
1
Medicine Dr. Samar
Nutritional problems:
M Obesity in western world.
M Protein – energy malnutrition.
Proportion of healthy well-balanced food:
c Fruits & vegetables:
c Bread, rise, potables.
c Milk & diary food.
c Meat, fish ,egg, beans.
c Food rich in fat & sugar.
Nutrition of disease:
# Animal food content ( saturated) : IHD, DM
# Vit A deficiency, high fat: cancer.
# Added carcinogen: nitrates for preserving foods.
# Accidental contamination: moulds producing a fat toxin.
# Processed food: high fat & sugar: obesity & dental caries.
# Industrial pollution of food: insecticides.
1- High fiber diet. ( constipation)
2- Low sodium diet in treatment. ( hypertension)
3- Gluten – free diet. ( in celiac diseases)
Role of doctor:
D Advise the patients to take a balanced diet.
D Help him avoid any food, faddism, because it is a commercial interest rather than
about health.

2
Nutrient two main groups:
j Macronutrients: fat, protein & carbohydrate ( produce fuel for energy)
j Micronutrients: vitamins & minerals ( small amount )
Energy balance (energy intake = energy expenditure)
Energy expenditure:-
1- BMR: obligatory energy expenditure to maintain metabolic functions in tissue &
sustain life.
Grader with fat, free mass = total body mass – fat mass (less in female)
2- Extra metabolic energy: growth, pregnancy, lactation, fever.
*Higher in smoke (BMR)
3- Thermal regulation.
4- Energy for food digestion.
5- Muscle activity vary with occupation & life style.
Energy intake: depend on:-
1- Macronutrients in necessary to provide with energy.
2- Oxidation in mitochondria of CHO, fat, protein, alcohol to generate energy
as: ATP.
W
Each macronutrient produce different amount of energy
Fat 8 kcal/g
CHO 4 kcal/g
Protein 4 kcal/g
Regulation of energy balance:-
o Coordinated in hypothalamus, received afferent fibers from stomach.
E Ghrelin, falls after eating, rise gradually to suppress satiety.
E Leptin increase with growing fat mas.
E Saturation with low insulin ( glycogenolysis , TG, lipid ,ketosis , proteolytic
muscle)
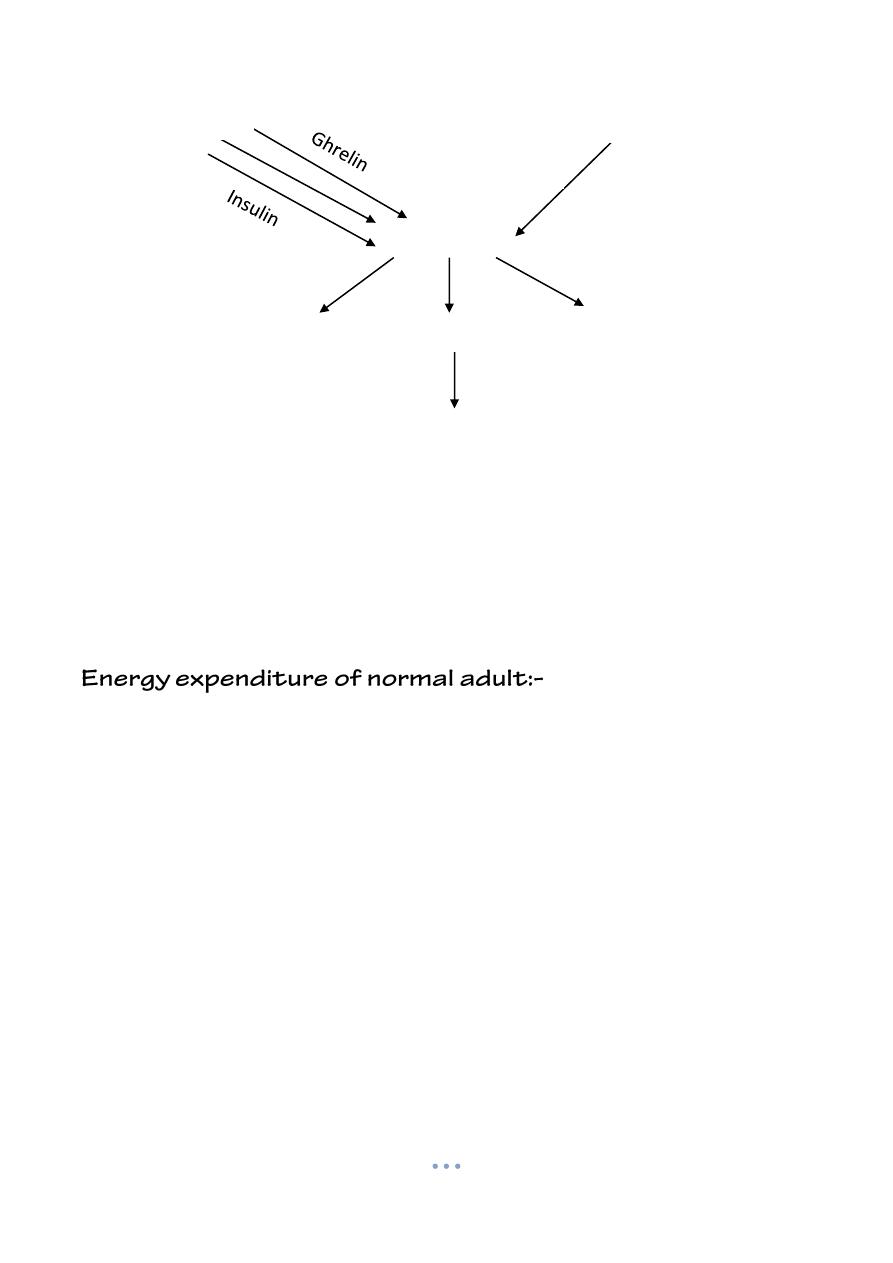
3
Hypothalamus
Over nutrition:-
- BMR increase, TG storage, fat deposition in liver (fatty liver).
- Accumulation of fat in liver & muscle.
Male: rest: 1600 kcal
Light work: 2400 kcal
Heavy work: 2800 kcal.
Female: rest: 1300 kcal.
Light work: 1900 kcal
Heavy work: 2300 kcal
Energy requirement increase in:
1- Exercise
2- Fever.
3- Trauma.
4- Rapid growth.
5- Pregnancy.
Hormone
Stomach
Adipose tissue
Leptin
Satiety
Hormone for fertility
Energy expenditure or
storage

4
Average daily requirement:
Female: 1940 kcal.
Male: 2550 kcal.
50% CHO.
35% fat.
15% protein
Protein
:-
b 20 amino acid, nine essential.
b 5 AA conditionally essential.
b Biological value: proportion of essential AA, egg, milk, meat.
b 2 different vegetable protein complementary in vagan.
Sara Abdulbasit
