Fifth Stage
E.N.T
Dr. Mushtaq – Lecture 3
1
Otitis Media
Inflammation and /or infection of the middle ear cleft .
•
SUPPURATIVE O.M.
•
NON SUPPURATIVE O.M.
Suppurative O.M.
1. Acute suppurative O.M.
2. Chronic suppurative O.M.
ACUTE S.O.M.
Aetiology :
common in children/ viral
* extension from infected N/Px via
sub mucosal lymphatic's OR via
an infected exudates through E.T.
** through perforated T.M.
*** haematogenous route.
Bacteriology:
Wide range of microorganism:
Strep . Pneumonia
Hemolytic strept.
Staph aureous
H . influenza
Branhamella catahralis
Beta- lactamase producing organism
Pathology :
❖
tubal occlusion
❖
Engorgement & oedema of the cleft`s lining.
❖
Exudation into the tympanic cavity ,/serous at beginning ----mucopurulent
2
❖
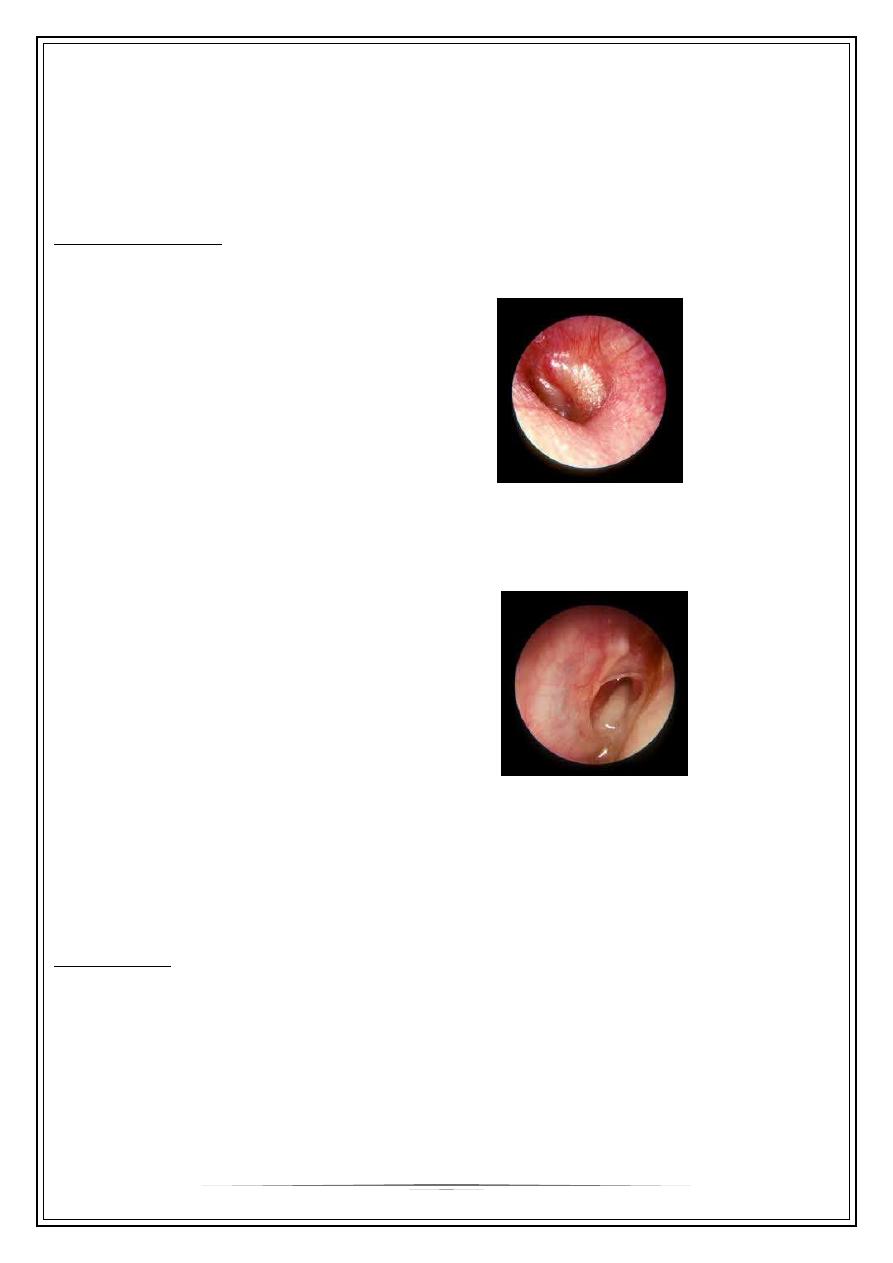
Bulging of the T.M.
❖
Pressure necrosis>>>rupture of the T.M. & otorrhoea
❖
Exudation may be found in the mastoid process causes osteitis (mastoiditis)&
erosion of the cortex >>>subperiosteal abscess
Clinical features:
➢
Before perforation; (acute tubal occlusion)
_ fullness in the ear.
_ deafness.
_ discomfort.
_ bubbling sound in the ear
_ autophonia
_ red t.m.
_ bulging.
➢
After perforation
- Relief of pain.
- otorrhoea
Retention of pus in the mastoid(mastoiditis)
pain in the mastoid region
Oedema over the mastoid process
Increase constitutional features/ fever,pain ,malaise….etc
Treatment :
rest & sedation
Analgesia
Local heat
Swab for C/S (discharge)
Systemic antibiotics
Local treatment AB. +/- steroid
Nasal decongestant drops
Cortical mastoidectomy
3
Chronic suppurative otitis media
•
Non cholesteatoma
•
cholesteatoma
Non cholesteatoma
Oedematous Aetiology:
* residue of acute s.o.m.
** re infection
Pathology of non cholesteatoma c.s.o.m.
•
Perforation
•
mucosa of the ty. Cavity
•
Occasionally gr. t. or polyp
•
Metaplasia of sq. epith. >>> sec. col. epith.
•
Same changes in the mastoid air cells>>chronic mastoiditis (mastoid reservoir)
Clinical features:
1) Discharge ; often scanty mucoid, but becomes copious & purulent during
exacerbation / U.R.T.I.
2) Conductive deafness
3) Radiological findings reveals , sclerosis of the mastoid air cells
Treatment:
1. Swab for C/S
2. Aural toilet
3. Systemic& local AB.
4. Removal of the polyp & gr. t. if present
5. Elimination of the adjacent foci of infection/ts., sinusitis…etc
6. Mastoid exploration
7. Myringoplasty for dry perforation

4
Cholesteatoma /attic
•
Dangerous disease
•
Ass. Cholesteatoma (epidermoid cyst containing
keratin with cholestrol crystals)
Pathology:
•
Limited at attic region (pars flaccida),extrusion into ext.canal.
•
Extension into the tymp. Cavity +/- ossicular chain disruption.
•
Expansion into the mastoid bone >>absorption of the bone(automastoidectomy)
•
Gr. T. & polyp
•
Invasion of the labyrinth >> fistula & SNHL.
•
Invasion of the meninges >>meningitis
•
Pressure on the facial n.>> palsy
Clinical features :
1. Deafness
2. Malodourous scanty otorrhoea
3. Perforation // attic or mariginal
4. Cholesteotoma may be visible
5. Signs of complications may be found ; fever, headache ,earache, vertigo, facial
palsy .
6. Radiological findings shows bone destruction in the advance stage
Treatment:
1. Conservative R;
* if no complications or small cholesteatoma
via repeated suction clearance & regular follow up
2. Surgical R;
- complications
- fail of cons. R,
* atticotomy
* mastoidectomy // radical or modified radical
* tympanoplasty (removal of the disease & reconstruction of the ossicular chain)
5
Complications
1) Subperiosteal abscess
2) Facial n. palsy
3) Labyrinthitis
4) Meningitis
5) Thrombophlebitis of the sigmoid sinus
6) Brain abscess
7) septicaemia
Thank you,,,
