Diagnosis and treatment planning for removable partial denture
Ari AsoIntroduction
Most clinicians choose an RPD for a partially edentulous patient if they need to restore lost residual ridge, achieve appropriate esthetics, increase masticatory efficiency, and improve phonetics but are unable to do so with dental implants or fixed partial dentures due to financial constraints or patient desires” - Bohnenkamp DM Removable Partial Dentures.Diagnosis : the determination of the nature of a disease .
Treatment plan : the sequence of procedures planned for the treatment of a patient after diagnosis .Patient interview
The dentist should follow a sequence that includes1. Chief complaint and its history.
2. Medical history review.
3. Dental history review, especially related to previous prosthetic experience(s).
4. Patient expectations.
Clinical examination
Oral examination :An oral examination should be accomplished in the following sequence :
1-visual examination.
2- pain relief and temporary restorations.
3- radiographs.
4- evaluation of abutment and periodontium.
5- vitality tests of individual teeth.
6- determination of the floor of the mouth position.
7- Oral prophylaxis and impressions of each arch.
Visional examination
This includes : extra oral and intra oral examination.Extraoral examination :
TMJ - tenderness, mouth opening deviation & clicking.Intraoral examination :1-No of teeth present with their clinical evaluation 2-Malposed teeth 3-Carious teeth 4-Existing restoration- sensitivity to percussion 5-Periodontium 6-Residual ridges 7-Saliva 8- Investing structures 9-Occlusion and occlusal plane 10-Oral hygiene index.
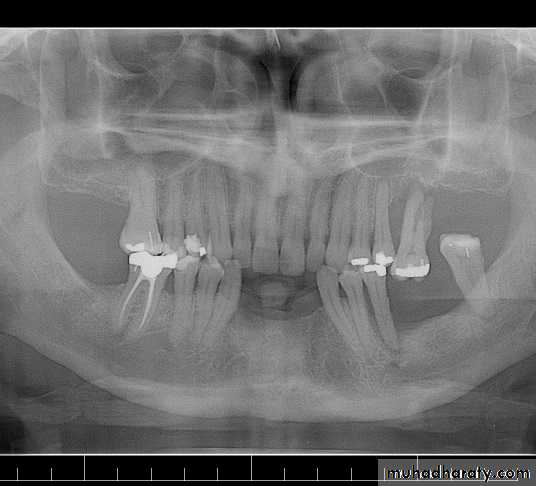
Radiographs
1-areas of infection and other pathologies .2-the presence of root fragments, foreign objects, bone spicules and irregular ridge formations.
3-the presence and extent of caries and the relation of carious lesions to the pulp and periodontal attachment .
4-evaluation of existing restorations : evidence of recurrent caries, marginal leakage, and overhanging gingival margins.
5-the presence of root canal fillings .
6-evaluation of periodontal conditions present .
7-to evaluate the alveolar support of abutment teeth, their number, the supporting length and morphology of their roots.
8-the relative amount of alveolar bone loss suffered through pathogenic processes, and the amount of alveolar support remaining.
determination of the floor of the mouth position :
To locate inferior borders of lingual mandibular major connectors.Oral prophylaxis and impressions :
oral hygiene status before prosthodontic treatment is important.Evalution of the abutment
Anatomic consideration -
Root length, size and form.
vitality tests.
caries evaluation .
Periodontal health .
Malpositions .
Analysis of Occlusal Factors.
Treatment planning
The objectives of any prosthodontic treatment may be stated as follows:1-the elimination of disease.
2-the preservation, restoration, and maintenance of the health of the remaining teeth and oral tissues.
3-the selected replacement of lost teeth; for the purpose of restoration of function.
4-comfort and in esthetically pleasing manner.
Prosthodontic treatment options
1-Implant supported fixed dental prosthesis.2-Fixed dental prosthesis.
3-Removable partial denture.
4-Complete denture.
5-Combination of the above.
6-No treatment at all.
Indication of removable partial denture
1-Distal extension situations.
2-After recent extractions.
3-Long span.
4-Need for cross-arch stabilization.
5-Excessive loss of residual bone.
6-Sound abutment teeth.
7-Abutment with guarded prognosis.
8-Economic considerations.
Development of treatment planning
(Phase I)1-Collection and evaluation of data
2-Pain, infection control
3-Biopsy
4-Patient motivation
(Phase II) 1-Removal of deep caries 2-Extirpation of necrotic pulp
3-Extraction of non- retainable teeth 4-Periodontal treatment
5- Interim prosthesis 6-Occlusal equilibrium
7-Patient education
(Phase III) 1- Preprosthetic surgical procedures 2-Definitive endodontic procedures 3-Definitive restoration of teeth 4-Fixed partial denture construction 5-Reinforcement of education and motivation of the patient.
(Phase IV) 1-Construction of removable partial denture
2-Reinforcement of education and motivation of patient
(Phase V) 1-Post insertion care 2-Periodic recall 3-Reinforcement of education and motivation of patient.