Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
1
Respiratory System
Methods of investigations:
1. Plain films ( Chest X-Ray ).
2. CT scanning.
3. Ultrasound.
4. Radionuclide studies.--- Perfusion & ventilation scans.
5. Pulmonary angiography---- Conventional & CT angiography.
6. Needle guided aspiration.
7. Others ( MRI, fluoroscopy, , bronchograhy, Ba studies----etc)
Computed tomography:( CT )
Advantages ??
1. Compared to conventional radiograph the range of density recorded is increased
approximately to 10-fold. ( conventional radiograph—4 basic densities ). ( wide
window range).
2. Absorption values ( Hounsfield Units--- HU)
3. Sectional images----- compared to 2-dimentional conventional X-Ray.
4. CT is usually performed in axial planes, reconstructions in other planes is also
possible.
5. High-Resolution CT (HRCT) ? . CT angiography ?
Disadvantages ??
High radiation dose ( CT of the thorax capable of giving an effective dose 50—500
times higher than a conventional chest radiograph).
Indications of CT in chest disease ?
1. Showing the presence & extent of mediastinal masses & other mediastinal
abnormalities.,,,, Can differential vascular mass ( like aneurysm) from solid mass.
2. Presence & extent of chest wall & pleural pathology.
3. Ascertaining the solitary nature of a pulmonary nodule or detection of other
unsuspected nodules
4. Contributing to the staging of lung cancer prior to treatment & monitoring of
response. e.g. demonstrate enlarged lymph node.
5. Localizing a mass prior to biopsy------ CT guided biopsy .
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
2
6. Can confirm the extent & severity of diffuse pulmonary parenchymal pathology.---
- HRCT.
7. Demonstrating the presence of disease when plain radiograph is normal. e.g.
detecting pulmonary metastases or demonstrating thymic tumors in patients with
myasthenia gravis.
8. Diagnosing pulmonary emboli using the technique CT pulmonary angiography.
Ultrasound of the thorax :
Demonstration of process in contact with the chest wall, notably pleural effusion &
pleural masses.
Guiding a needle to sample /drain /biopsy / aspirate pleural fluid or masses in
contact with chest wall.
Chest Radiograph ( Chest X-Ray):
➢
Is the most requested radiological examination.
➢
The standard view is ( Posterio -Anterior " PA" view ), lateral view should not be
undertaken routinely.
➢
Additional views :
AP/supine.
Oblique.
Decubitus.
Lordotic / Apical .
Portable / Mobile radiograph .
➢
Request form : " name, age, sex, date, clinical informations , examination
requested –views & provisional diagnosis " .
How to take a chest X-Ray ?
➢
Normal anatomical landmarks:
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
3
Viewing of the PA film : (interpretations Of PA chest film)
1 - Film labeling ( side marks).
2 - Technical quality of the film.
3 - Structural & tissue components of the film.
1. Film labeling ( side marks).
•
Name .
•
Date.
•
Side ( R----L).
•
Additional marks ( e.g. view , examiner & hospital name----etc.)
2. Technical quality of the film :
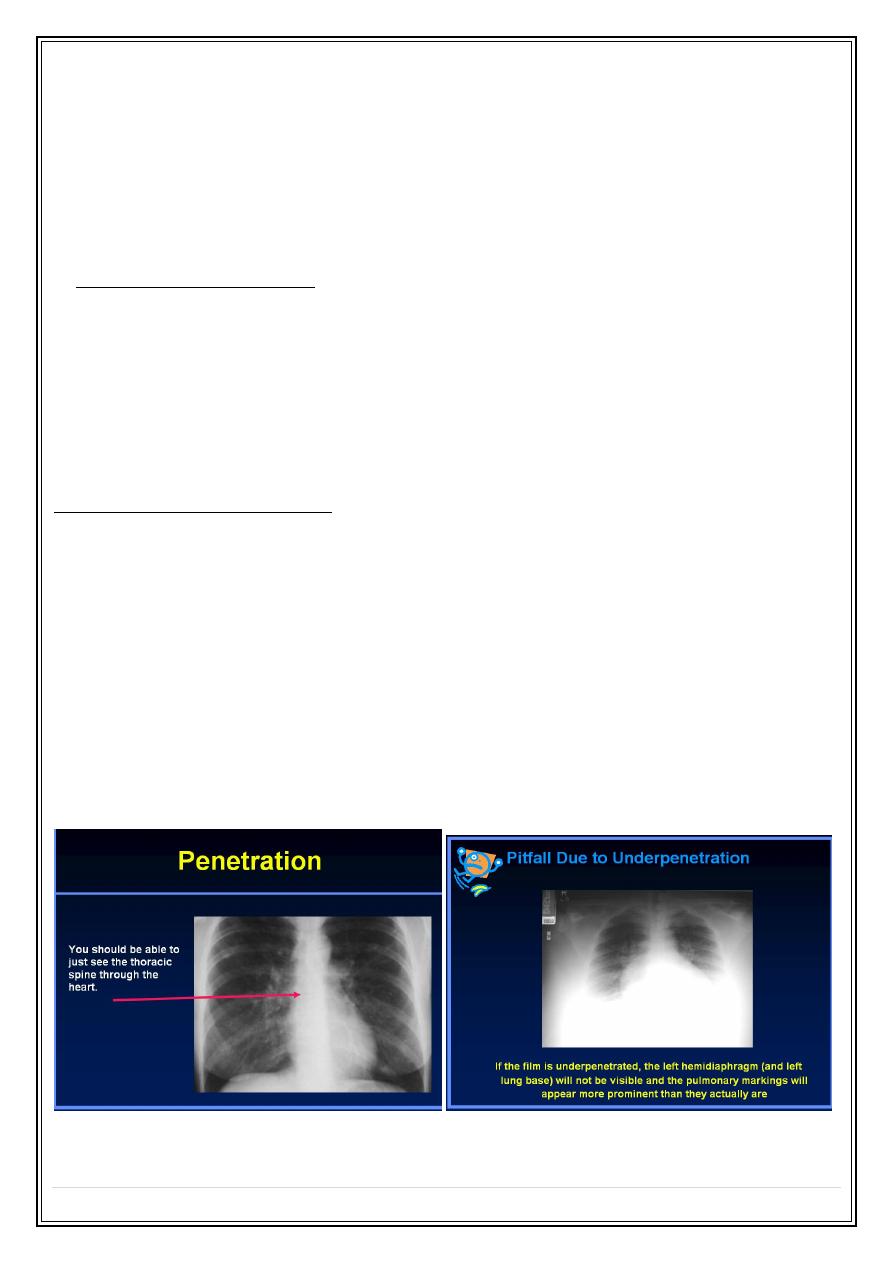
Factors to evaluate ?
•
Penetration.
•
Inspiration.
•
Rotation.
•
Angulations.
•
Magnification ( AP versus PA )
•
Radiographic technique (Body habitus).
Penetration
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
4
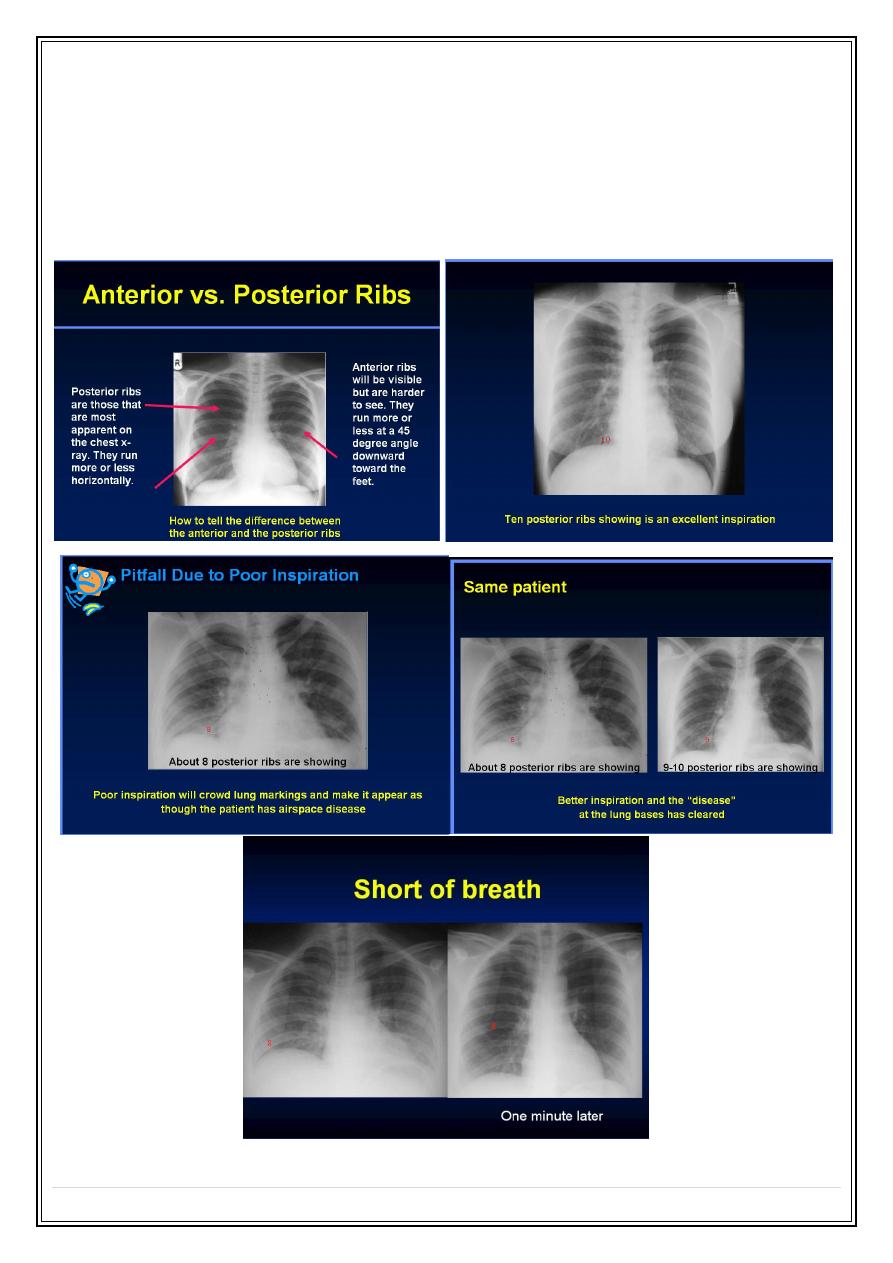
Inspiration
•
About 10 posterior or 6 anterior ribs visible is an excellent inspiration.
•
In many hospitalized patients 9 posterior or 5 anterior ribs is an adequate
inspiration.
•
At least 8-9 posterior ribs in difficult situations
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
5
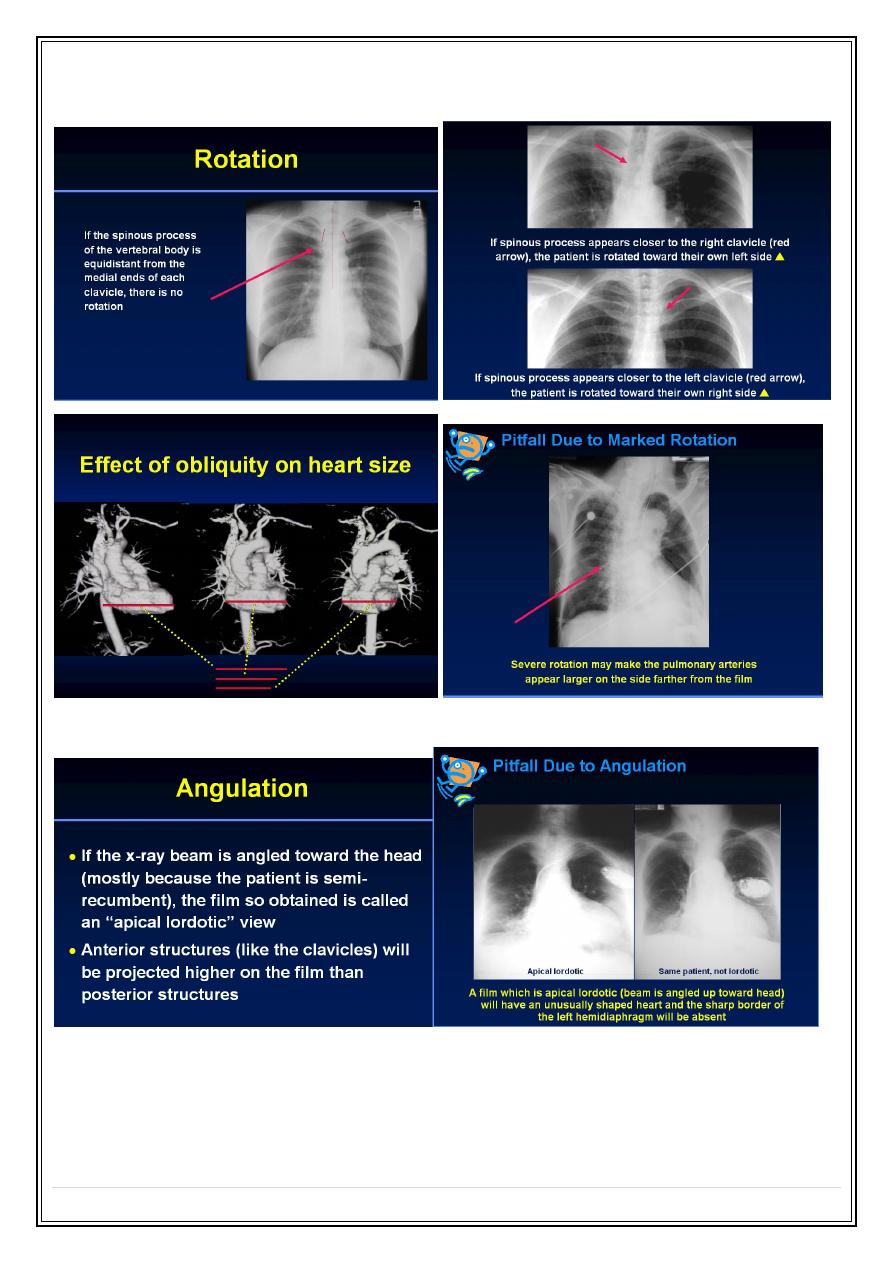
Rotation
Angulation
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
6
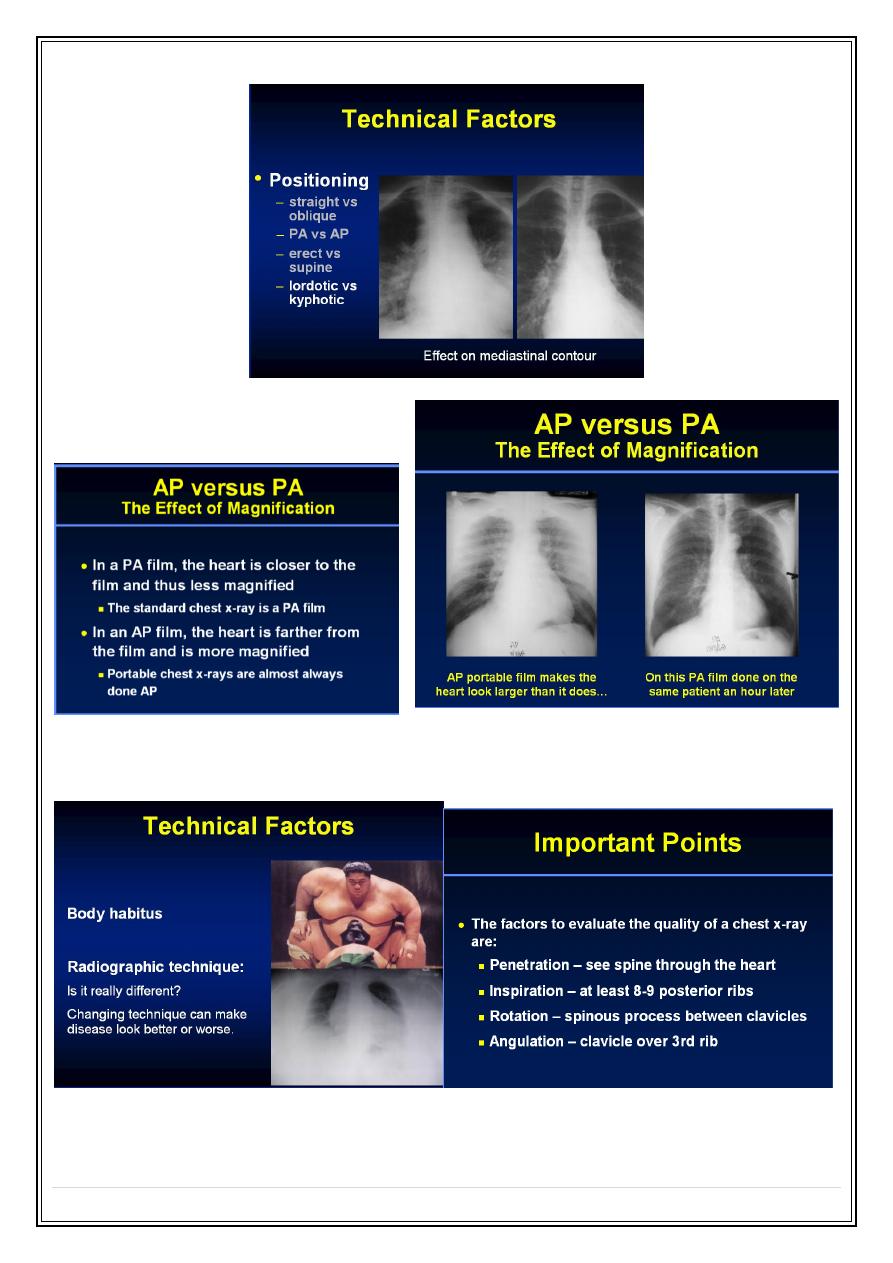
AP versus PA Magnifications
Body habitus - Radiographic technique
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
7
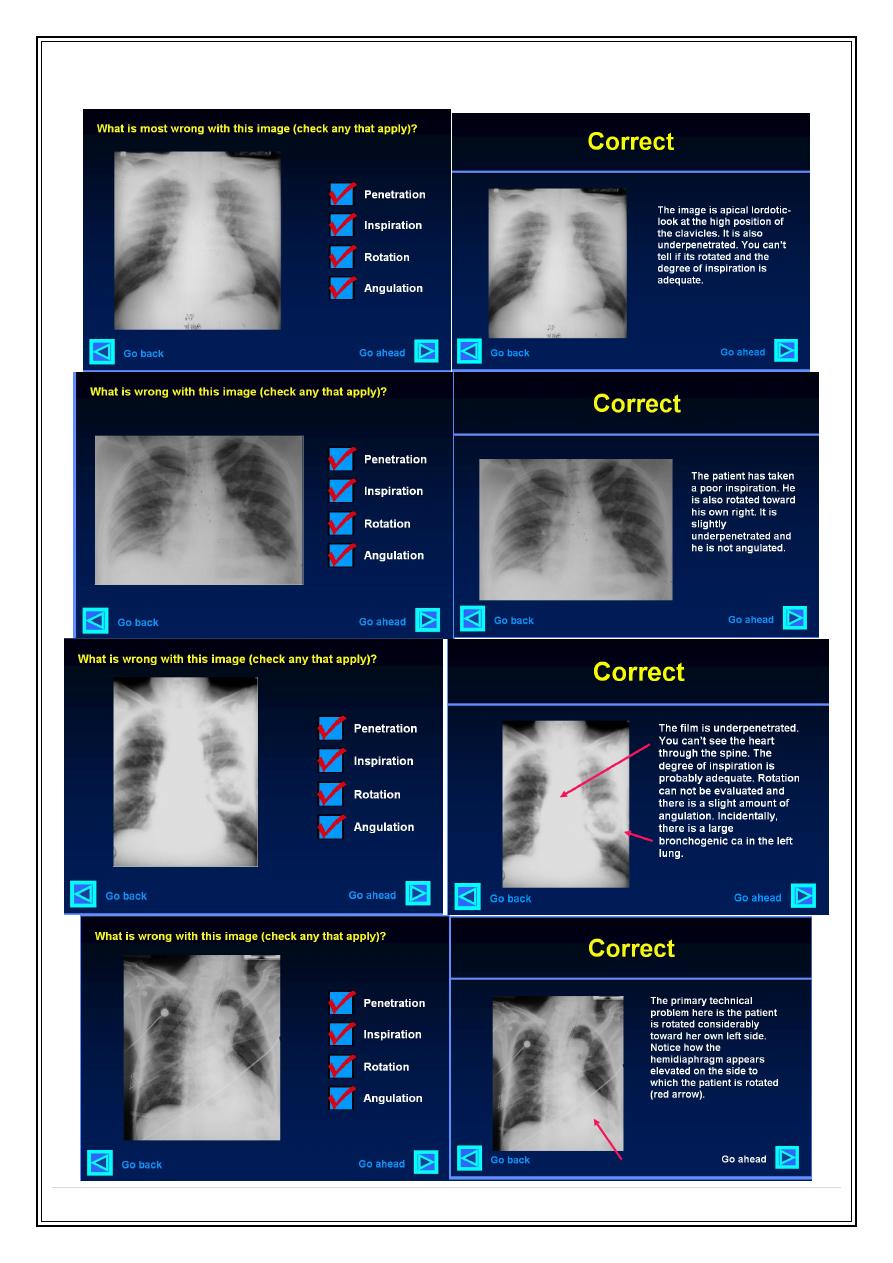
What is technically wrong with each of the following images?
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
8
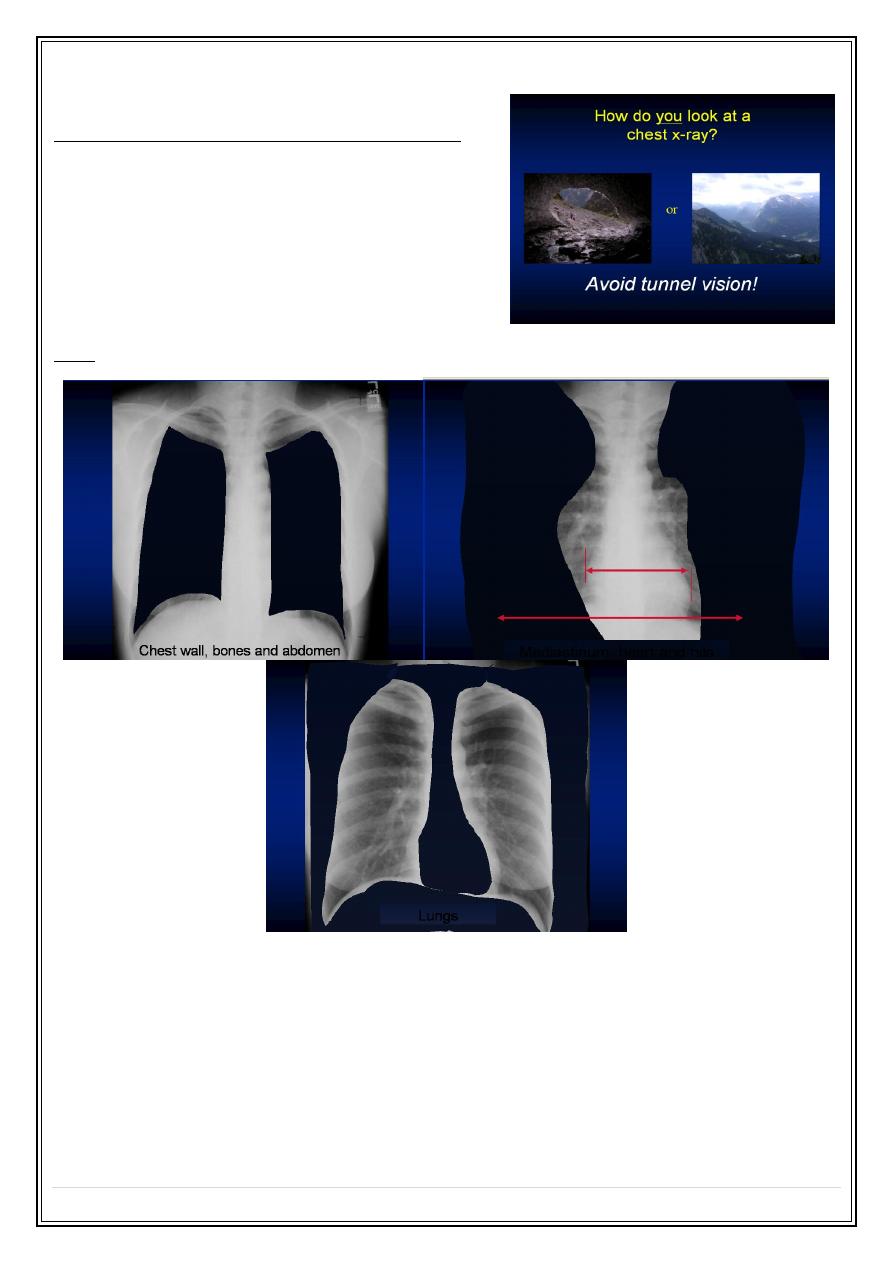
3- Structural & tissue components of the film .
1. Haphazard.
2.Systematic :
-- inner to outer
-- outer to inner
-- according to various tissue components.
Note if a pathology present describe it 1
st
.
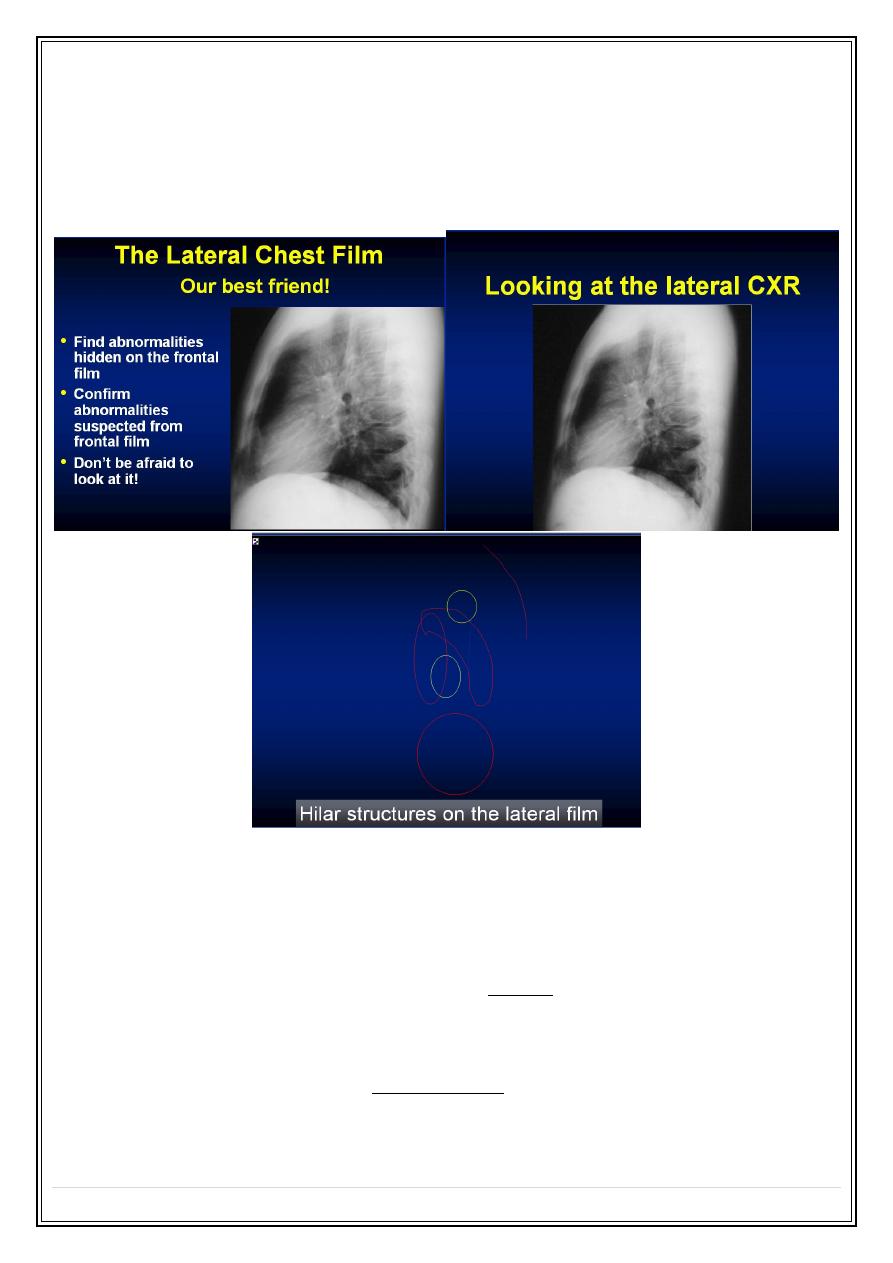
Viewing of lateral film: ( interpretation of lateral chest film )
1. The clear spaces ( retrosternal & retrocardiac).
2. Vertebral translucency.
3. Diaphragm outline.
4. Sternum .
Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
9
5. Complex hilar & mediastinal structures.( major vessels, heart )
6. Trachea .
7. Fissure outlines .
Diseases of the chest with a normal chest radiograph
1. Obstructive air ways diseases :Asthma & acute bronchitis may produce over
inflation of the lungs, but in many cases the chest film is normal.
2. Small lesions :Its usually impossible to see solitary lung masses or consolidations
of less than 1 cm in diameter
3. Pulmonary emboli without infarction, the chest radiograph is often normal.
4. Infections :Most patients with acute bacterial pneumonia present with
recognizable consolidations, but in other infections, notably pneumocystic carinii
pneumonia, obvious pulmonary consolidation may only develop after the onset of
symptoms.

Secret Lectures
(3)
/ Diagnostic Imaging / Dr.Riyadh A. Al-Kuzzay (M.B.Ch.B – FICMS-RD)
P a g e
10
5. Diffuse lung diseases . May be responsible for substantial alternation in lung
function test before any clear-cut abnormalities are evident on the chest
radiograph.
6. Pleural abnormalities. Dry pleurisy does not produce any radiological findings and
small amounts of pleural fluid may be impossible to recognize on standard PA and
lateral chest films.
7. mediastinal masses. Plain chest radiograph is very insensitive for the diagnoses of
mediastinal masses, lymph node enlargements,& mediastinal fluid collections.
