1
Introduction to Computers
Lecture -1-
Dr. Abdalrahman R. Qubaa
First StageSystems & Control Department
Electronics Engineering college
Nineveh University
2
What is a Computer?
A computer:- is a programmable, electronic device that accepts data, performs operations, presents the results, and can store the information or results.
A computer:- is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions (software) stored in its own memory unit, that can accept data (input), manipulate data (process), and produce information (output) from the processing.
Generally:- the term is used to describe a collection of devices that function together as a system.
3
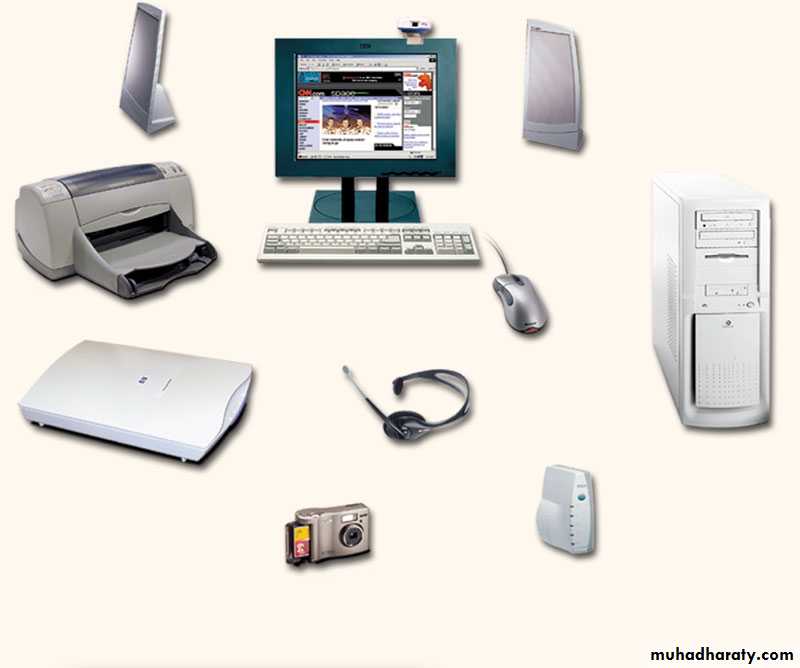
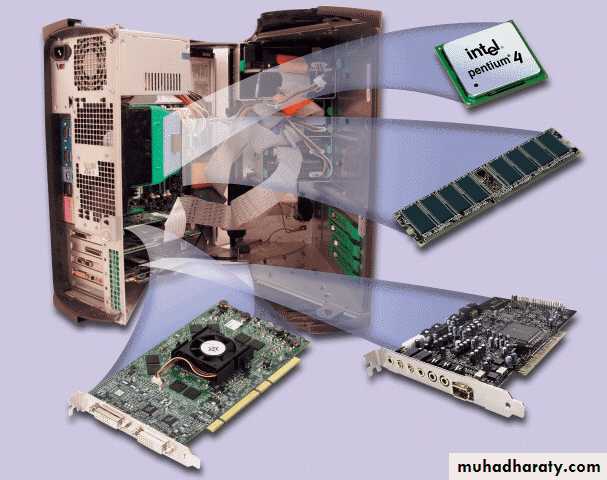
Devices that comprise a computer system
Printer (output)
Monitor (output)Speaker (output)
Scanner (input)
Mouse (input)
Keyboard (input)
System unit(processor, memory…)
Storage devices
(CD-RW, Floppy, Hard disk, zip,…)4
What does the computer do?
Computers can perform four general operations, which comprise the data processing cycle.
• Input— entering data into the computer.
• Processing— performing operations on the data.• Output— presenting the results.
• Storage— saving data, programs, or output for future use.
5
Data and Information
All computer processing requires :-
Data: which is a collection of raw facts, figures and symbols, such as numbers, words, images, video and sound, given to the computer during the input phase.
Computers manipulate data to create information.
Information: is a data that is organized, meaningful, and useful. During the output Phase, the information that has been created is put into some form, such as a printed report. The information can also be put in computer storage for future use.6
Why is the computer so powerful?
• The ability to perform the data processing cycle with amazing speed.
• Reliability and Accuracy (low failure rate).
• Ability to store huge amounts of data and information.
• Ability to communicate with other computers.
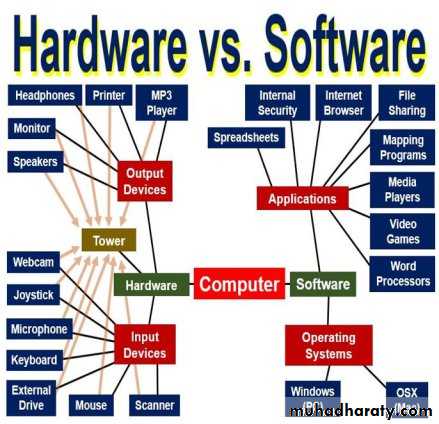
Hardware
The physical parts of a computerCan be internal (located inside the system unit) or external (located outside of the system unit).
Software
Programs or instructions used to tell the computer hardware what to do.
Main components of a computer system
Software
Hardware
8
How does the computer know what to do?
It must be given a detailed list of instructions, called a compute program or software, that tells it exactly what to do.
Before processing a specific job, the computer program corresponding to that job must be stored in memory.
Once the program is stored in memory the computer can start the operation by executing the program instructions one after the other.
9
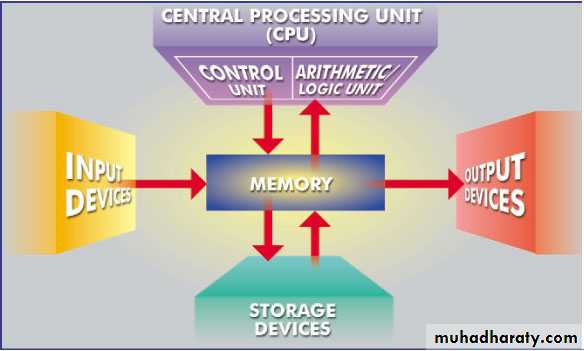
What are the primary components of a computer devise ? (Hardware)
• The Hardware consist of:
• Input devices.
• Central Processing Unit (CPU)
• Memory.
• Output devices.
• Storage devices.
•
10
1. Input devices
Keyboard.
Mouse.
Trackball
Optical Scanner
Bar-Code Reader
Touch Pad
Optical Painter
Joystick
Digital and Web Camera
Microphone
11
The Keyboard
keyboard: is the most commonly used input device on which data is entered by manually keying in or typing certain keys. A keyboard typically has 101 or 105 keys.
12
The Mouse
The Mouse: is a pointing device which is used to control the movement of a mouse pointer on the screen to make selections from the screen. A mouse has one to five buttons. The bottom of the mouse is flat and contains a mechanism that detects movement of the mouse.
13
2. Central Processing Unit
A Central Processing Unit (CPU):- is the electronic circuitry within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions.
CPU- is containing the control unit and the arithmetic/logic unit).
Traditionally, the term "CPU" refers to a processor, It is considered the “brain” of the computer.
14
3. Memory
• Random Access Memory RAM :- is the main memory of the computer. It consists of electronic components that store data including numbers, letters of the alphabet, graphics and sound. Any information stored in RAM is lost when the computer is turned off (it is temporary memory).
• Read Only Memory or ROM:- is a memory that is etched on a chip that has start-up information for your computer. Any information stored in ROM is not lost when the computer is turned off.
• (It is permanent memory).
15
How is memory size measured?
• The amount of memory in computers is typically measured by number of bytes available for storage (in bytes, kilobytes or megabytes).
• A memory location, or byte, usually stores one character. One kilobyte (KB) equals approximately 1,000 memory locations and one megabyte (MB) equals approximately one million locations.
Therefore, a computer with 8 MB of memory can store approximately 8 million characters. One megabyte can hold approximately 500 pages of text information.
How is the memory size measured?
Term Abbreviation Approximate Size
Kilobyte KB or K 1 thousand bytesMegabyte MB 1 million bytes
Gigabyte GB 1 billion bytes
Terabyte TB 1 trillion bytes
• by number of bytes available for storage as table below:
17
4. Output Devices
Output devices make the information resulting from the processing available for use. The two output devices more commonly used are the screen computer and the printer.
The computer screen produces a soft copy of your output, and the printer produces a hard copy of your output.
18
5. Storage Devices
Storage devices:- are used to store data when they are not being used in memory. The most common types of auxiliary storage used on personal computers are, floppy disks, hard disks, CD-ROM drives, and USB flash.
19
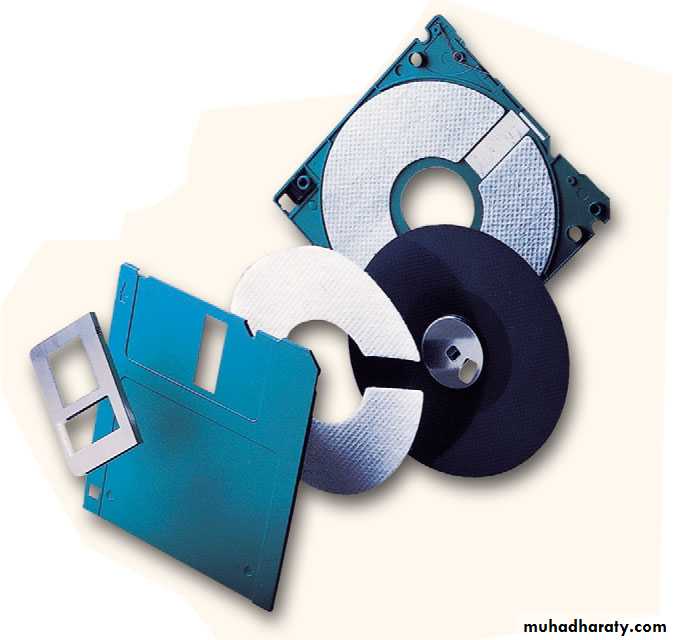
Storage DevicesFloppy Disks
A Floppy disk:- is a portable, inexpensive storage medium that consists of a thin, circular, flexible plastic disk with a magnetic coating enclosed in a square-shaped plastic shell, and it is a magnetic disk, which means that it used magnetic patterns to store data.
20
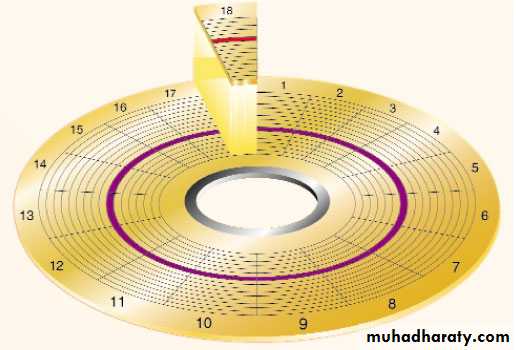
Storage DevicesStructure of Floppy Disks
Initially Floppy disks were 8-inches wide, they then shrank to 5.25 inches, and today the most widely used folly disks are 3.5 inches wide and can typically store 1.44 megabytes of data.
Data in floppy disks can be read from and written to.
Formatting is the process of preparing a disk for reading and writing.
A track is a narrow recording band that forms a full circle on the surface of the disk.
21
Storage DevicesStructure of Floppy Disks
The disk’s storage locations are divided into pie-shaped sections called sectors.
A sectors is capable of holding 512 bytes of data.
A typical disk stores data on both sides and has 80 tracks on each side with 18 sectors per track.
22
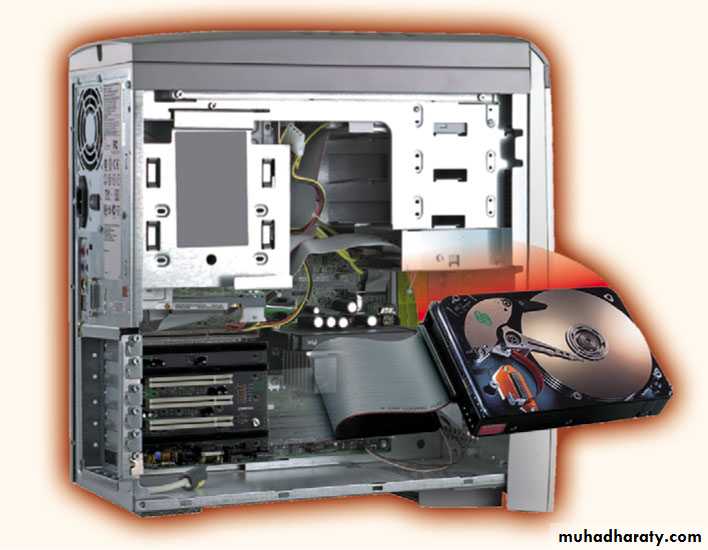
Storage DevicesHard Disks
A Hard disk:- is another form of auxiliary storage consists of one or more rigid metal plates coated with a metal oxide material that allows data to be magnetically recorded on the surface of the platters.
The hard disk platters spin at a high rate of speed, typically 5400 to 7200 revolutions per minute (RPM).
• Provides greater storage capacity than a floppy disk, CD rom, or USB flash drive.
• Storage capacities of hard disks for personal computers range from 120 GB to 1000 GB and more. (one billion bytes are called a gigabyte).
23
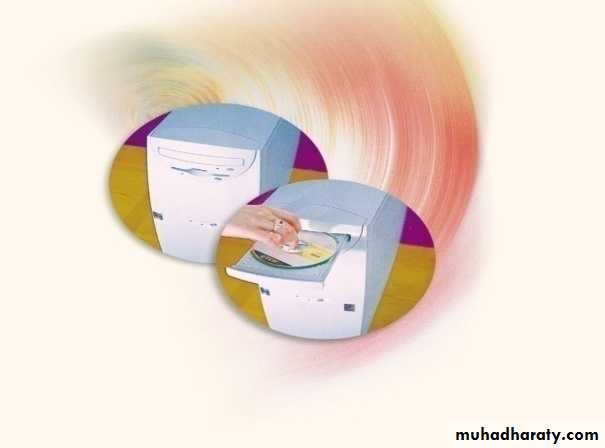
Storage DevicesCompact Discs
A compact disk (CD):- also called an optical disc, is a flat round, portable storage medium that is usually 4.75 inch in diameter.
A CD-ROM (Read Only Memory), is a compact disc that used the same laser technology as audio CDs for recording music. In addition it can contain other types of data such as text, graphics, and video.
The capacity of a CD-ROM is start from 650 MB of data and more.
USB flash drives: is a data storage device that includes memory with an integrated USB interface. It is typically removable, rewritable and much smaller than an optical disc. Most weight less than 30 g, first appearing on the market in late 2000. As of 2018, 2TB flash drives were the largest available in terms of storage capacity.
Compared with floppy disks or CDs, they are smaller, faster, have significantly more capacity, and are more durable due to a lack of moving parts. Additionally, they are immune to electromagnetic interference (unlike floppy disks), and are unharmed by surface scratches (unlike CDs).
24
Storage DevicesUSP Flash Drive (Flash memory)
The System Unit
What are common components inside the system unit?• Memory
• Adapter cards• Sound card
• Video card
• Ports
• Drive bays
• Power supply
power supply
ports
drive bays
processor
memory
sound card
video card
• Processor
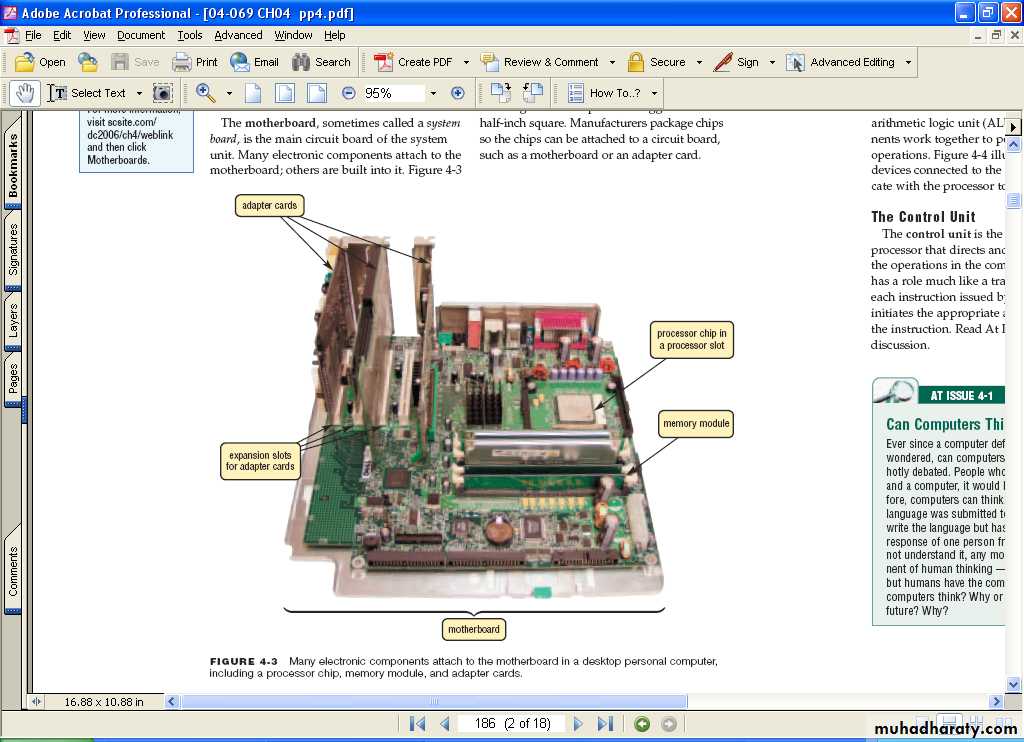
The System UnitWhat is the motherboard?
• Main circuit board in system unit.
• Contains adapter cards, processor chips, andmemory chips
27
Computer Software
Computer Software:- means any program work on computer, and it is the key to productive use of computers. Software can be categorized into two types:
• Operating System Software.
• Application Software.
28
1. Operating System Software
Operating System Software:- tells the computer how to perform the functions of loading, storing and executing an application and how to transfer data.
Today, many computers use an operating system that has a Graphical User Interface (GUI):- that provides visual clues such as icon symbols to help the user.
Microsoft Windows: is a widely used graphical operating system.
DOS (Disk Operating System): is an older but still widely used operating system that is text-based.
29
2. Application Software
Application Software:- is consists of programs that tell a computer how to produce information. Some of the more commonly used packages are:
Word processing
Electronic spreadsheet
Database
Presentation graphics
30
Word Processing
Word Processing Software (M. S. Word):- is used to create and print documents. A key advantage of word processing software is that users easily can make changes in documents.
31
Electronic Spreadsheets
Electronic spreadsheet software (M. S. Excel):- allows the user to add, subtract, and perform user-defined calculations on rows and columns of numbers. These numbers can be changed and the spreadsheet quickly recalculates the new results.
32
Database Software
Database Software (M. S. Access):- Allows the user to enter, retrieve, and update data in an organized and efficient manner, with flexible inquiry and reporting capabilities.
33
Presentation Graphics
Presentation Graphic Software (power Point):- allows the user to create documents called slides to be used in making the presentations. Using special projection devices, the slides display as they appear on the computer screen.