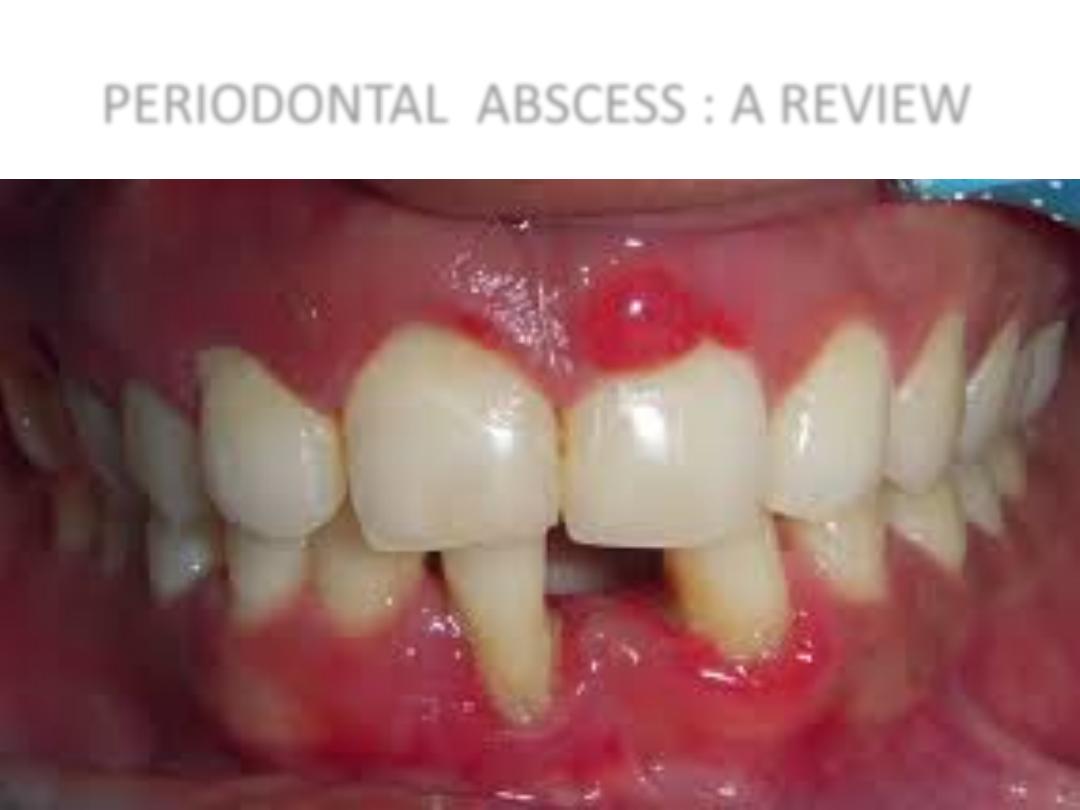
PERIODONTAL ABSCESS : A REVIEW
• PUNIT VAIBHAV PATEL,SHEETAL KUMAR,AMRITA PATEL
• JCDR – JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH
• YEAR: 2011 |MONTH: April|Volume :5 | Issue: 2
• By-
• Navneet Singh Randhawa
• MDS 1
st
year-
• Deptt.of Periodontology and Oral Implantology
Dr . Hussein al dabbagh

INTRODUCTION
• Among several acute conditions occuring in the
periodontium,the abscess is the most important.
• Abscesses of the periodontium are localised
acute baterial infections confined to tissues of the
periodontium.
• The Periodontal abscess represents a chronic and
refractory form of the disease.
• It is a destructive process resulting in localized
collection of pus,communicating with oral cavity
predominantly through gingival sulcus
CHARACTERISTICS
• Localised accumulation of pus in gingival wall
of periodontal pockets
• Usually occuring on the lateral aspect of the
tooth
• Oedematous red and shiny gingiva
• Dome like appearance or may come to a
distinct point

PREVALENCE
• Prevalence of periodontal abscess is relatively
high
• Accounts for 6-14% of all emergencies
• It is the 3d most common dental emergency
after pulpal infection and pericoronitis
• Among dental emergencies periodontal
abscesses represent appr. 8% of all dental
emergencies in the world

CLASSIFCATION
3 types of classifications :-
--Based on anatomic locations
--Based on course of disease
--Based on number
• Based on anatomic locations
:-
Gingival abscess which is a localised purulent
infection involving marginal gngiva
Pericoronal abscesses
Combined perio/endo abscesses
Parietal abscesses

• Based on course of disease
Acute periodontal abscess
Chronic periodontal absce
• Based on number
Single abscess - confined to a single tooth
Multiple abscess – Abscess confined to more
than one tooth

MICROBIOLOGY
• Micro organisms colonizing periodontal abscesses
are primarily Gram negative anaerobic rods
• Porphyromonas gingivalis has highest prevalence
present in about 55-100% of cases
• Fusobacterium nucleatum comes next with
presence in 44-65%
• Capylobacter rectus ,another common bacteria,
has a prevalence rate of about 36%
• Prevotella intermedia,Prevotella melaninogenica
have a prevalence rate of 25-100% and 22-30%
respectively

PATHOGENESIS
The sequelae of periodontal abscess is as
follows:-
Infiltration of pathogenic bacteria
Initiation of inflammatory response
Tissue destruction cased by inflammatory cells
• Formation of inflammatory infiltrate
• Destruction of connective tissue
• Encapsulation of bacterial mass and pus
formation
• Entry of bacteria into soft tissue wall initiates
periodontal abscess formation

PREDISPOSING FACTORS
• Changes in composition of microflora,bacterial
virulence and host defence
• Closure of the margins of periodontal pockets can lead
to extension of infection in surrounding tissue
• Fibrin secretions lead to local accumulation of pus
• Tortuous periodontal pockets assoiated with furcation
defects become isolated and favour the formation of
periodontal abscess
• Inadequate scaling allows calculus to remain in deep
pockets,resolution occurs in coronal portion which
subsequentely blocks drainage

In absence of periodontitis periodontal
abscess can develop due to:-
Impaction
Infection of lateral cysts
Local factors affecting the morphology of
root

IATROGENIC FACTORS ASSOSIATED
WITH PERIDONTAL ABSCESS
• Post non surgical periodontal abscess can occur due to
presence of small remaining fragment of calculus
which obstructs pocket entrance
• Post surgical periodontal abscess occurs immediately
following periodontal surgery
• It can be due to:-
Incomplete removal of subgingival calculus
Perforation of tooth wall by endodontic instrument
Presence of foreign body in periodontal tissue
Post antibiotic periodontal abscess
Treatment with systemic antibiotics without subgingival
debridement in patients with advanced periodontitis

DIAGNOSIS
• The diagnosis of periodontal abscess is based
on the chief complaint and the history of
presenting illness
• Points to be noted while taking history are:-
Any medical condition
Whether patient is currently on medication or not
Any previous dental treatment
Smoking history

• The main steps and aids in diagnosis are:-
• GENERAL EXAMINATION
– Examination of features that may indicate on going
systemic diseases, immune status, fatigue, extremes of age
etc
• EXTRA ORAL EXAMINATION
– Includes evaluation of symmetry of face for swelling,
redness, fluctuance, sinus, trismus and examination of
cervical lymph nodes
• INTRA ORAL EXAMINATION
– Examination of the oral mucosa and dentition for gingival
swelling, redness and tenderness, checking for
suppuration, checking for mobility and elevation,
evaluation of oral hygiene and examination of
periodontium including periodontal screening

• Supplemental diagnostic aids are:-
RADIOGRAPHS
PULP VIALITY TESTS
MICROBIAL TESTS
LAB FINDINGS
• RADIOGRAPHS
– Radiographical techniques such as IOPA,BITEWIGS,OPG are
useful in detection of level of crestal bone,marginal bone loss
and periapical condition of tooth involved
• PULP VITALTY TEST
– Thermal tests or electrical tests are used to assess the viality
of tooth and the subsequent ruling out of the pulpal
infections

• MICROBIAL TESTS
– Samples of pus from sinus/abscess expressed from
gingival sulcus could be sent for culture and senstivity
tests.
• LAB FINDINGS
– Lab tests such as TLC,DLC whose elevated levels can
be an indication of inflammatory response of body to
bacterial toxins
– Assesment of blood glucose level through HbA1c
test/random blood glucose test/fasting blood glucose
levels is mandatory in diabetic patients as it can
predispose to abscess formation

TREATMENT
• Principles for the management of simple dental
infections are:-
• LOCAL MEASURES:-
Drainage
Maintain drainage
Eliminate cause
• SYSTEMIC MANAGEMENT IN 3 STAGES
Immediate management
Initial management
Definitive therapy

IMMEDIATE MANAGEMENT
• Advocated in life threatening infections which
lead to space infections of orofacial regions
• Hospitalization with supportive therapy plus
systemic antibiotics is recommended
• In non life threatening infections oral
analgesics and antimicrobial chemotherapy
are sufficient
• Dosage of antibiotics depends on severity of
infection

• Common antibiotics used are:-
1. Phenoxymethylpenicillin 250-500mg qid 5/7
2. Amoxycillin 250-500 mg tds 5-7 days
3. Metronidazole 200-400 mg tds 5-7 days
• In case of allergy to pencilln:-
1. Erythromycin 250-500 mg qid 5-7 days
2. Doxycyline 100 mg bd 7-14 days
3. Clindamycin 150-300 mg qid 5-7 days

INITIAL THERAPY
• It comprises of:-
1) Irrigation of abscessed pocket with saline
2) Removal of foreign bodies if present
3) Drainage through sulcus with a probe
4) Compression and debridement of soft tissue
5) Oral hygiene instructions
6) Review after 24-48 hrs

• Drainage through periodontal pocket
Treatment of choice if no other complication
Steps are:-
Topical/local anaesthesia
Retraction of pocket wall with probe/curette
Gentle digital pressure
If lesion is small and has good access then treatment
modality Scaling + Curettage
If lesion is large and drainage cannot be established
then treatment modality Antibiotic therapy +Scaling +
Curettage

• Drainage through an external incision:-
• If lesion is large,pin pointing and fluctuating,an
external incision can be made to drain the abscess
• The steps are as follows:-
Topical/local anaesthesia
Vertical incision placed with #11 or #15 blade
The tissue lateral to incision is separated with a periosteal
elevator
Digital pressure applied with gauze
In patients with marked swelling tension and pain systemic
antibiotics only should be used as initial treatment
After acute condition has receded mechanical
debridement is performed

• Periodontal surgery:-
• Main objective of surgical therapy is to
eliminate remaining calculus and to obtain
drainage
• Surgical therapy is advocated in cases of:-
Deep vertical defects
When calculus is left subgingivally after treatment

• Systemic antibiotics with or without local
drainage
• Antibiotics are the prefferred mode of treatment
• Local drainge of abscess is mandatory to eliminate etiological factors
•
Recommended antibiotic regimen is as follows:-
1. Phenoxymethylpenicillin 250-500mg qid 5/7
2. Amoxycillin 250-500 mg tds 5-7 days
3. Metronidazole 200-400 mg tds 5-7 days
•
In case of allergy to pencilln:-
1. Erythromycin 250-500 mg qid 5-7 days
2. Doxycyline 100 mg bd 7-14 days
3. Clindamycin 150-300 mg qid 5-7 days

• Extraction of teeth
• Extraction of teeth/tooth is the last resort to treat
the periodontal abscess
• Certain guidelines for assessing poor prognosis
before extracting tooth are:-
a) Horizontal mobility more than 1mm
b) Class 2-3 furcation involvement of a molar
c) Probing depth >8 mm
d) Poor response to therapy
e) More than 40% alveolar bone loss

CONCLUSION
• Early diagnosis and appropiate intervention
are extremely important for the management
of periodontal abscess
• A single tooth diagnosed with periodontal
abscess that responds favourably to treatment
will not affect longevity of tooth
• Decision to extract a tooth should be taken
only after through clinical assessment
