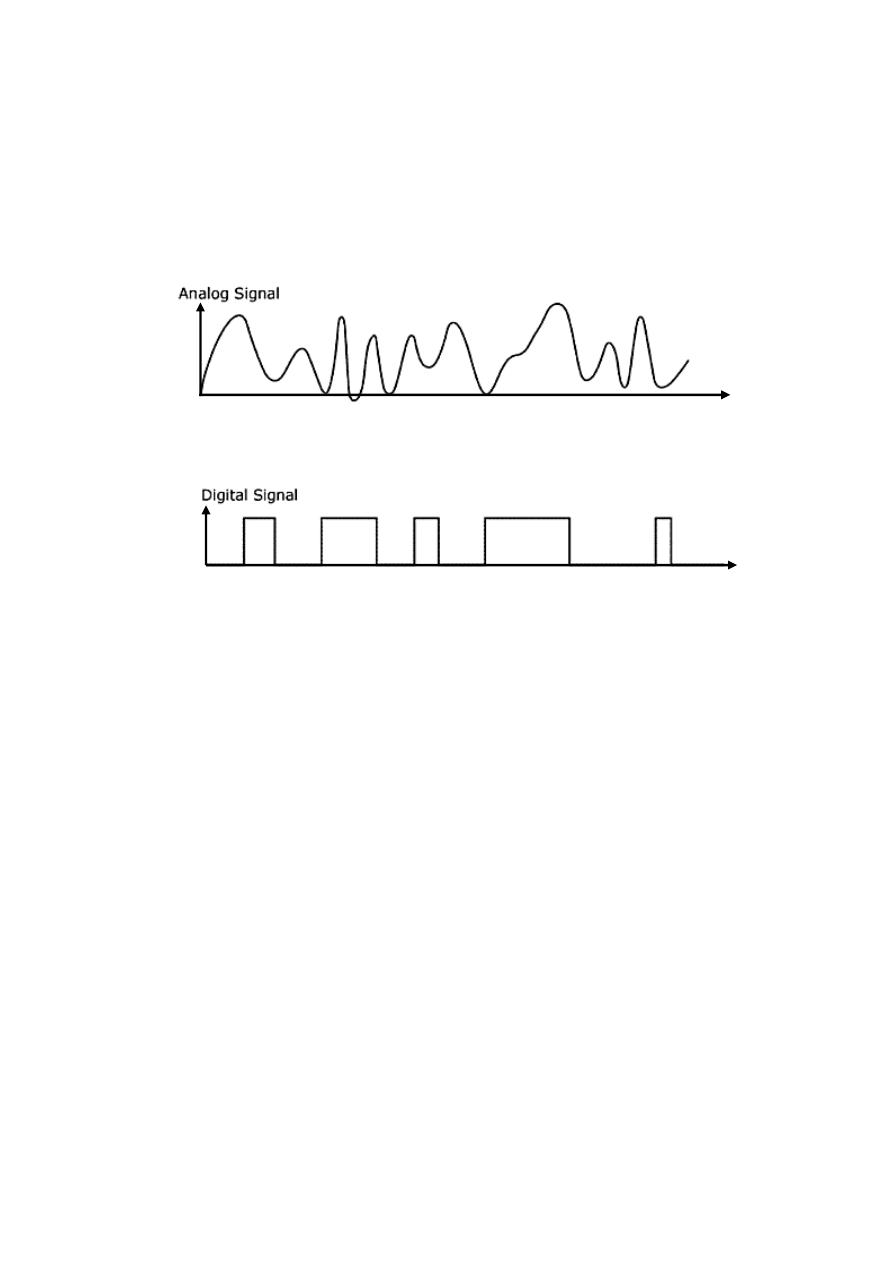
Signals and Systems
Signal is a function that represent the variation of a physical quantity with respect to
time.
Signals is usually classified into two main types:
a. Analog Signal: is a signal which can take any value within the given limit.
b. Digital Signal: is a signal which can only take a specific number of values.
Data in digital system is composed of a discrete value that is called bit (0 or 1). Bits
are usually represented by electrical signals such as voltage and current. Information
in digital system are represented with groups of bits called binary codes.
Digital System deals with signals represented in digital form.
Analog System deals with signals that are represented in analog form.
Advantages of Digital Techniques
Digital systems are generally easier to design
Digital circuits are less affected by noise.
Information storage is easy.
Limitations of Digital Techniques
o Most physical quantities are analog in nature.
o Processing digitized signals takes time.
0V
10
t
0V
5V
t
Number System
Many number systems are in use in digital technology such as
Decimal System
Binary System
Octal System
Hexadecimal Systems
With a decimal system we have 10 different digits, which are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
and 9.
Ex: (6)
10
, (25)
10,
(100)
10
A binary system has only 2 different digits 0 and 1. So to deal with a binary number
system is quite easier than a decimal system. So we generally use the binary system
when we deal with the digital world.
Ex: (01011)
2,
(110011)
2
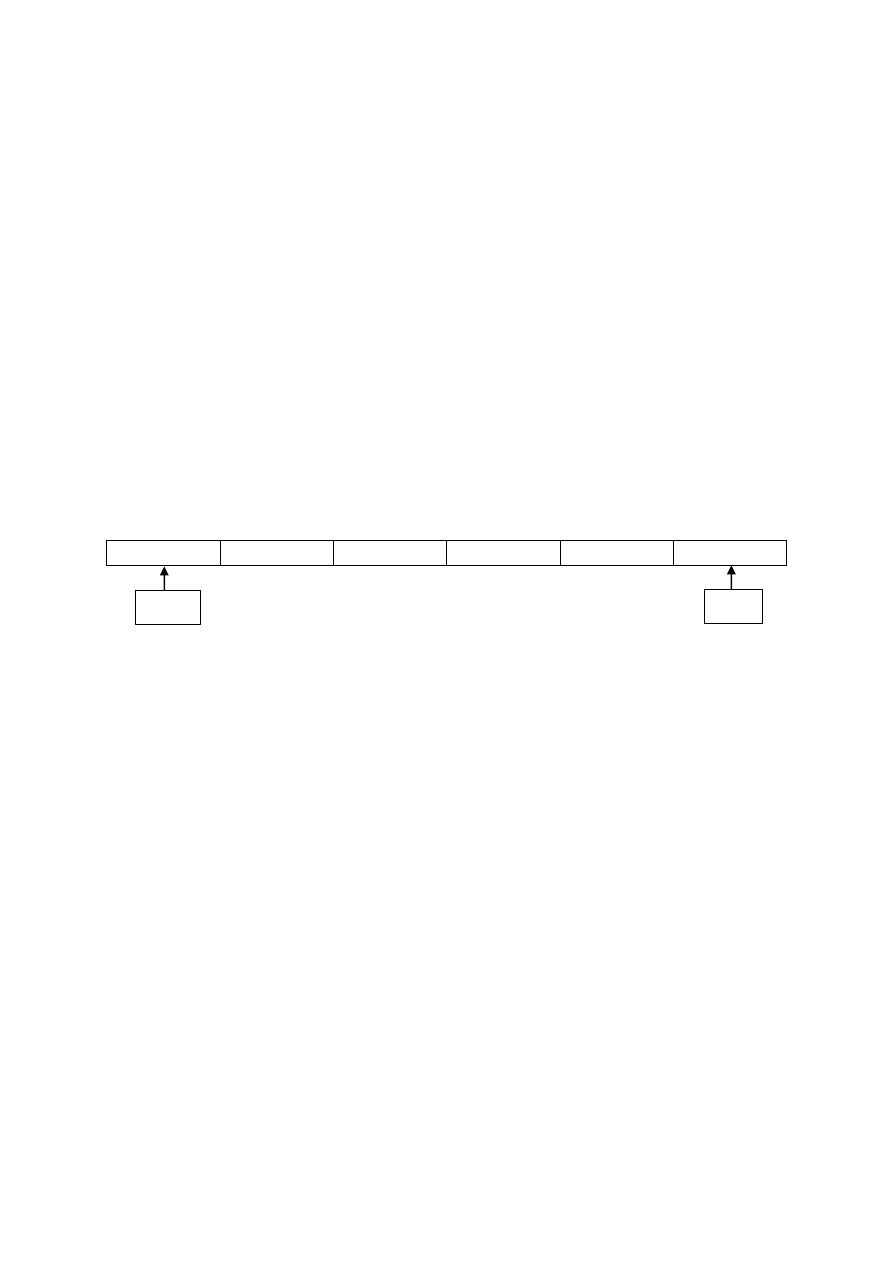
The right most digit in a number system is called the ‘Least Significant Bit’ (LSB) and
the left most digit in a number system is called the ‘Most Significant Bit’ (MSB)
1
1
0
0
1
1
In an octal number system there are 8 digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. Hence, any octal
number cannot have any digit greater than 7.
Ex: (6)
8
, (37)
8,
(255)
8
Similarly, a hexadecimal number system has 16 digits 0 to 9 and the rest of the six
digits are specified by letter symbols as A, B, C, D, E, and F. Here A, B, C, D, E, and
F represent decimal 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 respectively.
Ex: (6)
16
, (16A)
16
, (9F)
16
, (7E)
16
10, 8 and 2: are called the base or radix and they are used to indicate the type of the
number system.
As human we use decimal Number system. However, Computers only understand
zeros and ones, therefore Binary System is introduced.
However, dealing with a long binary code is usually confusing and may lead to
erroneous result. Therefore, octal and hexadecimal systems are used to represent
long binary codes.
MSB
LSB

Conversion Between Number Systems
Decimal to Binary Conversion
To convert a number in decimal to a number in binary we have to divide the decimal
number by 2 repeatedly, until the quotient
ناتج
القسمممممممممممم
)
of zero is obtained. Then the
column of the remainder is read in reverse order (from
bottom to top).
Ex) Convert (26)
10
into a binary number.
Ex) Convert (75)
10
into a binary number.
Fractional Conversion
So far we have dealt with the conversion of integer numbers only. If the number
contains a fractional part, we have to deal with integer part as before then deal with
fraction as follow:
Ex: Convert (25.625)
10
into a binary number.

Integer Part
Then, we deal with the Fractional Part
Ex) Convert (34.75)
10
into a binary number.
