PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT
CONTENT
DEFINITIONPRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
- classification of fractures
- displacement types
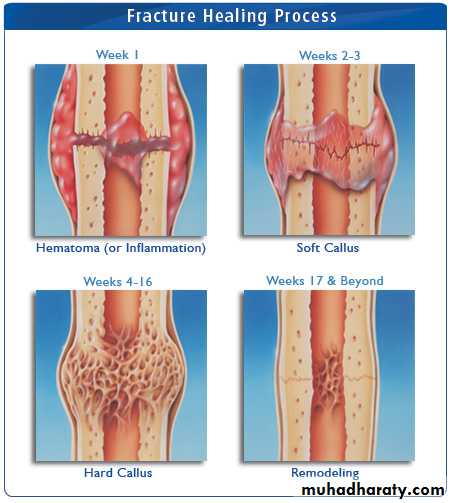
- fracture healing
- principles of treatment
COMPLICATIONS
DEFINITION
CAUSES OF FRACTURES• Sudden trauma
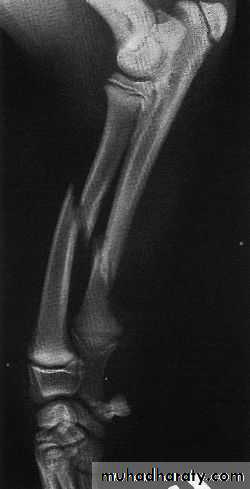
Direct : ( Transverse fracture of the tibia caused by a car hit )
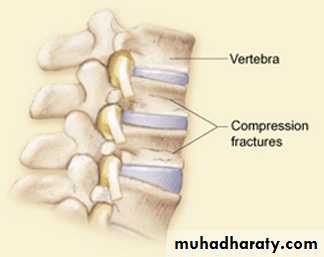
Indirect : ( spiral fractures of the tibia and fibula due to torsion of the leg, vertebral compression fractures, avulsion fractures)
• Stress or fatigue-repetitive stress(athletes, dancers, army recruits)
• Pathological(osteoporosis, Paget’s disease, bone tumors)
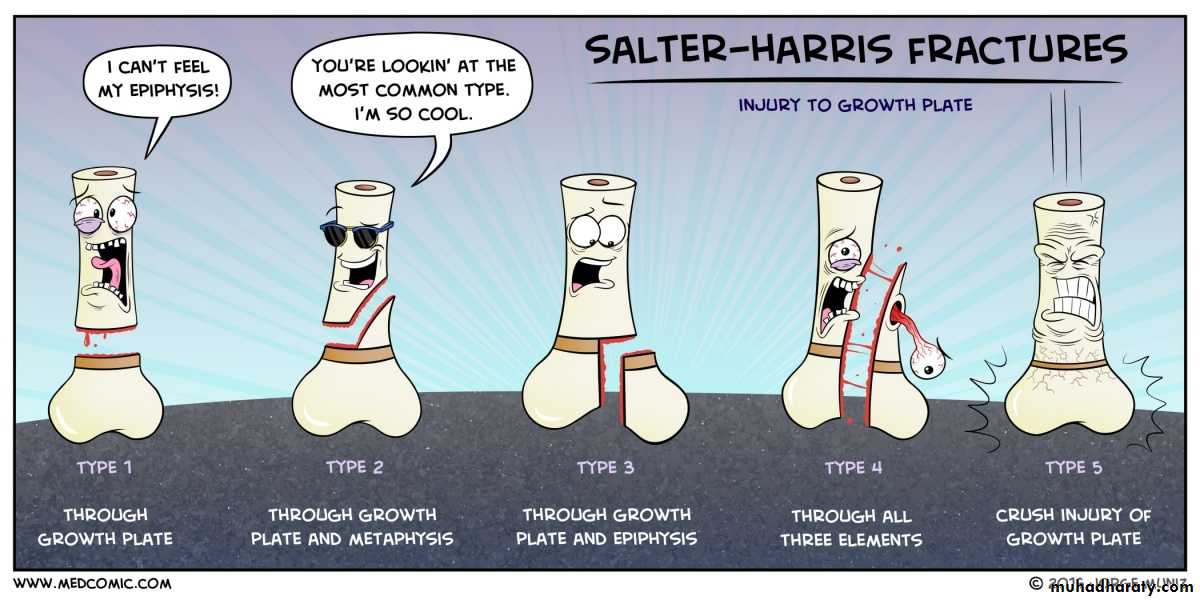
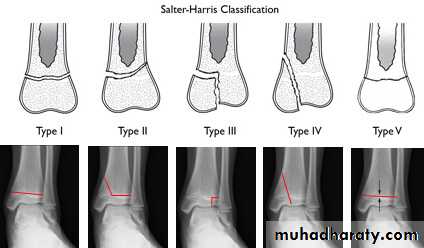
FRACTURE CLASSIFICATION
According to presence of a wound
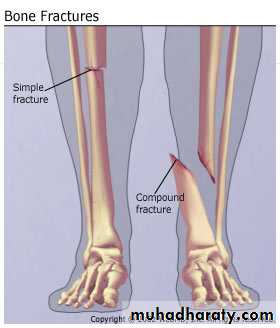
- closed fractures
- open fractures
According to completeness
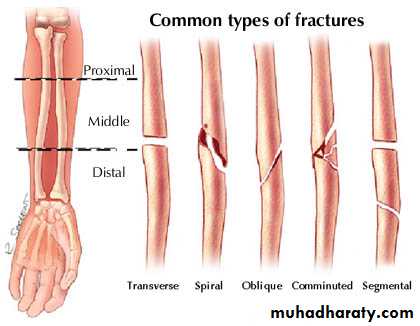
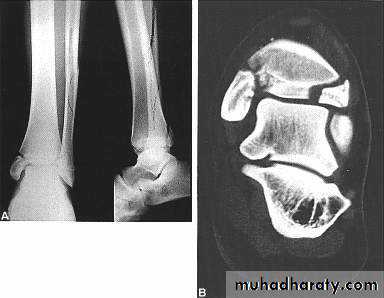
- complete ( subdivided according to the geometry into transverse , oblique , spiral , comminuted , segmental )
- incomplete
According to AO ( usually for academic purposes)
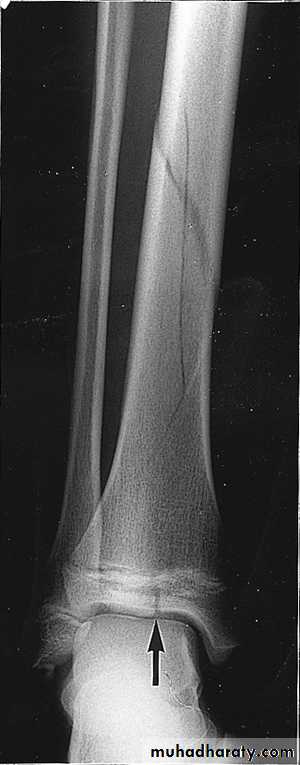
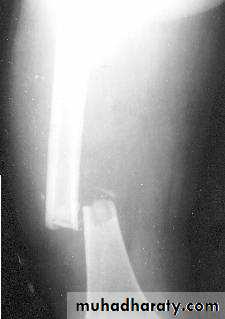
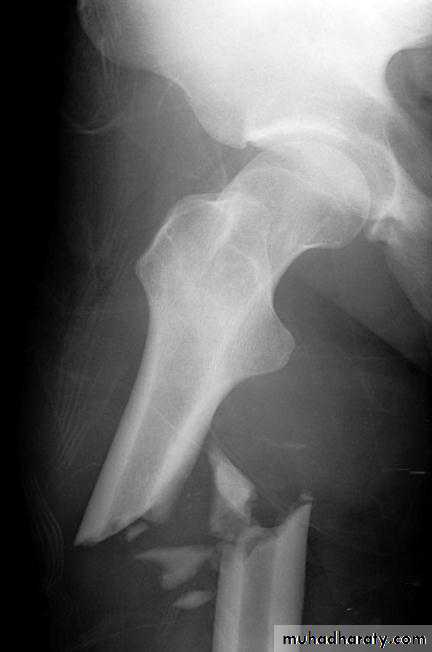
COMPLETE FRACTURES
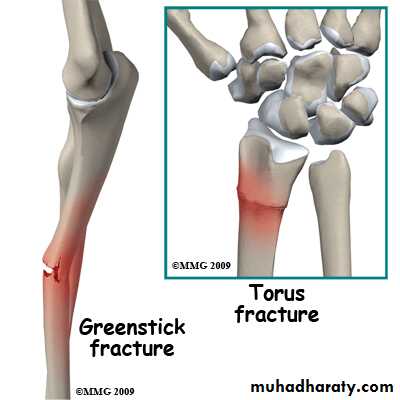
INCOMPLETE FRACTURE
FRACTURES DISPLACEMENT
Why complete fracture fragments displace :
by the force of injury
by gravity
by the pull of muscles attached to them.
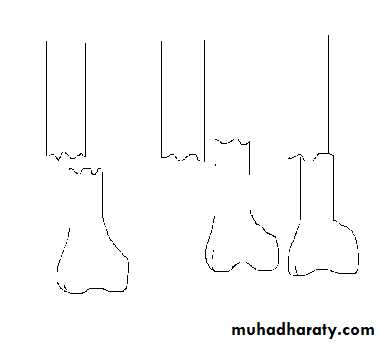
Types of fracture displacement
4 types :Translation/Shift
Alignment/Angulation
Rotation/Twist
Altered length ( shortening or distraction )
• SHIFT
• ANGULATION /TILT• TWIST/
• ROTATION
•
SIDEWAYS
OVERLAPIMPACTION
FRACTURE DIAGNOSIS
Clinical assessmentPain
Deformity
Swelling
Impaired function
Tenderness
RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT
• Plain radiography : ( rule of 2 )2 Views
2 joints
2 limbs
2 occasions
2- CT scan : such as in palvic and spine fractures and in intra articular fracures
3- MRI : to assess the associated injuries ( spine)
4- Bone scan : like in stress fractureHow fracture heals ?
PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE TREATMENT
Treatment of fractures
ATLS ( Advanced trauma life support )Splint the fracture
Associated injuries
- Vascular injuries
- Nerve injuries
Decide for definitive treatment
AO PRINCIPLES
• Anatomic reduction
Fracture reduction and fixation to restore functional anatomical relationships.
2. Stable fixation
Stability by rigid fixation or splintage, as the personality of the fracture and the injury requires
3. Preservation of blood supply
Preservation of the blood supply to soft tissue and bone by careful handling and gentle reduction techniques.4. Early mobilization
Early and safe mobilization of the part and patient.
Principle Of Treatment
The Fracture QuartetOutline
ReduceAim for adequate apposition and normal alignment of the bone fragments
The greater contact surface area between fragments, the more likely is healing to occur
Reduction
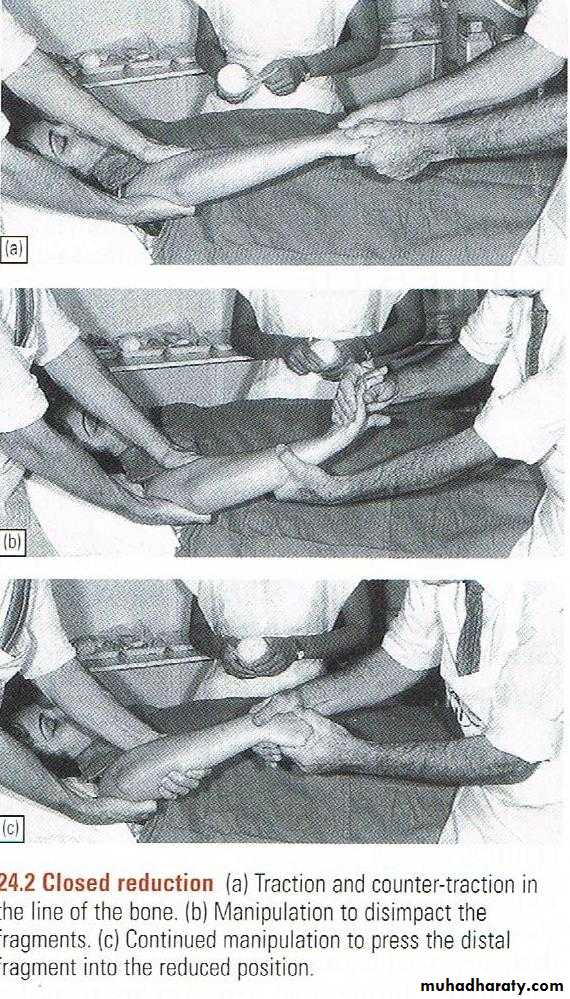
Closed Reduction
Suitable forMinimally displaced fractures
Most fractures in children
Fractures that are likely to be stable after reduction
Most effective when the periosteum and muscles on one side of fracture remain intact
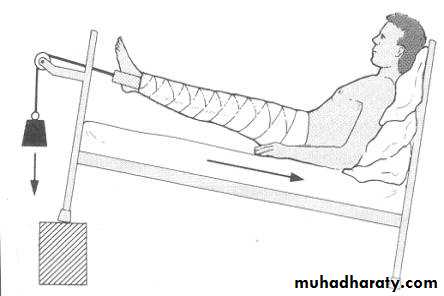
Mechanical Traction
Some fractures (example fracture of femoral shaft) are difficult to reduce by manipulation because of powerful muscle pullHowever, they can be reduced by sustained mechanical traction.
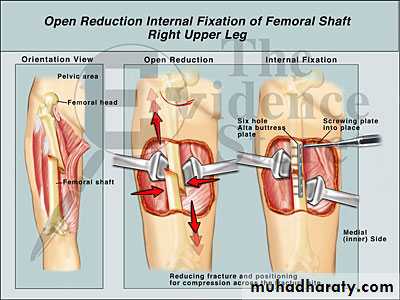
Open Reduction
Operative reduction under direct visionIndications:
When closed reduction fails
When there is a large articular fragment that needs accurate positioning
When an operation is needed for associated injuries
When a fracture needs an internal fixation
Hold
WHY TO HOLDHOLD
Sustained TractionTraction is applied to limb distal to the fracture
To exert continuous pull along the long axis of the bone
Disadvantage and complications
Patient kept on bed for long timePressure ulcer
General weakness
Pulmonary infection
Contracture
Pin tract infection
Thromboembolic event
Methods
Traction by gravity
Balanced traction
Fixed traction
Traction By Gravity
Example:Fracture of humerus
Weight of arm to supply traction
Forearm is supported in a wrist sling
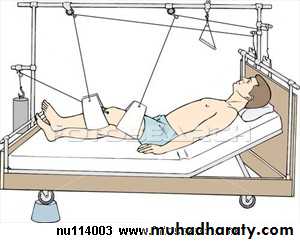
Balanced Traction
SKELETAL TRACTION
Fixed Traction
Useful for when patient has to be transportedThomas’s splint
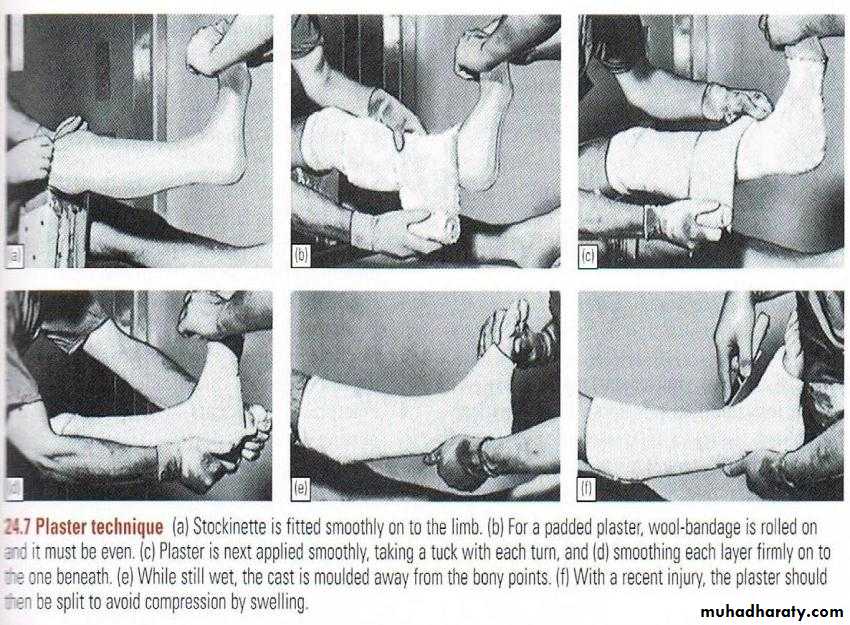
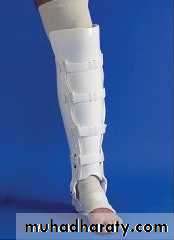
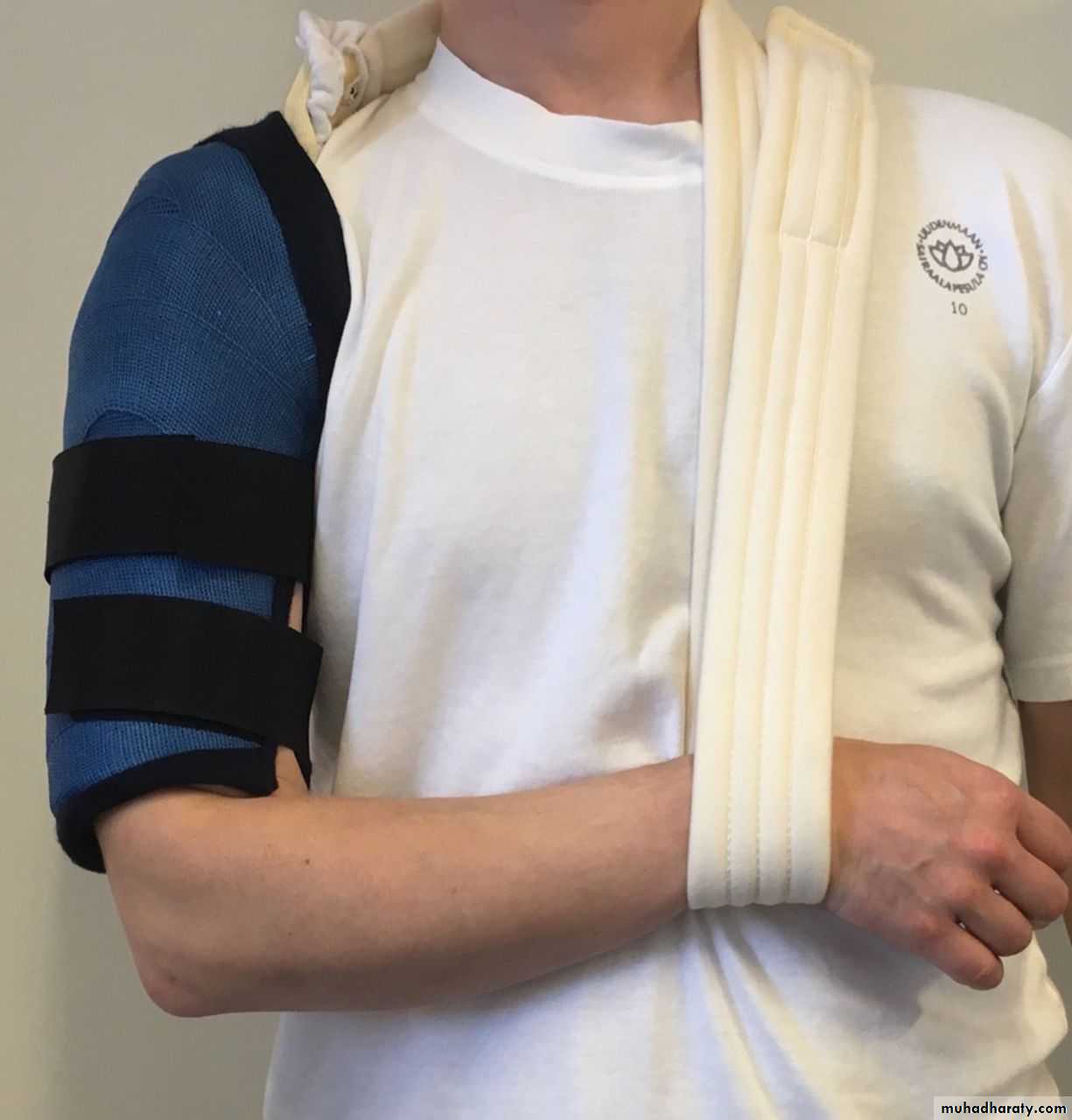
Cast Splintage
TYPES:Plaster of Paris
Fibreglass
Especially for distal limb # and for most children #
Disadvantage: joint encased in plaster cannot move and liable to stiffen
Complications
COMPLICATIONS OF CASTFunctional Bracing
Functional braceFunctional brace
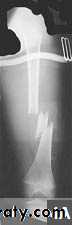
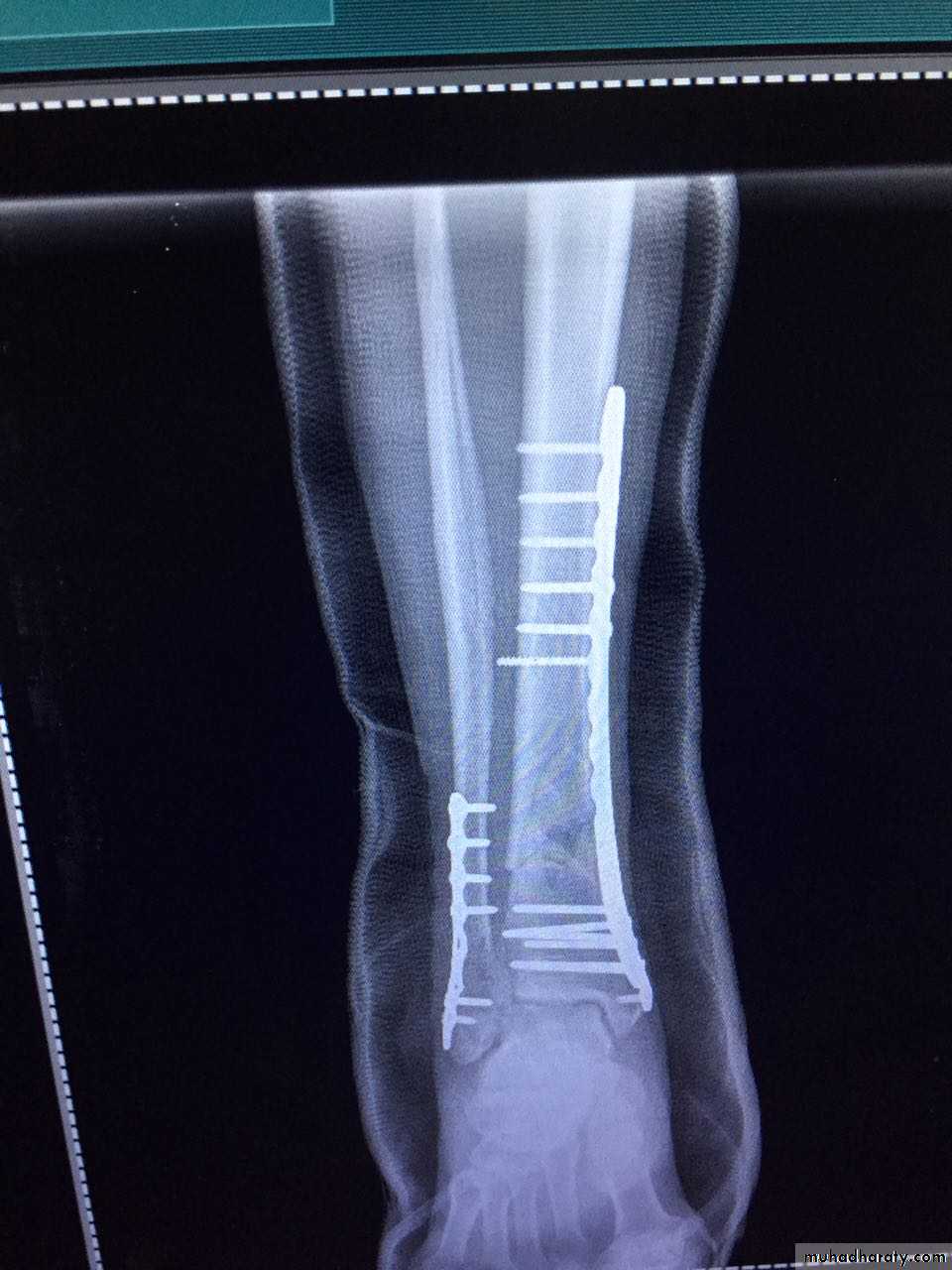
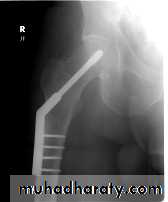
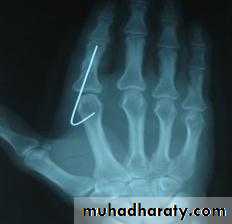
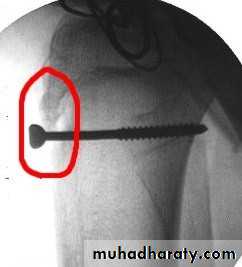
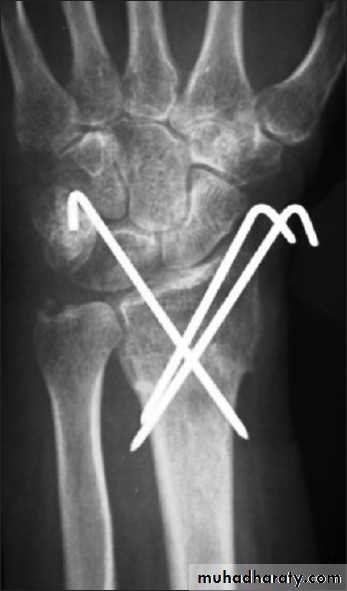
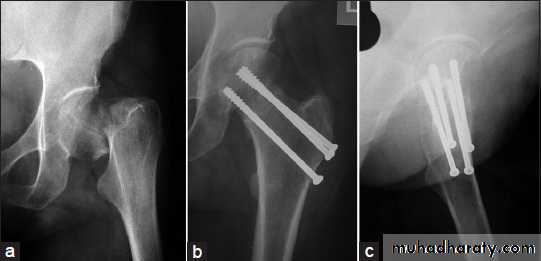
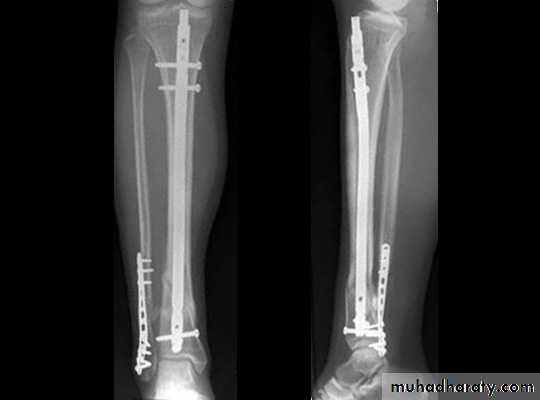
INTERNAL FIXATION
Indications
advantages
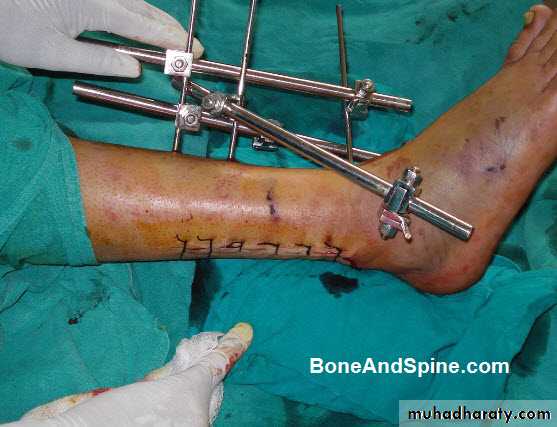
EXTERNAL FIXATIONPrinciple
IndicationsAdvantages
Exercise ( rehabilitation )Prevention of edema
active exercise and elevation
Active exercise also stimulates the circulation. Prevents soft-tissue adhesion and promotes fracture healing.
Preserve the joint movement
Restore muscle power
Functional activity
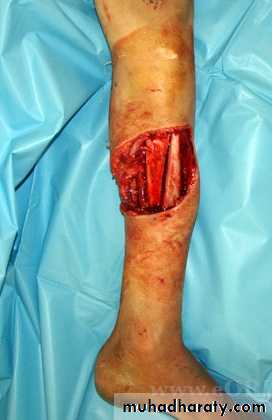
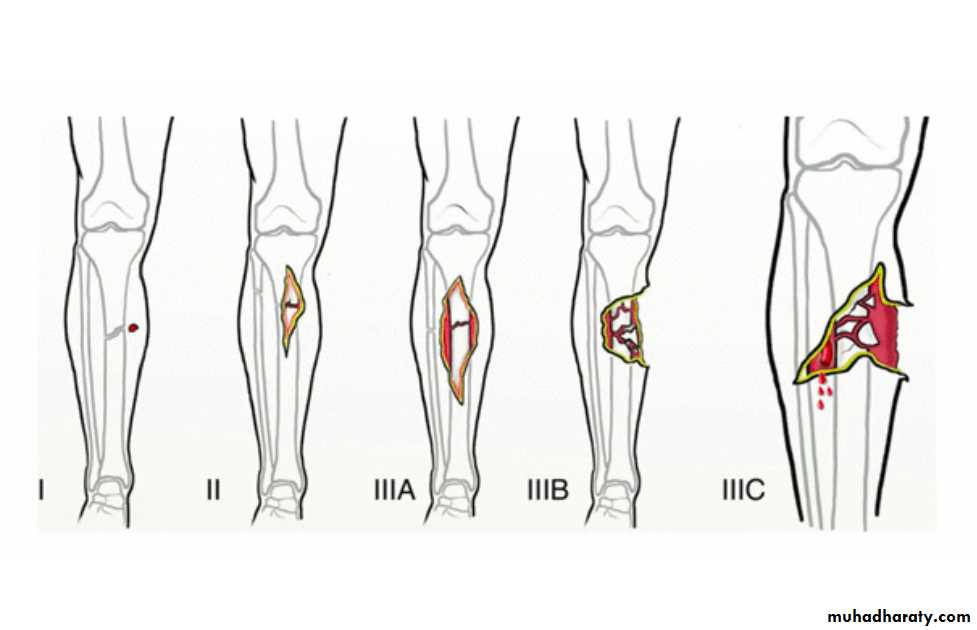
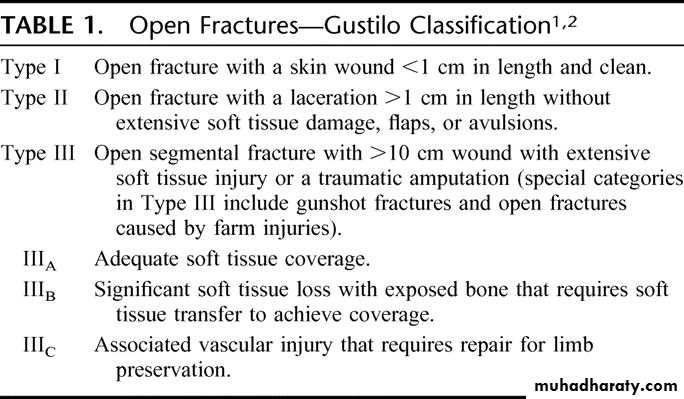
Open Fractures
A break in skin and underlying soft tissues leading directly to communicating with the fracture
Emergency Management of Open Fracture
A,B,CSplint the limb
Sterile cover - prevent contamination
Look for other associate injury
Check distal circulation – is distal circulation satisfactory?
Check neurology – are the nerve intact?
AMPLE history- Allergies, Medications, Past medical history, Last meal, Events
69
Relieve pain
Tetanus prophylaxisAntibiotics
Washout / Irrigation
Wound debridement
fracture stabilization ( according to grade)
Deal with soft tissue and skin injury.