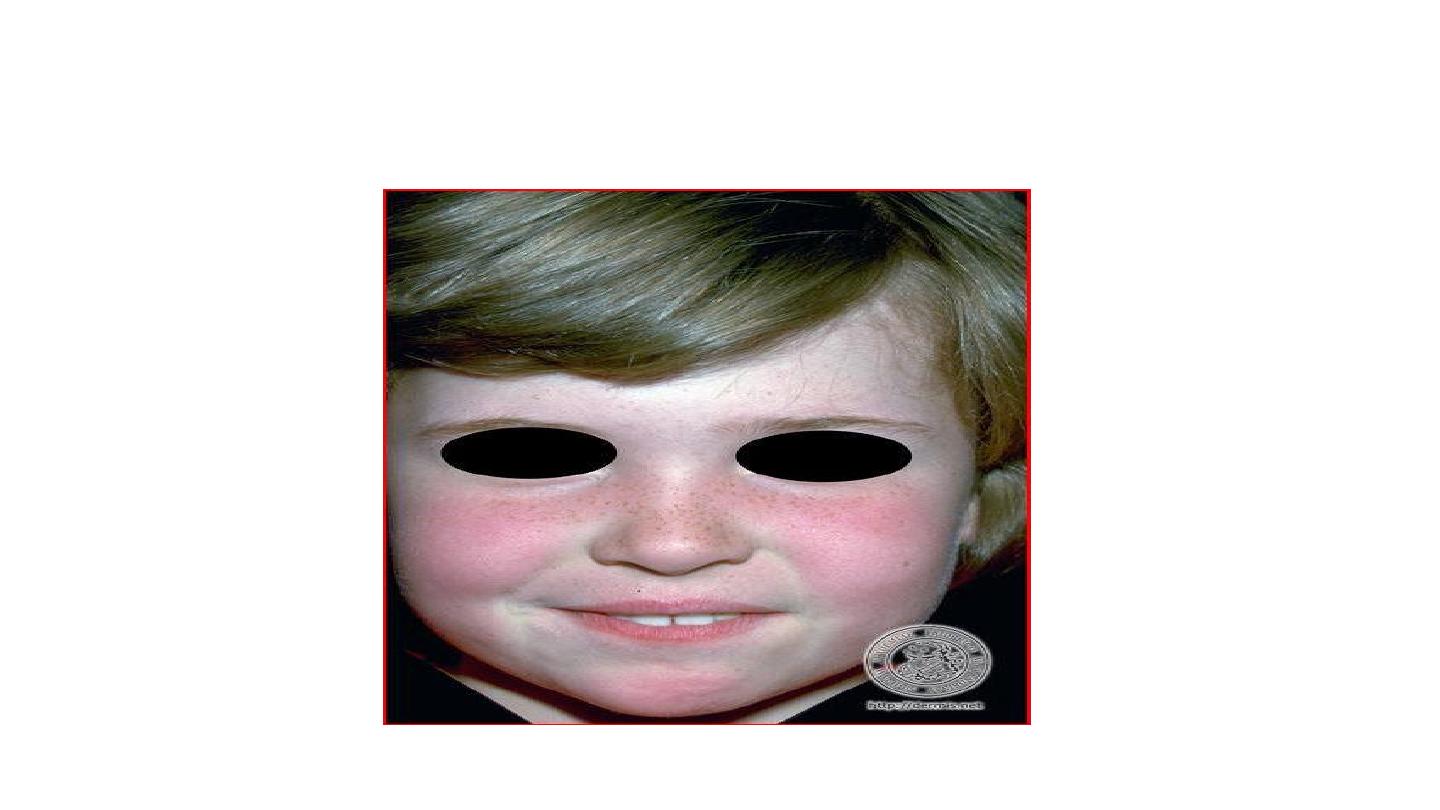

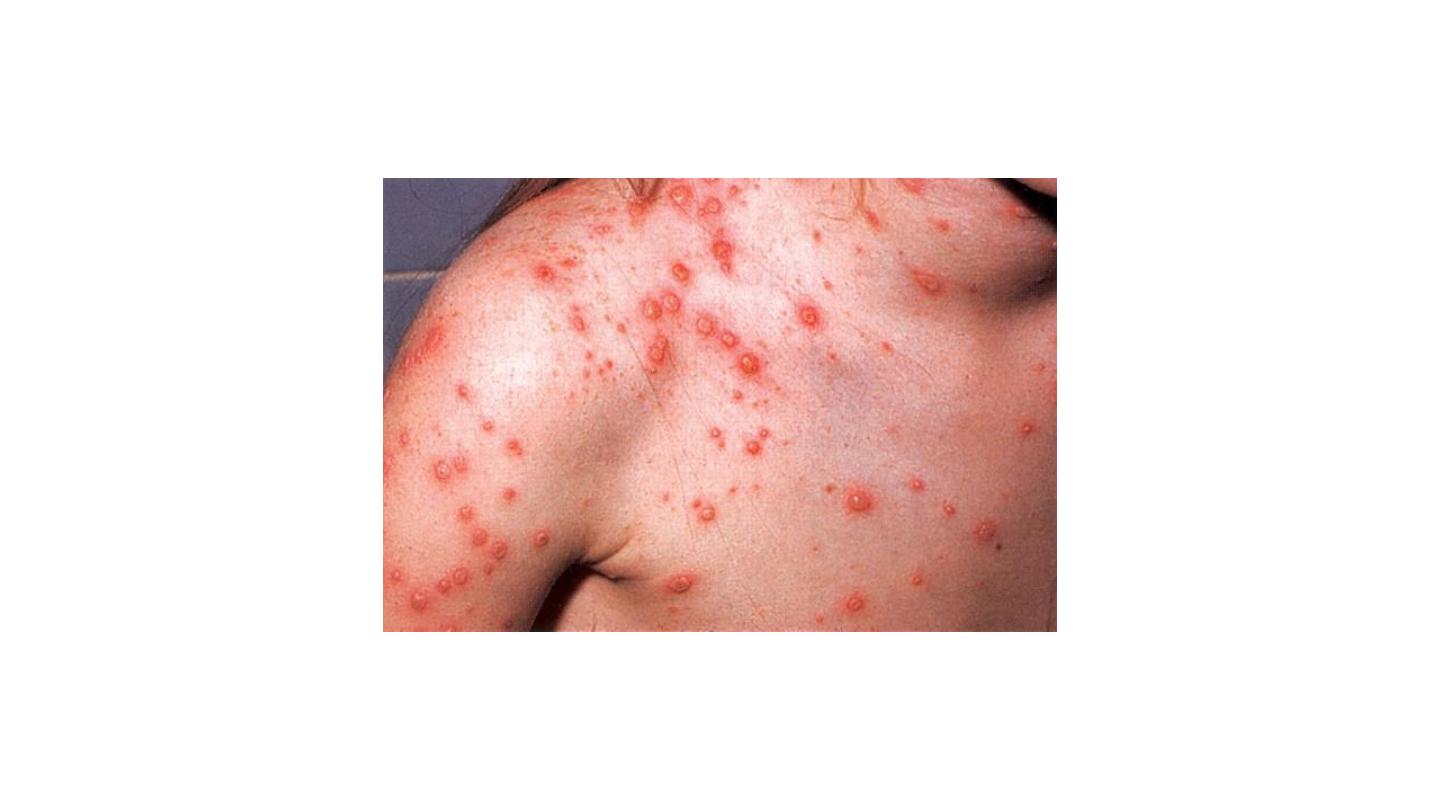
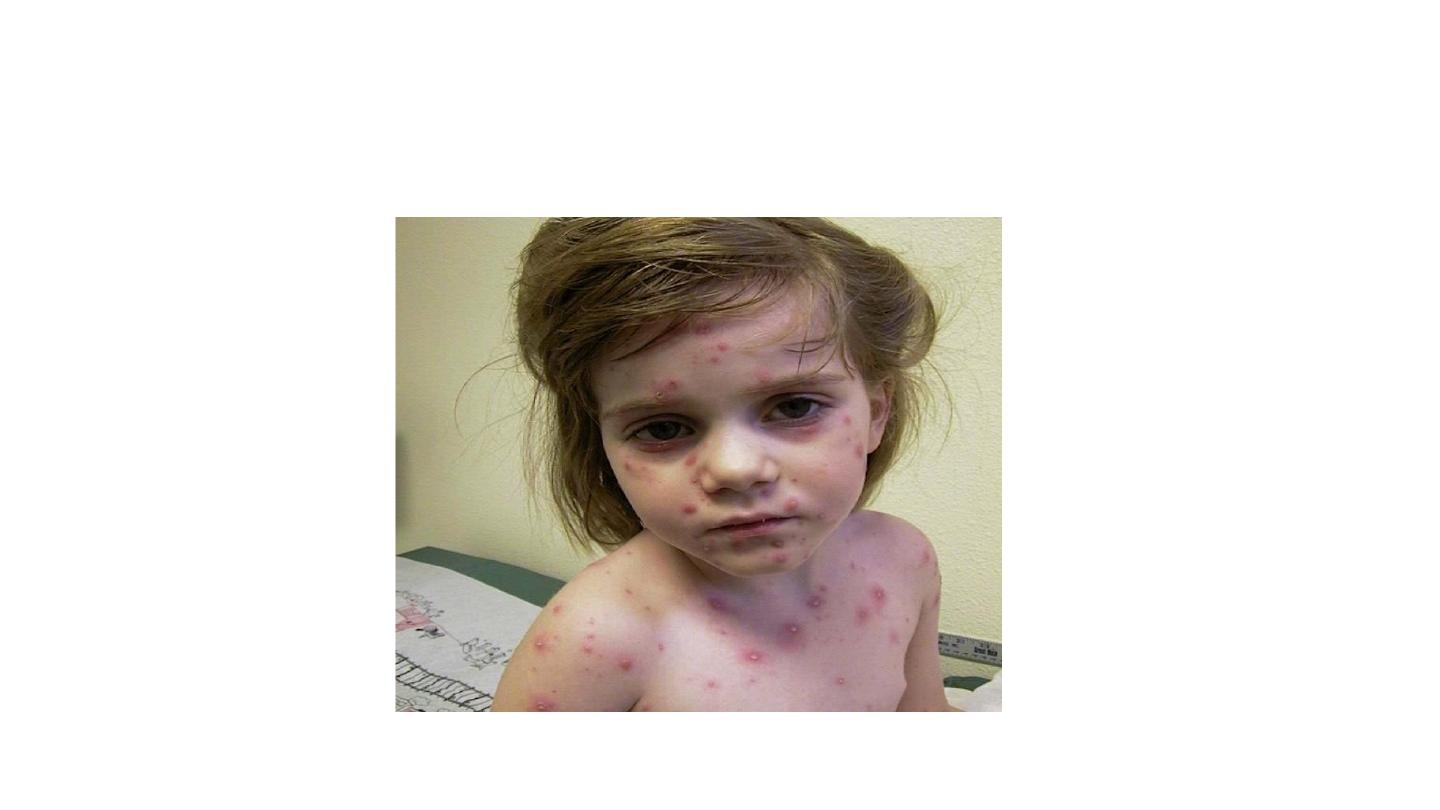
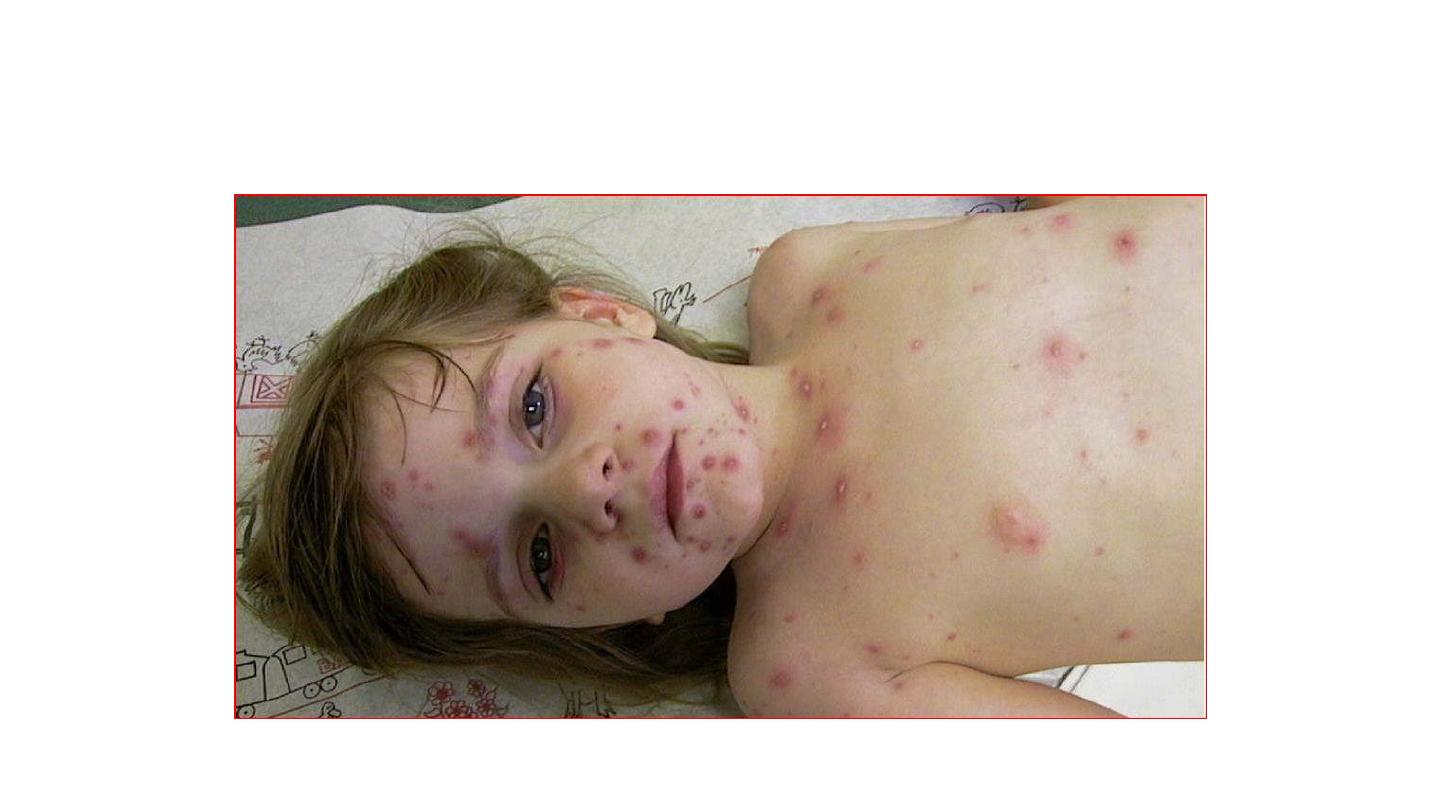
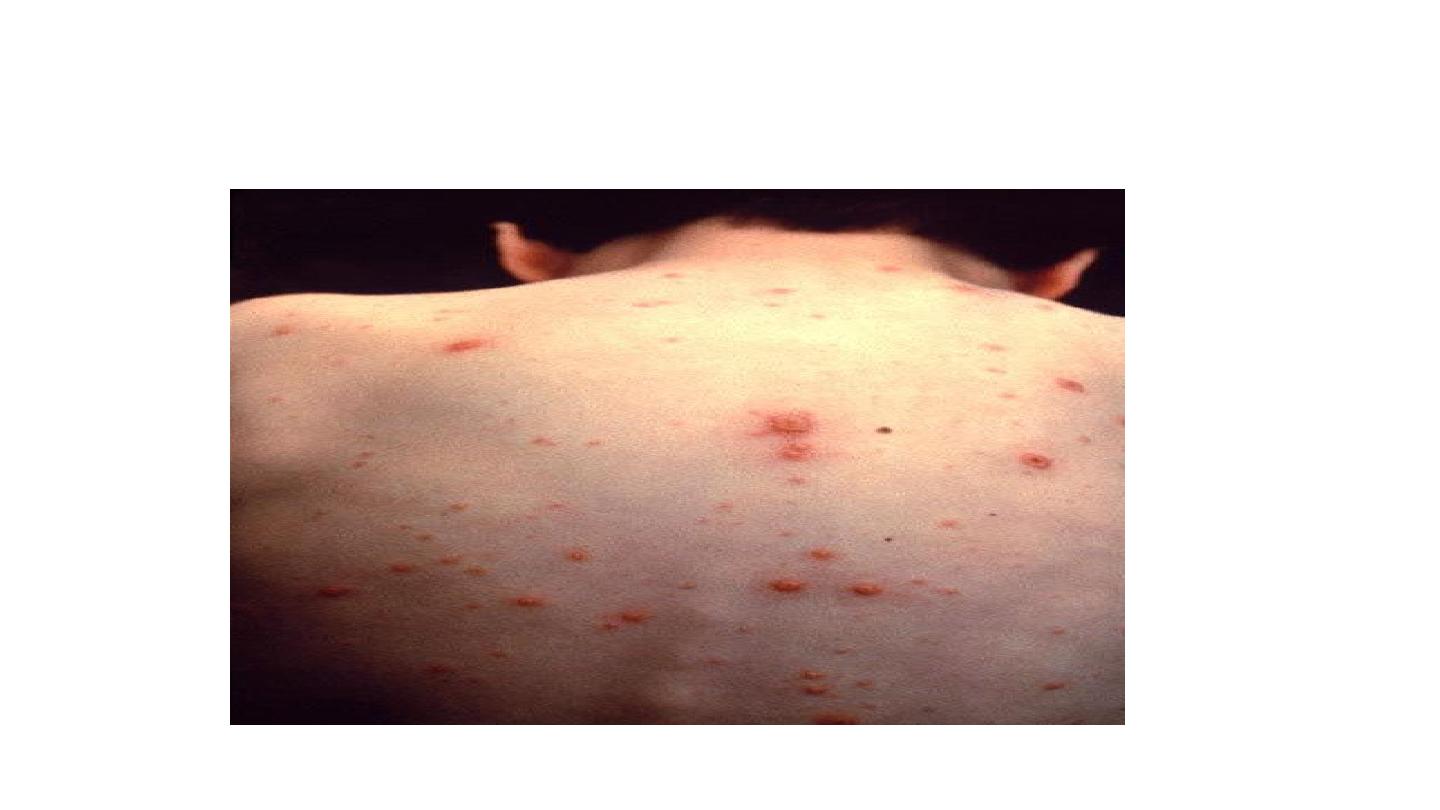
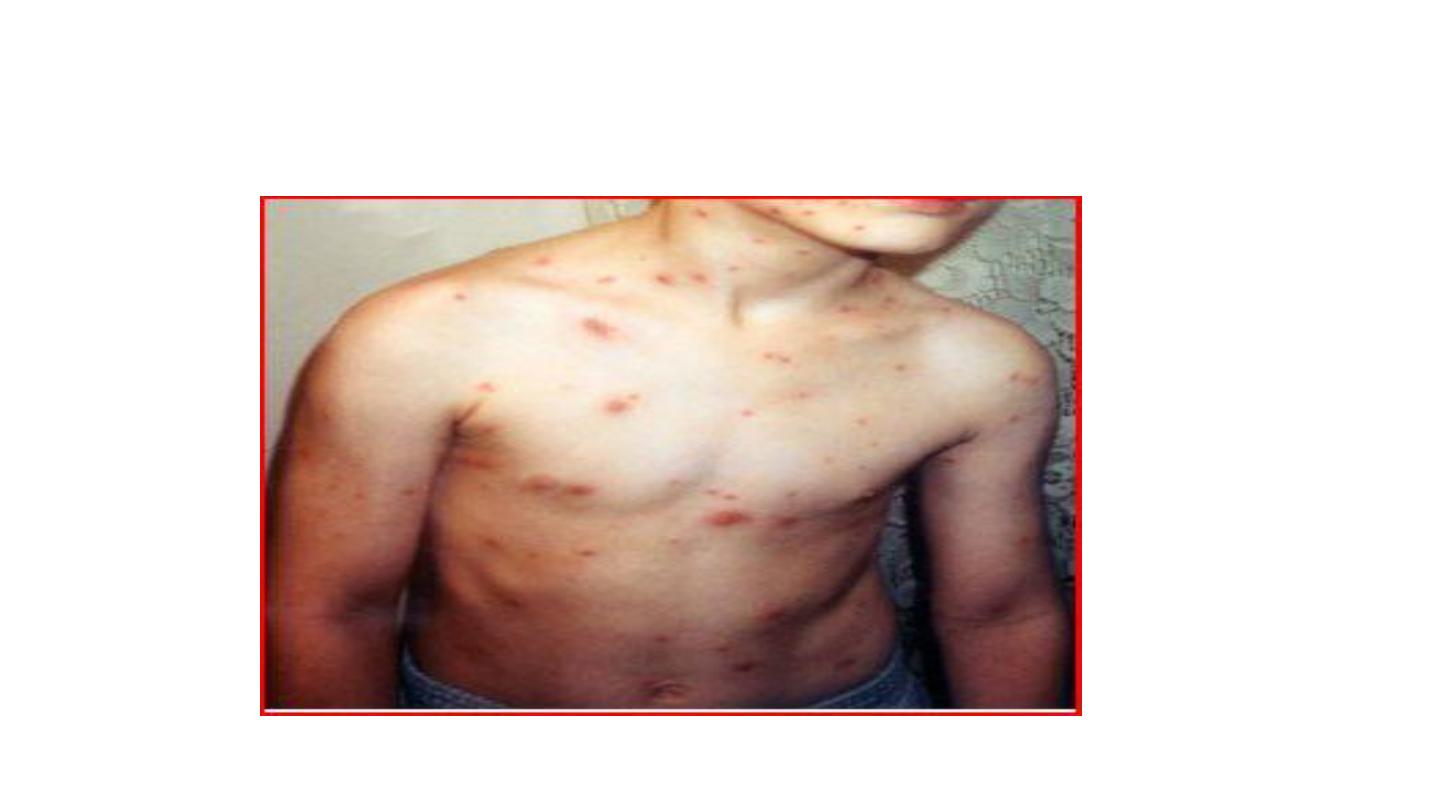
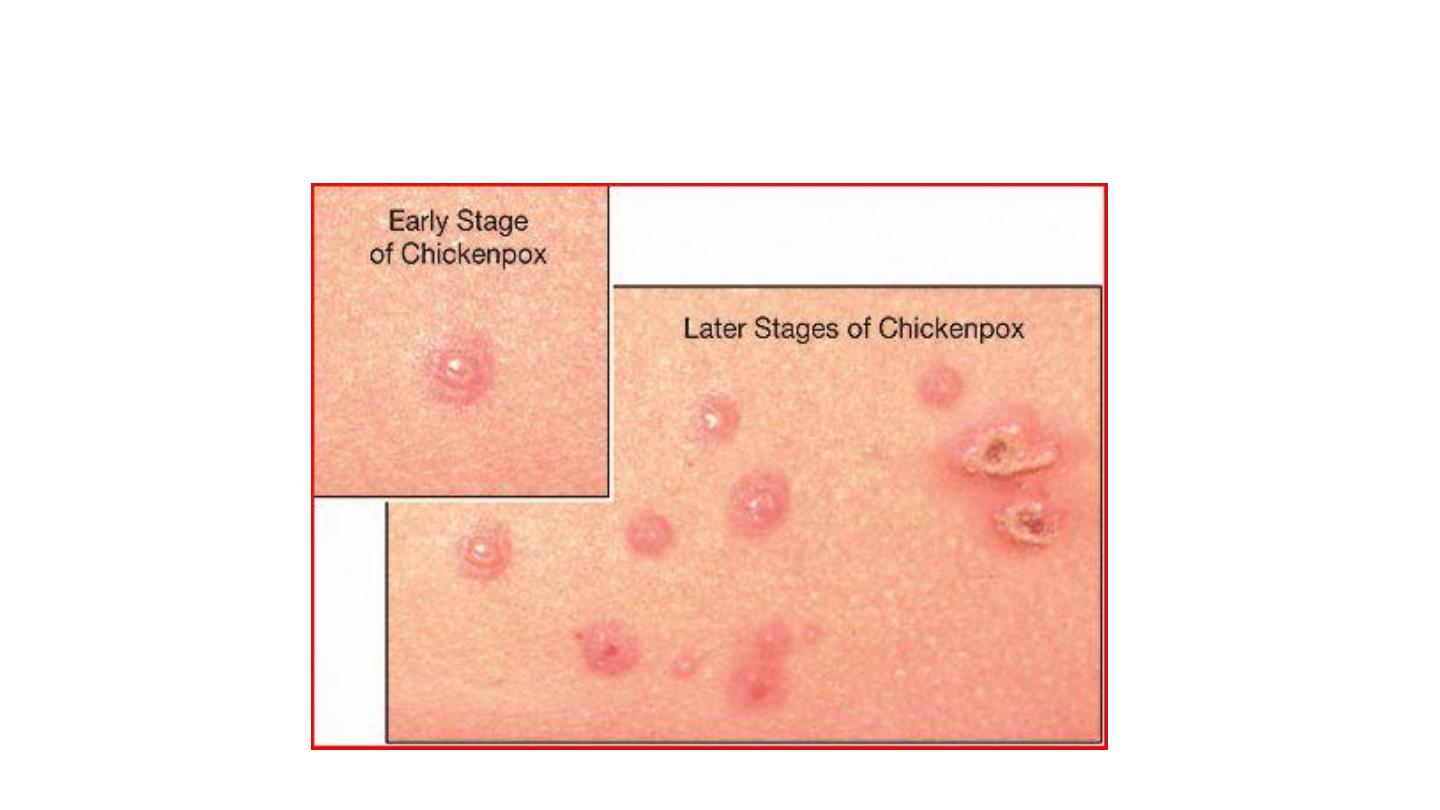
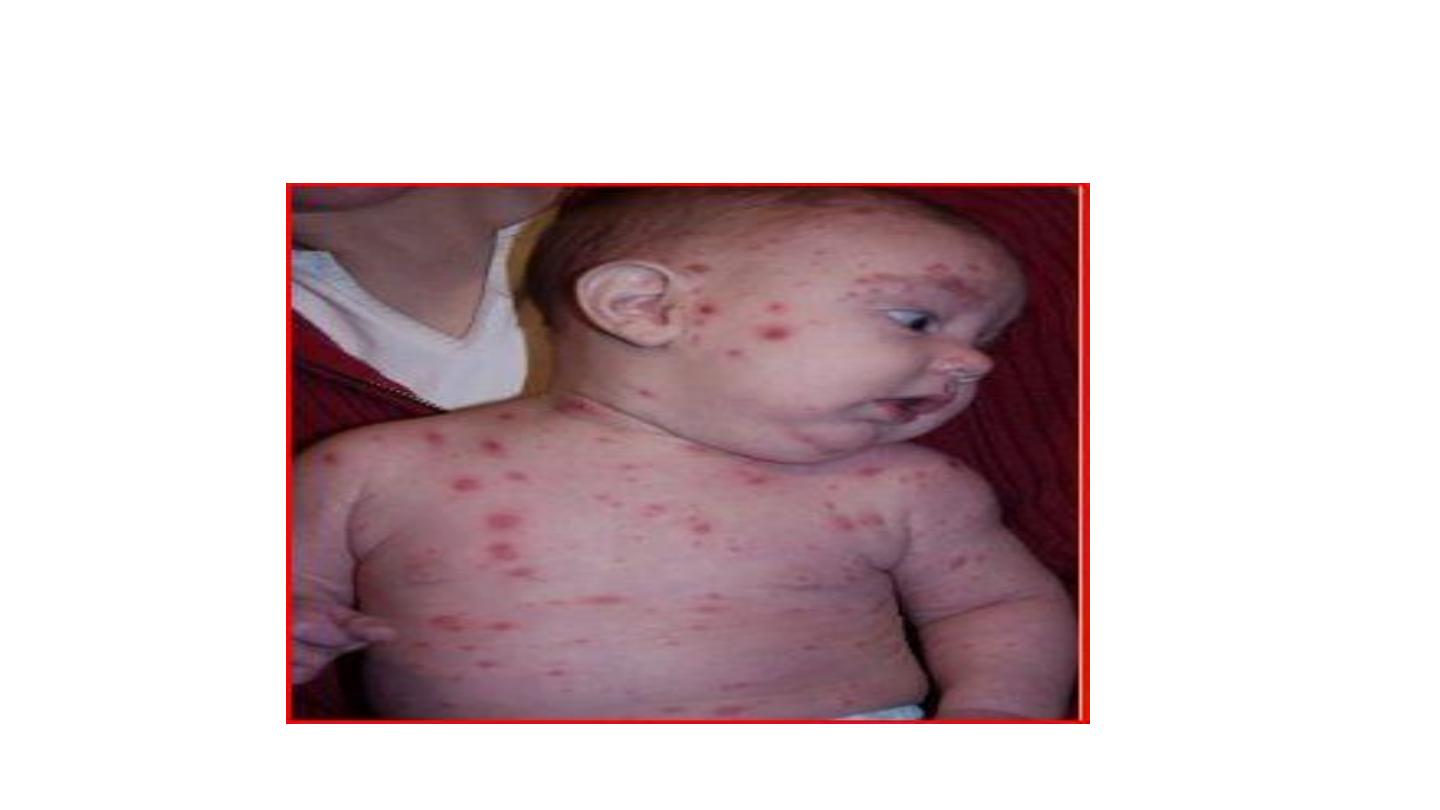
CHICKENPOX

Chicken pox

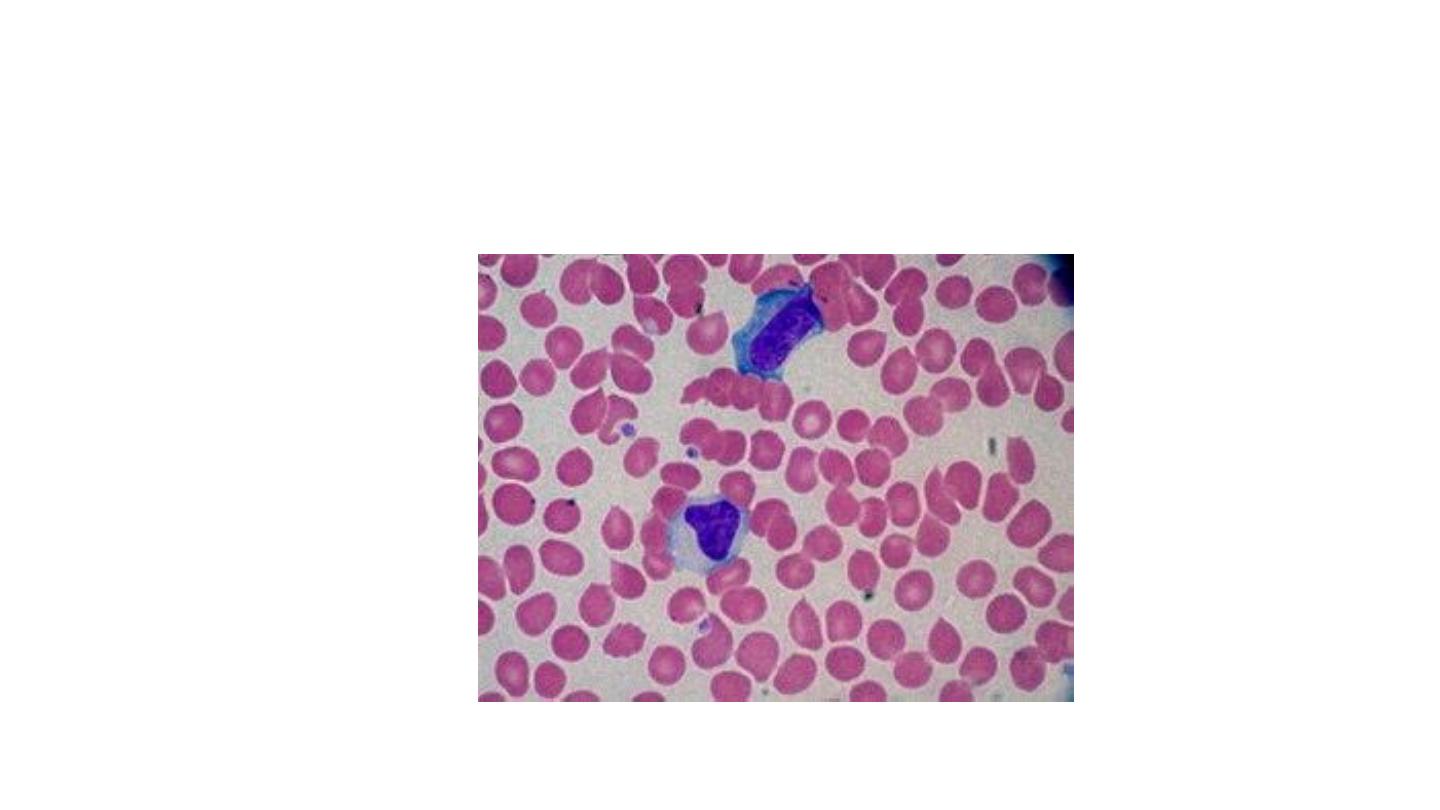
Infectious mononucleosis
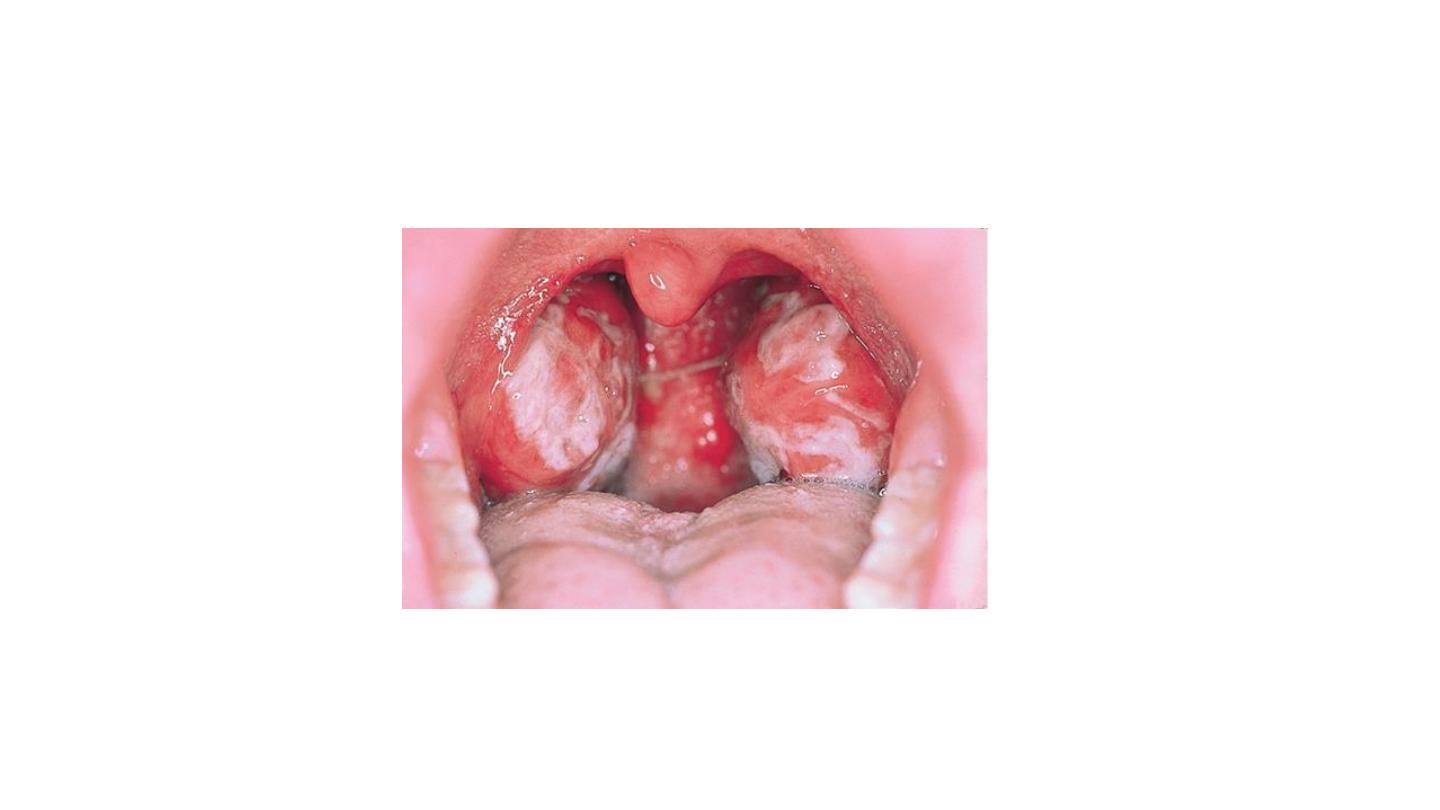
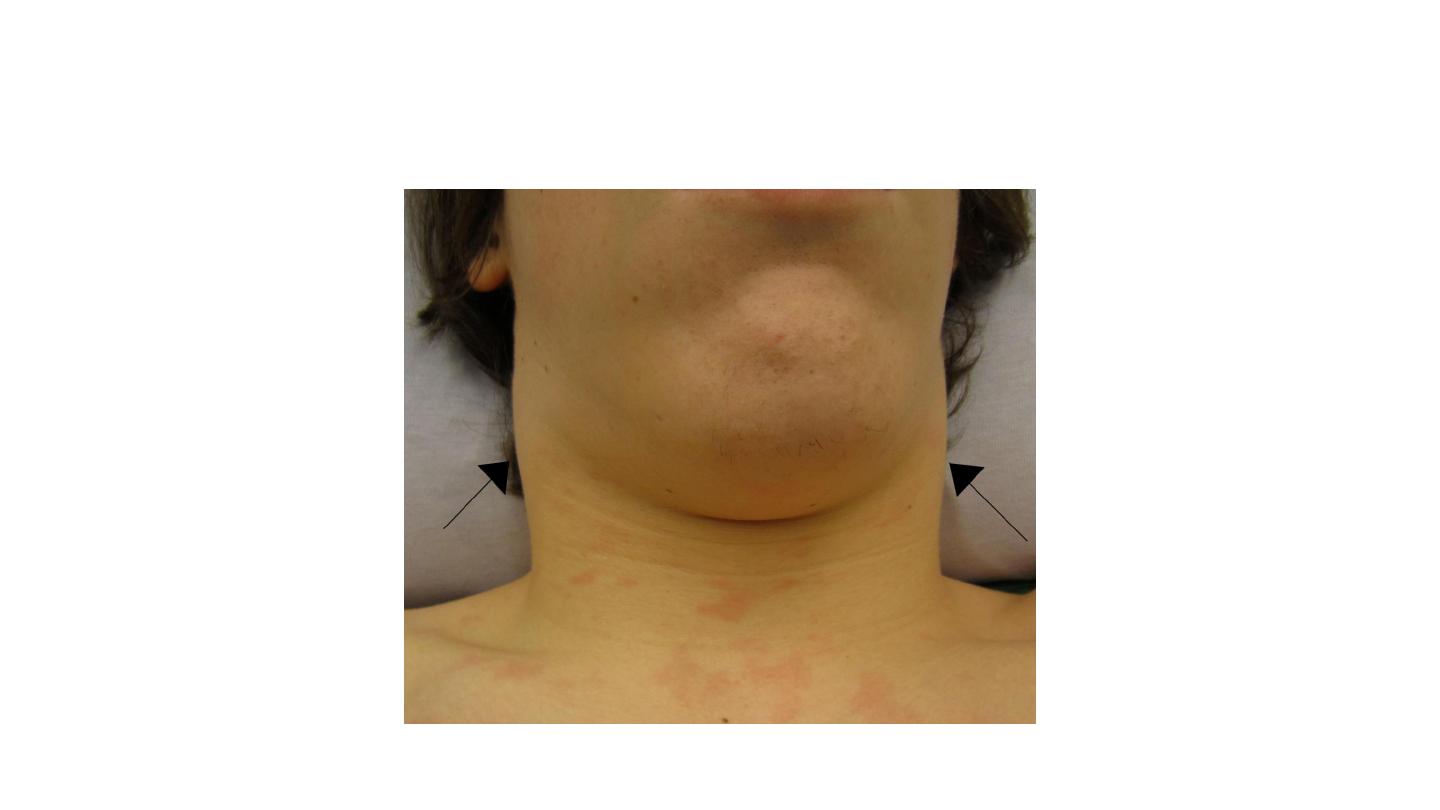
LYMPHADENOPATHY in IMN
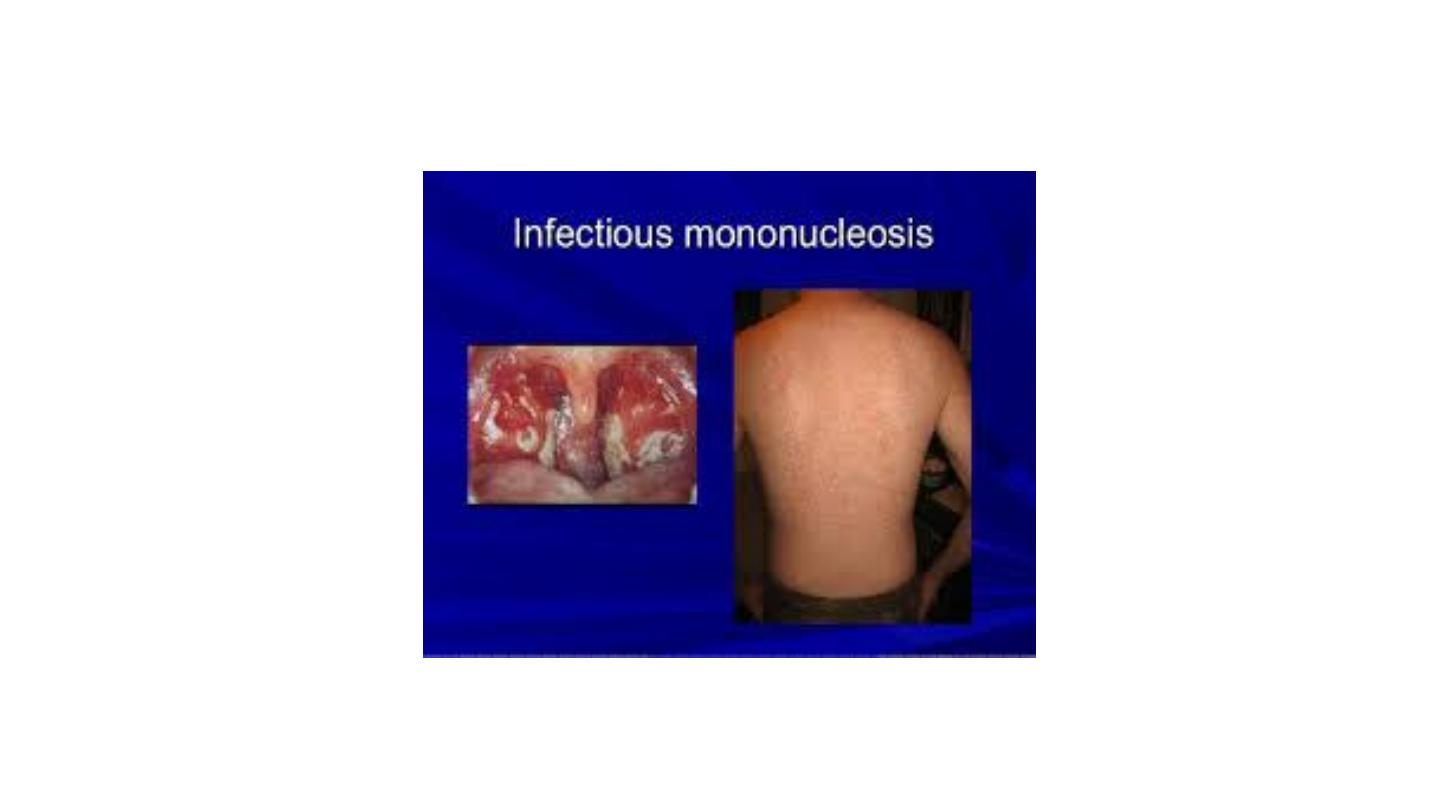
Rash of ampicillin in IMN,
TONSILLITIS
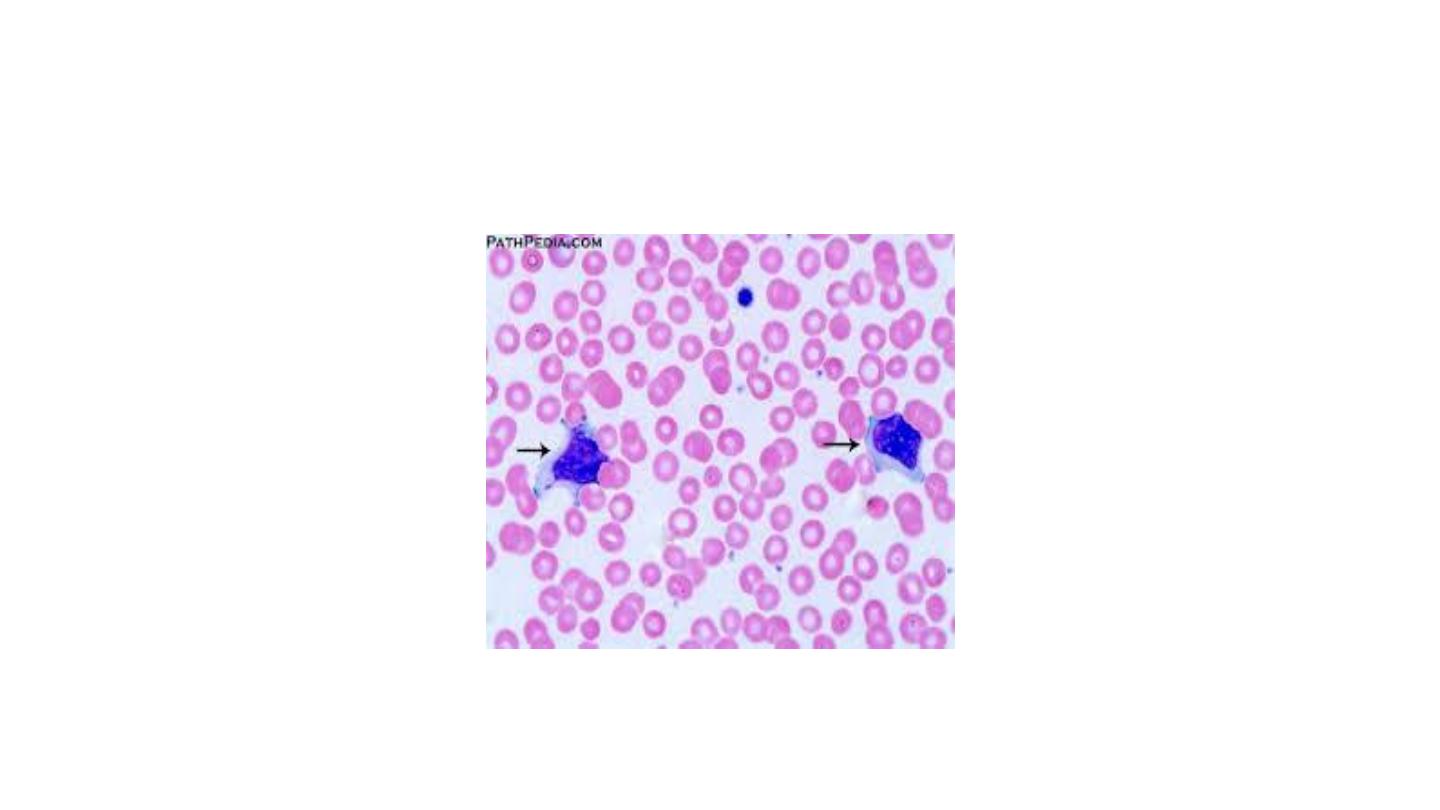
Atypical lymphocytes
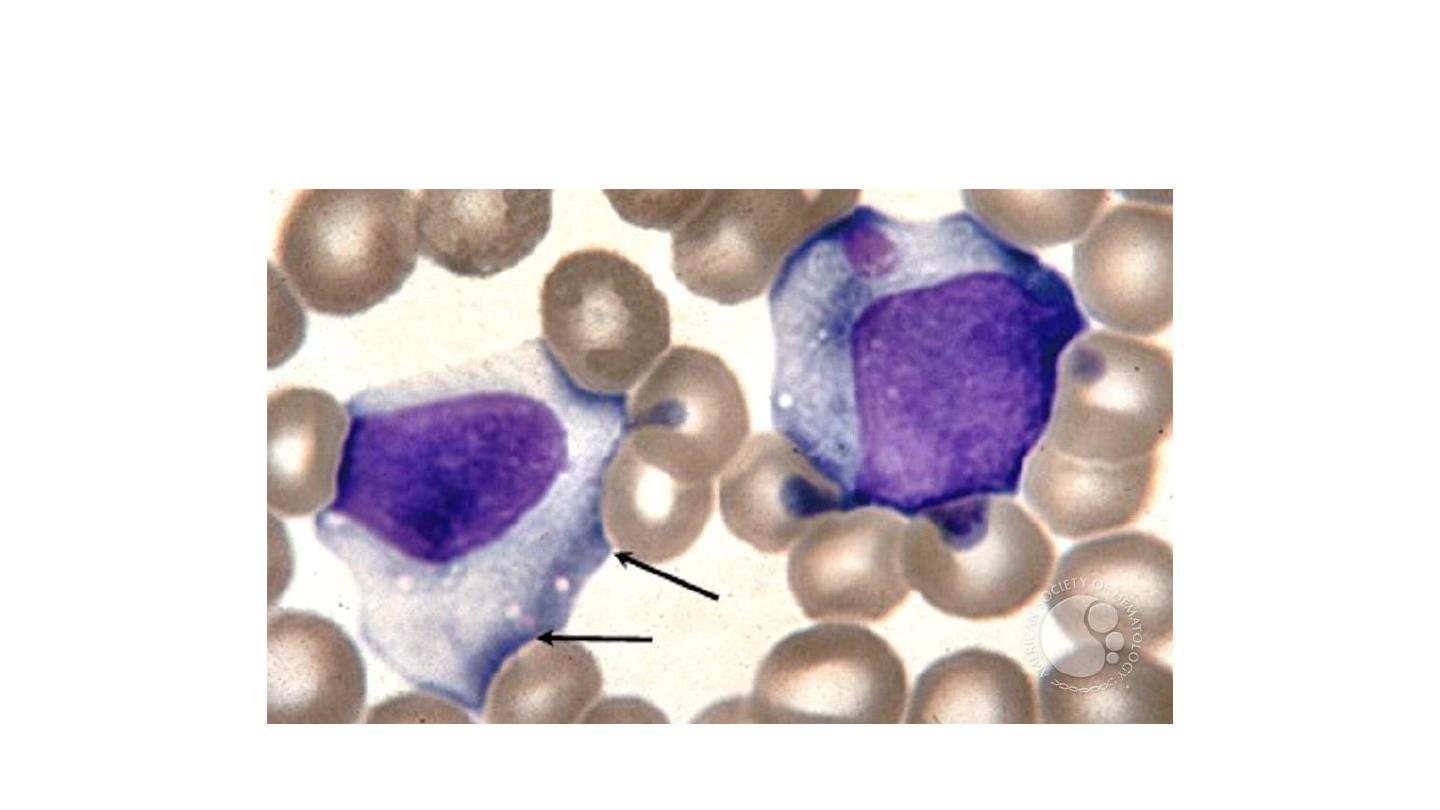
large cytoplasm,nucleoli in the nucleus, indented
by surrounding RBCs

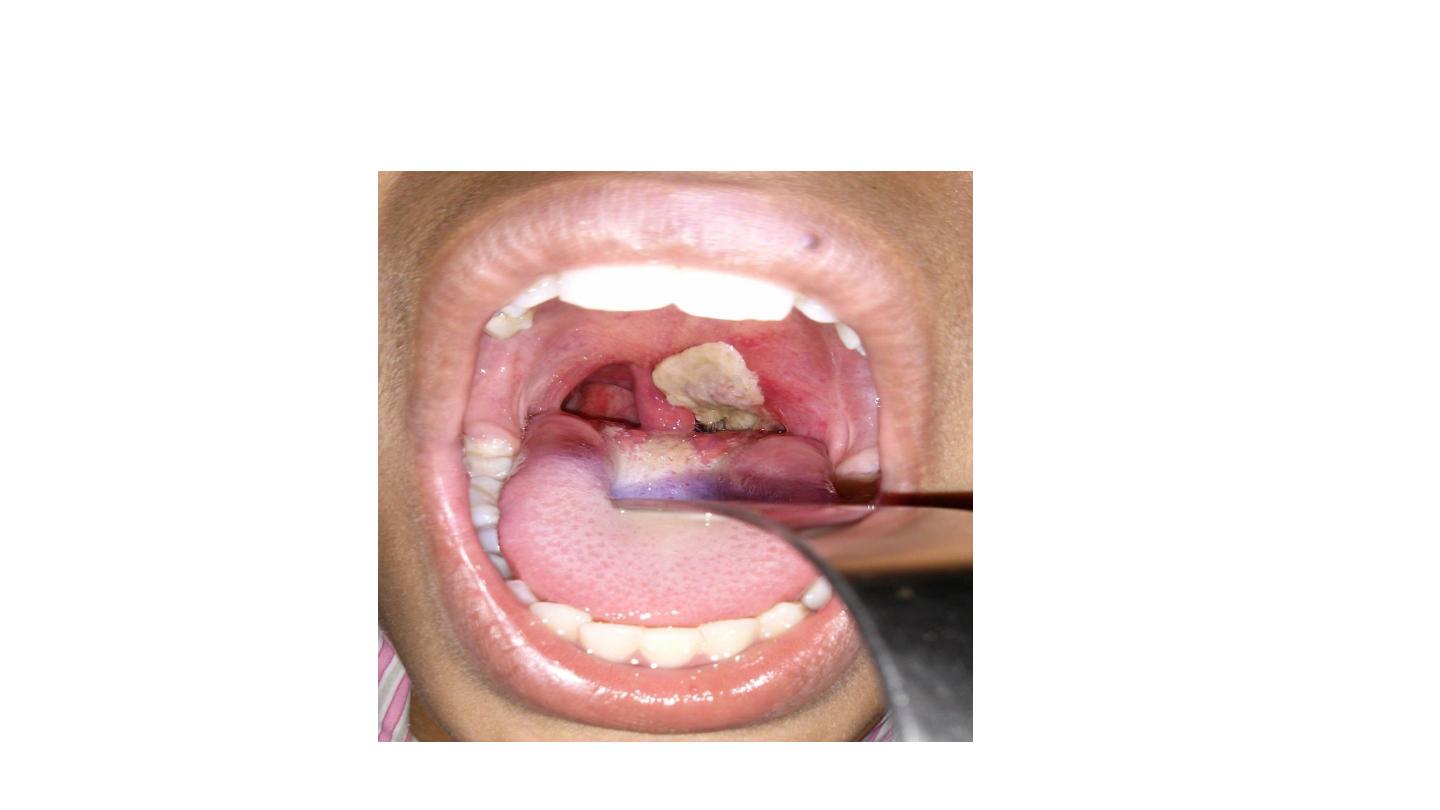
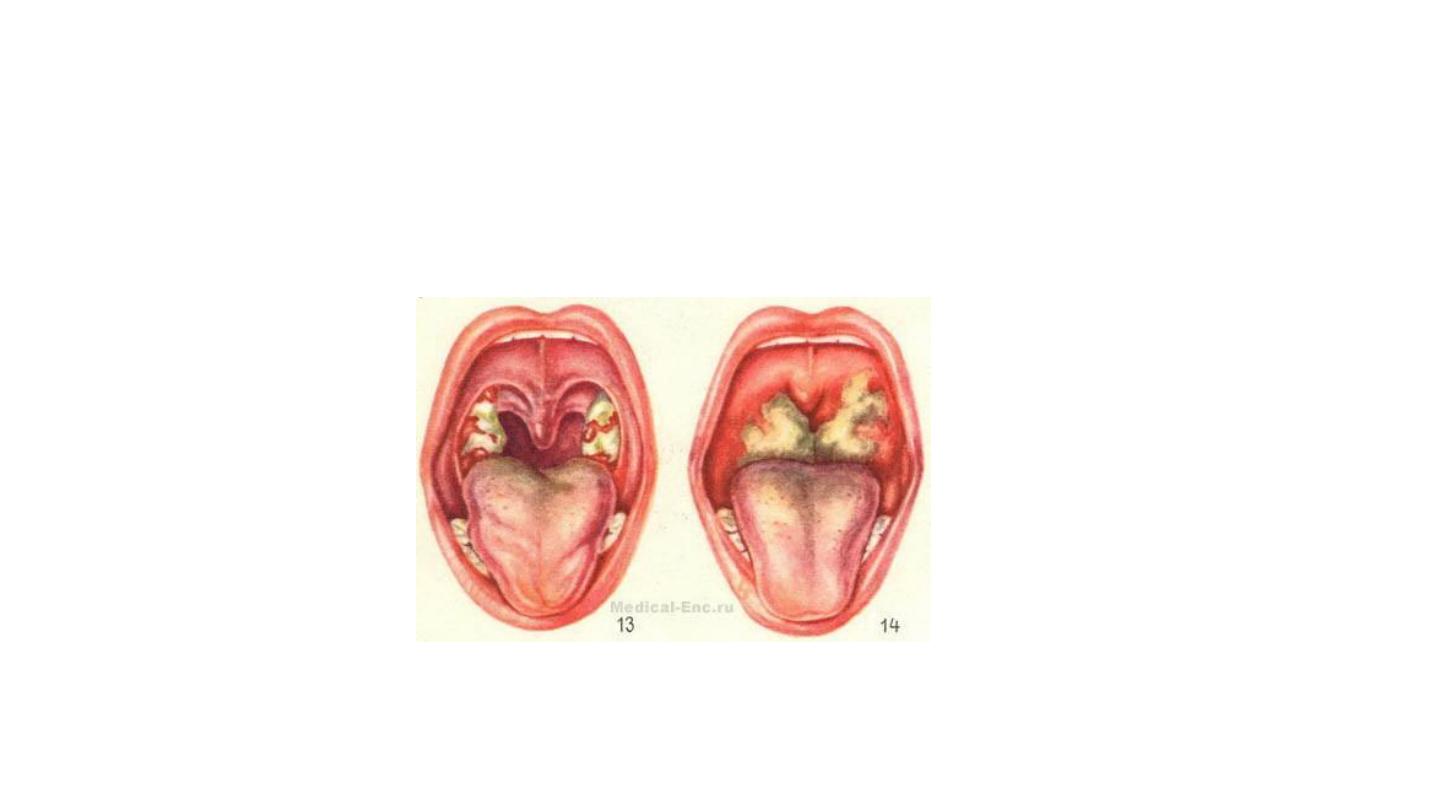
Diphtheria
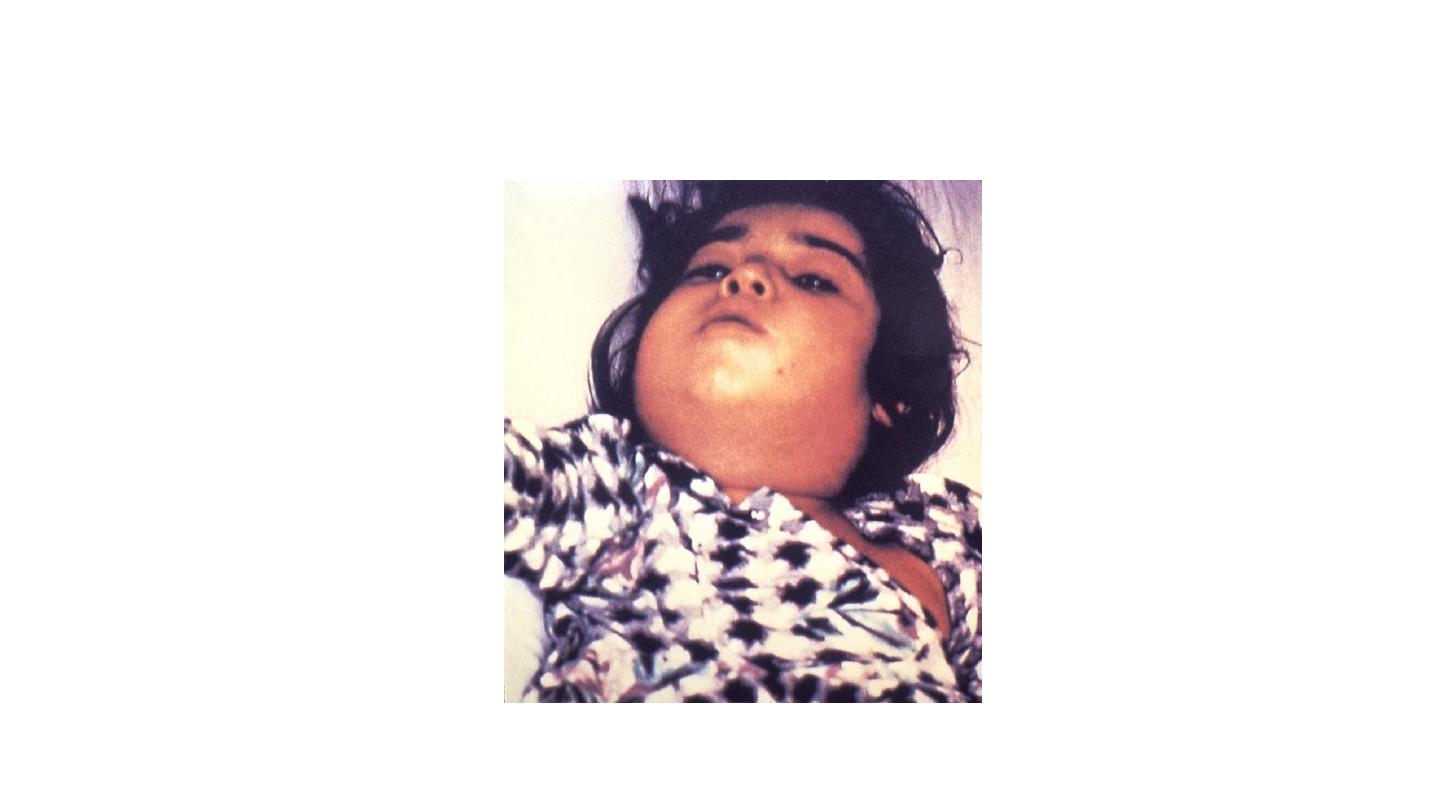
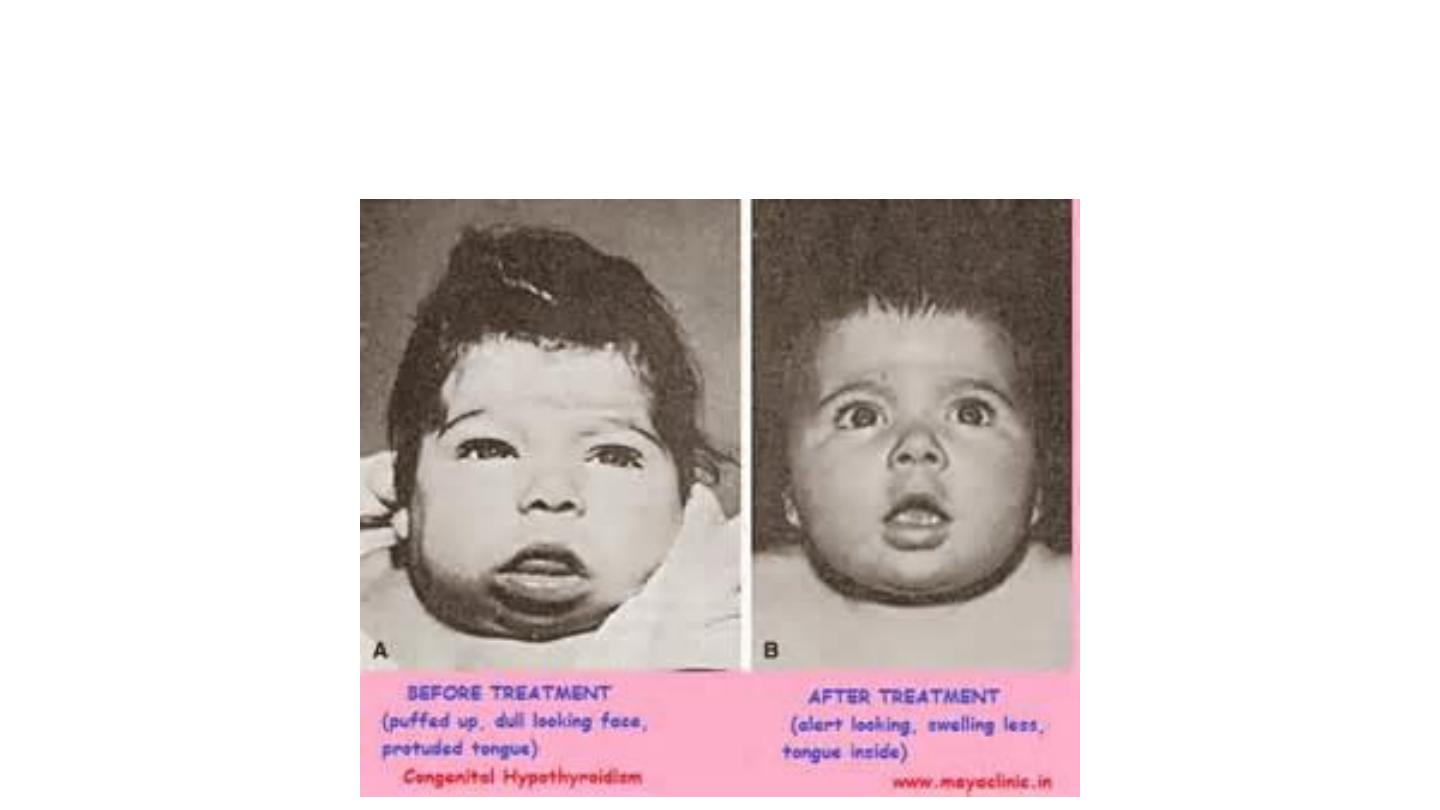
Congenital hypothyroidism
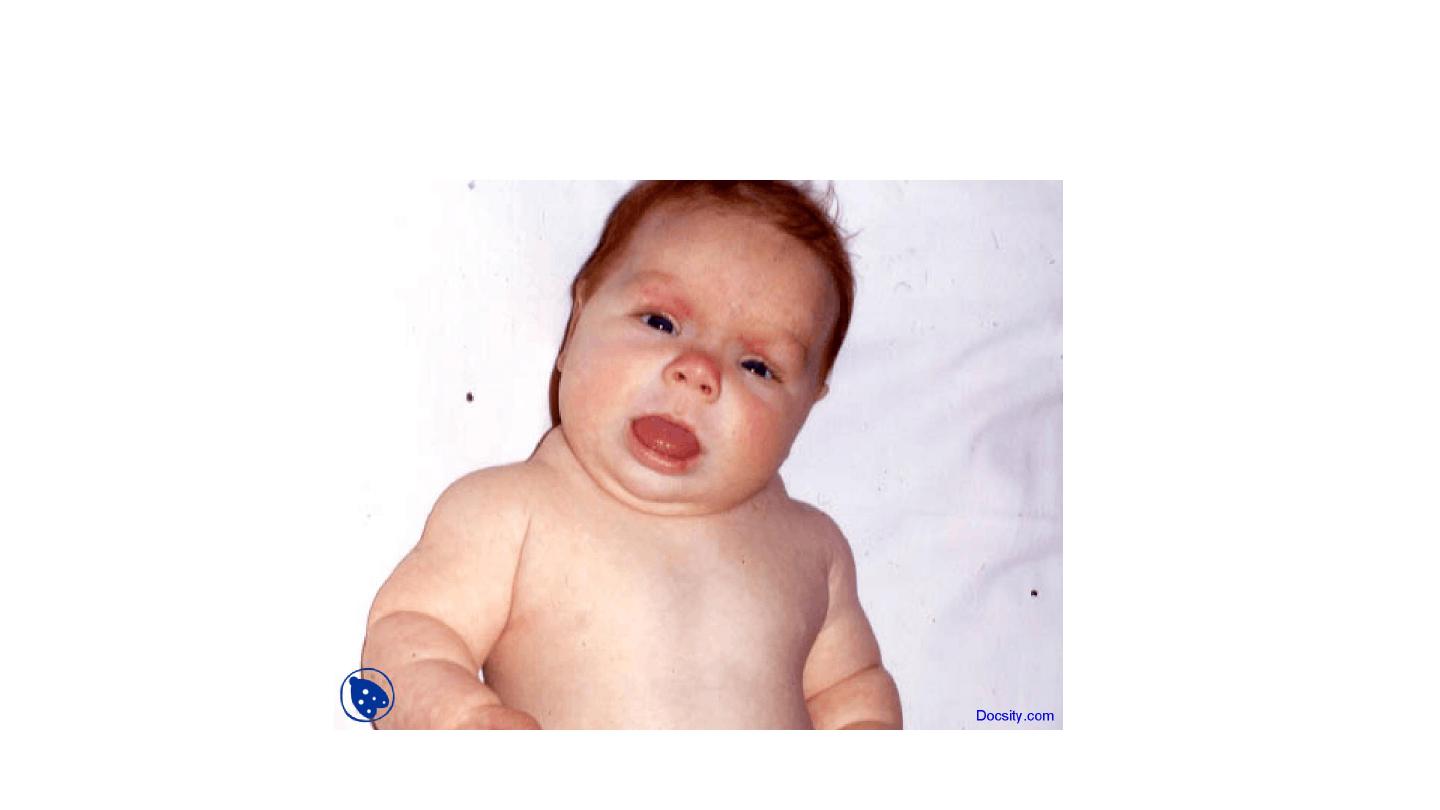
Congenital hypothyroidism
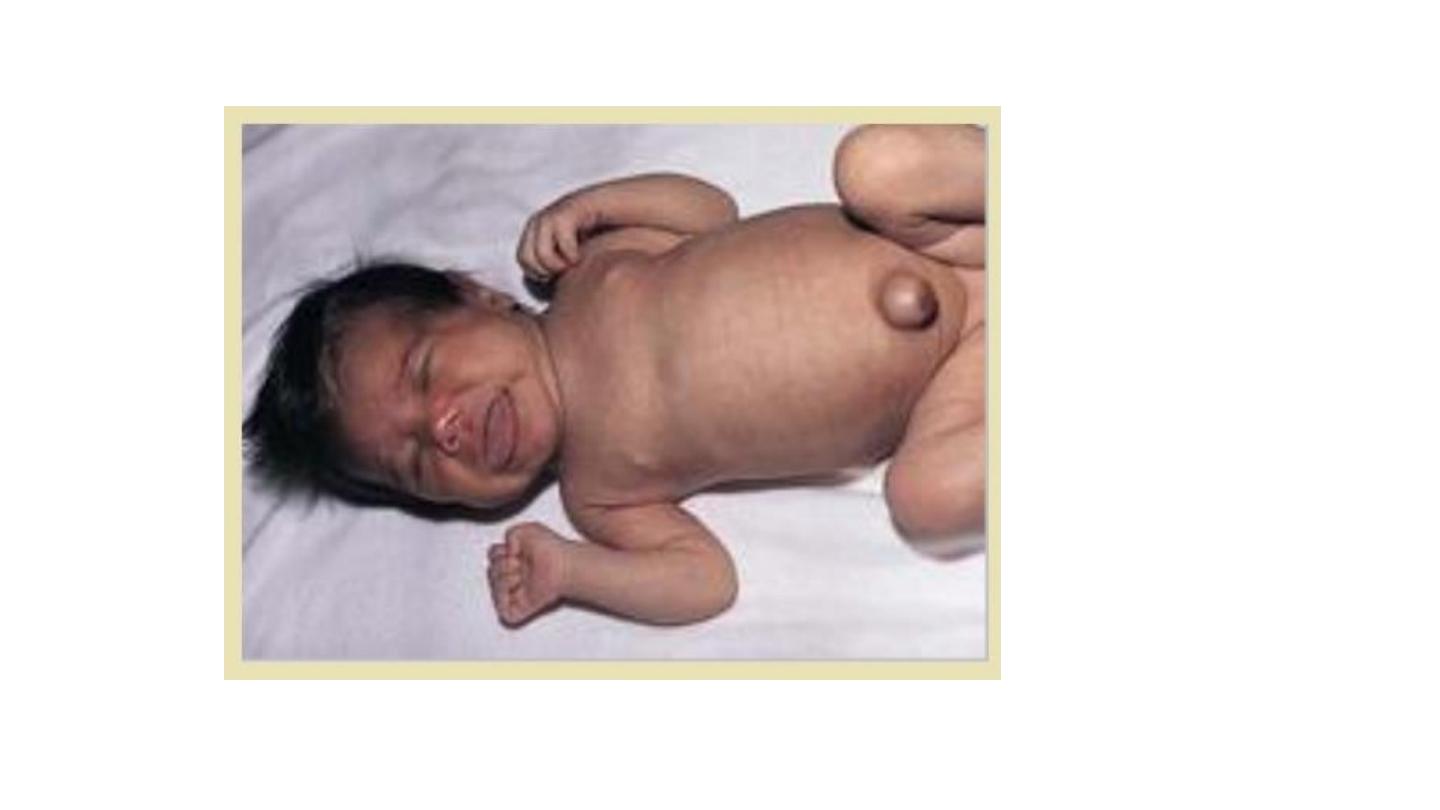
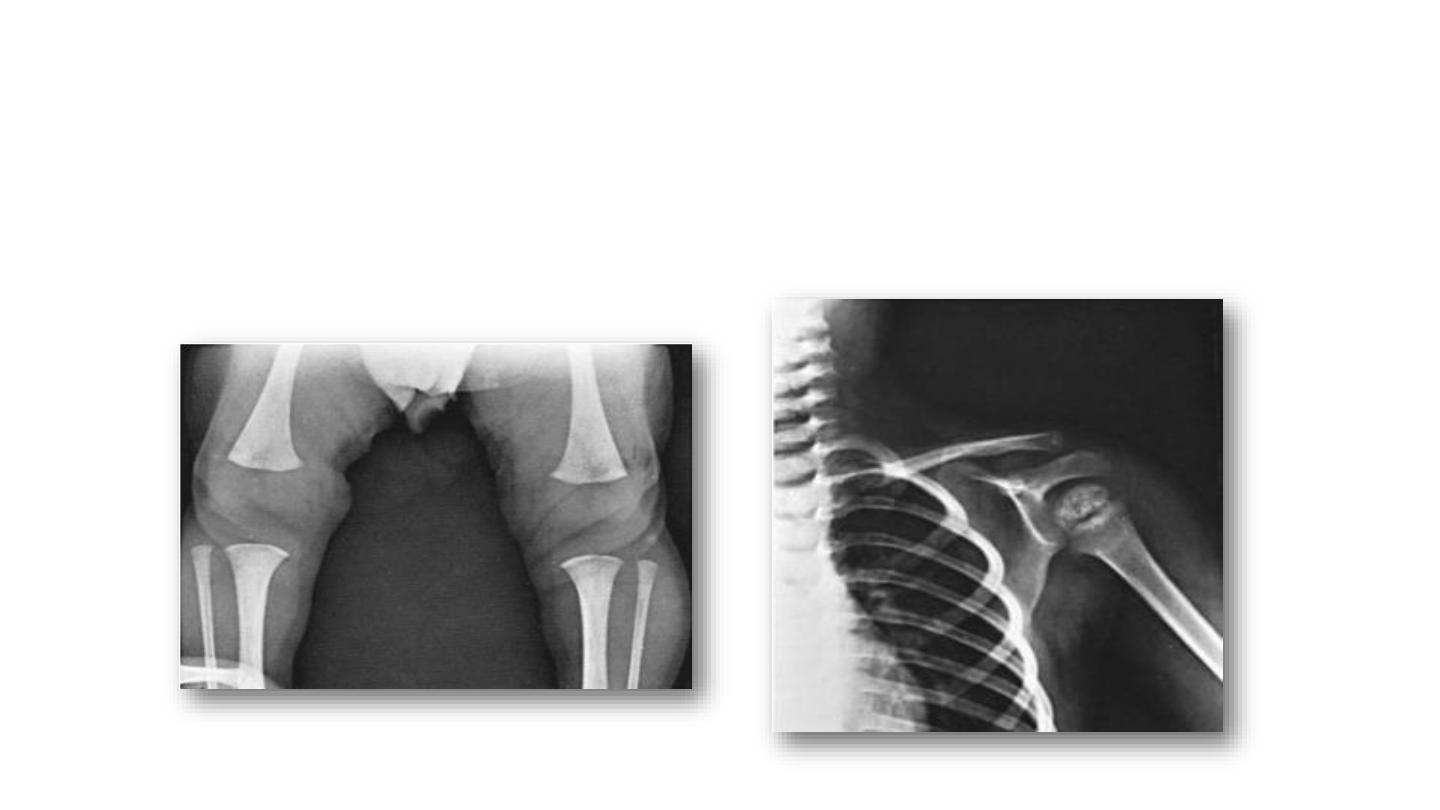
Epiphyseal dysplasia
• Absent femoral epiphysis
Congenital hypothyroidism

Renal
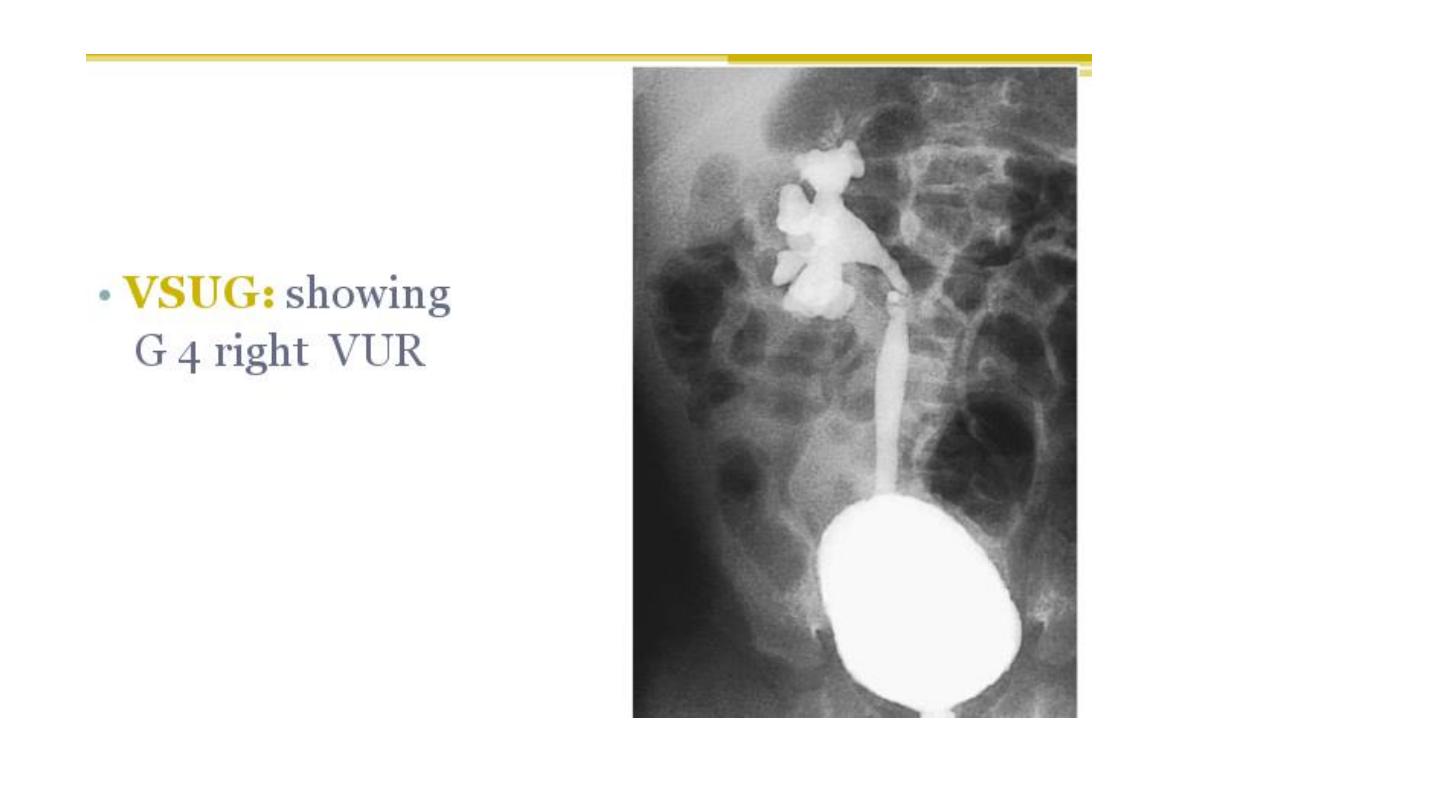
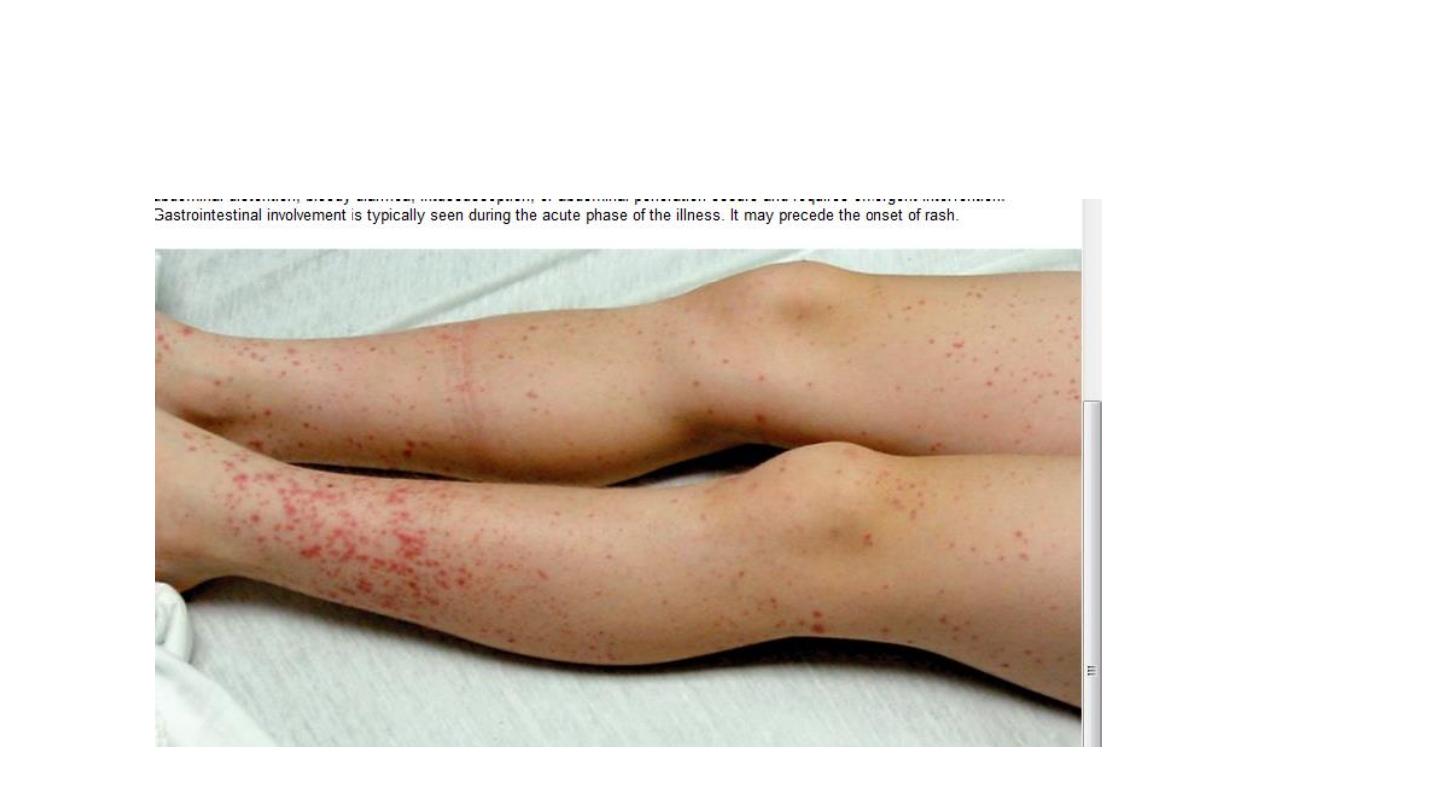
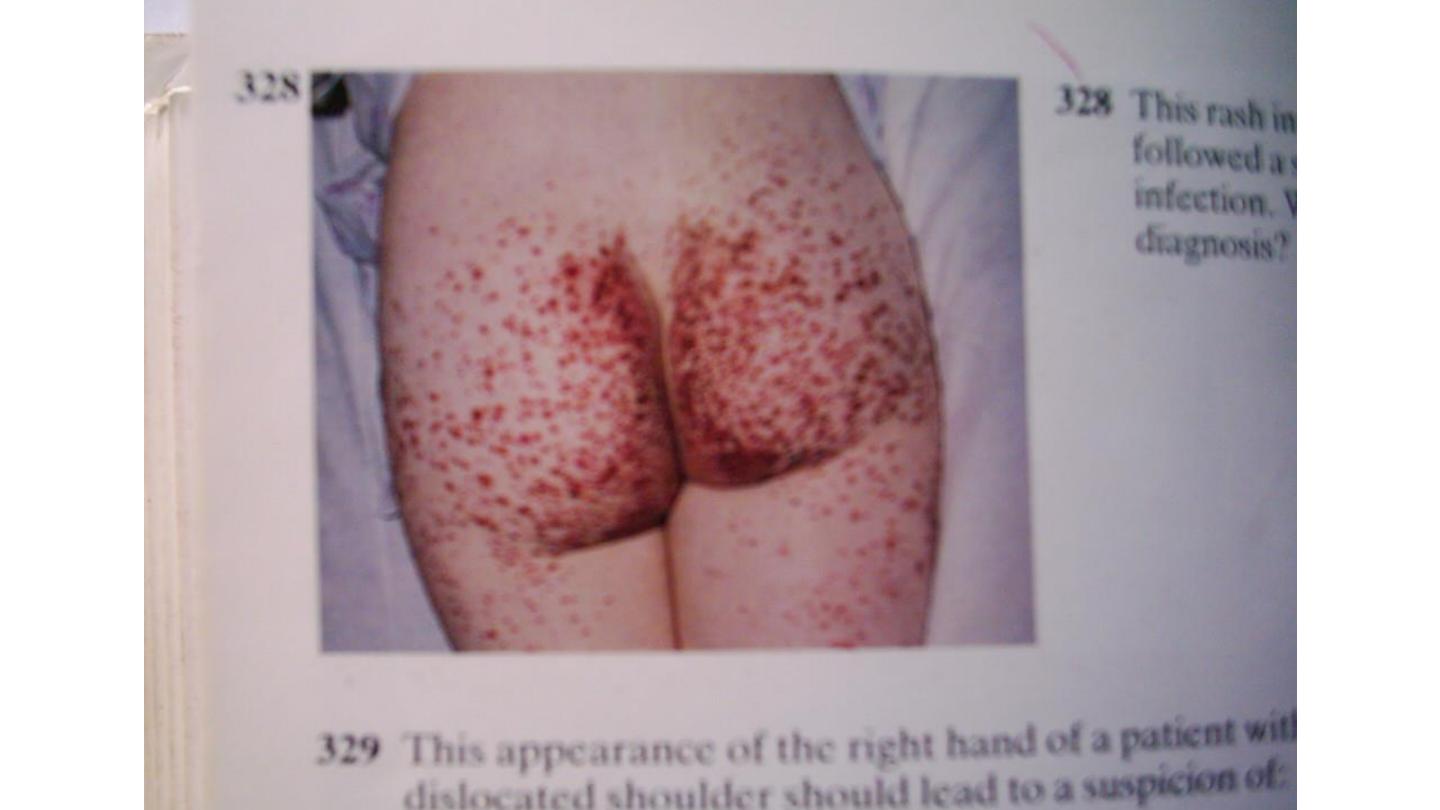
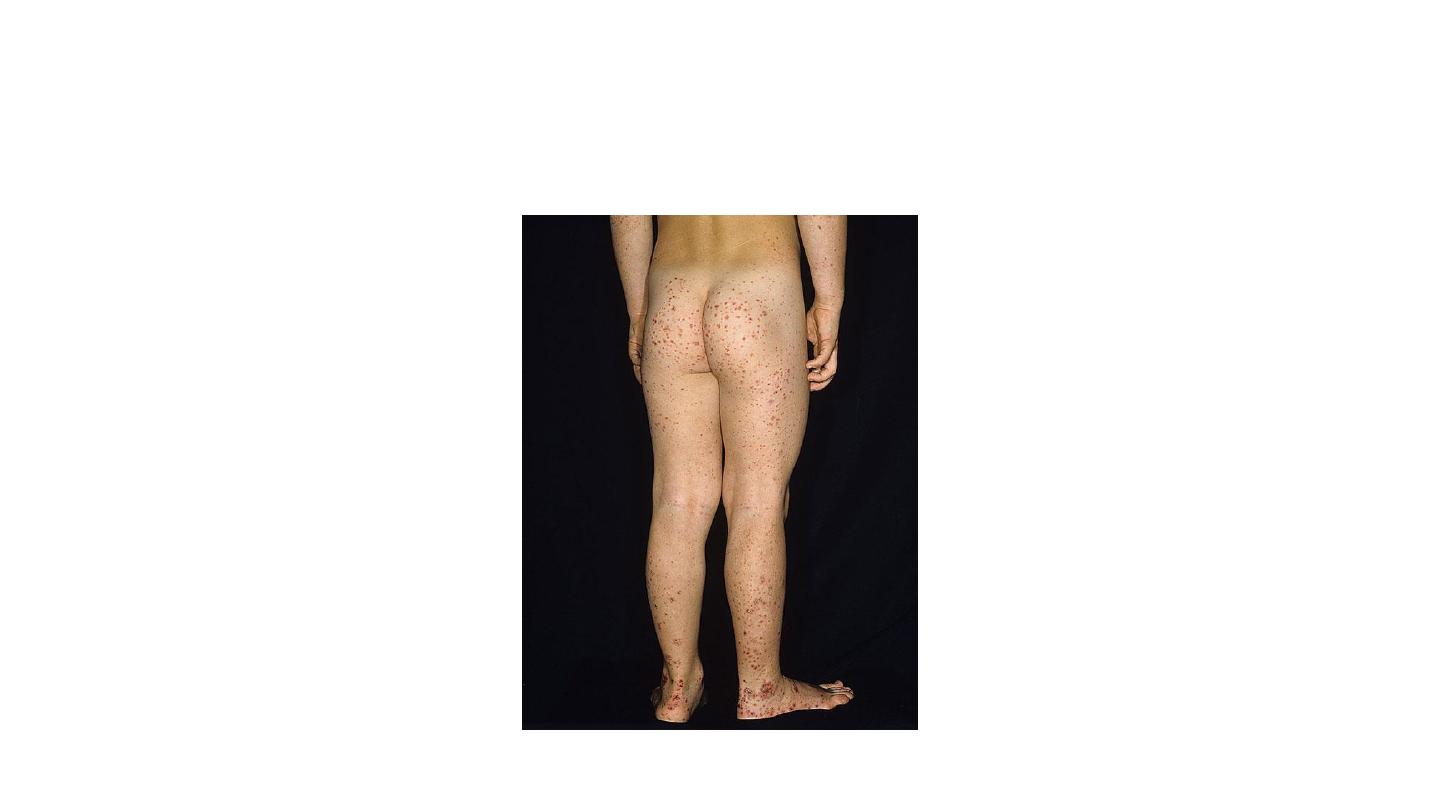
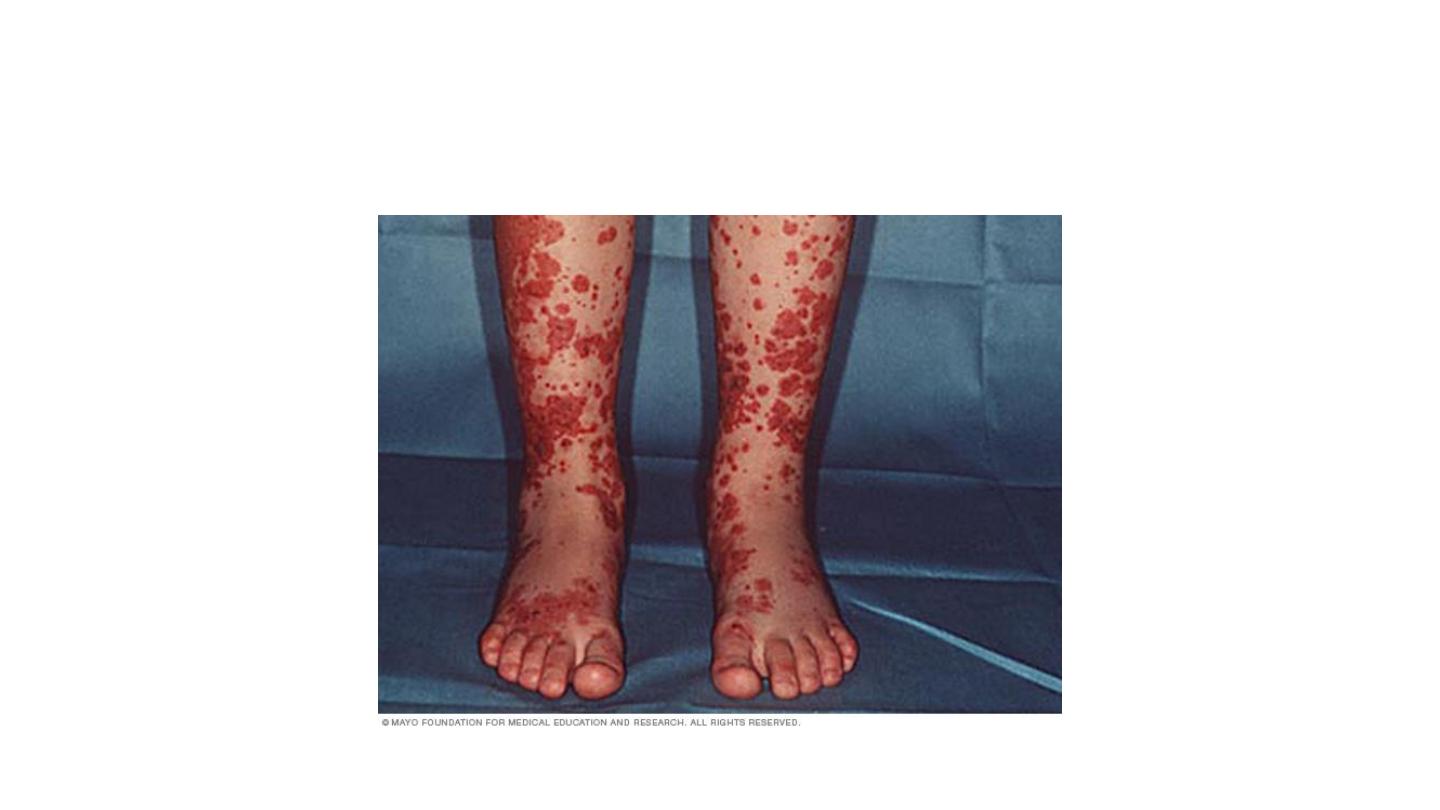
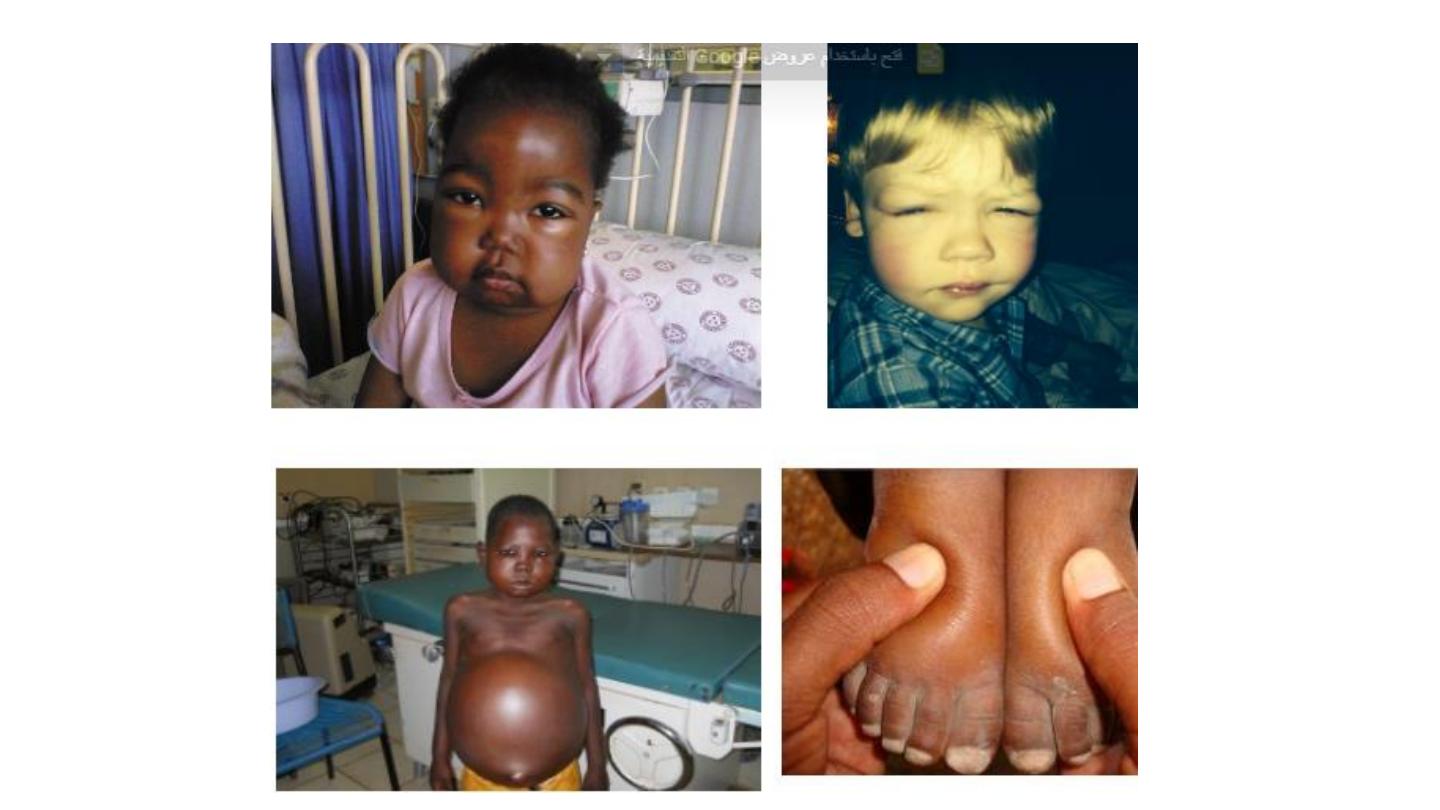
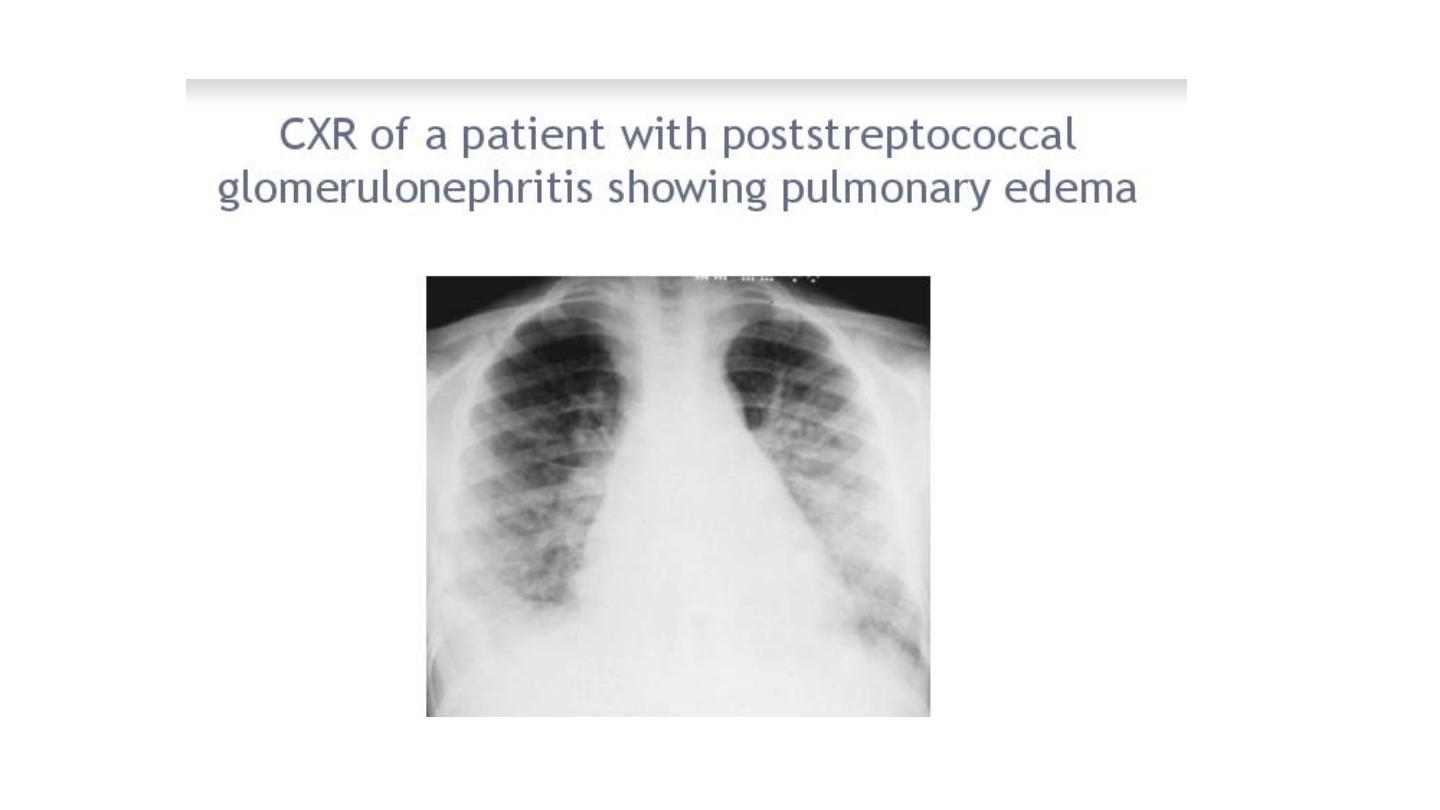
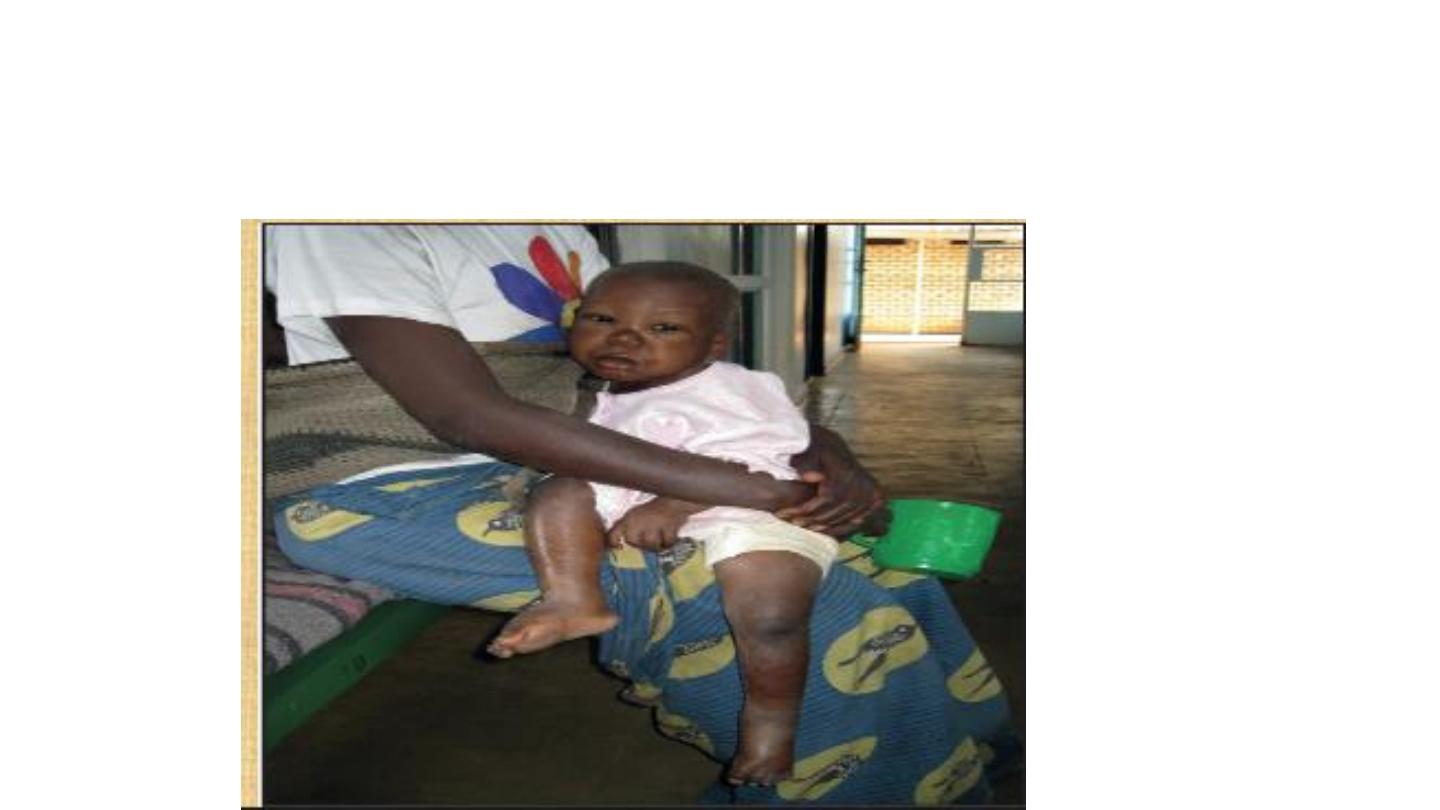
Henoch scoline purpura
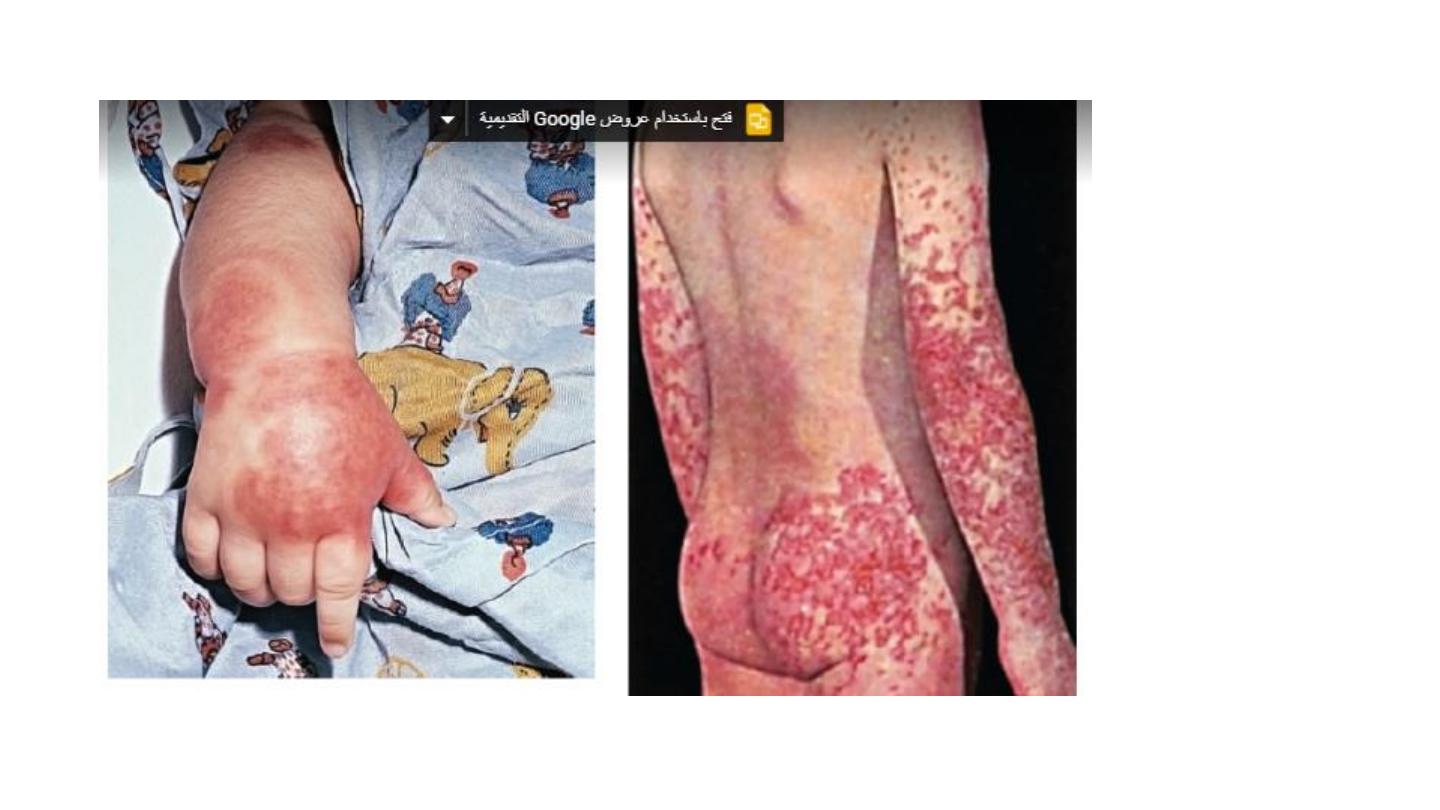
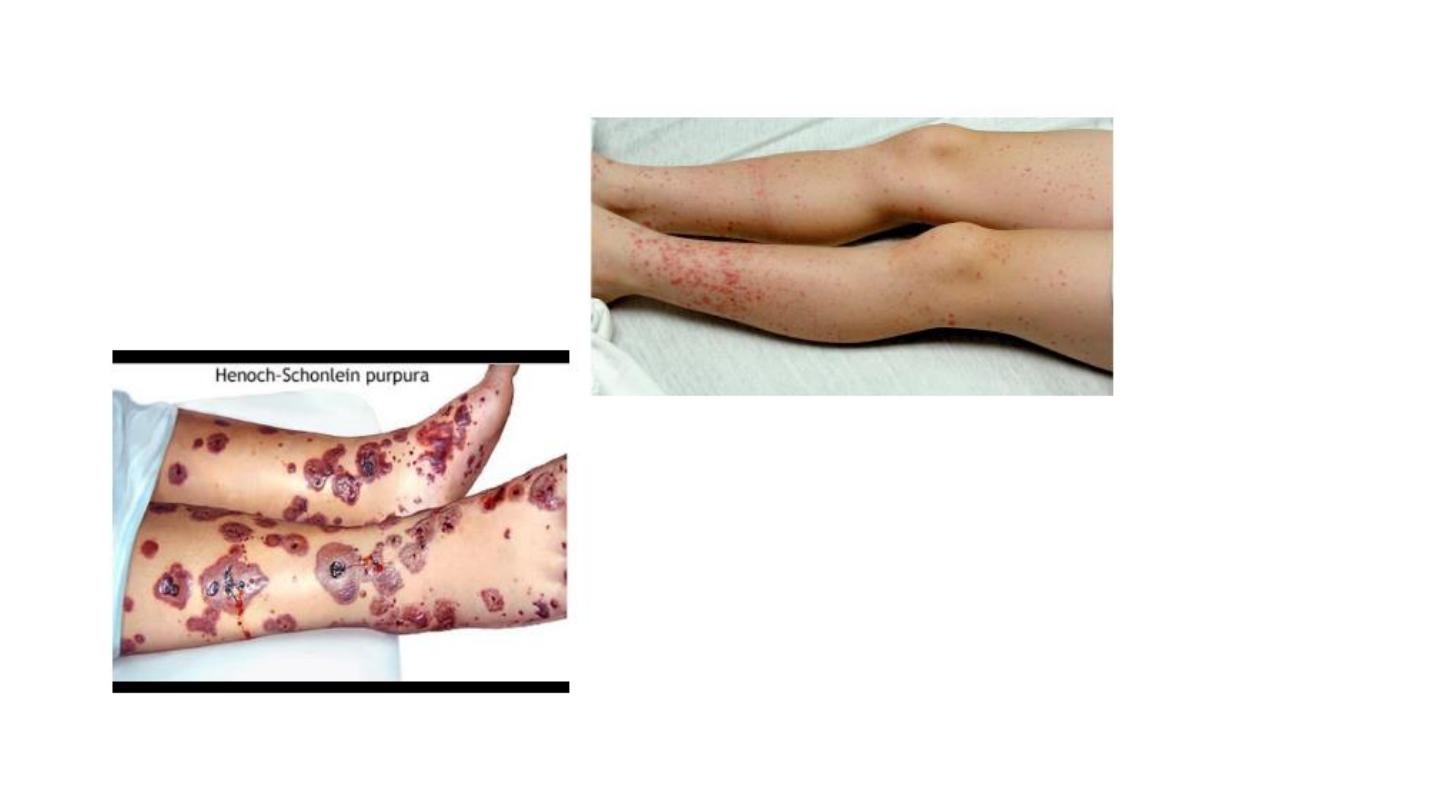
N.S
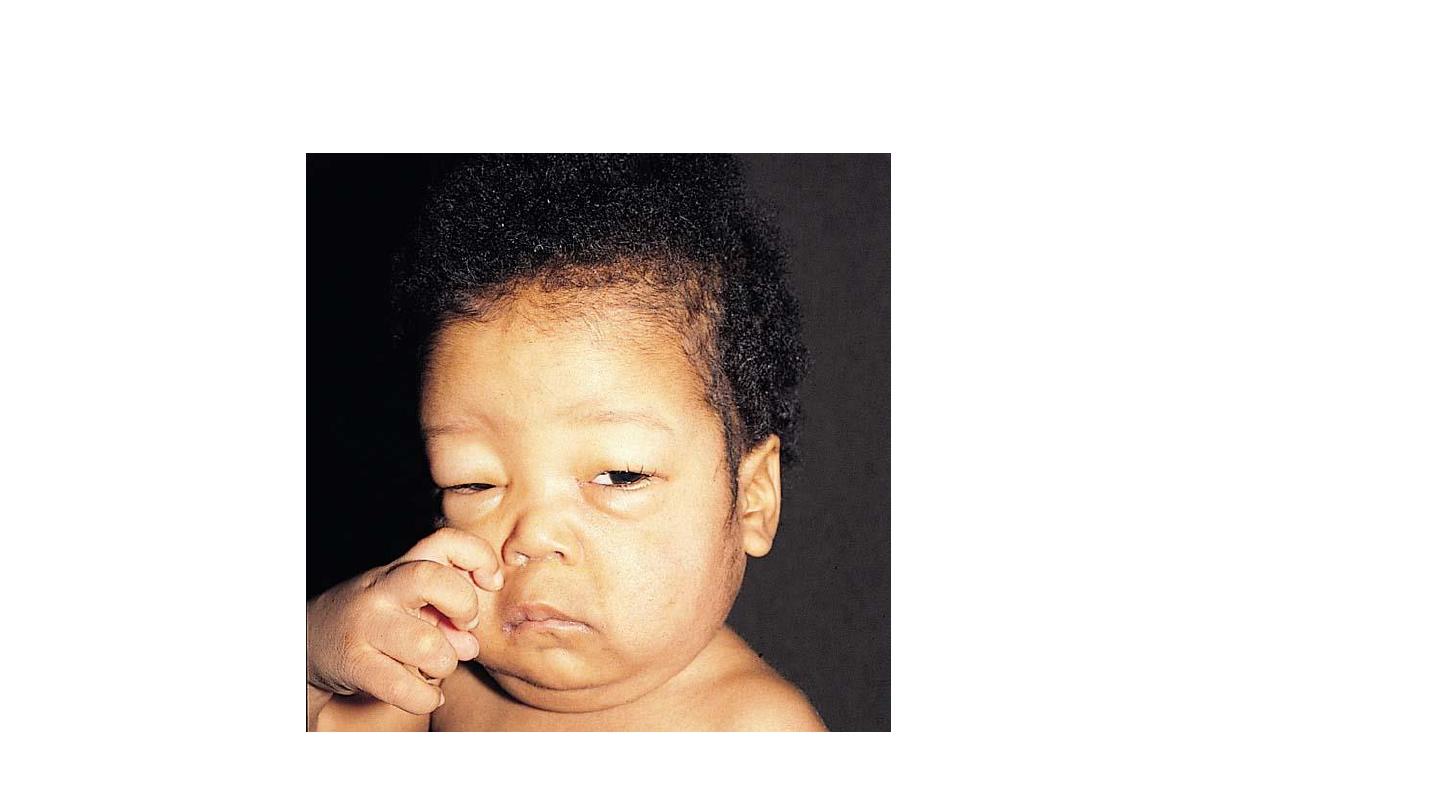
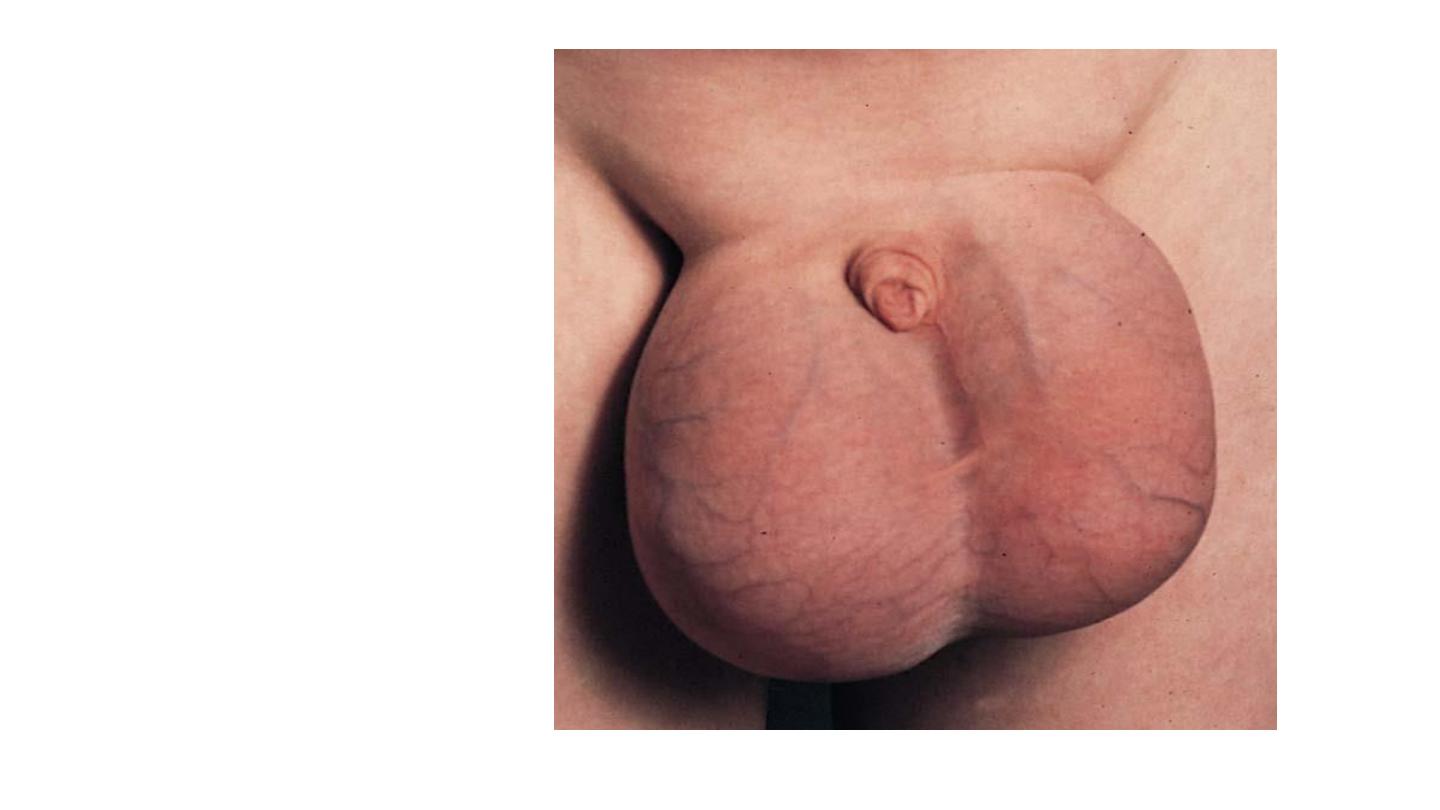
• Scrotal edema
• In NS
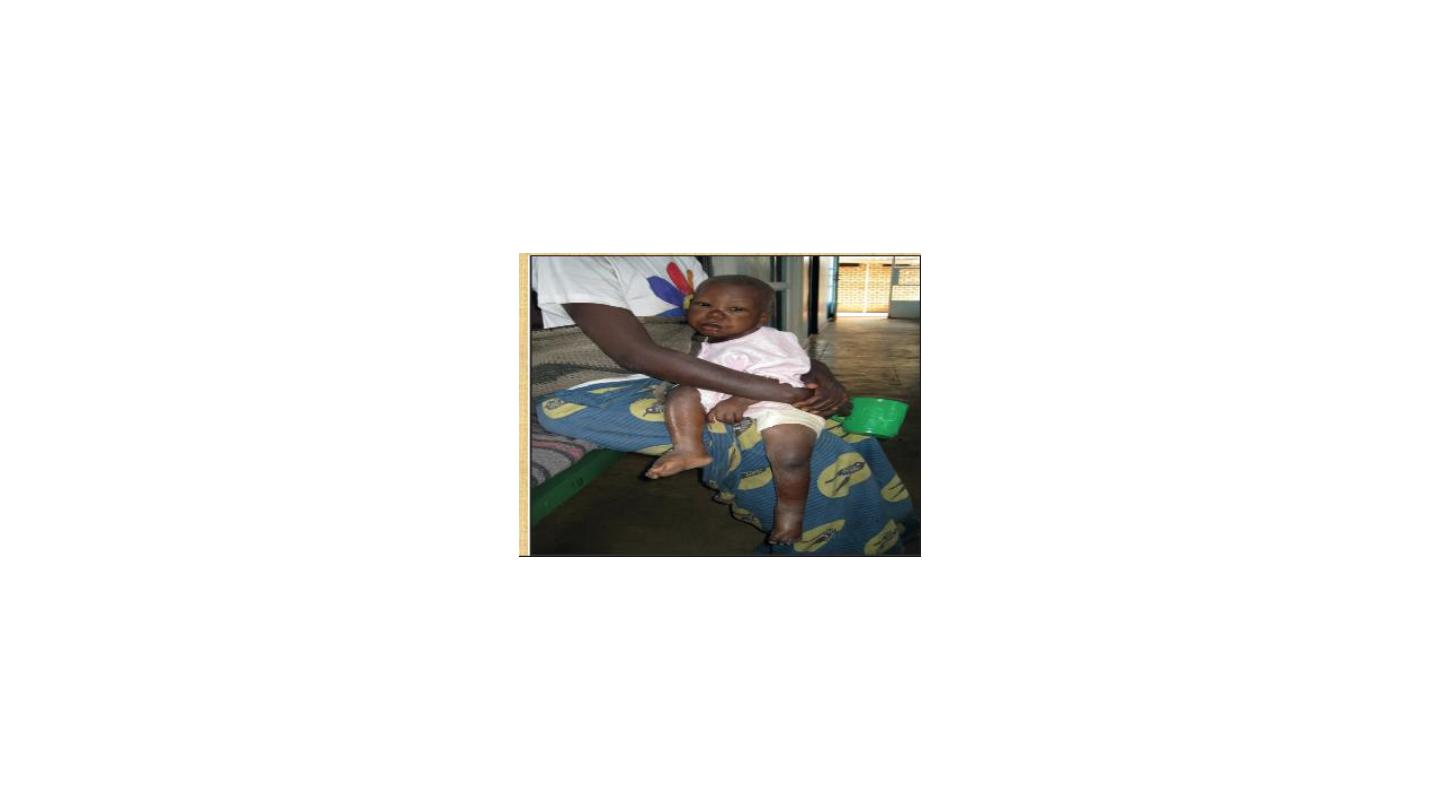

GIT
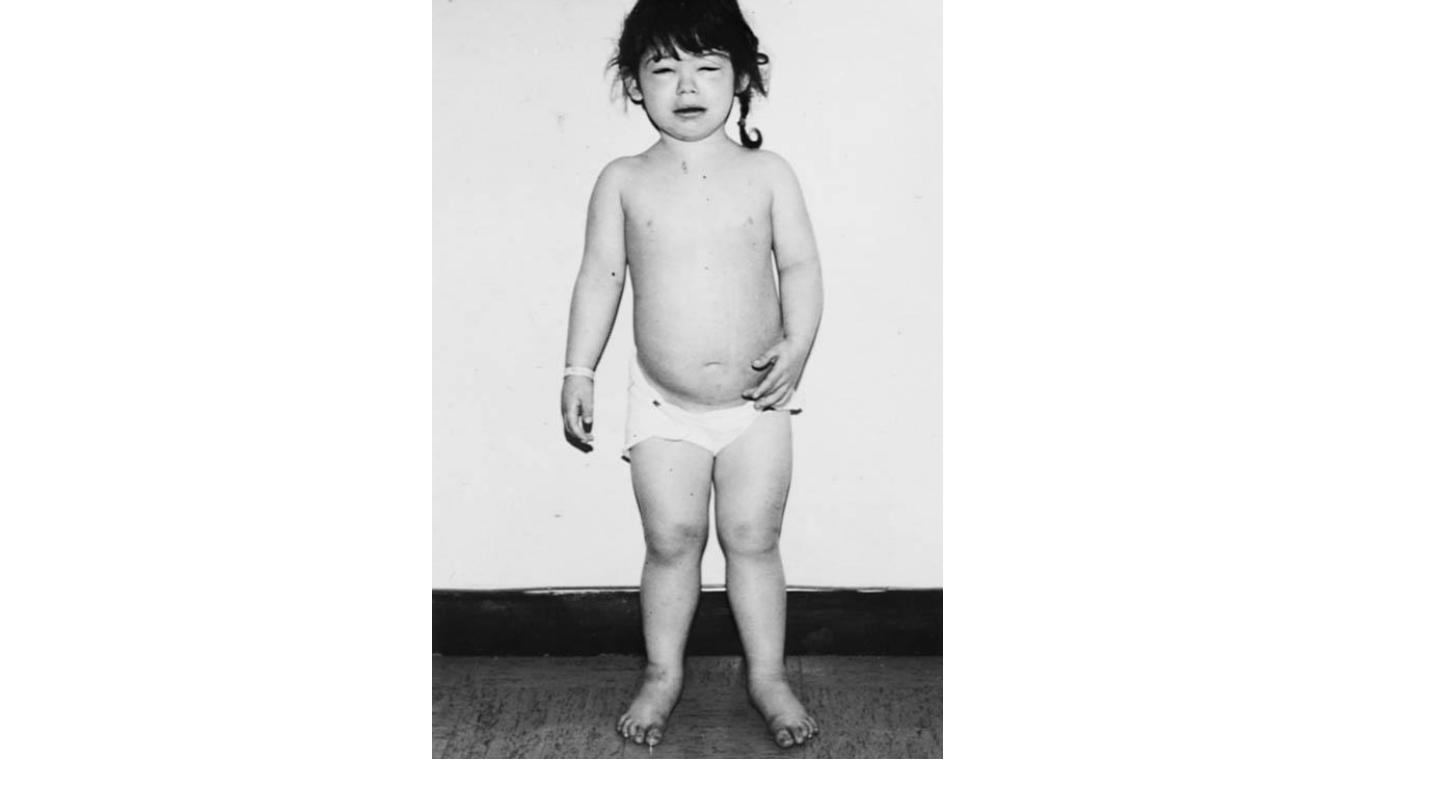
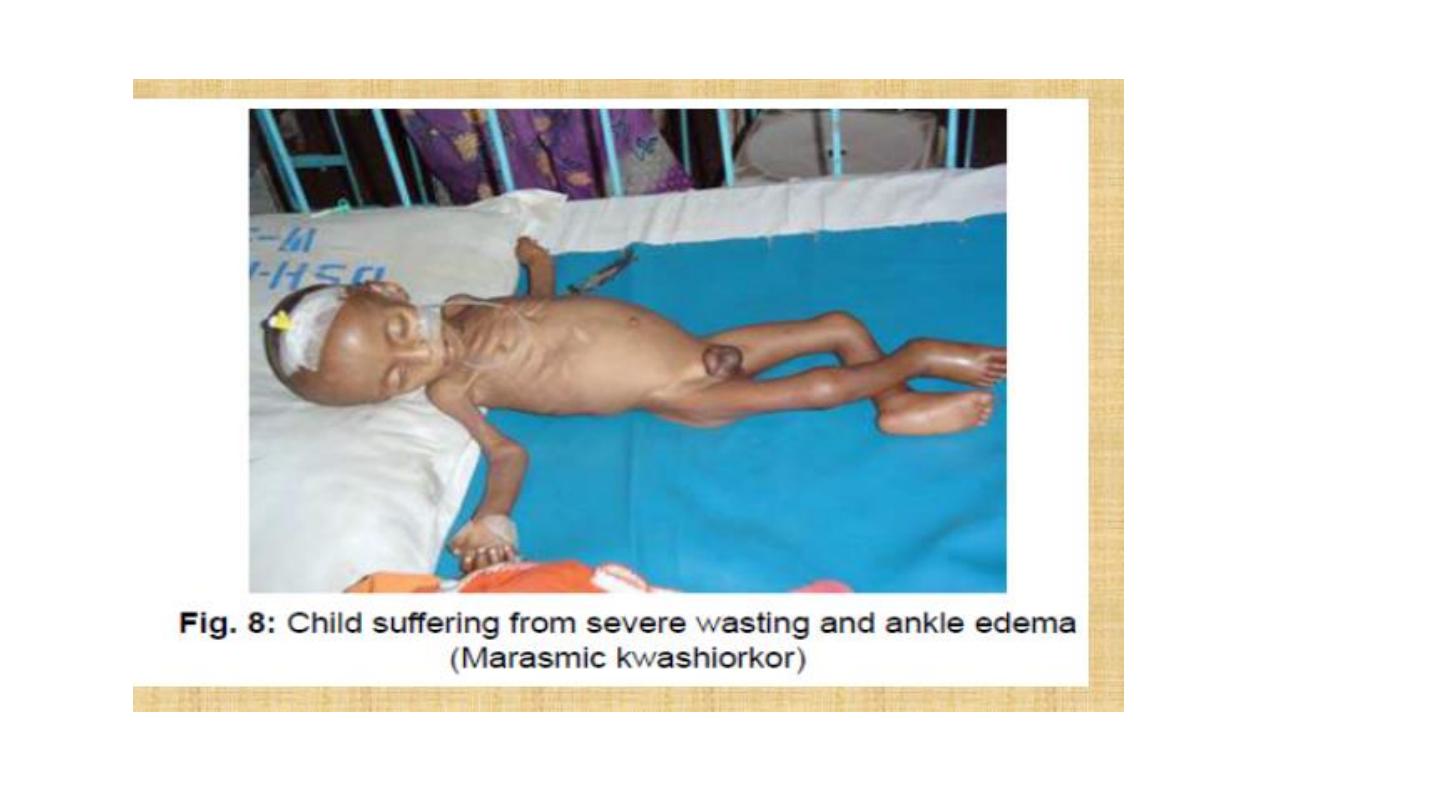
kwashirkor
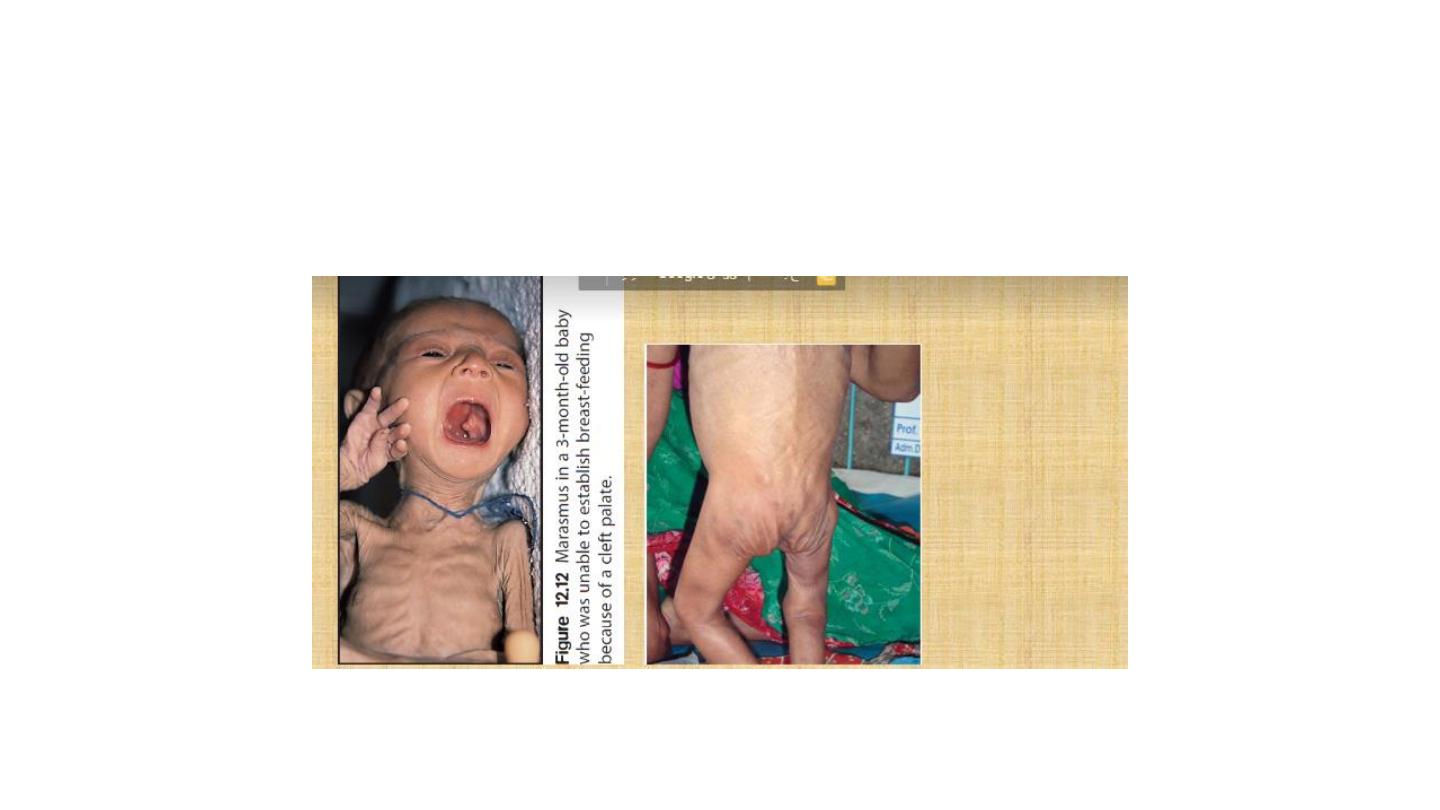
marasmus
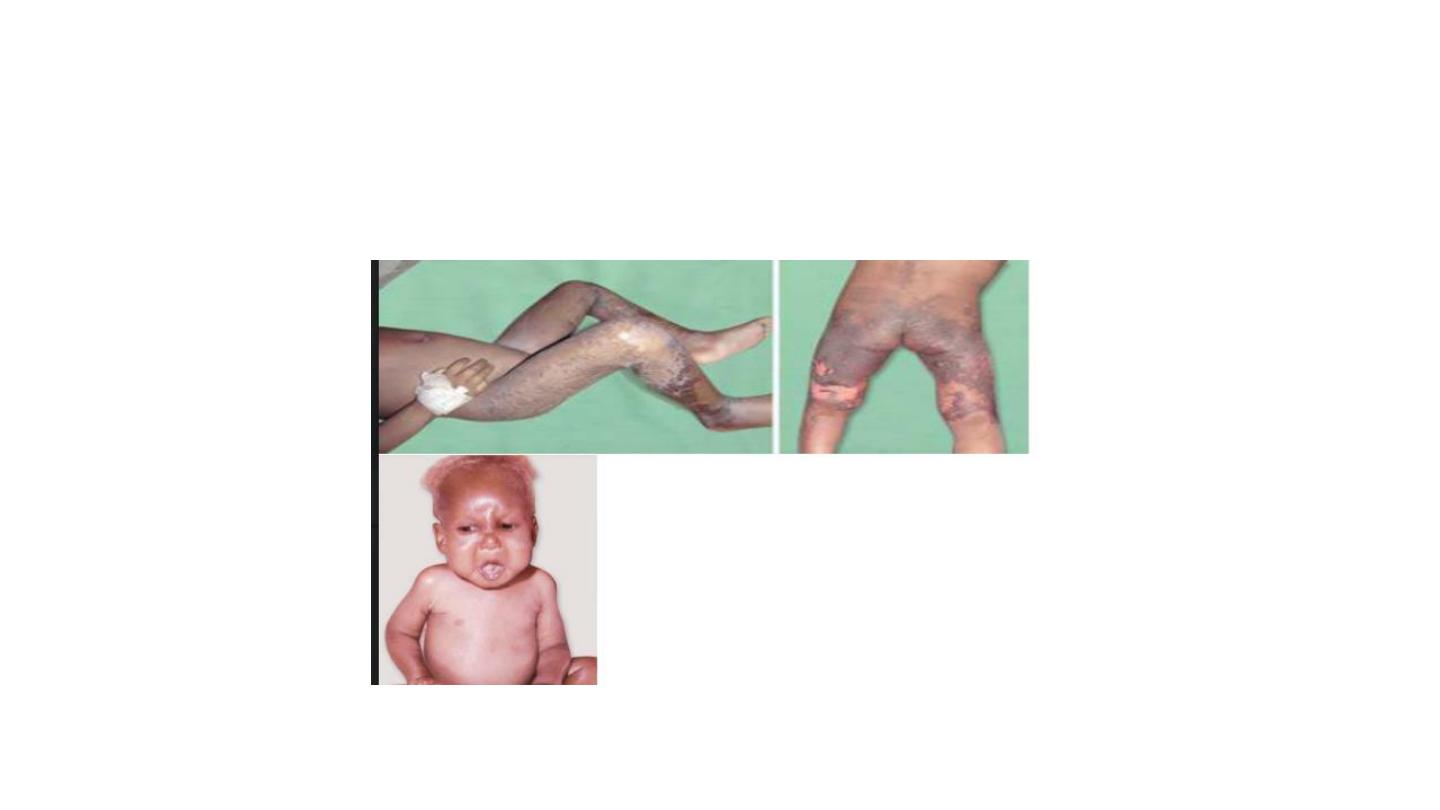
kwashirkor








blood
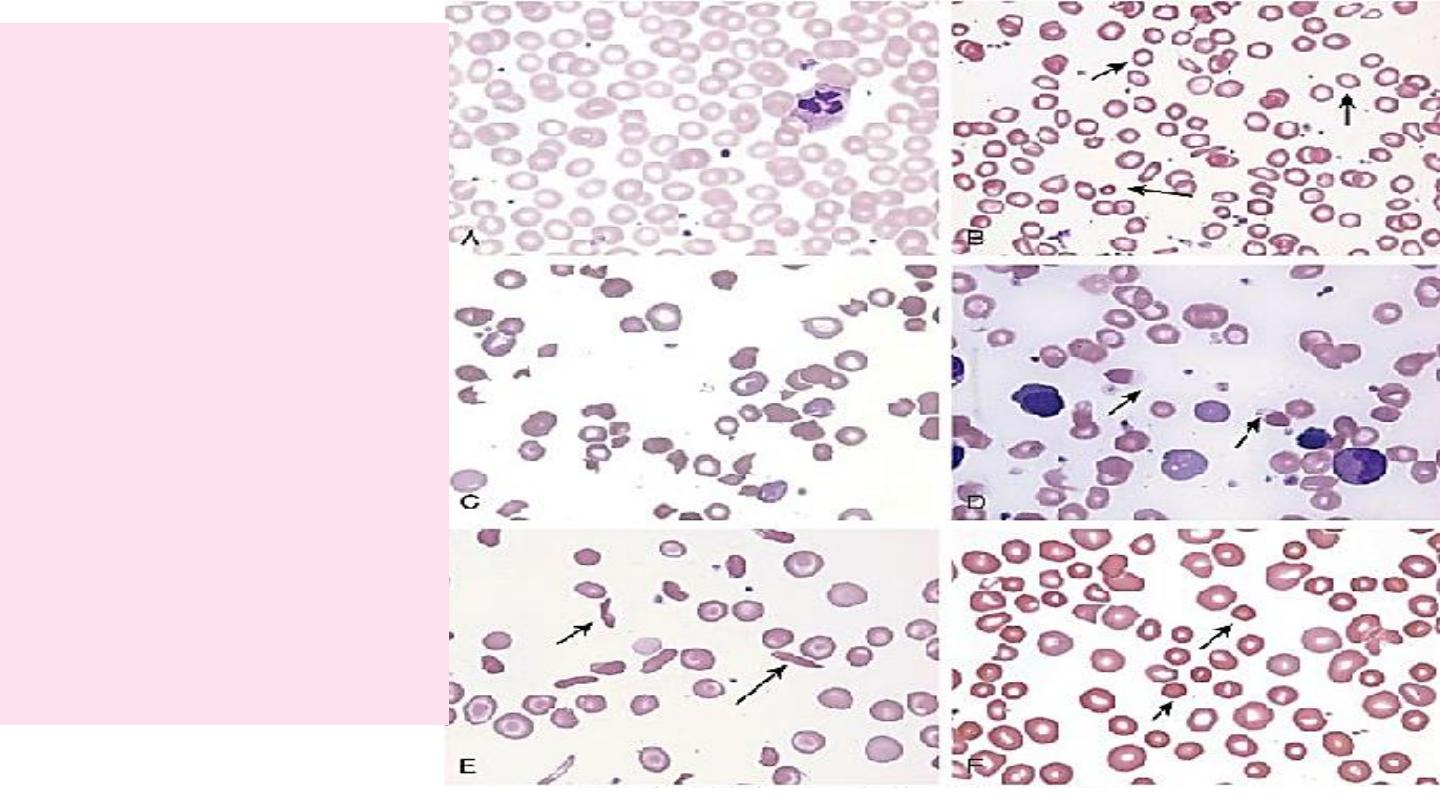
A.
Normal
B.
Hypochromic
microcytes (IDA)
C.
Schistocytes (HUS)
D.
Blister cells (G6PD)
E.
Sickle cells (SCD)
F.
Spherocytes
(autoimmune HA)
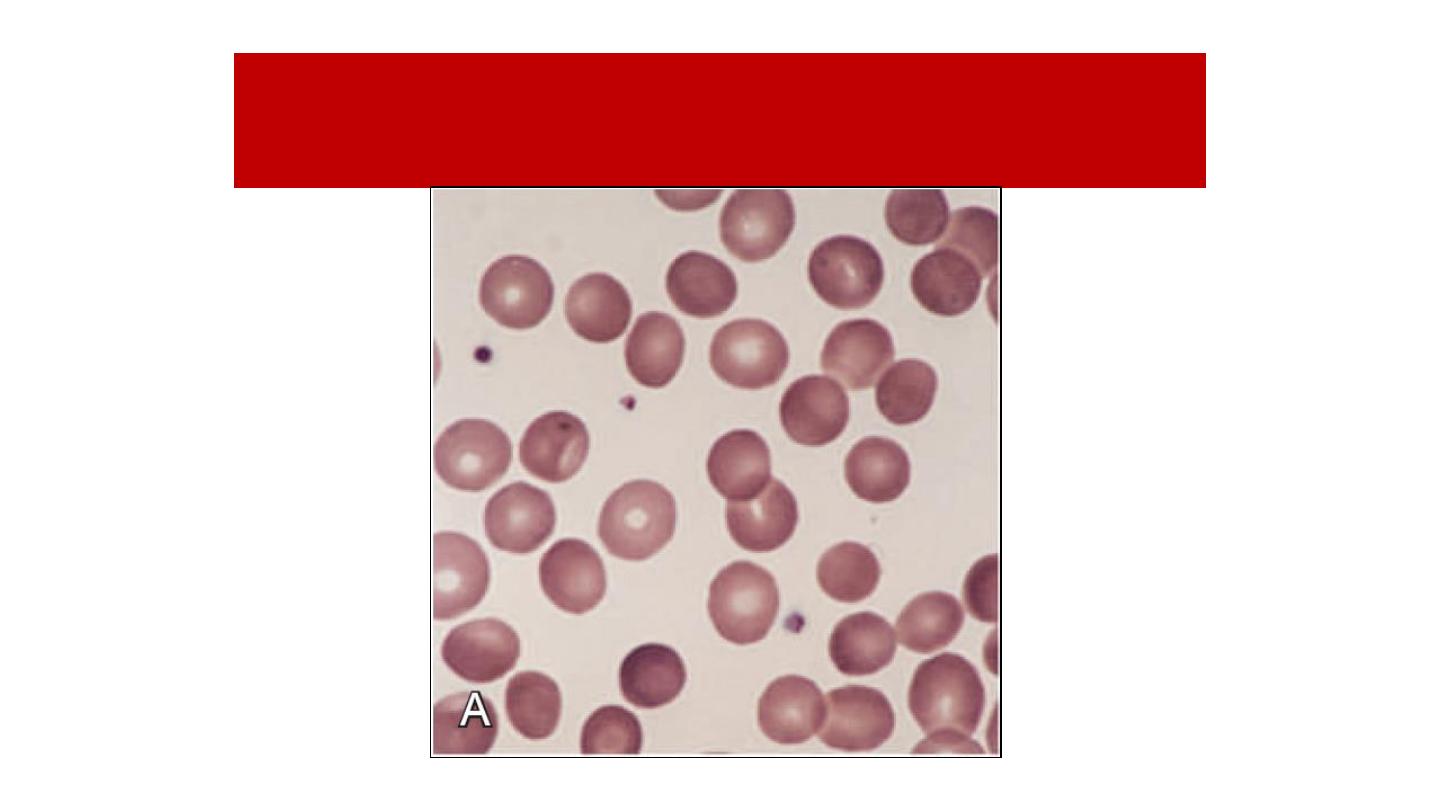
Blood Film of Hereditary Spherocytosis
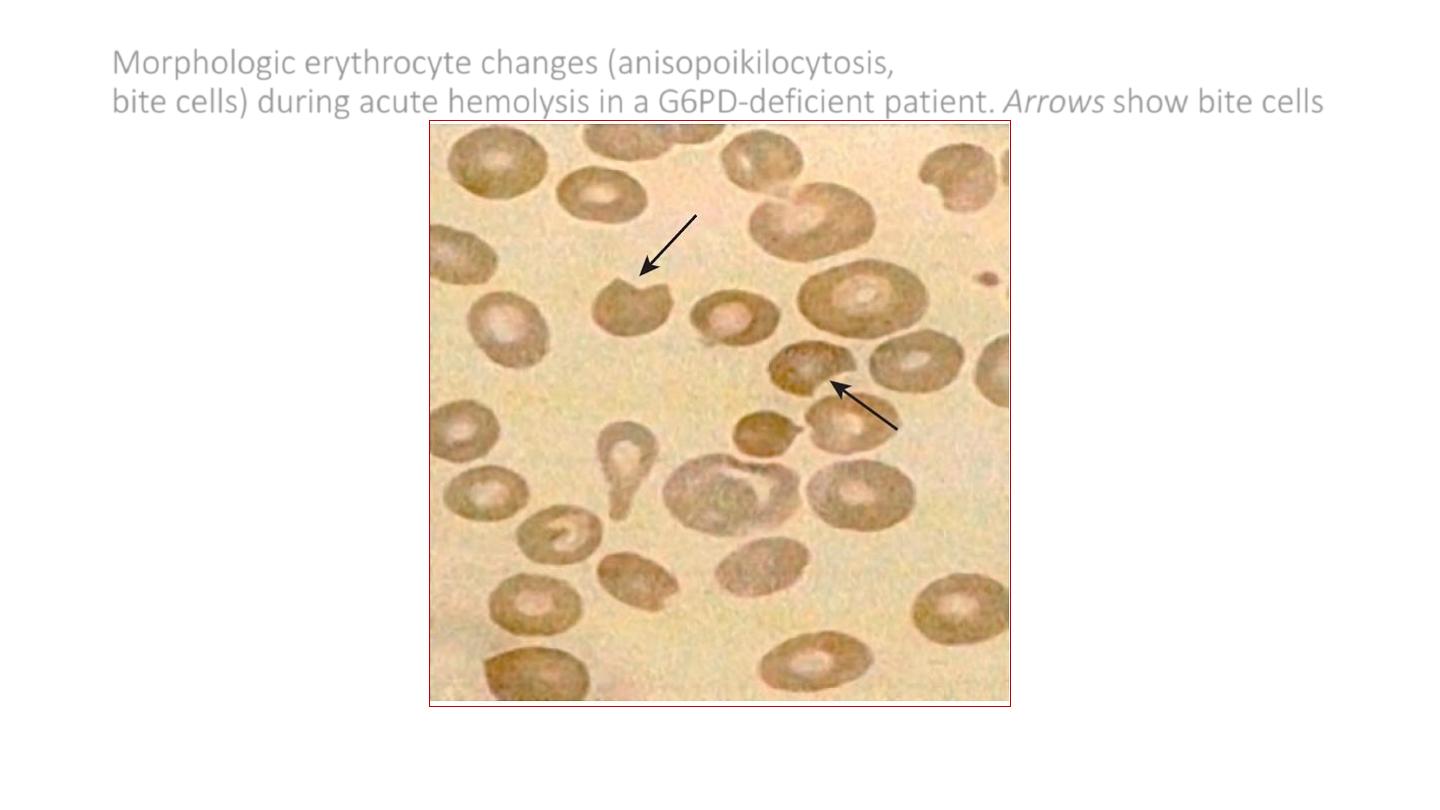
Morphologic erythrocyte changes (anisopoikilocytosis,
bite cells) during acute hemolysis in a G6PD-deficient patient. Arrows show bite cells
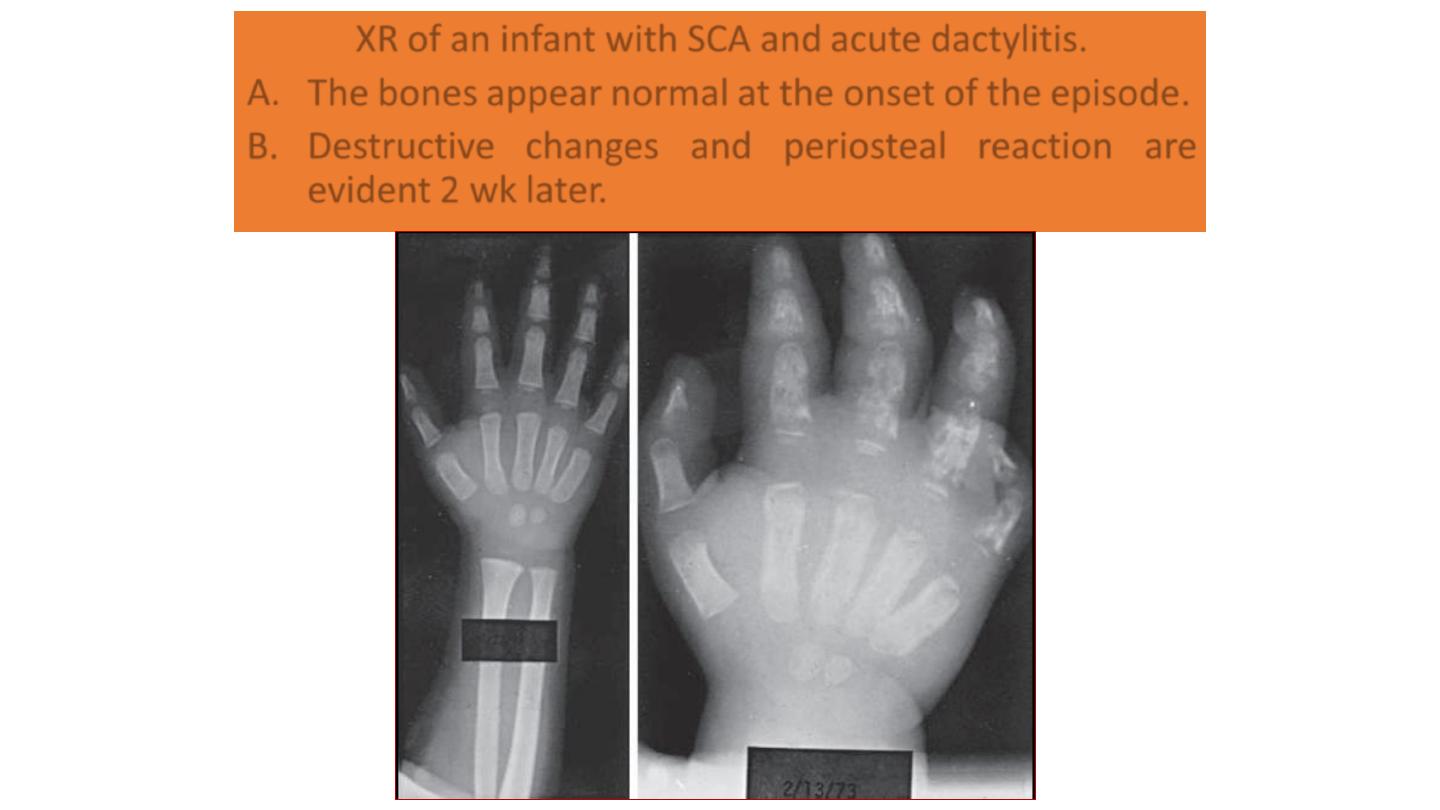
XR of an infant with SCA and acute dactylitis.
A. The bones appear normal at the onset of the episode.
B. Destructive changes and periosteal reaction are
evident 2 wk later.
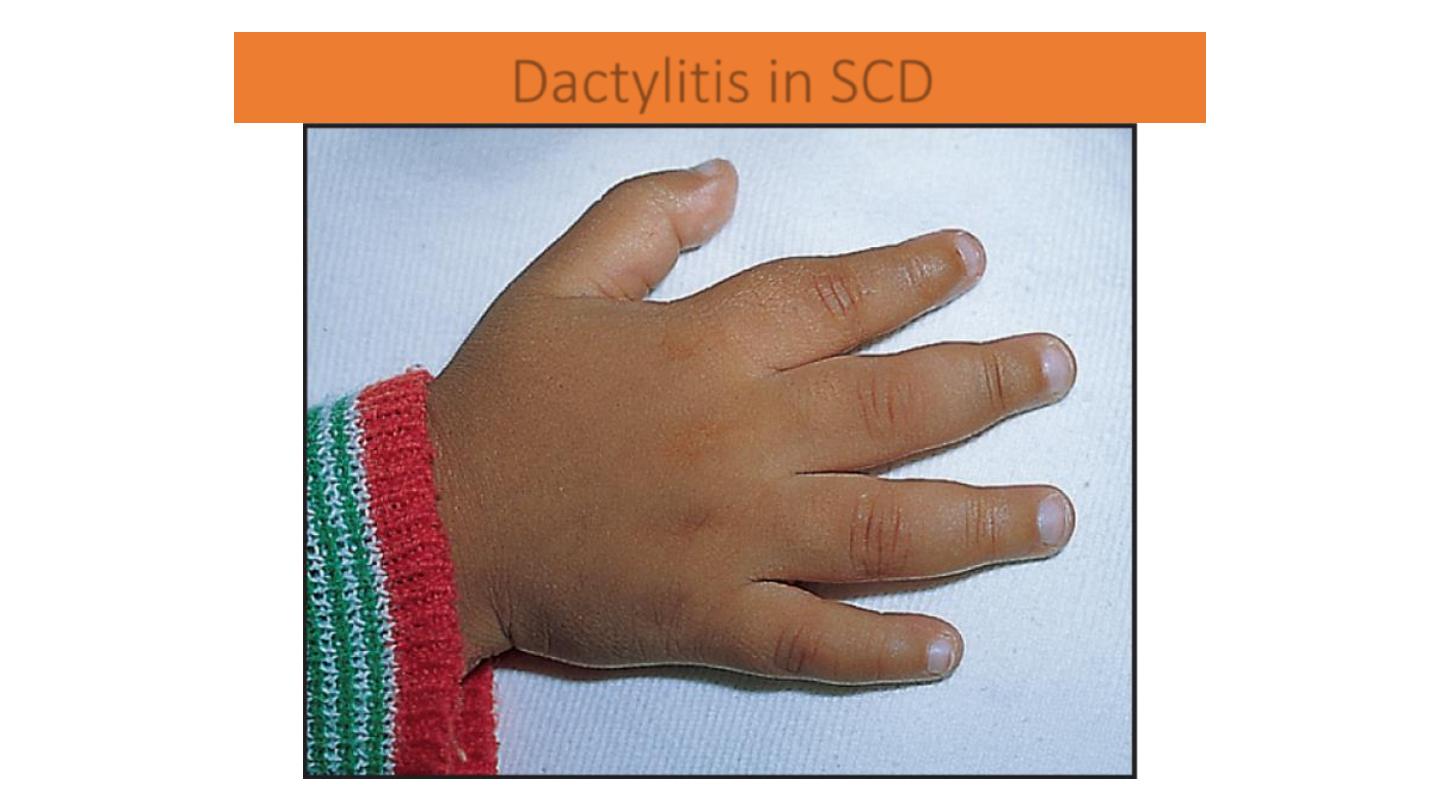
Dactylitis in SCD
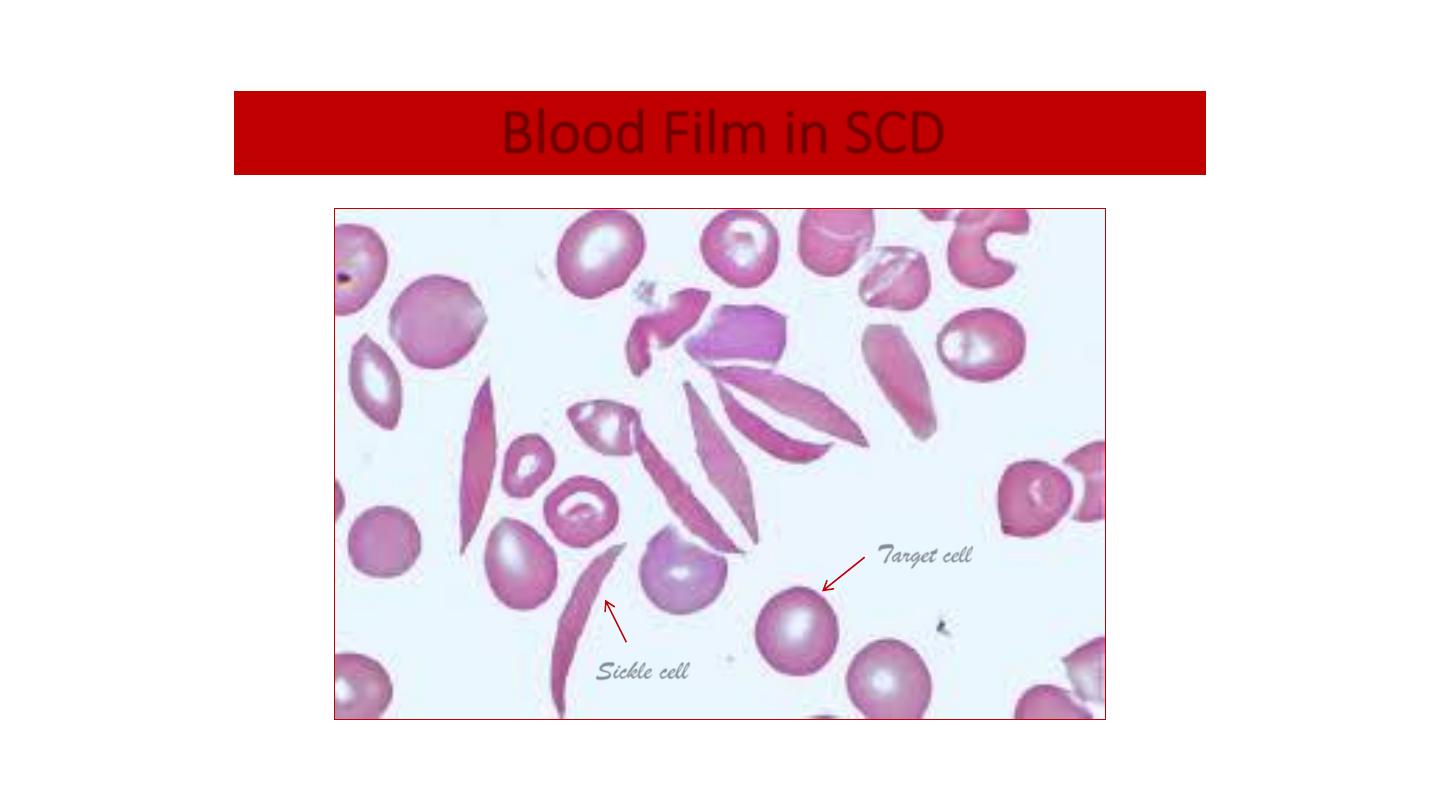
Blood Film in SCD
Target cell
Sickle cell
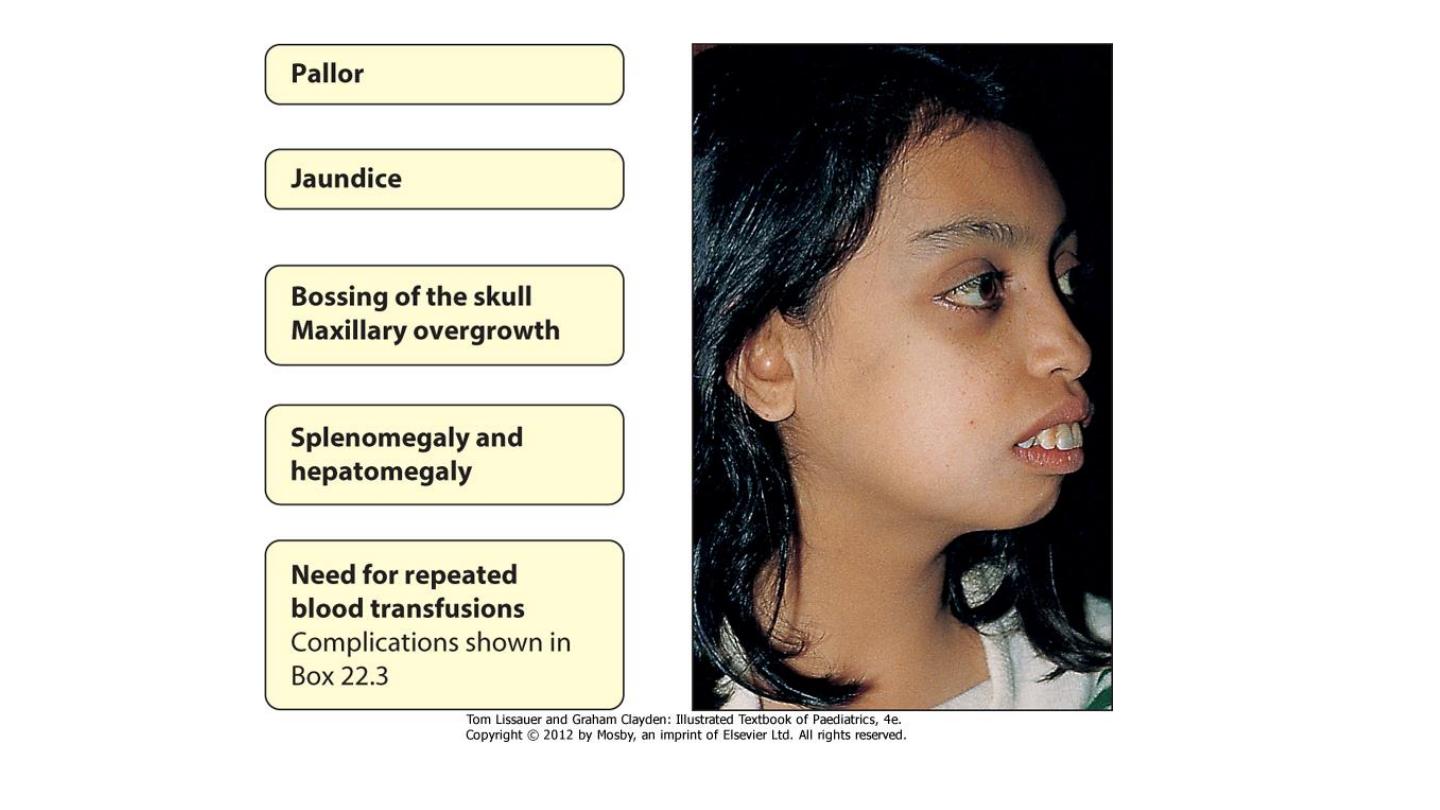
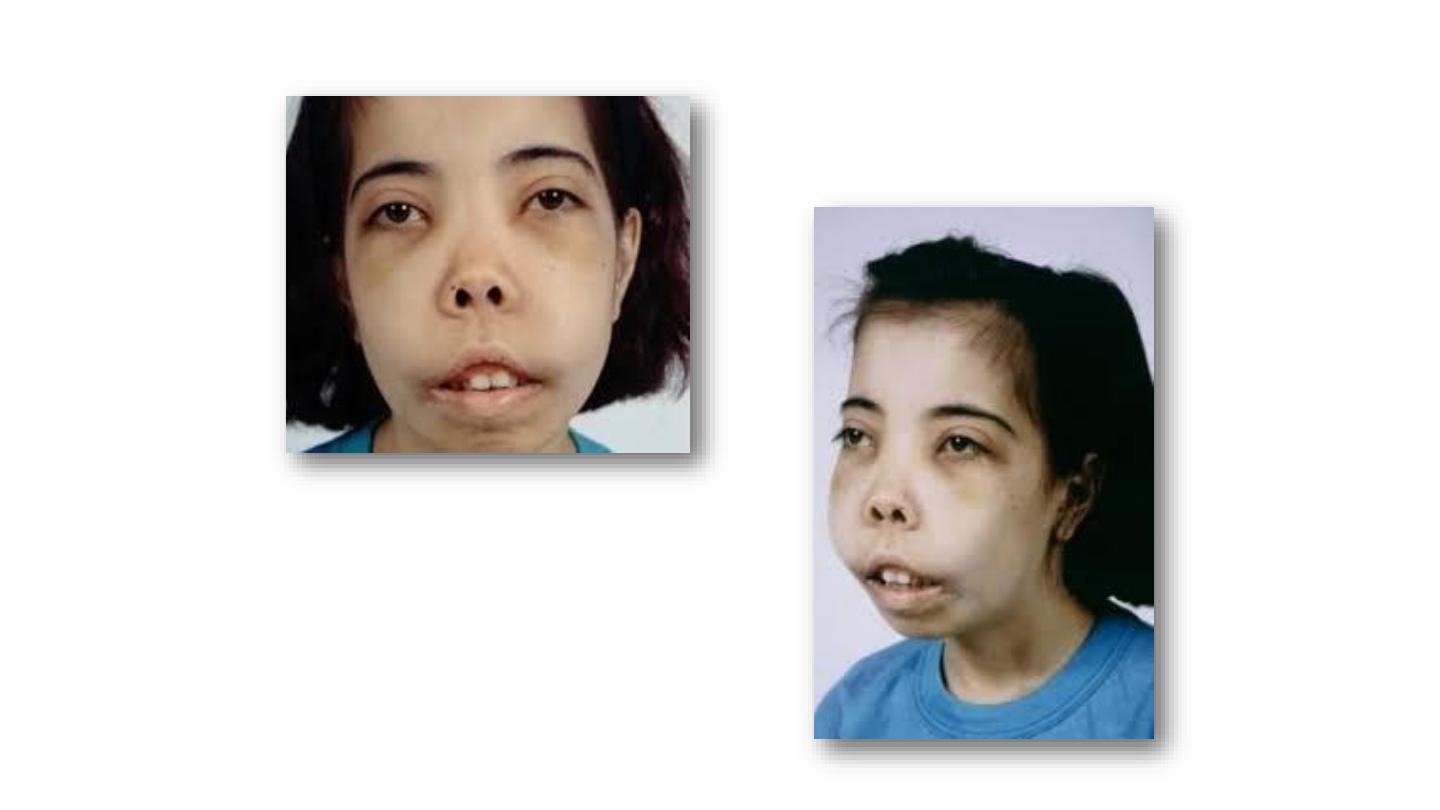
β-Thalassemia
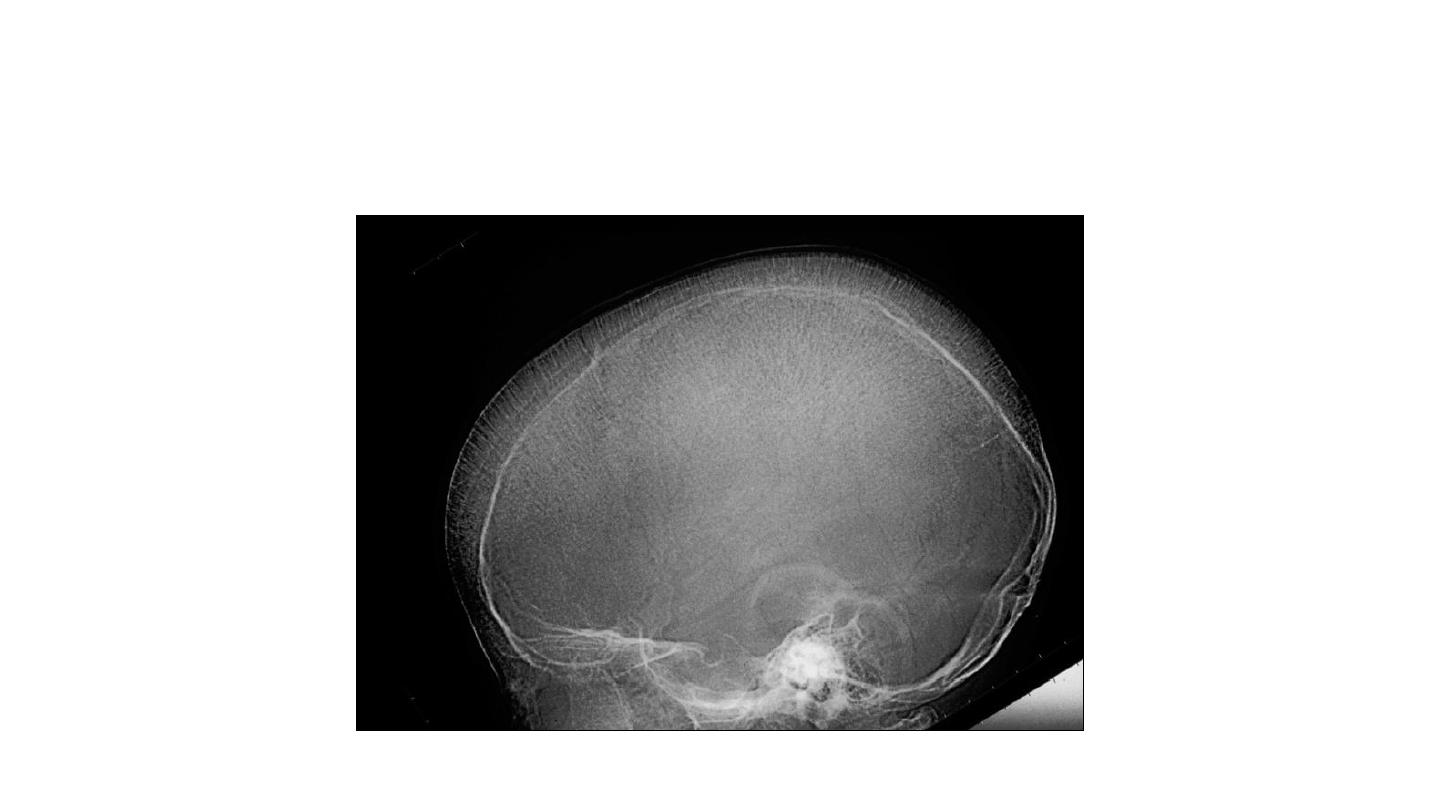
Hair on end appearance SCA
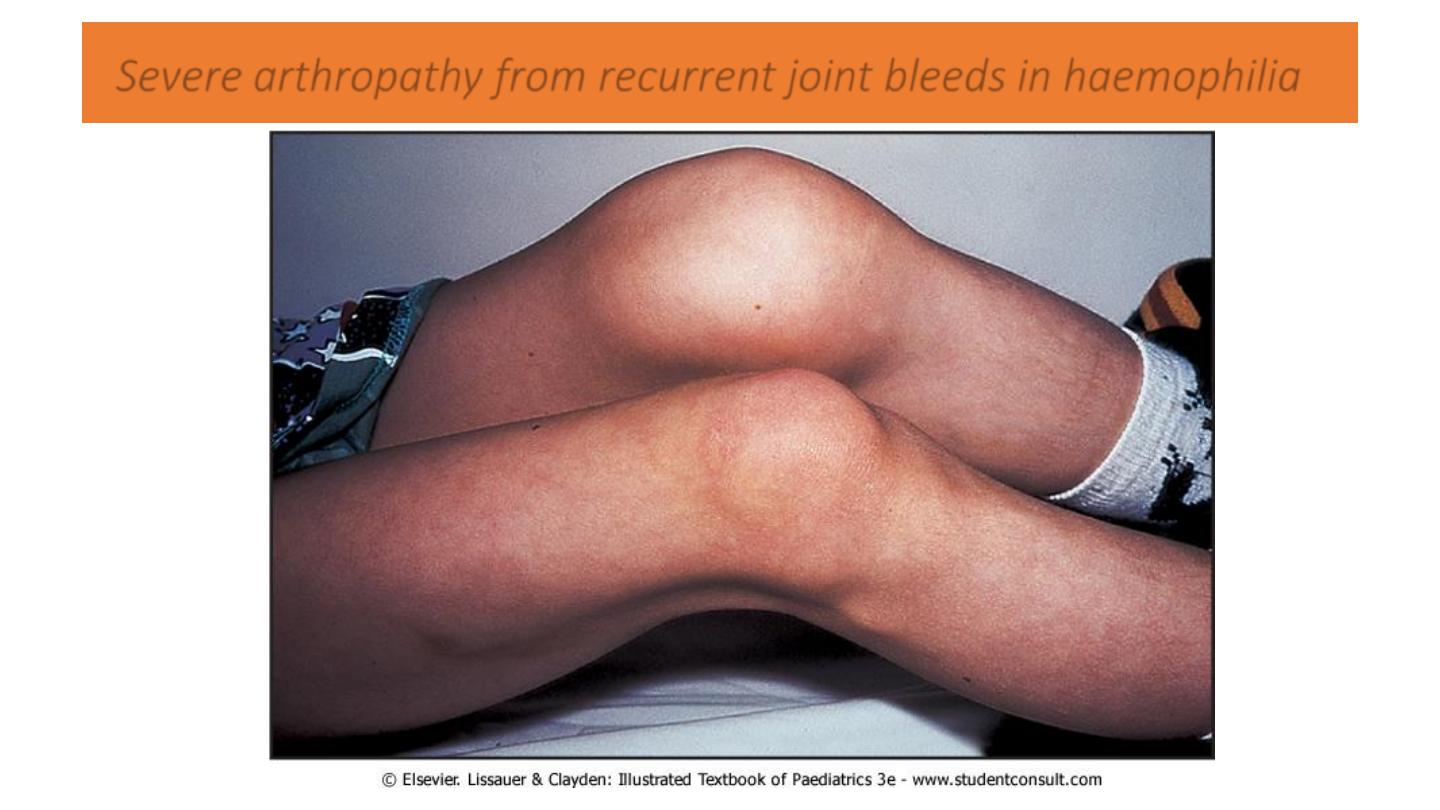
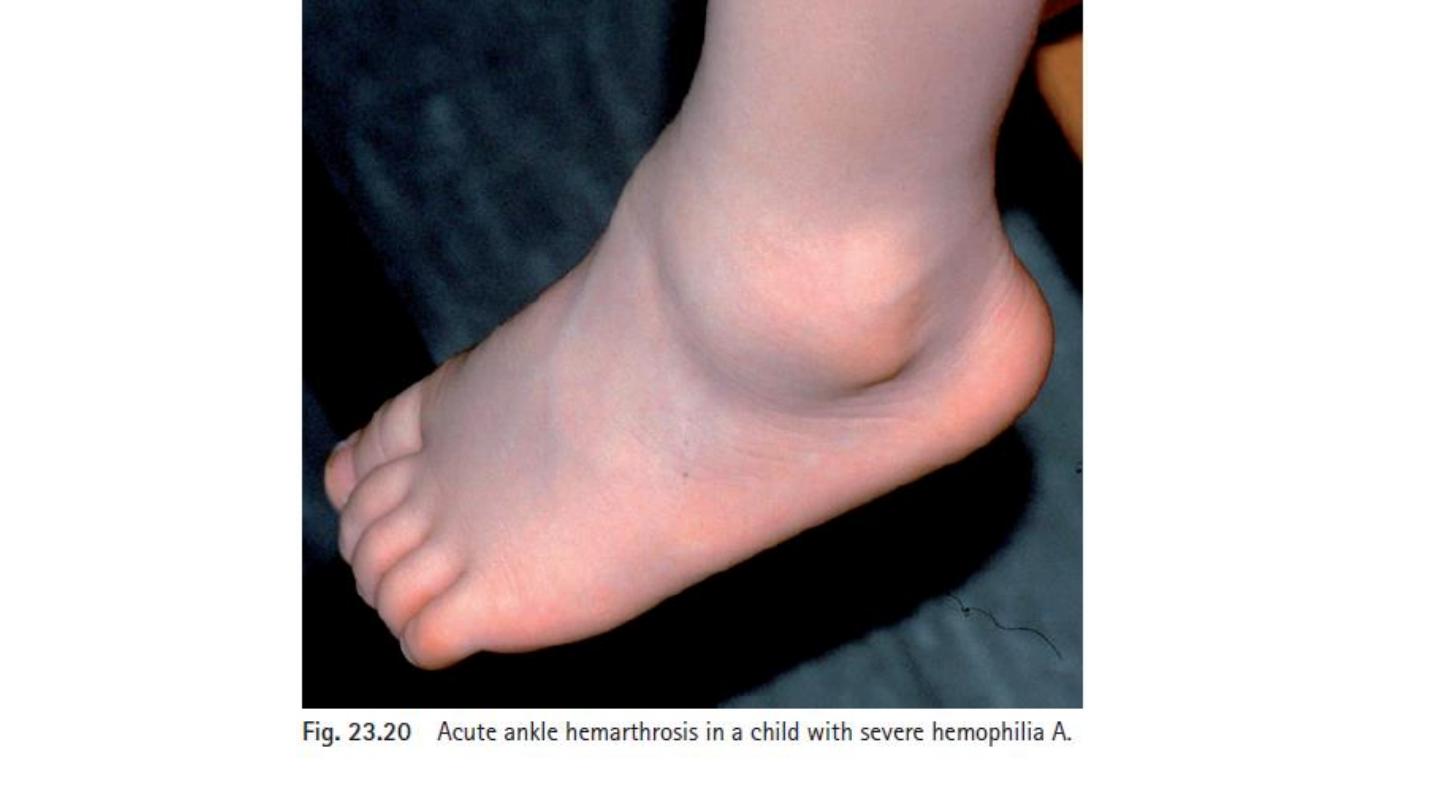
Severe arthropathy from recurrent joint bleeds in haemophilia
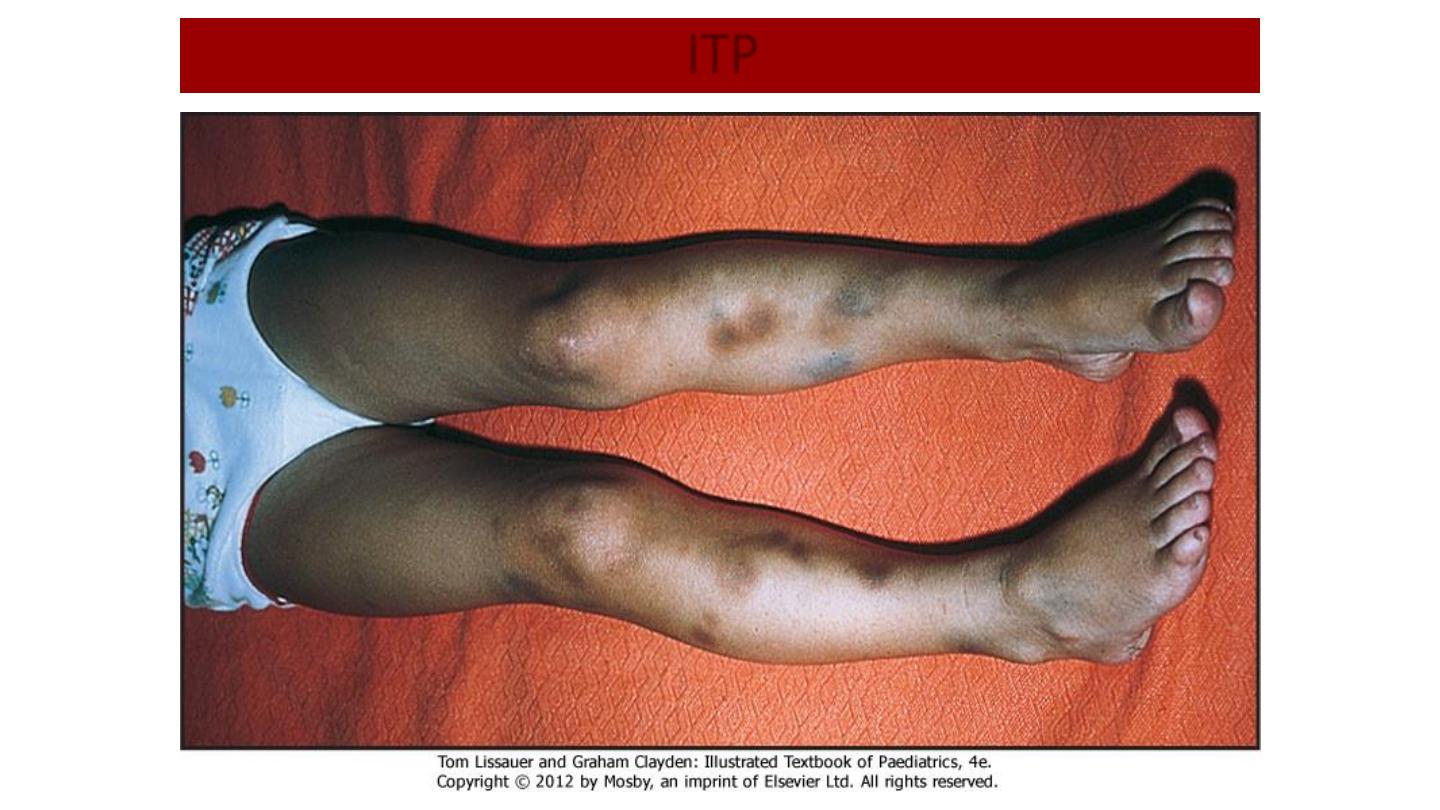
ITP
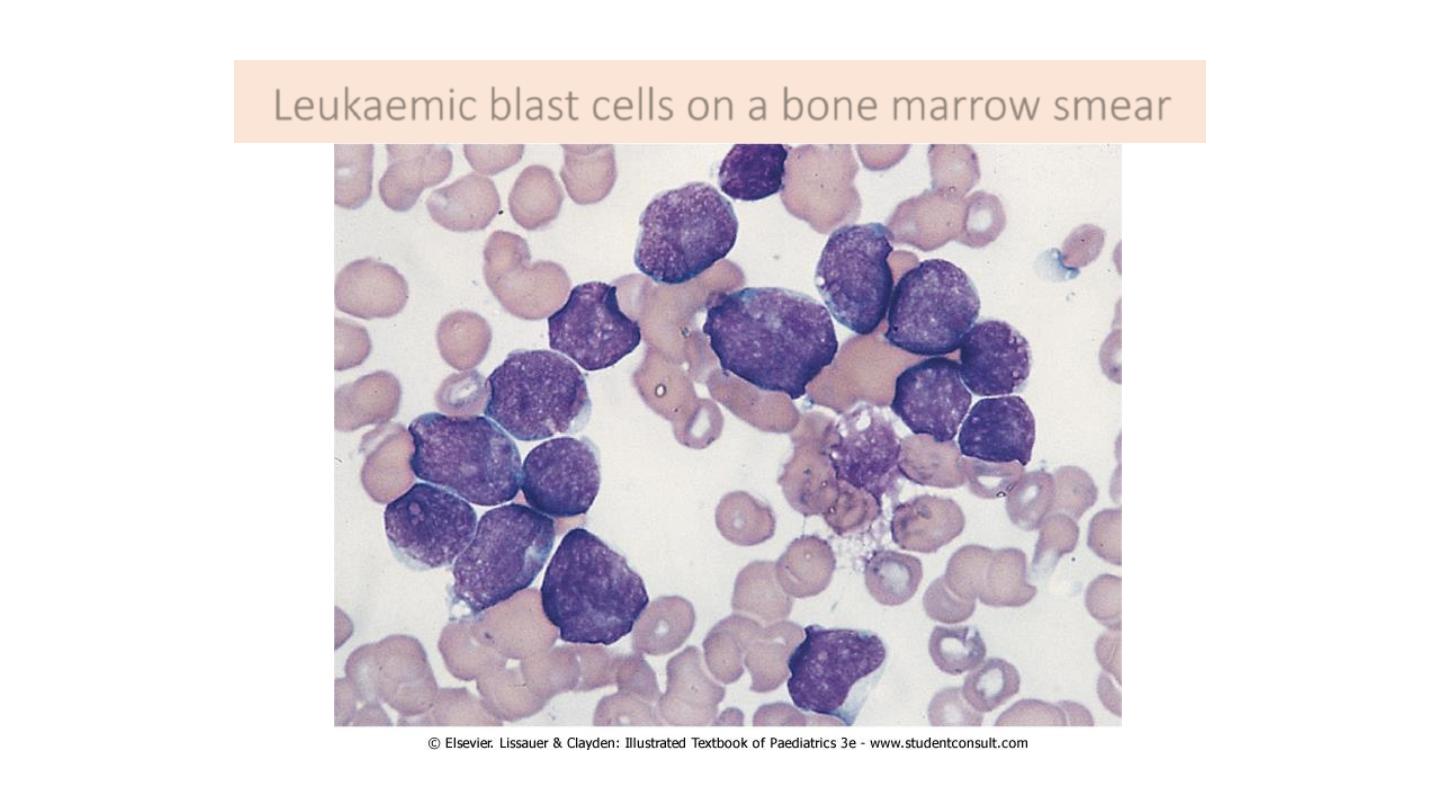
Leukaemic blast cells on a bone marrow smear
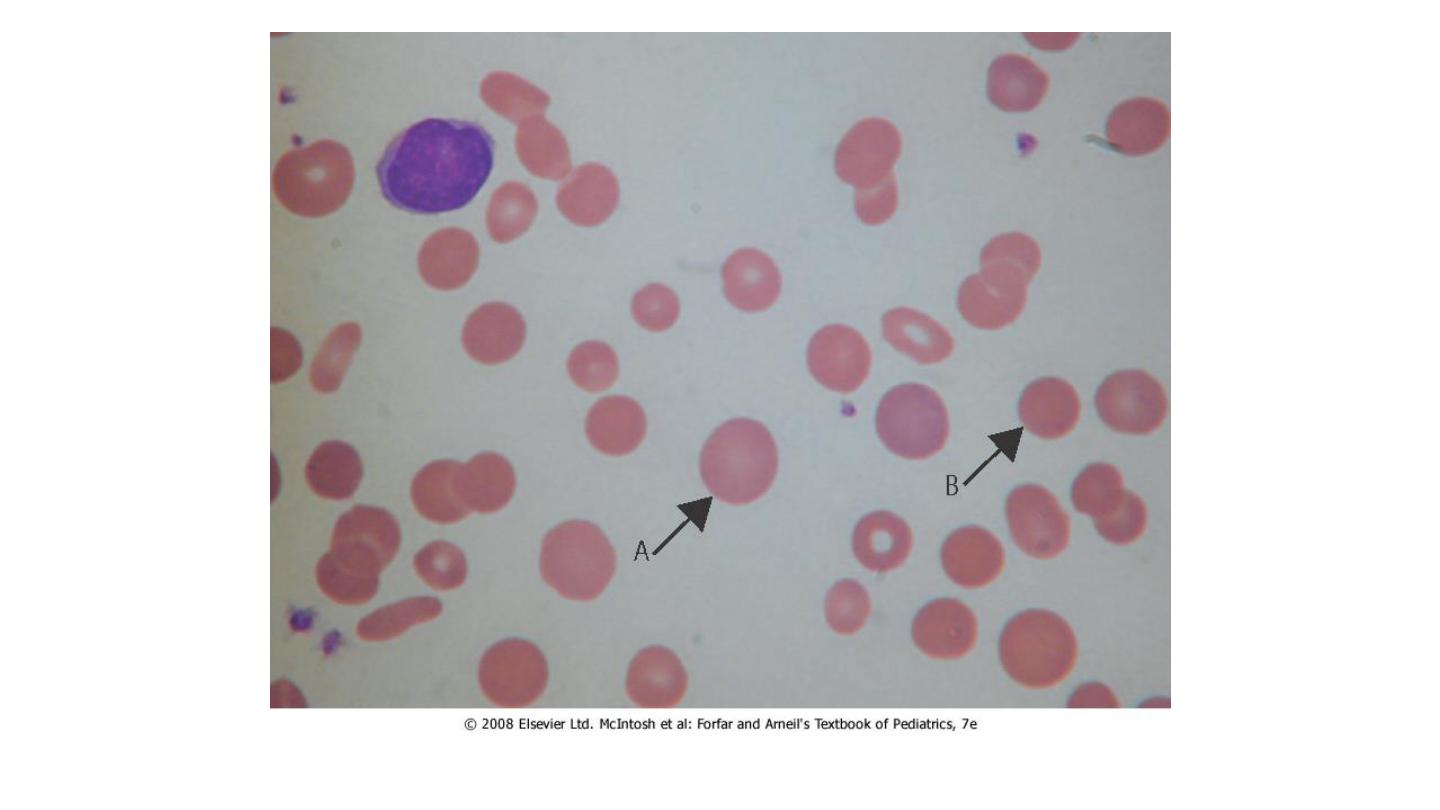
HS
A, polychromatic cell; B, microspherocyte
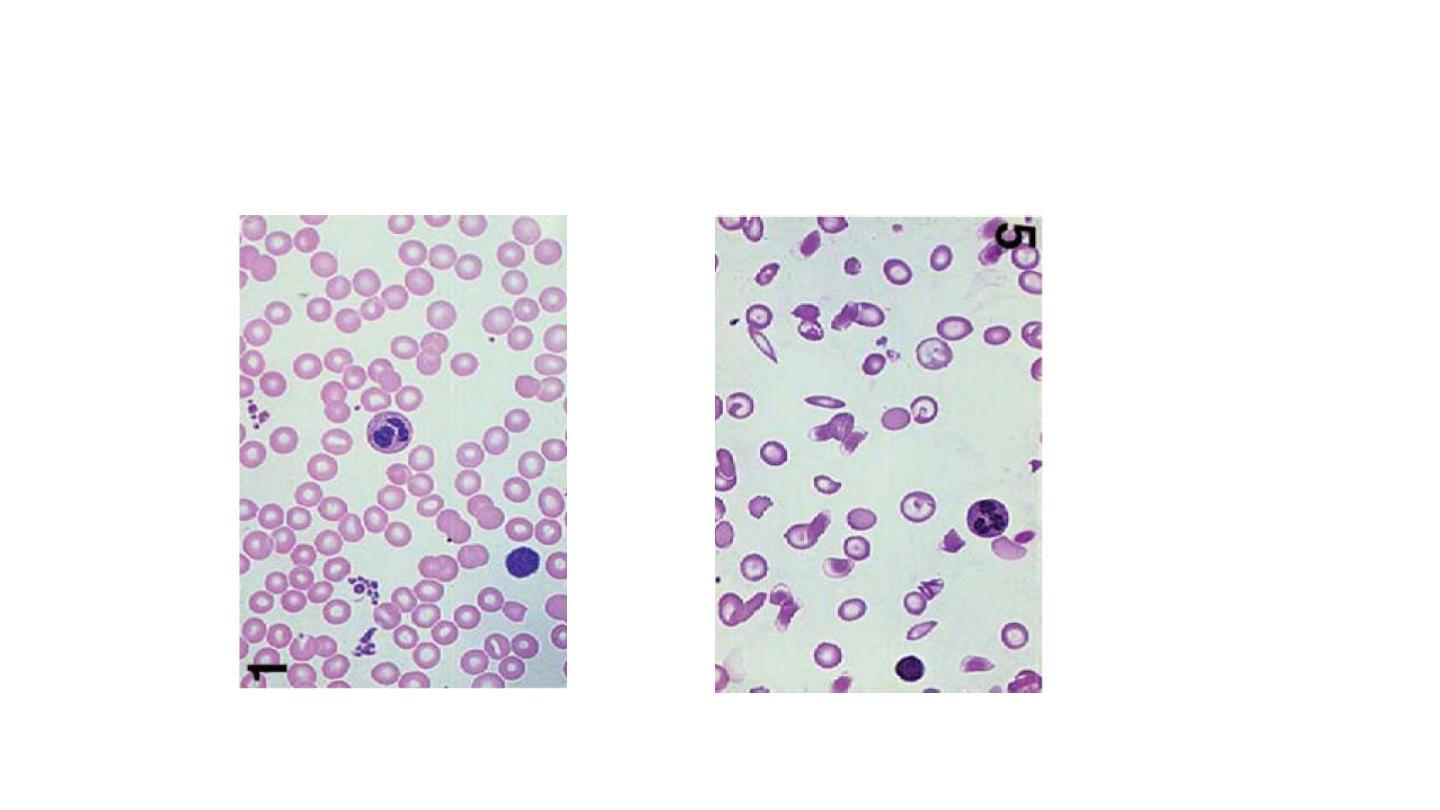
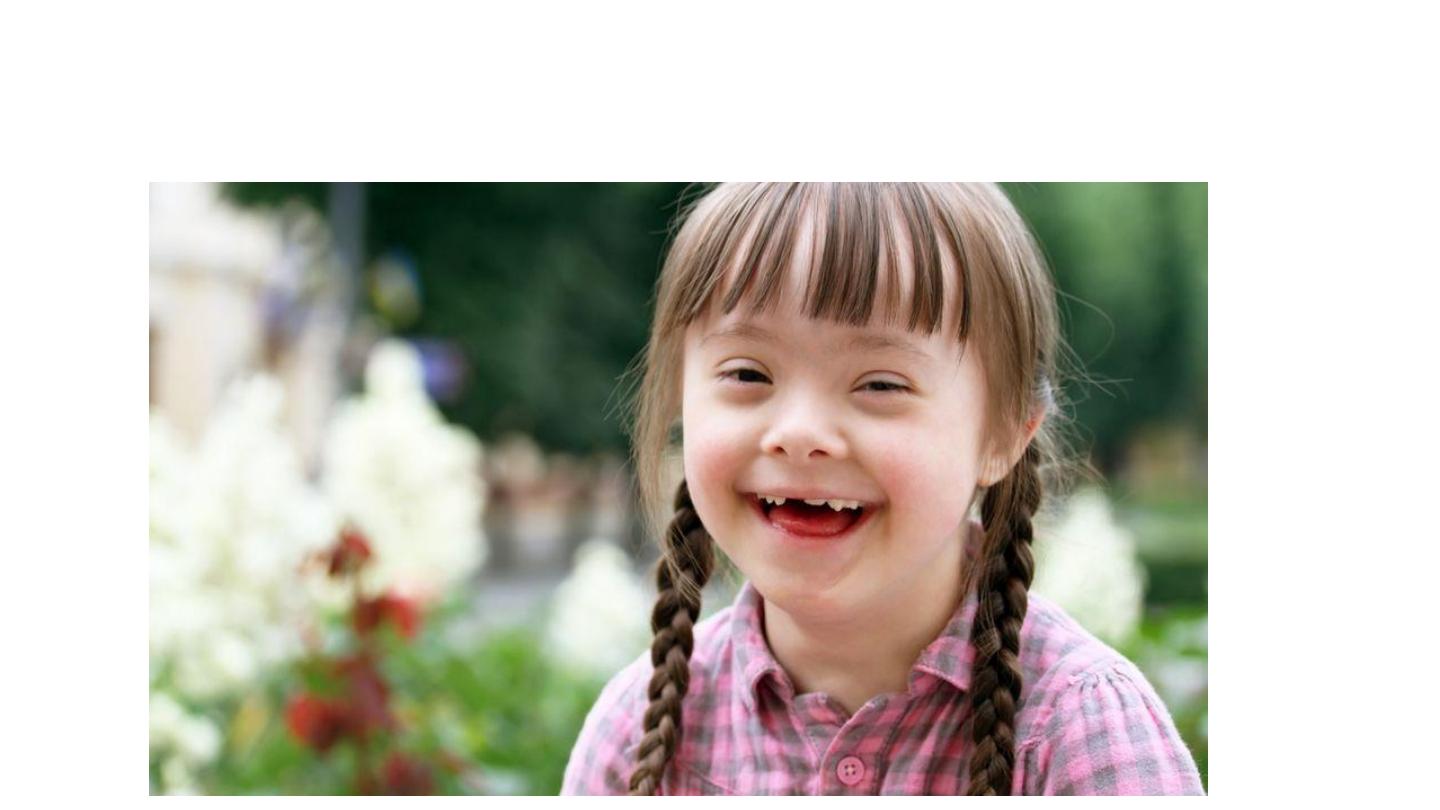
SCA
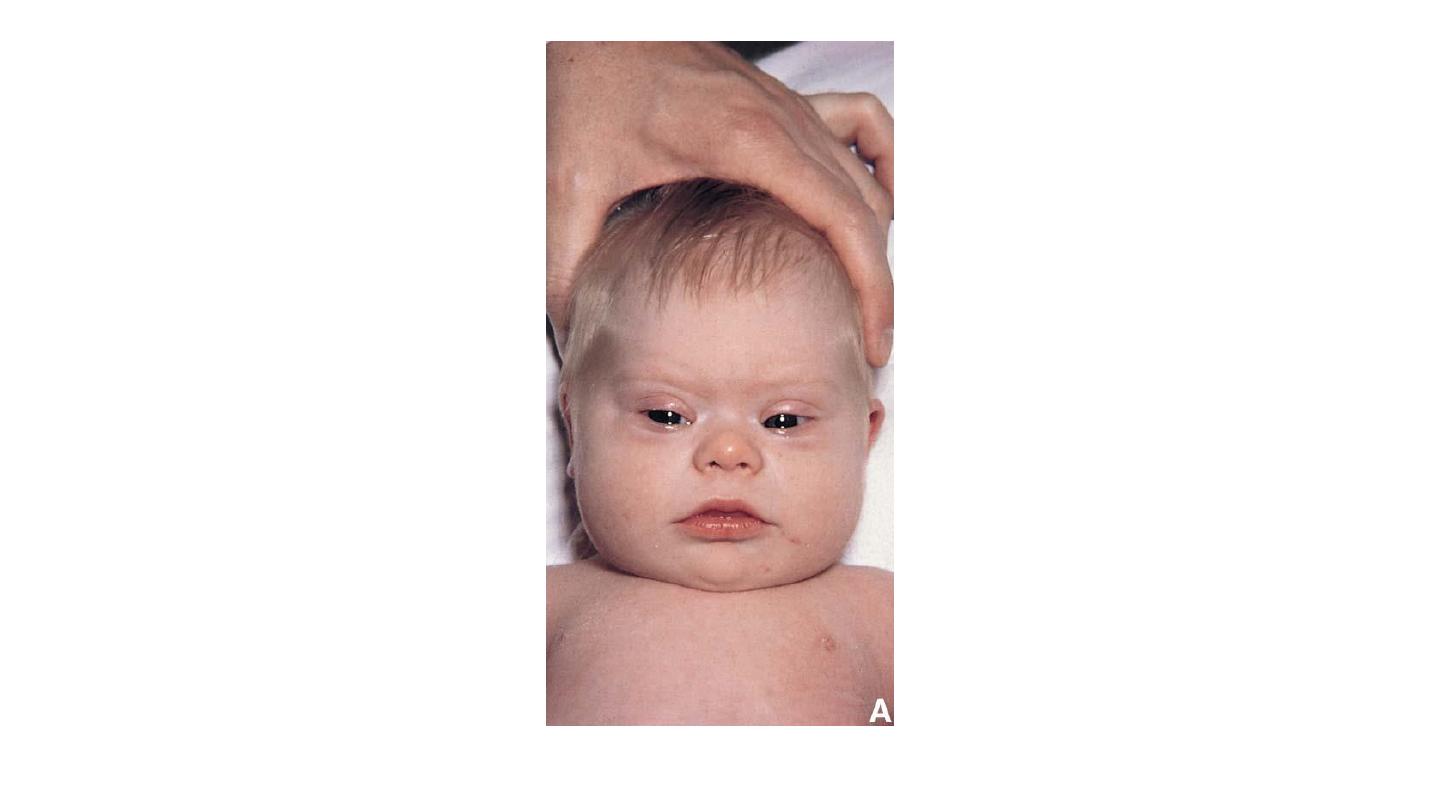
Trisomy 21
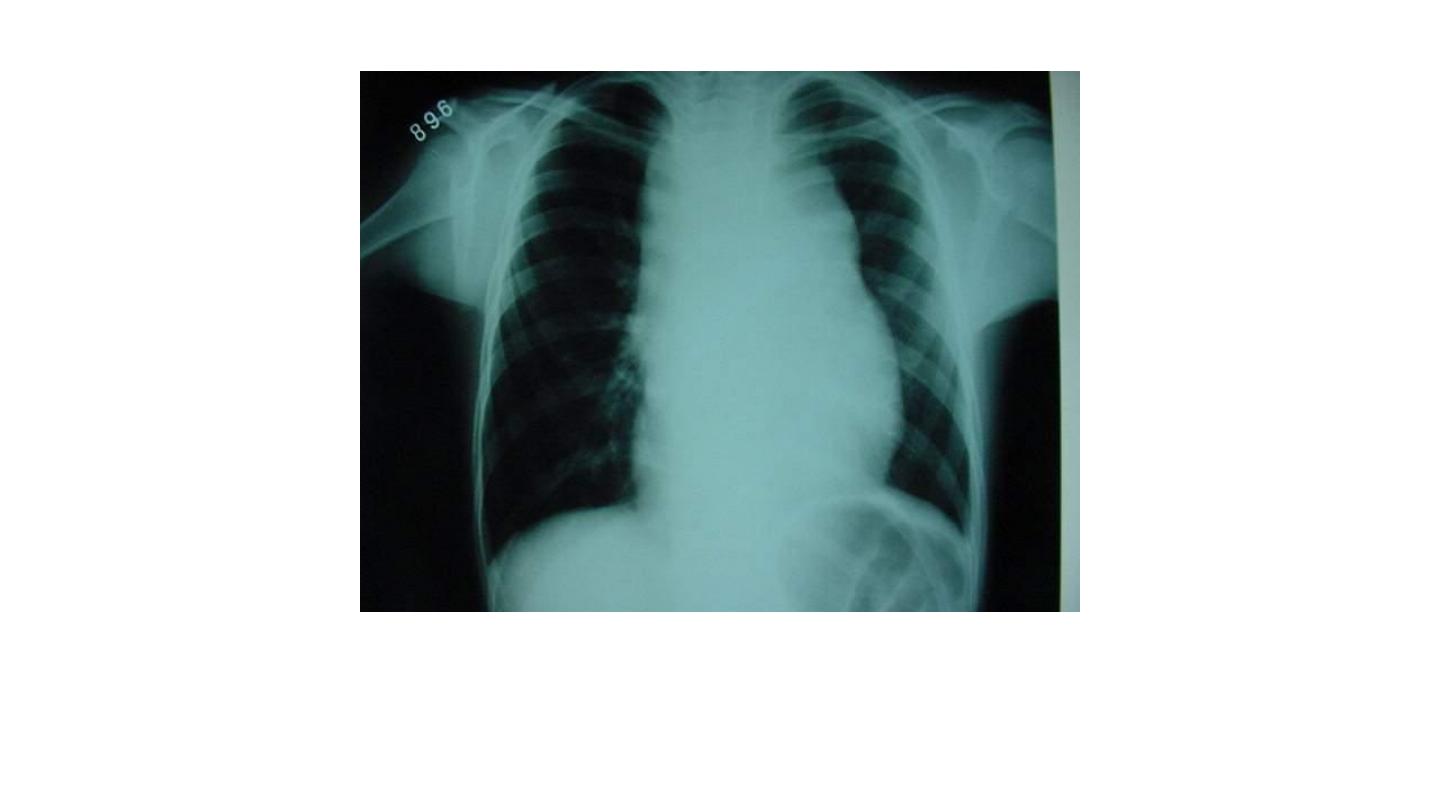
Mediastinal involvement by lymphoblastic lymphoma
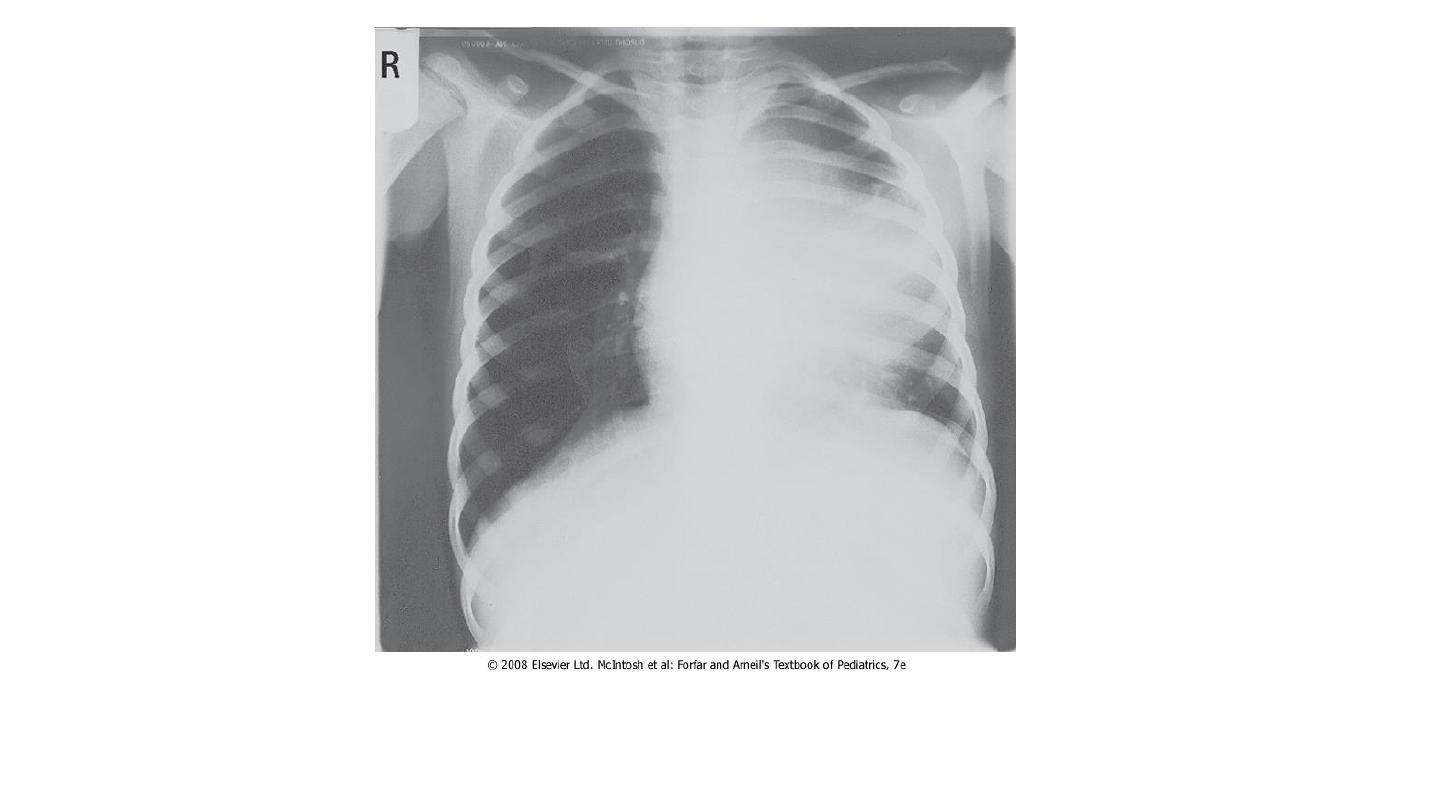
Chest X-ray appearances in acute T cell leukemia with mediastinal
widening and hilar lymphadenopathy causing superior vena cava
obstruction.

Syndroms
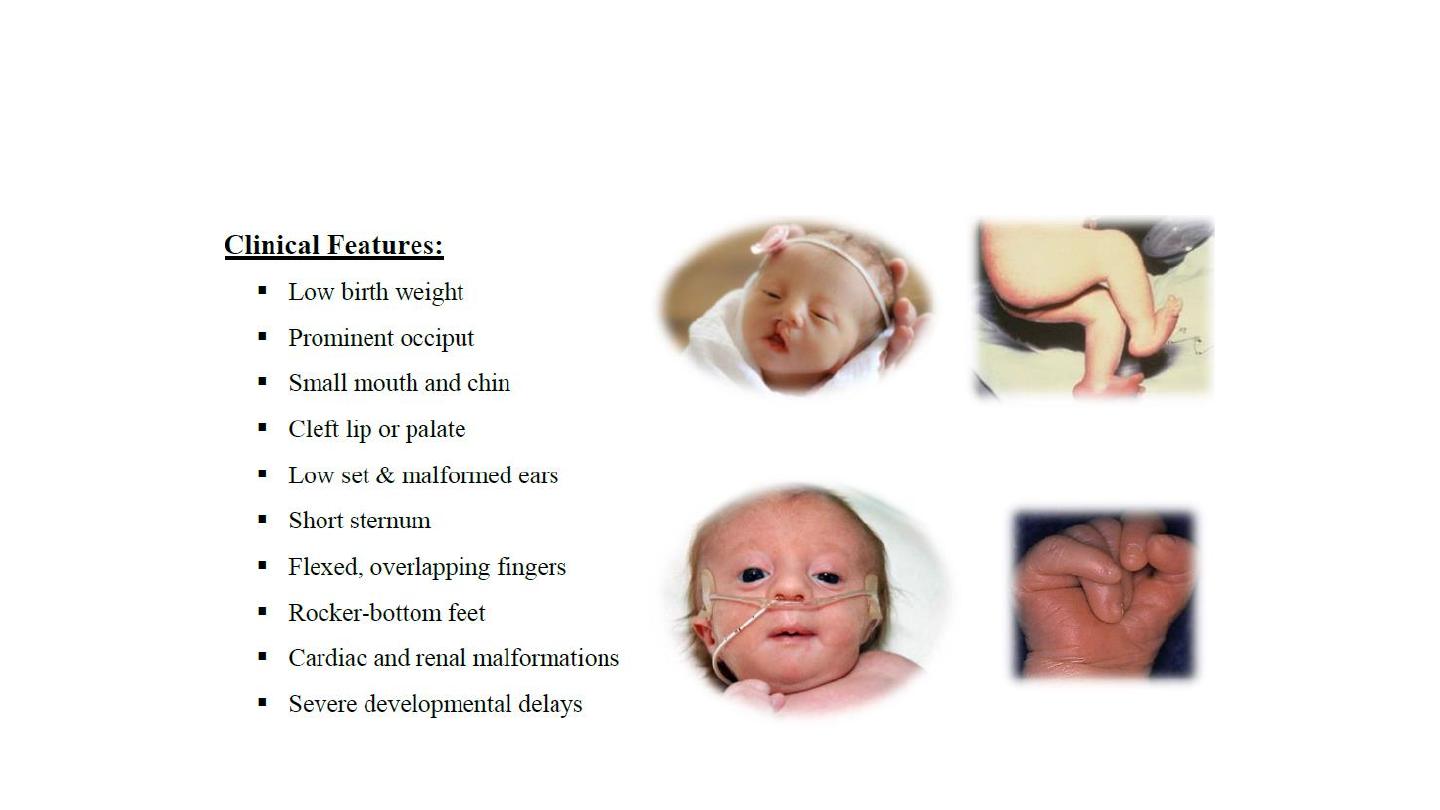
EDWARD trisomy 18
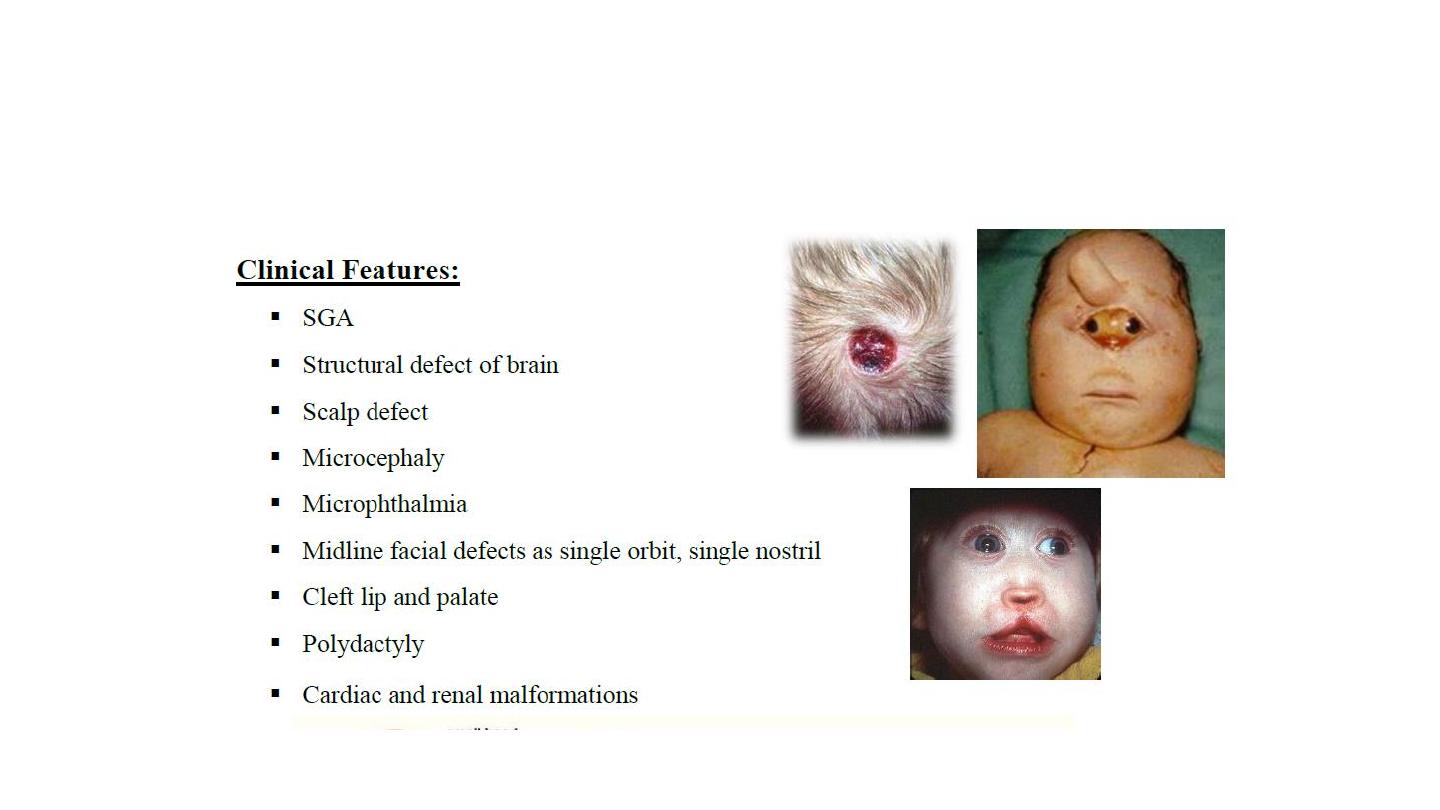
Pataue trisomy 13
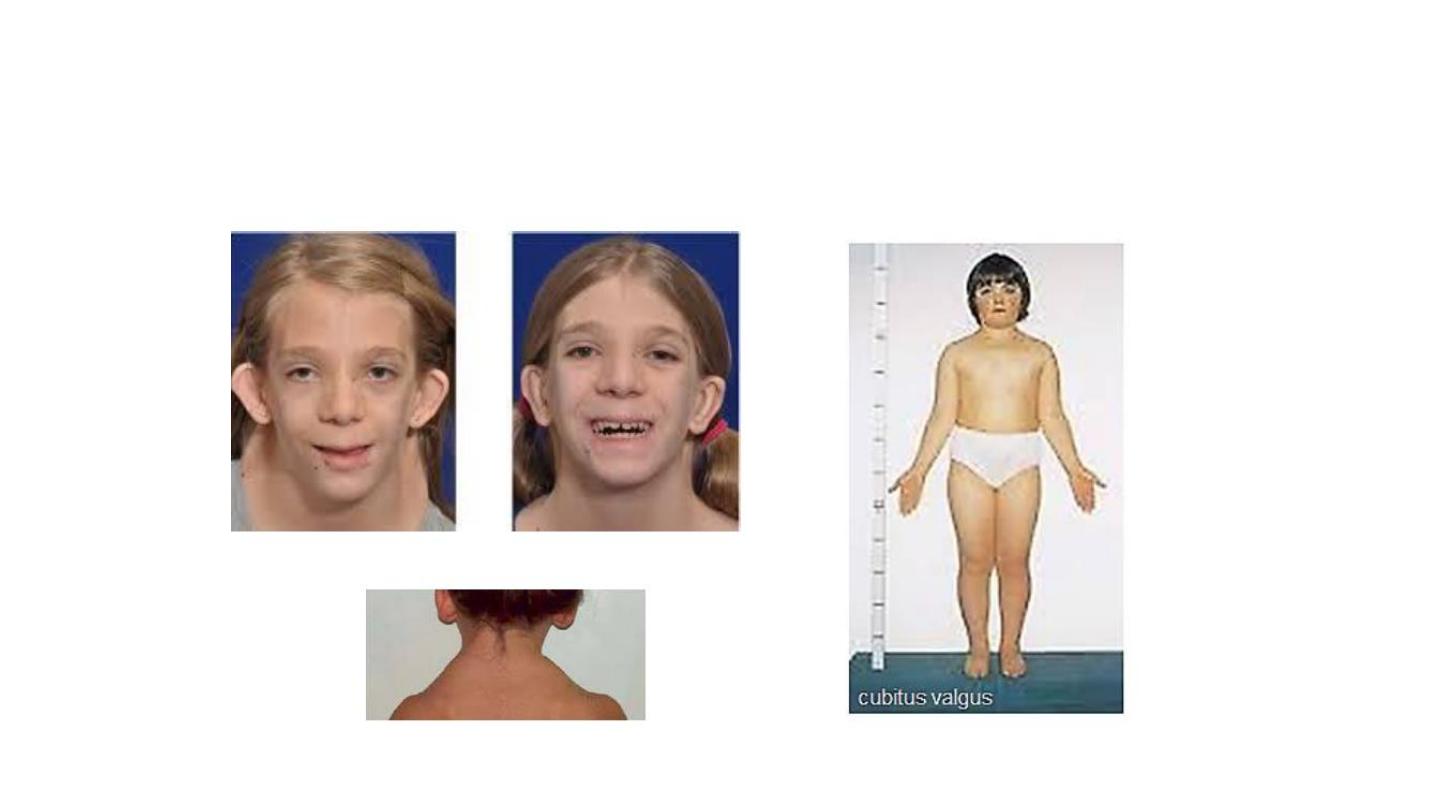
Turner
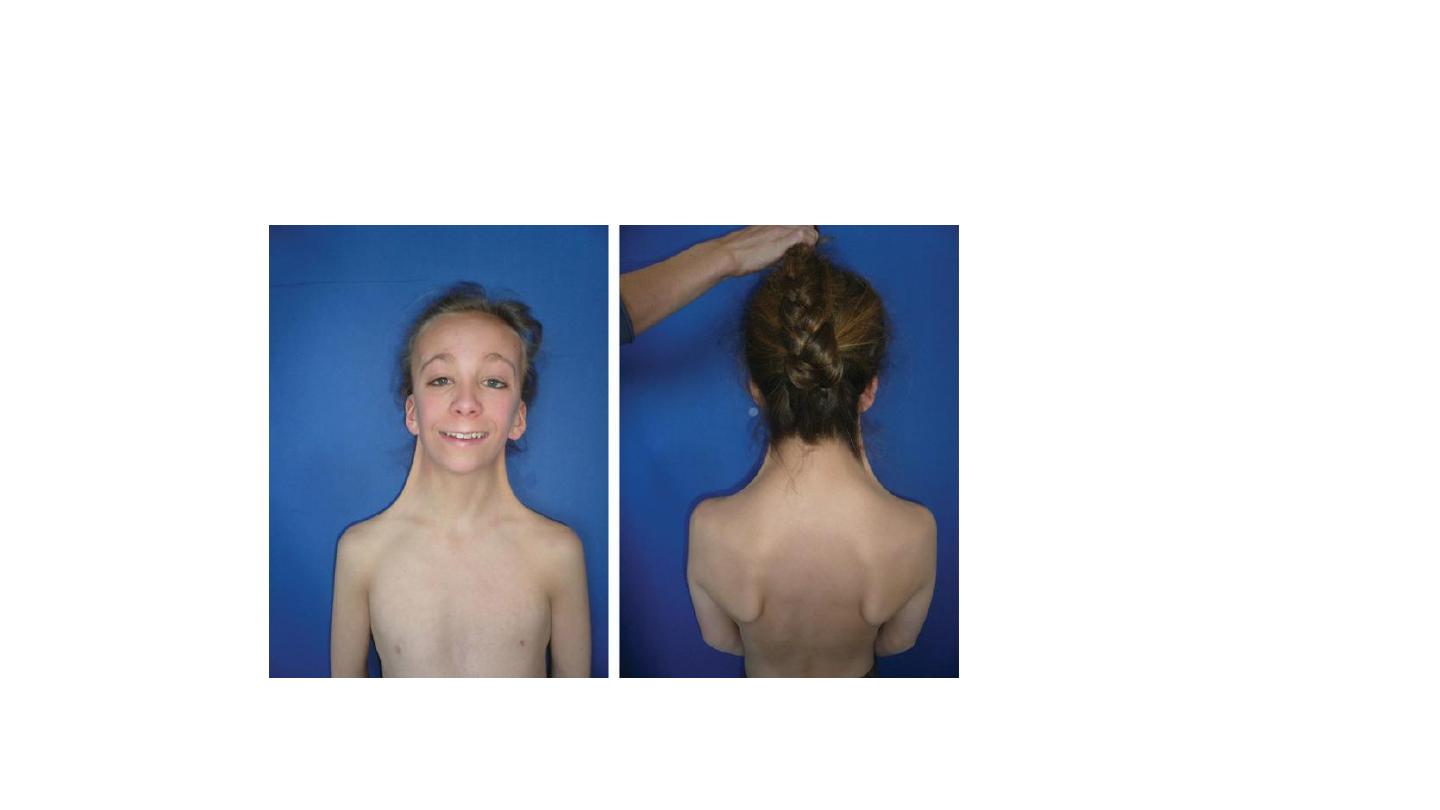
Turner

