
1
Introduction to Computers

2
What Is A Computer?
A computer is an electronic device, operating
under the control of instructions (software)
stored in its own memory unit, that can
accept
data
(input),
manipulate
data
(process), and produce information (output)
from the processing. Generally, the term is
used to describe a collection of devices that
function together as a system.

3
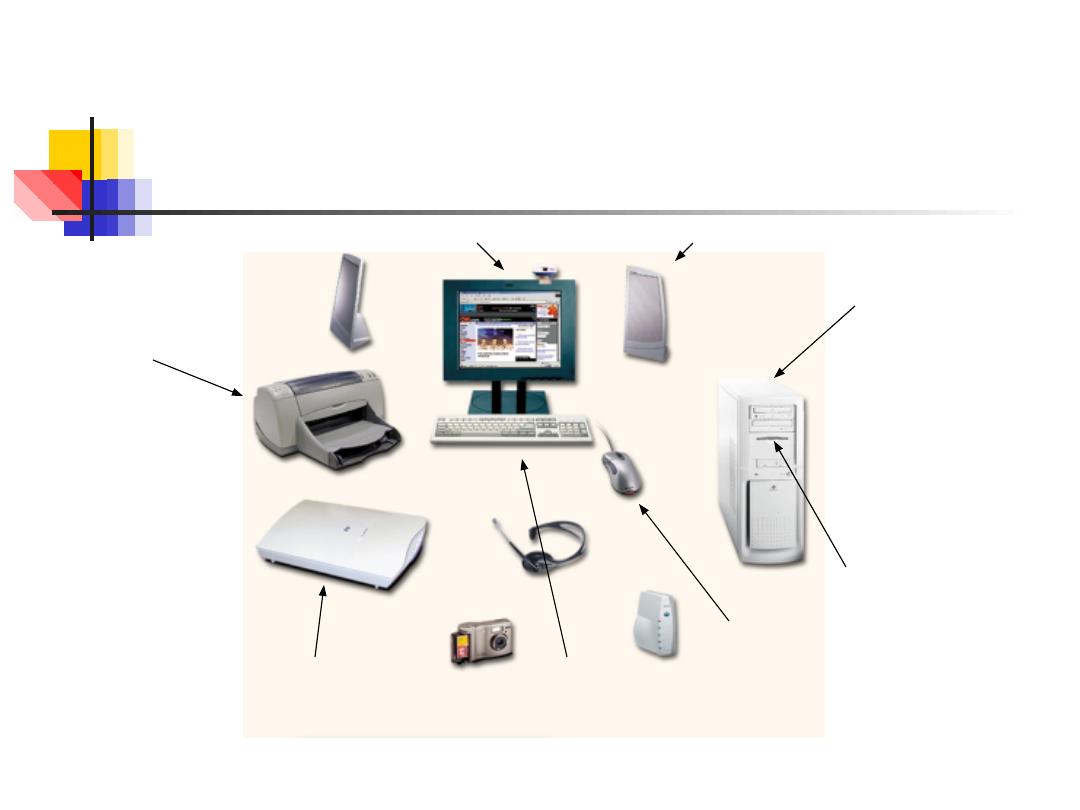
Devices that comprise a computer system
Printer
(output)
Monitor
(output)
Speaker
(output)
Scanner
(input)
Mouse
(input)
Keyboard
(input)
System unit
(processor, memory
…)
Storage devices
(CDRW, Floppy,
Hard disk, zip,
…)

4
What Does A Computer Do?
Computers
can
perform
four
general
operations, which comprise the information
processing cycle.
■
Input
■
Process
■
Output
■
Storage
5
What Do Computers Do?
■
Input, Process, Output, & Store
data
Input
Process
Output
Store Data

6
Data and Information
■
All computer processing requires data, which is a collection of
raw facts, figures and symbols, such as numbers, words,
images, video and sound, given to the computer during the
input phase.
■
Computers
manipulate
data
to
create
information.
Information is data that is organized, meaningful, and useful.
■
During the output Phase, the information that has been created
is put into some form, such as a printed report.
■
The information can also be put in computer storage for future
use.

7
Why Is A Computer So Powerful?
■
The ability to perform the information
processing cycle with amazing speed.
■
Reliability (low failure rate).
■
Accuracy.
■
Ability to store huge amounts of data and
information.
■
Ability to communicate with other computers.

8
How Does a Computer Know
what to do?
■
It must be given a detailed list of instructions,
called a compute program or software,
that tells it exactly what to do.
■
Before processing a specific job, the
computer program corresponding to that job
must be stored in memory.
■
Once the program is stored in memory the
compute can start the operation by
executing the program instructions one after
the other.
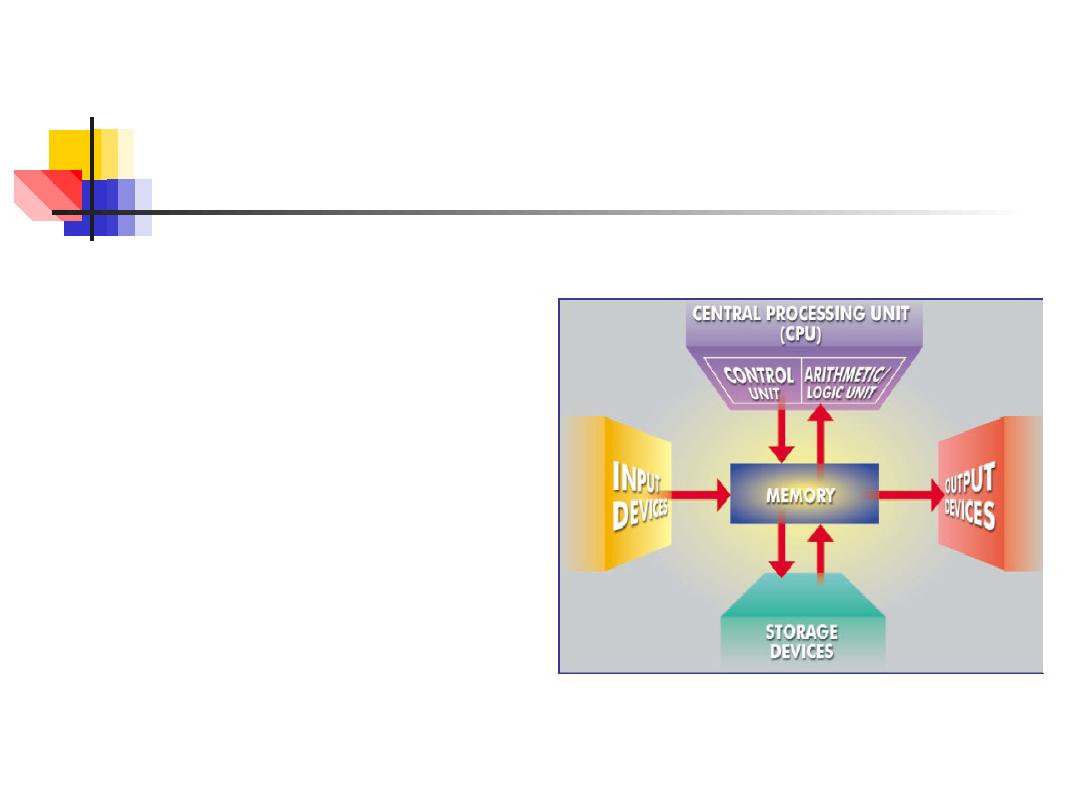
9
What Are The Primary
Components Of A Computer ?
■
Input devices.
■
Central Processing Unit
(containing the control
unit and the arithmetic/
logic unit).
■
Memory.
■
Output devices.
■
Storage devices.

10
Uses of Computer
PC at Home
Common uses for the computer within the home
■
Computer games
■
Working from Home
■
Banking from Home
■
Connecting to the Web

11
Uses of Computer
Office Applications
Stock Control
Stock control is ideal for automation and in many
companies it is now completely computerized. The
stock control system keeps track of the number of
items in stock and can automatically order
replacement items when required.
Accounts / Payroll
In most large organizations the accounts are
maintained by a computerized system. Due to the
repetitive nature of accounts a computer system is
ideally suited to this task and accuracy is
guaranteed.

12
Uses of Computer
Automated Production Systems
Many car factories are almost completely automated and
the cars are assembled by computercontrolled robots.
This automation is becoming increasingly common
throughout industry.
Design Systems
Many products are designed using CAD (Computer Aided
Design) programs to produce exact specifications and
detailed drawings on the computer before producing
models of new products.

13
Uses of Computer
Computers in Daily Life
■
Accounts
■
Games
■
Educational
■
Online banking
■
Smart ID cards
■
Supermarkets
■
Working from home (Teleworking)
■
Internet
