
1
Course: Clinical Analysis
Lecturer: Dr. Weam Saad
Lecture: Roles of the Clinical Laboratories and biosafety
Roles of the Clinical Laboratories and biosafety
Duties of Clinical Laboratories:
1. Rapid isolation, identification and diagnosis of microorganisms that
caused disease to patient to help physicians in giving the appropriate
treatment as soon as possible.
2. Help in diagnosis of physiological defects that lead to diseases (e.g.
Diabetes) and discovering metabolic disorders.
3. Help in noticing outbreaks and new isolates during routine work.
4. Reference laboratories give advices and help for scientists and
researchers.
Specifications of Laboratory Staff:
1. Well practiced and trained with scientific education for this field.
2. Able to deal with patients and clinical samples (collection, labeling,
saving and transporting samples.
3. Must be careful to avoid contamination mixing and confusion (of
specimens from different patients and for different testes.
4. Professional clinical laboratory staff must be up-to-date or know
about the recently information about standard levels, equipment, new
approaches and technology.
5. Laboratory workers must follow biosafety levels in order to protect
themselves and avoid spreading pathogen from contaminated
samples, specimens and the first step is wearing laboratory coats.

2
Hazards of Clinical Laboratory Work
Workers in clinical laboratories are subject to the following risks:
1. Chemical Hazards.
Chemicals can be harmful by inhalation, skin contact or by entering
mouth. Chemicals like carcinogens, acids, bases or others should only
handle under hood and never pipette by mouth, gloves and eye guards are
necessary.
2. Biological Hazards
Microbiological hazard are the greatest hazards in clinical laboratories,
not only to laboratory workers but also to anyone enters the laboratory,
even visitors and cleaning workers. All specimens collected for
microbiological studies must be assumed as dangerous and infectious,
some countries do immunization for laboratory workers against certain
infection (e.g. hepatitis B, rabies, S. typhi and poliovrus).
3. Radiation Hazards:
This type of hazards occurs only for radioactive workers mainly the
technicians whom deal with radio-therapy for cancer patients. They should
have monitor film badges and special gloves, coats and equipment and they
should know decontamination process after accidents.
3
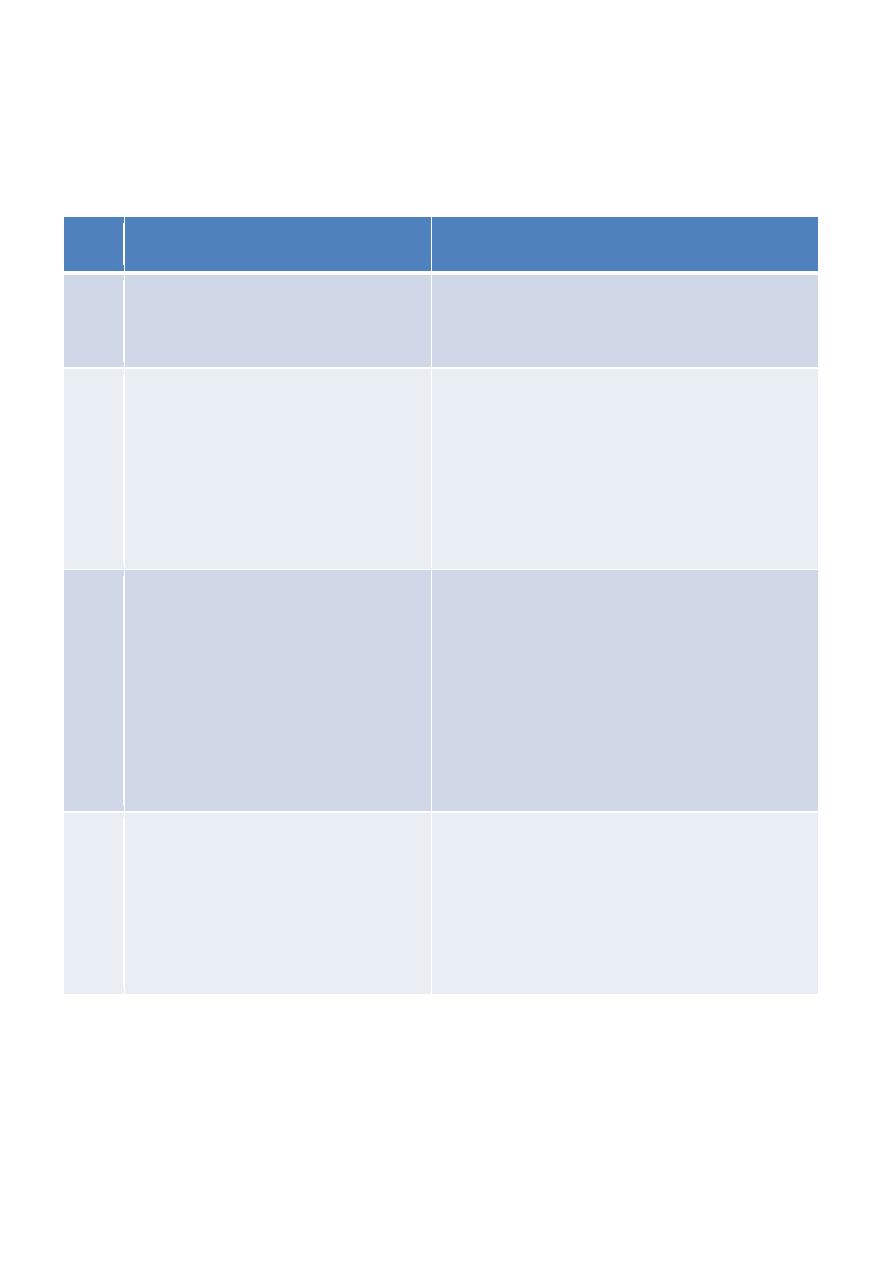
Biosafety Levels;
The following table shows Biosafety Levels (BSL):
Practices
Agents
BSL
BSL1:
Standard Microbiological Practices
Do not cause diseases:
e.g. Lactobacillus casei
1
BSL1: plus BSL2:
• Limited access
• Biohazard warning signs
• Sharp
objects
decontamination
carefully in special containers.
Associated with human diseases and
potentially hazardous, mode of
transmission via ingestion and
mucous membranes: e.g.
Salmonella typhi, E.coli O157:H7
and Staphylococcus aureus
2
BSL2 plus BLS3:
• Controlled access
• Decontamination of all wastes
• Decontamination of lab clothing before
laundering
• Periodic checkup for workers serum
Diseases with aerosol transmission
and lethal consequences e.g.
Yersinia pestis.
3
BLS3 plus BLS4:
• Clothing change before entering
• Shower on exit
• All material decontaminated on exit
Dangerous agents with high risks of
life-threatening disease, aerosol-
transmitted
lab
infections.
Or
related to unknown agents e.g. viral
infections like Hemorrhagic fever
viruses.
4

4
Prevention Advices for lab workers:
1. No eating, drinking, cosmetic use, gum and smoking in the lab.
2. Tied hair, lab coat, and gloves, also covering exposed wounds.
3. Do not put objects like pencils in mouth and avoid touching phones.
4. Work place should be disinfected before and after work.
5. Avoid injuries by sharp objects (e.g. needles, broken glass).
6. Get rid of medical wastes.
