PRINCIPLES OF RADIOGRAPHIC
INTERPRETATIONInterpretation:
Step by step analytical process that provides an exact idea of the clinical problem and helps to achieve the final diagnosis of any particular lesion.Often some clinical signs or symptoms from the patient’s history indicates the need for a radiologic examination.
Acquiring Appropriate Diagnostic Images:
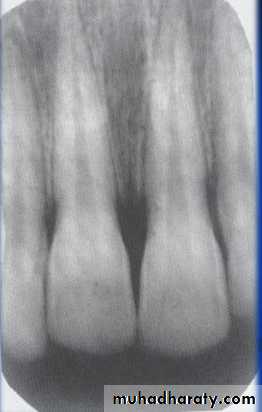
1:Quality of the Diagnostic ImageChecking for elongation/shortage/distortion/ overexposed/ underexposed image………
Which image is useful for R.R.T?
Number and Type of Available Images:Sometime the dentist needs more than one film or view to reach the diagnosis.
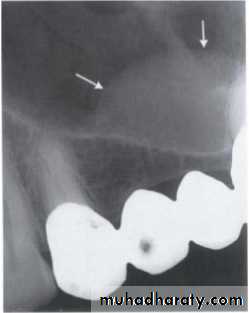
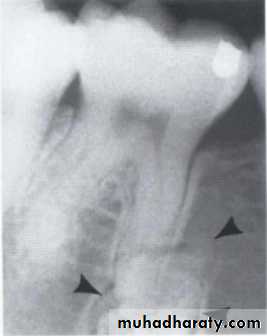
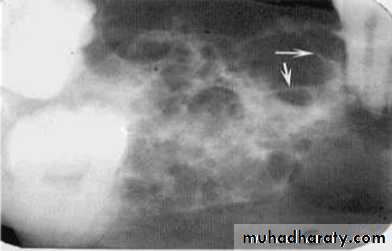
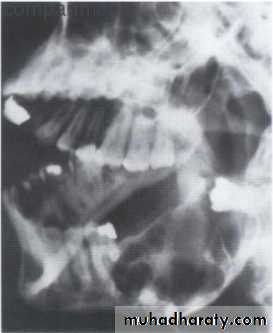
Foreign Body
2:Image Analysis (Intraoral images):Identify normal anatomic landmarks.
Knowledge of normal VS abnormal.
Attention to all regions on the film systematically.
Three visual circuits.
First visual circuit
Periapical before bitewing images
Right maxilla to left; left mandible to right.
*One anatomic structure at a time : eg . In posterior maxilla look at: maxillary sinus, maxillary tuberosity, zygomatic process
*Normal anatomy: eg.bones, canals, foramina.
*Check for symmetry.
Second visual circuit
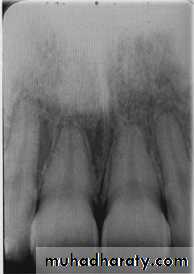
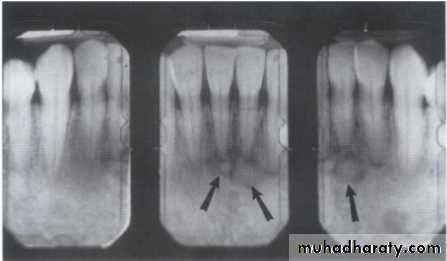
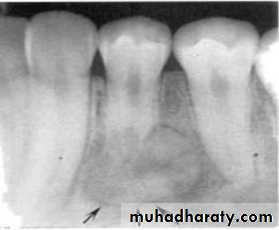
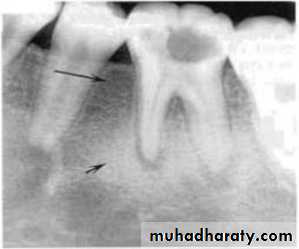
Examination of bone:Height of alveolar bone
Crest relative to teeth
Loss of height-more than 1.5 mm periodontal disease
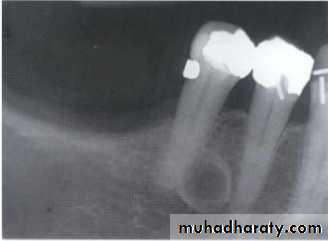
Lamina dura + PDL space + tooth roots
Carcinoma erosion of alveolar crest & ill defined borders.
Third visual circuit
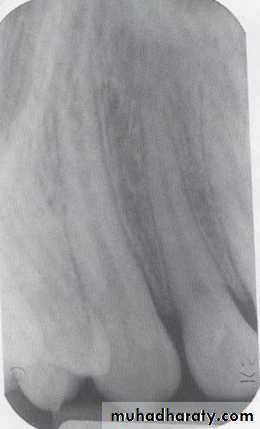
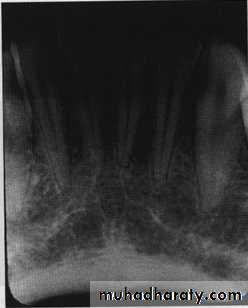
Examination of dentition & associated structures.Number, Sequence, appearance, root structure.
Crowns :defective enamel, caries.
Intreproximal areas & restorations.
Pulp chamber: size, content.
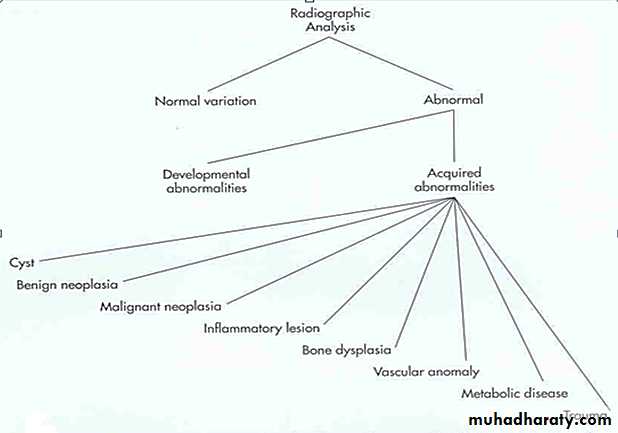
Bone: radiolucent / radiopaque lesions.
Intraosseous Lesions:
Characteristic features of lesional tissue:
1.Multilocular or unilocular.
2.Circumscribed or not.
well circumscribed benign or cystic poorly circumscribed malignant.
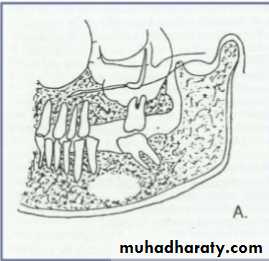
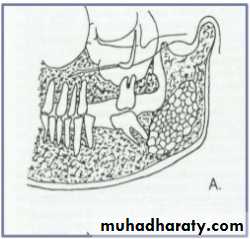
3.Radiolucent lesions without septation have three pattern of bone destruction:
A:Geographic, B:moth eaten ,and C: permeative.
A:Geographic pattern: Single ,large area of
lysis, more than I cm, less aggressivethan malignant lesion.
• Monolocular or non separated benign lesion.
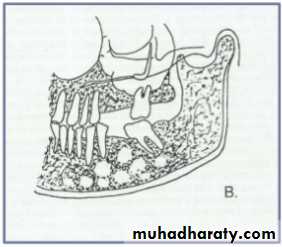
• B:Moth eaten pattern:
• Smaller areas of bone destruction• Less well defined 3 to 5 mm.
• Indicate: benign , malignant & Inflammatory
• conditions like osteomyelitis &osteonecrosis.
• More destructive than geographic pattern.
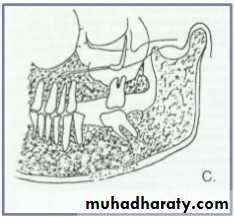
• C:Permeative pattern:
• Much smaller &poorly defined,• 1-2 mm in size
• Aggressive, rapidly destructive lesion
• with cortex involvement.
4:Radiolucent Lesions with Septations
• A:Honeycomb Pattern:• Loculations are small and numerous which
• represent earlier changes than soap bubble
• parttern eg.ameloblastoma.
•
• B:Soap Bubble pattern
• Larger and less numerous loculations due to breakdown of honeycomb pattern eg.ameloblastoma.• D:Tennis Racket Pattern
• Septa intersect at right angles.• eg.Odontogenic myxoma.
• E:Scalloped Pattern
• Incomplete septation gives a falseimpression of multilocularty.• eg.Odontogenic keratocyst
D.
1.Localized or Generalized:
Location helps in diagnosis maxilla /mandible unilateral/bilateral incisor /premolar/molar angle/ramus/body area localized or generalizedStep 1: Localize the Abnormality 1.Localized or Generalized.
2. Position in the Jaws.
3. Single or Multifocal.
4.Size.
Analysis of the Intraosseous Lesions:
• 2.Position in the jaws:
• - Epicenter coronal to tooth- odontogenic epithelium.
• - Epicenter of the lesion is above the mandibular canal-odontogenic in origin .
• - Epicenter -below lDC- non odontogenic
• - Cartilaginous lesion, osteochondroma –condylar region
• - If the epicenter of the lesion is in the sinus, non odontogenic .
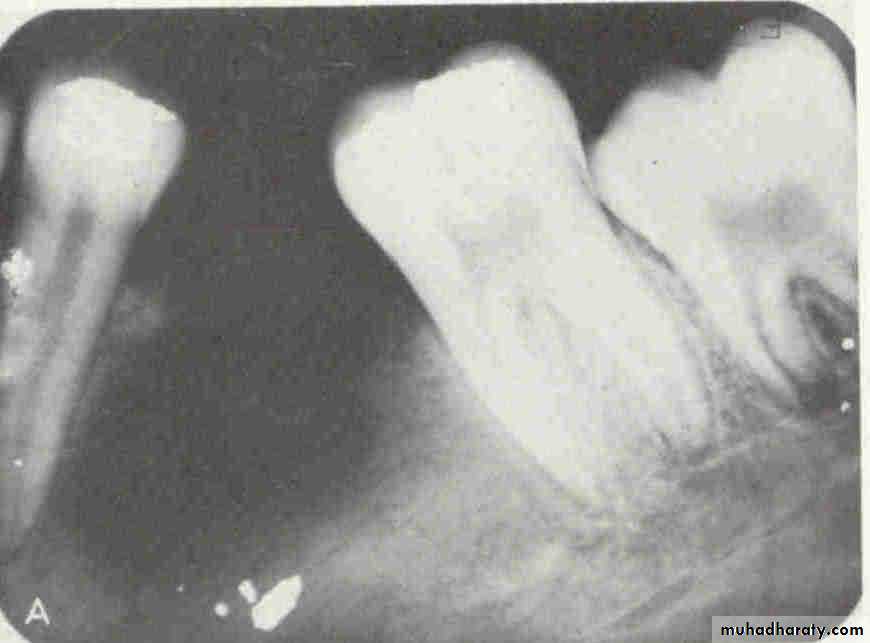
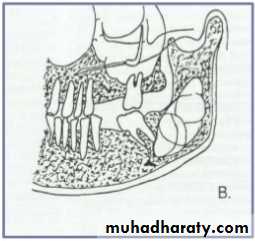
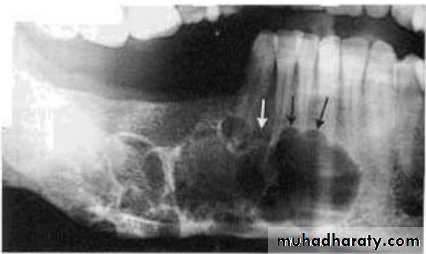
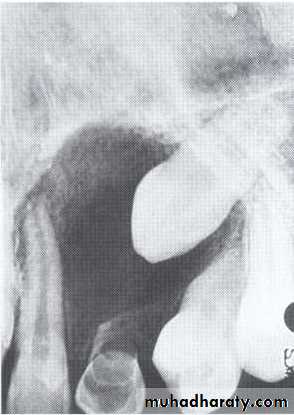
Cystic ameloblastoma displaced IDC (odontogenic origin)
Epicenter coronal to tooth(odontogenic epithelium )
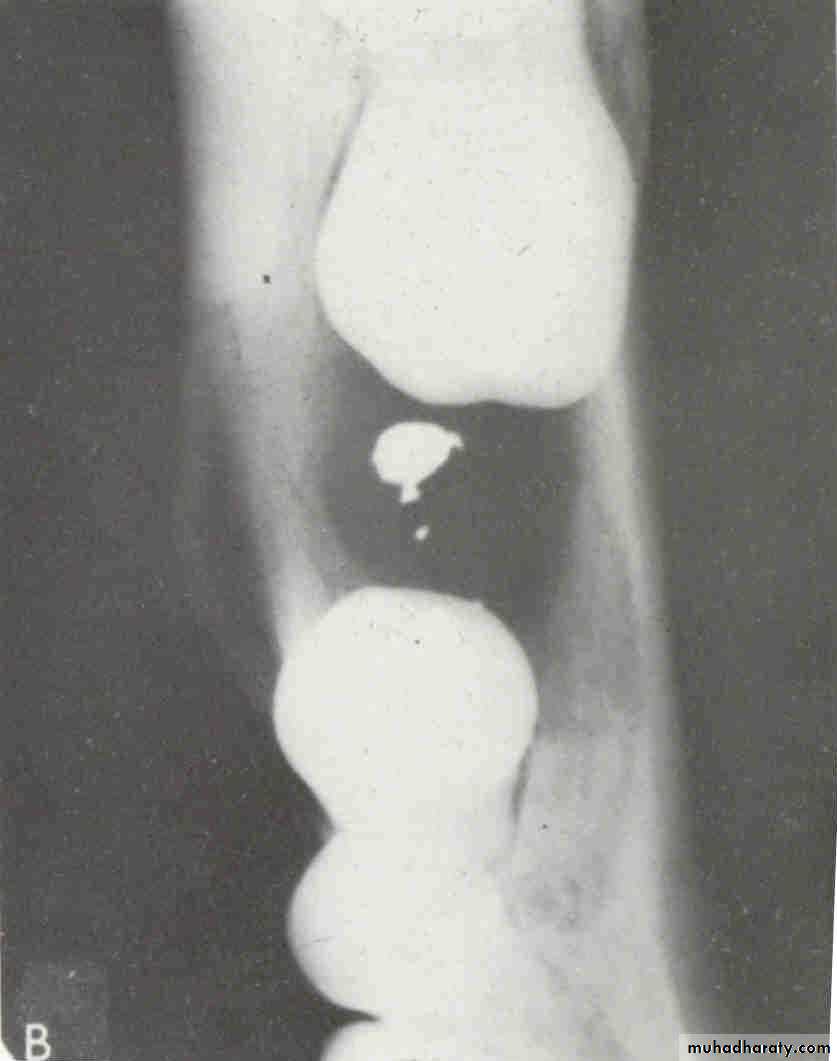
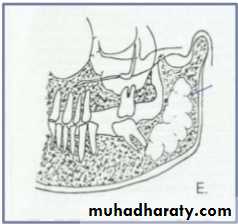
• A lesion (developmental salivary gland
• defect) below the IAC• (non- odontogenic origin).
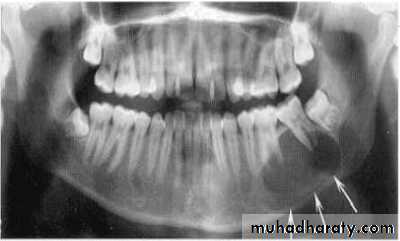
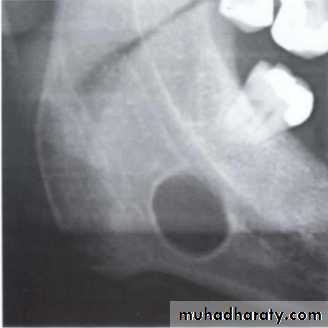
Benign cyst: lack of peripheral cortex(retention
pseudo cyst) indicates that it originated in thesinus (non-odontogenic origin).
• Step 2: Assess the Periphery &Shape
• A:Well Defined borders:Sharp margins:Punched out-sharp- eg.multiple myeloma.
Corticated margins: thin radiopaque line of reactive bone at the periphery of a lesion eg. cysts
•
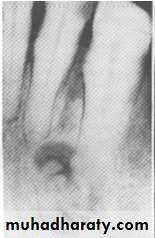
Lateral periapical cyst-well defined corticated margin
Multiple myeloma -punched out lesionSclerotic margins: wide, uneven radiopaque border eg. Periapical cemental dysplasia.
Radiolucent band:Radiolucent (periphery) + corticated eg.Odontoma , Cementoblastoma
Periapical cemental dysplasia
Radiolucent band CementoblastomaOdontoma
• B: Ill Defined Borders:
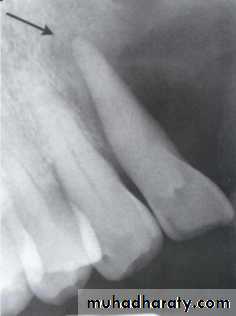
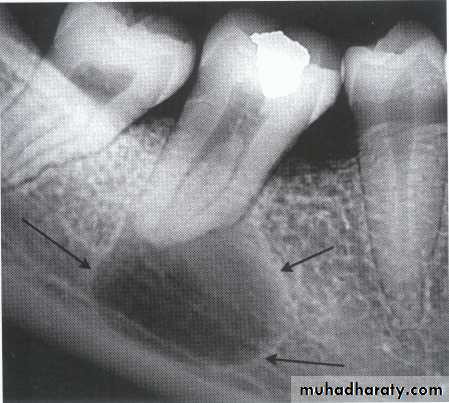
Blending border into adjacent area –gradual transition-normalappearing bone & abnormal appearing trabeculae -sclerosing osteitis• Invasive irregular border-bone destruction-malignancy.
Invasive irregular border-bone destruction/SCC
Blending border. A gradual transition from the dense trabecular of sclerosing osteitis (short arrow) to the normal trabecular pattern (long arrow).• C:Shape
• Circular• Oval
• Scalloped
• Multilocular
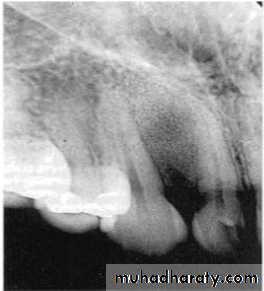
Scalloped/Keratocyst
Multilocular/Ameloblastoma• Step 3 :Analyze the Internal Structure
• Radiolucent• Mixed
• Radiopaque
• Trabeculation
• Septa
• Calcifications
• Tooth or similar entities
• Step4: Analyse the effects of the Lesion on Surrounding Structures:
• Teeth , lamina dura , periodontal ligament space• Inferior alveolar canal & mental foramen
• Maxillary antrum
• Surrounding bone density & trabecular pattern
• Outer cortical bone & periosteal reaction
• Step 5 : Formulate a radiographic interpretation:
• Radiographic report
• Patient & general information• Imaging procedure
• Clinical information
• Findings
• Radiographic interpretation