Diagnostic imaging in oral and maxillofacial surgery
Technological advances in the imaging science improve the accuracy in clinical diagnosis,. There are many diagnostic modalities which are widely used throughout the world, from this clinician must select the right choice.The imaging modalities classified into:I. Invasive or interventional imaging.
II. Non- Invasive imaging
I. Invasive (interventional) and minimally invasive imaging:
It is defined as a medical procedure which breaks the skin in some way and it may leave a scar. Mostly used for diagnostic as well as therapeutic purposes e.g. sinoscopy, arthroscopy, laryngoscopy, angiography, angioplasty, embolization, catheterization, delivery of cytotoxic drugs, calculus destruction. The main advantages of interventional procedure are that it gives palliative treatment with minimum morbidity and mortality and it also avoids open surgery in unfit patients.II. Non-invasive imaging:
It is defined as a medical procedure which doesn't break the skin. It ismainly used for diagnosis but it may also used for treatment as radiotherapy for the treatment of tumors.
Types:
1. conventional radiography (Plain x-ray):X-rays was discovered by Roentgen in 1895, and are now used in all forms of conventional radiography as well as CT scan. The scientific unit for measurement the radiation dose (effective dose), is the millisievert (mSv). Other measurement units include rad, roentgen, and sievert. The term effective dose is used when referring to the radiation risk averaged over the entire body.
Different type of tissues produces different degrees of X-ray attenuation depending on their densities e.g.
Air (lung) ---- radiolucent
Calcified tissue (bone) ---- radiopaque
Soft tissue (muscle) --- Grey
Soft tissue (Fat) --- Dark Grey
Radiographical views:
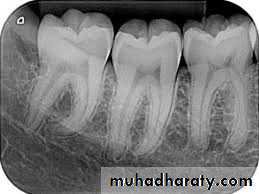
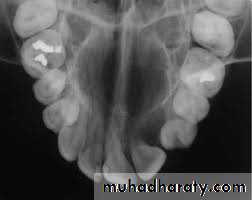
A. Intra oral (periapical, bitewing, occlusal)
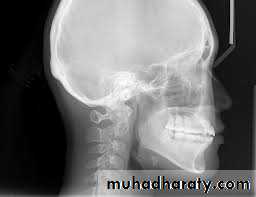
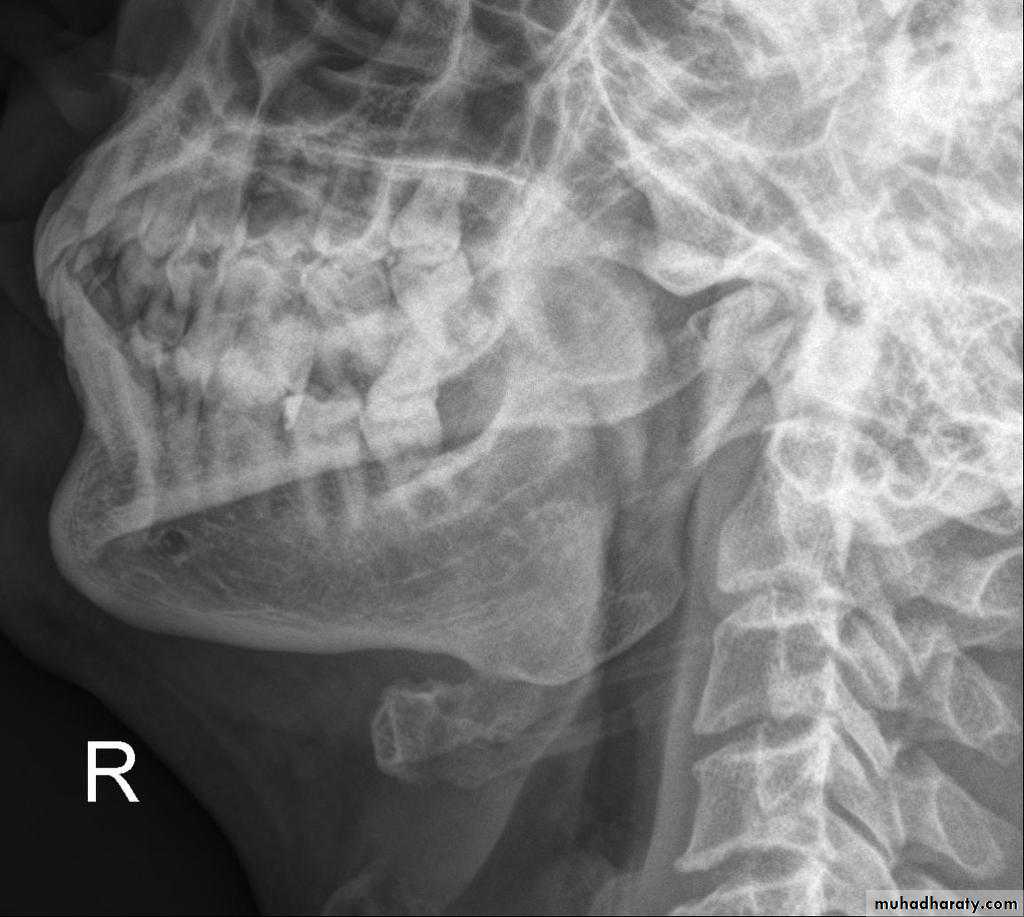
B. Extra oral (Postero-anterior "PA", Anteroposterior "AP", Cephalometric(true lateral), Oblique Lateral, Ocipito-mental, OPG, Submentovertex, TMJ View,etc.).
disadvantages of conventional radiograph
1. lonizing radiation (X-ray)2. It gives two dimensional record
3. Requires multiple projections
4. Superimposition of various structures in the pathway of X-ray in the
region of interest.
5. Difficult to detect subtle pathology or trauma (insensitive until pathology is well established, at least 30% of mineral content change is required).
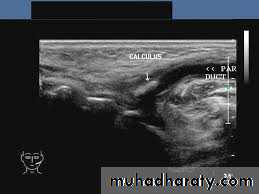
2. Ultrasonography (USG):
Ultrasound means high frequency sound waves above the limit of human audibility (20 kHz)
USG procedure:
A transducer (probe) converts electrical energy into high frequency sound waves, which pass into the tissues of different densities. The echo of US are reflected back to the scanning transducer, where converted into electrical energy, which are displayed on a monitor as images.
Reflection of US waves by various tissues:
*Fluid (Urine, blood and cyst) all the waves are allowed to pass withoutreflection.
*Bone and air (lung) all the waves are reflected back and not allowed
passing
*Soft tissue (muscle, fat)waves are partly allowed to pass.
Advantages of USG:
1.Outdoor procedure (portable equipment)2. Safe (no adverse reaction)
3.Non invasive
4. Painless
5. Not expensive
6. Easily repeatable
Disadvantages of USG:
Since bone and air in lung completely reflect the US waves, so any
intracranial and intrathoracic lesions can't be evaluated.
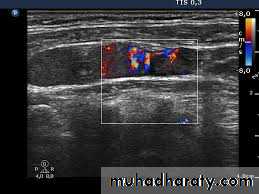
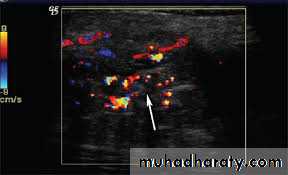
Doppler Ultrasound:
It is used to detect and measure the rate of movement of any fluid such as blood.in "color Doppler'" the direction of flowing blood is distinguished by different colors.
applications or uses of USG:
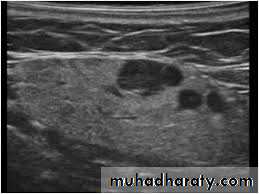
1. For detection of cervical lymphadenopathy.2. Examination of various masses including thyroid gland, abscess, salivary glands.
3. Vascular abnormalities (Doppler US)
4. Aids in differentiation of solid or cystic masses.
5. Valuable for guided fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNA).
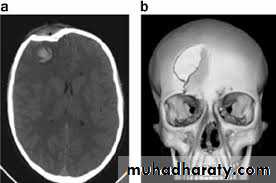
3. Computed tomography scanning (CT scan):
Tomography = Tomo (slice), graph (picture)Early CT scanners took several minutes to acquire a single slice while modern scanner can acquire 64 slices, 128 slices, and 620 slices in 10-50 Seconds (scan time) by use of advanced powerful computers. Slices 0.5-.3 mm width provide very good detail of the tissues. The standard plane of CT scan is obtained in axial plane. The X-ray attenuation values of CT scan are scored from -1000 to 1000 Hounsfield Units (HU
It reveals: hypodense or hyperdense.
* Air and fat : -ve HU.* cyst, fluid and blood L: +35 to+ 50 HU.
* Bone: +300 HU cancellous bones to +1000 HU and more for dense
bones.
Thus fat represent an excellent contrast medium in CT scan. However, the use of contrast agents can artificially increase the resolution of CT scan.Thus, intravenous contrast (iodine) will enhance blood vessels resolution, and oral contrast (barium) will delineate bowel.
types of CT scan:
Computed tomography can be divided into 2 categories based onacquisition x-ray beam geometry; namely: fan beam and cone beam
* Spiral CT:
This type of CT obtains a volume of contiguous slices (128-620 slices) as thin as 0.625mm within seconds. Spiral CT has many advantages over conventional or axial CT:
1. It minimizes motion artifacts because the entire scan time can be performed during a single breath hold.
2. It reduces the X-ray dose to the patient.
3. It improves spatial resolution by giving 3D picture.
Cone Beam CT (CBCT):
Applicated in dentistry sine 1998.Cone Beam CT has many applicetions in oral and maxillofacial defects, and it is especially used for preoperative planning for the placement of dental implants. The quality and quantity of measured easily from point to point. Selection the proper length and diameter of the implant can be easily done. CBCT used to assess the precise relationship between the impacted tooth and the adjacent structures, also used for the evaluation of bone density CBT has advantage over conventional CT by giving 3 D image and exposing the tissues to relatively small doses of radiation.CBCT=3-28 OPG radiation dose
Medical CT=33-82 OPG radiation dose
Advantages of CT scan:
1.Non invasive.2.Quick imaging, scan time less than 1 minute, so reduced patient
motion artifacts,
3. Evaluation of bony structure and soft tissue.
4. Contrast resolution of CT is much better than conventional x-ray
5. It gives 3-D image of the body, so it gives the exact site, size of the lesion and it's relation to adjacent normal structure.
6.CT differentiates various body structures from each other and
demonstrates their relationship (no superimposition).
7. Used for postoperative evaluation and follow-up
Disadvantages of CT:
1. Ionizing radiation (x- ray)2. Expensive
3.Children require sedation
4. Respiratory motion or body motion leads to degradation of the image.
5. Allergic reaction to contrast medium (iodine).
6. Artifact scatters due to presence of dental amalgam fillings and metallic crowns.
7. Radiation dose of medical CT exceeds that of CBCT & conventional
panoramic radiography.
applications or uses of CT scan:
1.Head and facial skeleton: fractures, osteolytic lesions, and hyperostosis.
2. Intracranial lesions: hematoma, infarction, abscess, tumors.
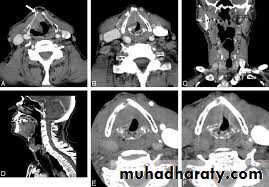
3. Intraoral mass, paranasal sinuses, larynx, nasopharynx salivary glands.
4. Cervical lymphadenopathy and neck masses.
5. Effective means of guiding the placement of FNA for biopsy.
6. Angiography (using contrast agent).
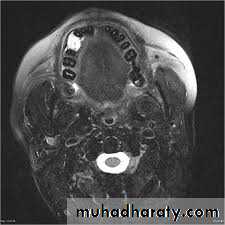
4. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI can be used to distinguish oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood and named as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), and publish the first functionalimage using bold signal with T2 in 1992. The principle of RI is based
on the magnetic properties of hydrogen protons (body tissues that contain
hydrogen atoms). In MRI examination, he patient is placed in apowerful magnetic field in which the protons within the body become aligned longitudinally (TI). When increasing the radiowaves, a radiofrequency