
) أ.م.د. احمد عبداالمير دفار ( اختصاصي جراحة الصدر و القلب و االوعية الدموية
1
1
PDA (Patent Ductus Arteriosus)
Objective : To show the definition and management of PDA ( Patent
Ductus Arteriosus )
Embryology and Pathologic Anatomy
The ductus arteriosus normally extends from the main or left pulmonary artery to the
descending aorta just distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery.
Closure occurs usually after birth. Final closure may occur at any age but is
uncommon after 6 months.
Incidence, Mortality, and Morbidity
The incidence increases greatly with prematurity and with decreasing birth
weight and is related to several factors, including decreased smooth muscle
in the ductal wall, diminished responsiveness of the ductal smooth muscle to
oxygen, and possibly elevated circulating levels of vasodilatory pros-
taglandins.
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
Tachypnea, poor feeding, growth failure, recurrent respiratory tract infections,
exercise intolerance. Eisenmenger’s complex or cardiac failure may develop if a large
PDA is not treated early.
Those with a small PDA are either asymptomatic or are minimally sympyomatic.
Physical examination
A machinery murmur
a systolic or continuous murmur, which is heard best in the
pulmonic area and radiates toward the middle third of the clavicle.
Investigation
- CXR
It may be normal or shows pulmonary congestion (plethoric lungs) while
cardiomegaly is seen if cardiac failure is present.
- Electrocardiogram
- Echocardiography
It is diagnostic
- Cardiac catheterization
It's not required for those with classic findings.

) أ.م.د. احمد عبداالمير دفار ( اختصاصي جراحة الصدر و القلب و االوعية الدموية
2
2
Treatment
Surgery is indicated for large PDAs or for those PDAs which didn't close
spontaneously
.
Management of PDA in Premature Infants
Two therapeutic options are available:
1. Pharmacologic closure with prostaglandin inhibitors such as indomethacin
Final closure may be achieved in more than 70% of infants, although the ductus may
reopen transiently in some children. Reopening occurs most frequently in the most
premature infants and may be treated with a second course of indomethacin, but the
success rate is lower. The success of therapy with indomethacin is related to the birth
weight and postnatal age of the infant. Term infants are generally unresponsive to
pharmacologic therapy.
2. Surgical closure
Used if there is a contraindication to indomethacin or failure of the PDA to close.
) أ.م.د. احمد عبداالمير دفار ( اختصاصي جراحة الصدر و القلب و االوعية الدموية
3
3
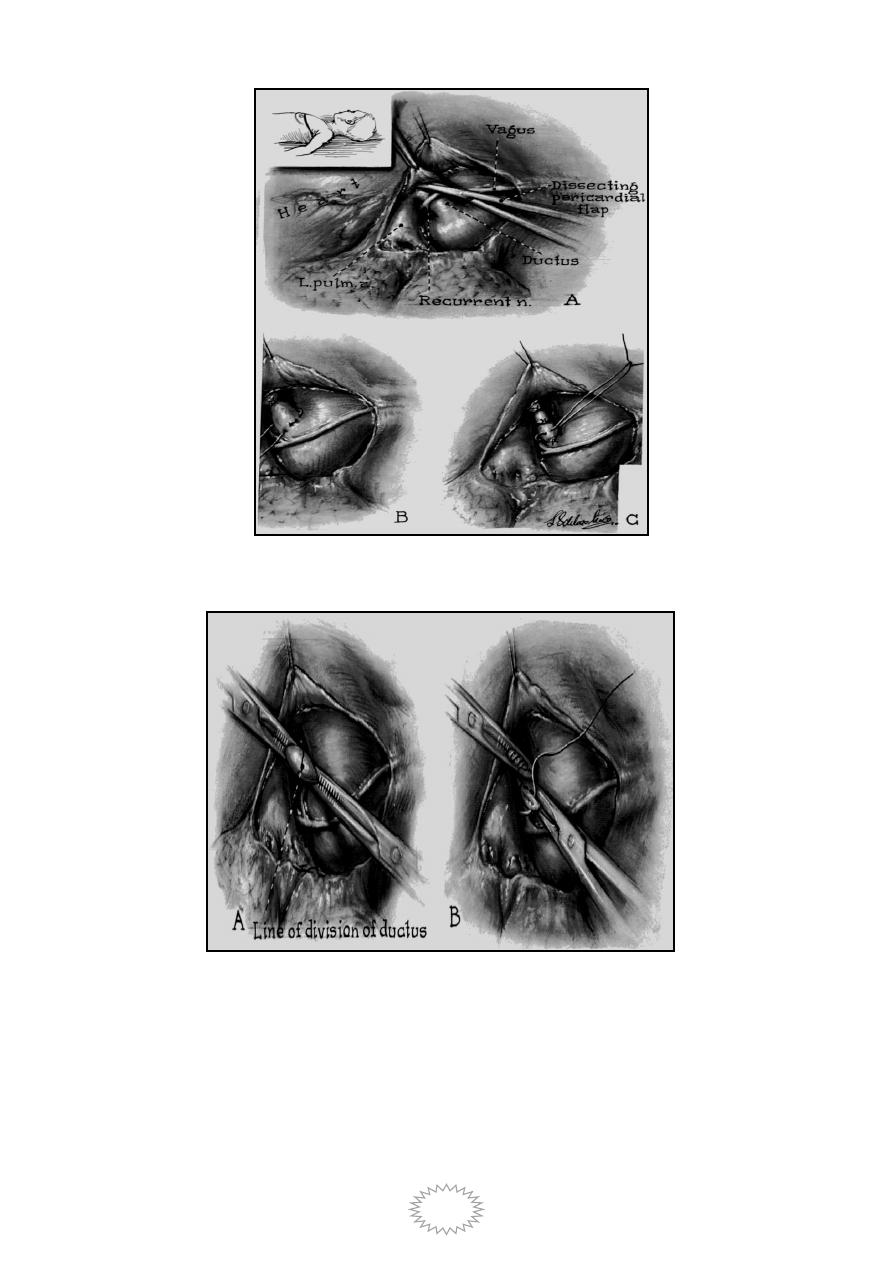
Operative treatment of PDA by ligation.
Treatment of PDA by division.
) أ.م.د. احمد عبداالمير دفار ( اختصاصي جراحة الصدر و القلب و االوعية الدموية
4
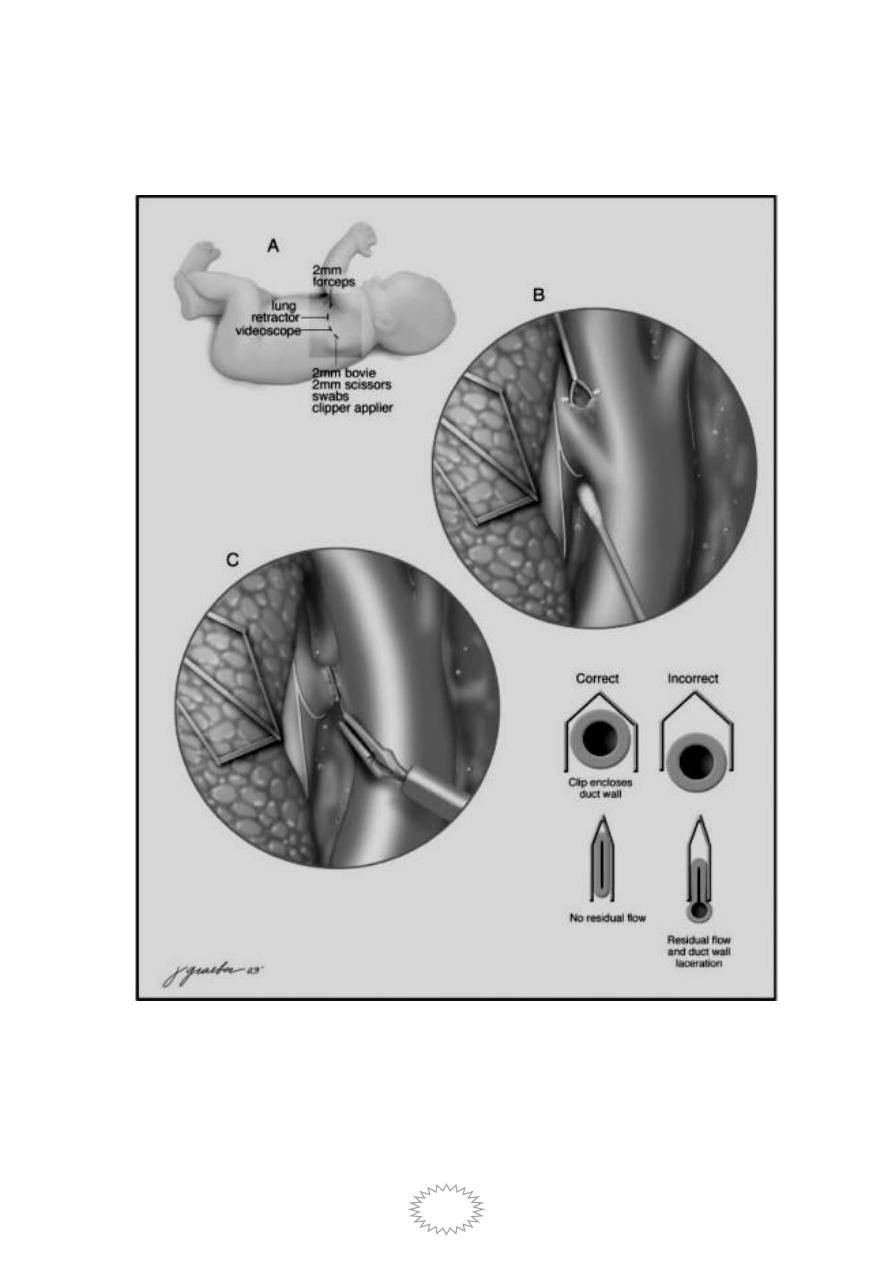
Video-assisted dissection technique for ligation of PDA.
