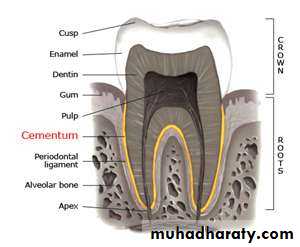
PERIODONTIUM
is defined as the supporting surrounding tissues of the teeth, including :
1. alveolar bone2. the gingiva,
• the periodontal ligaments,4. and the outer layer of the tooth roots (covered with cementum).
The periodontium
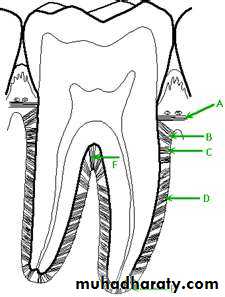
1. Alveolar Process
Lamina Dura
Alveolar eminenceare raised ridges of bone externally overlying prominent tooth root convexities.
Alveolar Process:
Supporting bone is made up of the thickened inner (lingual) and outer (facial) dense cortical plate with less dense trabecular bone sandwiched in between. Cortical plate are thicker in the mandible than maxillaTrabecular bone is composed of many plate-like bone partitions that separate the irregularly shaped marrow spaces located within this bone.
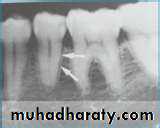
The lamina dura is the much thinner, compact bony layer that lines the wall of each tooth socket (or alveolus).
4
Structure of the Alveolar Bone
Cortical Plate – outermost partAlveolar bone proper or lamina
Spongiosa – spongy bone
6
Cortical Plate
Thicker in the mandible than maxillaGenerally greater on the lingual than on the buccal/facial
7
Alveolar Bone Proper or Lamina
Lamina DuraIn radiograph, appears as radioopaque line distinct from the adjacent spongy bone
8
Spongiosa
Are spongy (or cancellous/trabecullar) bone between the 2 bony plates and between the lamina cribriformis of adjacent teeth or rootsConsists of delicate trabeculae, between which are marrow spaces, filled mostly with fatty marrow
9
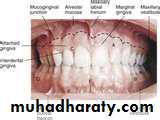
2. The gingiva
unattached gingiva, which includes the free gingiva and the interproximal papillae
attached gingivait's that part of the masticatory (keratinized) oral mucous membrane that covers the alveolar processes of the jaws and surrounds the portions of the teeth near where the root and crown join (cervical portion)
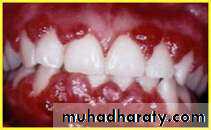
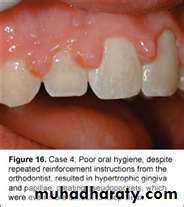
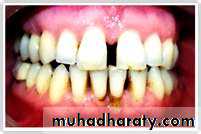
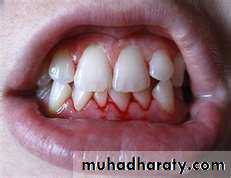
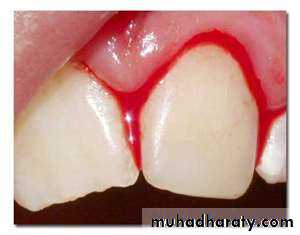
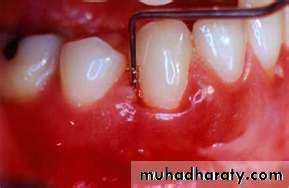
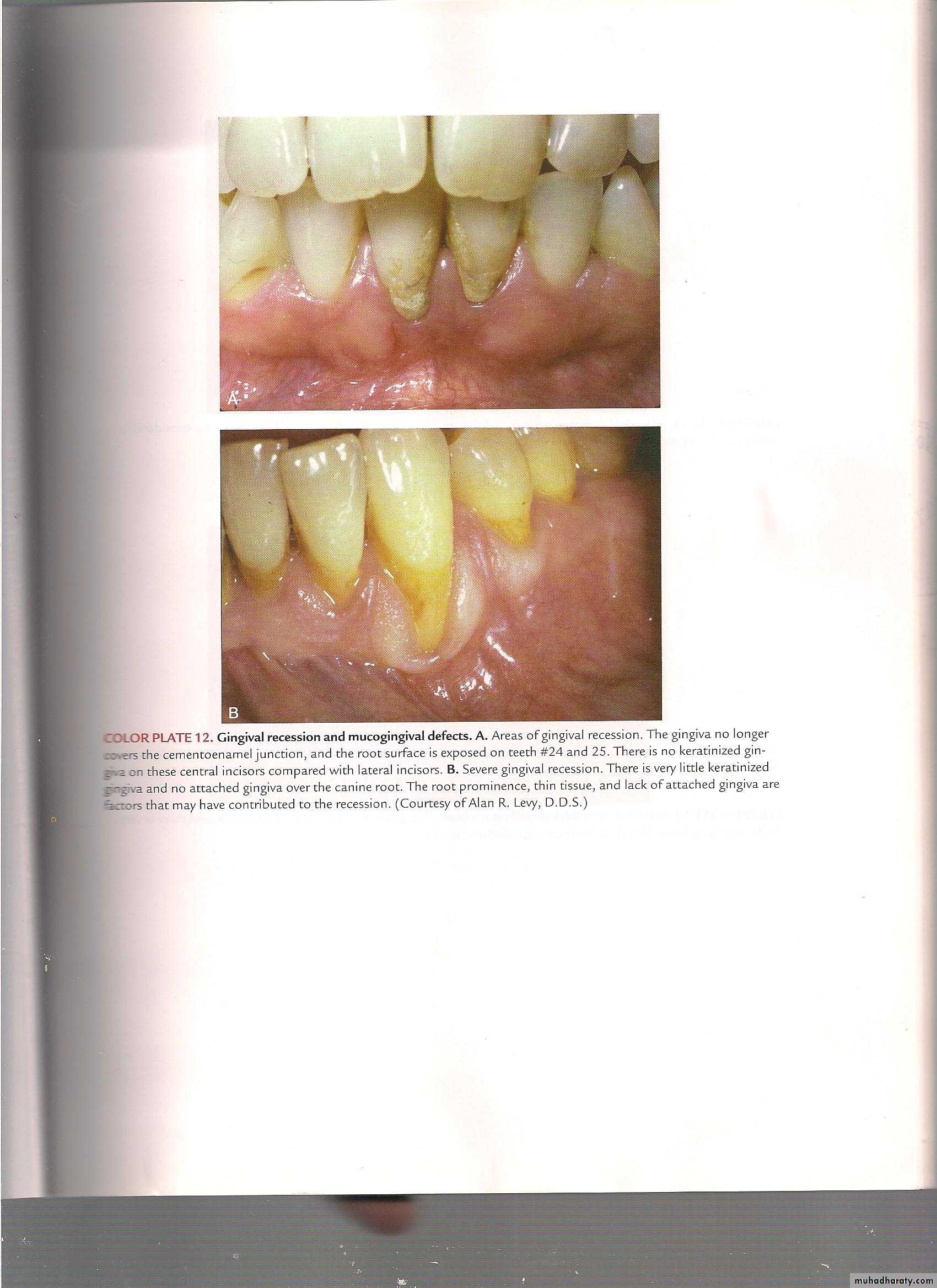
Characteristics of healthy gingiva
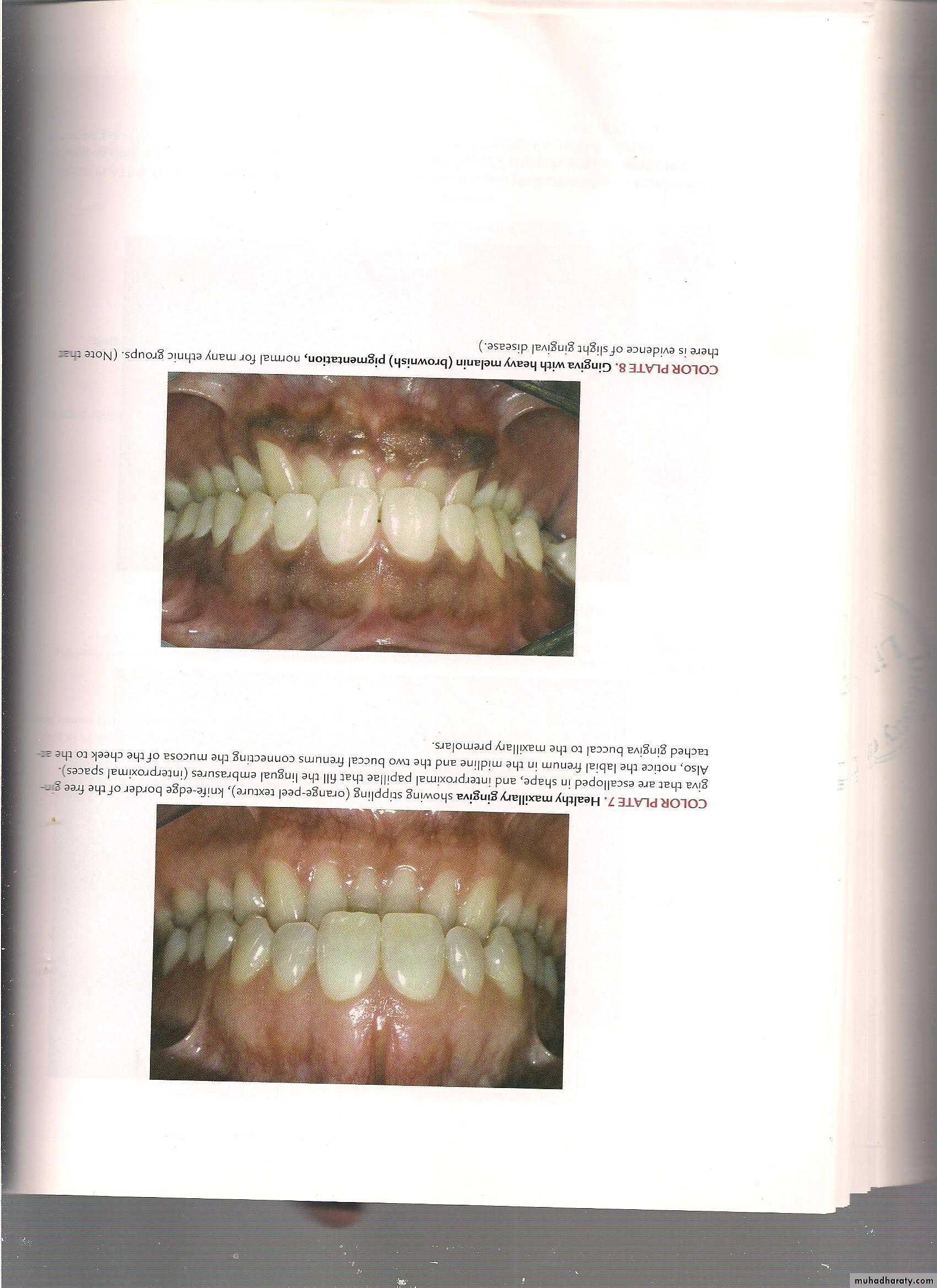
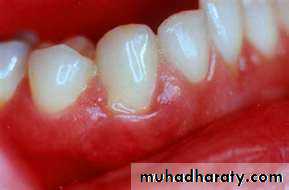
ColorHealthy gingiva usually has a color that has been described as "coral pink." Other colors like red, white, and blue can signify inflammation (gingivitis) or pathology. normal racial pigmentation makes the gingiva appear darker. Because the color of gingiva varies due to racial pigmentation, uniformity of color is more important than the underlying color itself.
Texture
Healthy gingiva has a firm texture that is resistant to movement, and the surface texture often exhibits surface stippling. Unhealthy gingiva, on the other hand, is often swollen and mushy. Healthy gingiva has an orange-peel like texture to it.
Contour
inflamed gums have a "puffy" or "rolled" margin.
Healthy gingiva has a smooth arcuate or scalloped appearance around each tooth.Reaction to disturbance
Healthy gums usually have no reaction to normal disturbance such as brushing or periodontal probing. Unhealthy gums on the other hand will show bleeding on probing and/or purulent exudate3. The periodontal ligament
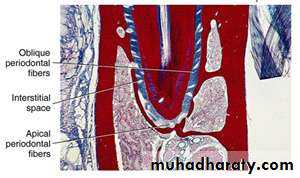
is a very thin ligament composed of many fibers that connects the outer layer of the tooth root (which is covered with cementum) with the thin layer of dense bone (lamina dura) lining each alveolus or tooth socket.
4. Cementum
`
is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. Sharpey's fibers are portions of the principal collagenous fibers of the periodontal ligament embedded in the cementum and alveolar bone to attach the tooth to the alveolus. Cementum is avascular. The cementum is light yellow and slightly lighter in color than dentin. It has the highest fluoride content of all mineralized tissue. It is formed continuously throughout life
FUNCTIONS OF HEALTHY GENGIVA
• Support• Esthetics
• Protection
• Phonetics