Prenatal diagnosis
ByDr.Tahani Ali
C.A.B.O.G
Definition
Prenatal diagnosis is the identification of a disease prior to birth.Classification
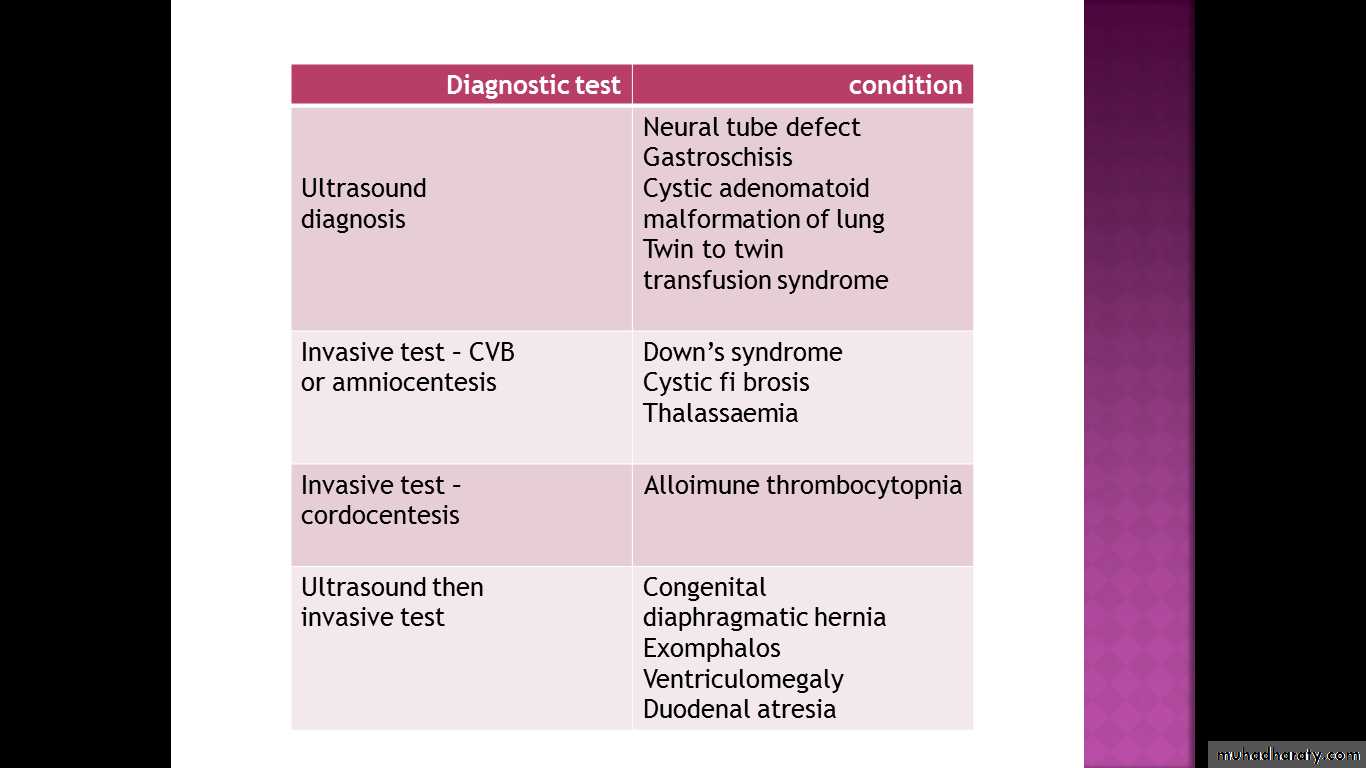
Prenatal diagnostic tests can be divided intononinvasive tests
US
Maternal blood
invasive tests.
CVS
Amniocentesis
Cordocentesis
The main non-invasive test
ultrasound scanning for structural fetal abnormalities, such as neural tube defects, gastroschisis, cystic adenomatoid malformation of lung, renal abnormalities
Maternal blood can be tested for exposure to viruses (viral serology)(IgG, IgM).
It is usually only tested if features on ultrasound are suggestive of infection having occurred, for example hydrops or ventriculomegaly or if there is a history of exposure to a particular virus
Free fetal DNA can be extracted from maternal blood to determine fetal blood group in cases of alloimmunization, or to determine the sex of the fetus in X-linked disorders.
Amniocentesis and chorion villus biopsy (CVB)
are the two most common invasive tests and are commonly used for checking the karyotype of the fetus, or to look for single gene disorders. These tests carry a small risk of miscarriage, therefore the risk of being affected by the condition and the seriousness of the condition should be severe enough to warrant taking the risk.Rarely, cordocentesis is used as an invasive diagnostic test.
Frequently, non-invasive tests and invasive tests are used together.
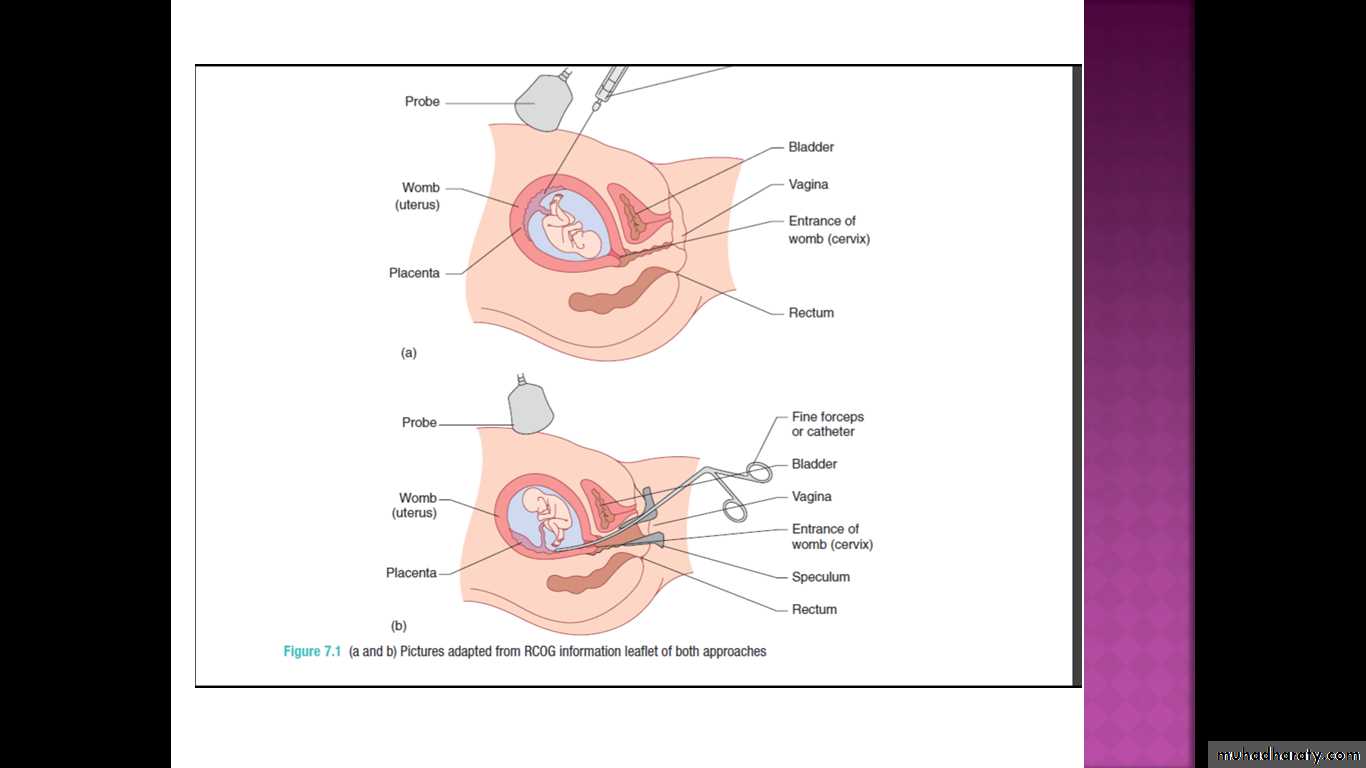
The ultrasound scan may diagnose a structural problem in the fetus such as a congenital diaphragmatic hernia, but since congenital diaphragmatic hernias are associated with underlying chromosomal abnormalities, an invasive test would then be offeredChorion villus sampling (also known as chorion villus biopsy)
. A CVB procedure aims to take a sample of the Fetal trophoblast cells in the mesenchyme of the villi that divide rapidly in the first trimesterese in the developing placenta.This is done either by passing a needle under ultrasound guidance through the abdominal wall into the placenta, or by passing a fine catheter (or biopsy forceps) through the cervix into the placenta .
The woman is scanned initially:
to confirm that the pregnancy is viable prior to the procedure;
to ensure that it is a singleton pregnancy (prenatal diagnosis in multiple pregnancy is more complex)
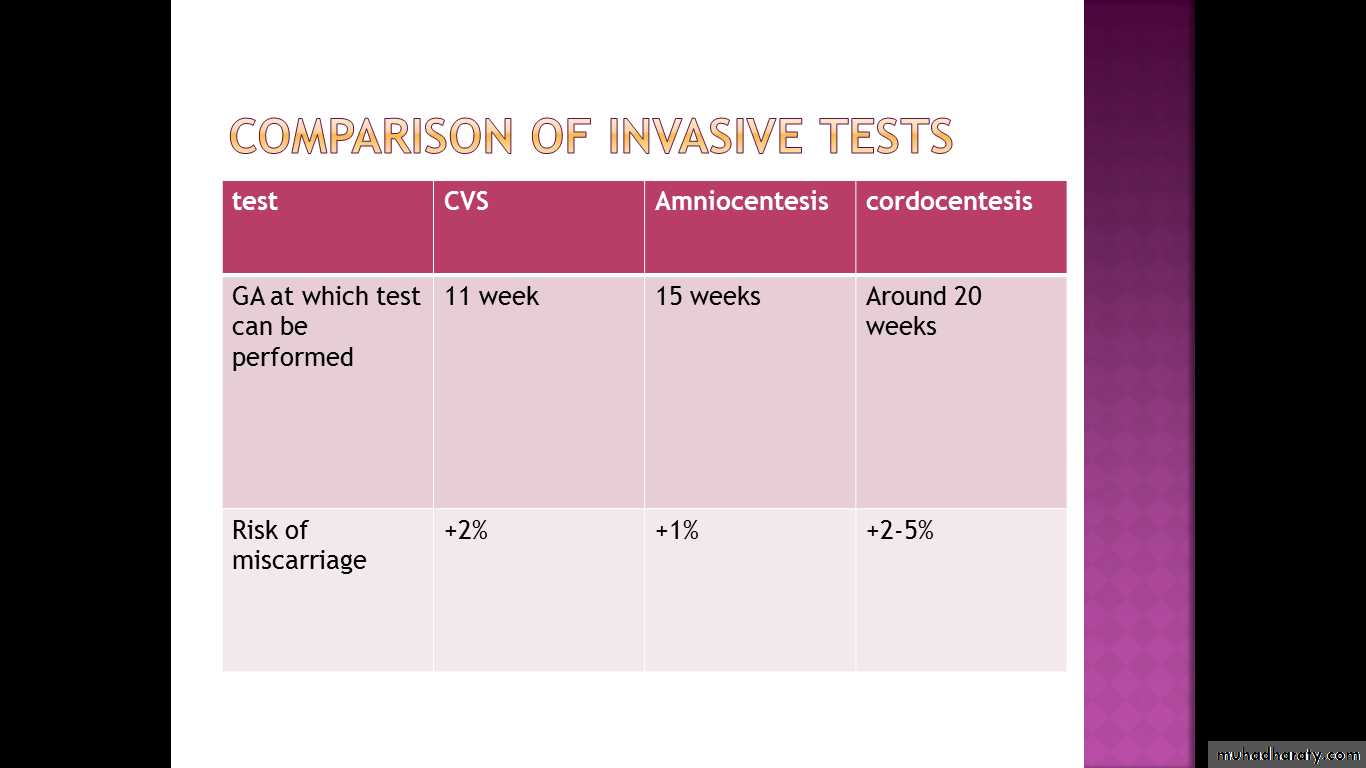
to confi rm gestational age (should not be performed before 10 weeks gestation);
to localize the placenta and determine whether a transabdominal or transcervical approach is more appropriate.
Transabdominal procedures are performed more commonly, but may not be feasible if the uterus is retroverted or the placenta is low on the posterior wall of the uterus.
The additional overall risk of miscarriage from chorion villus sampling (CVS) is approximately 2 per cent. This is in addition to the background (natural) risk of miscarriage for a first trimester pregnancy.
result for common aneuploidies (T21, 18 and 13)can be provided within 48 hours for a CVS sample.
Full culture results take approximately 7–10 days and results for genetic disorders take varying amounts of time.
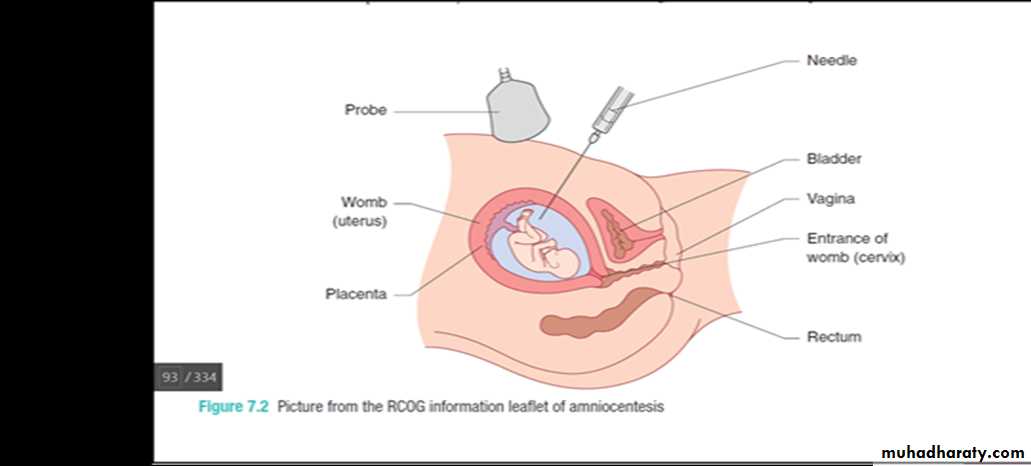
Amniocentesis
An amniocentesis procedure takes a sample (15–20 mL) of amniotic fluid which contains amniocytes and fi broblasts shed from fetal membranes, skin and the fetal genitourinary tract.This is done by passing a needle under continuous direct ultrasound control through the abdominal wall into the amniotic cavity and aspirating the fluid .
Risk of abortion is 1%
Many laboratories can provide a result for common aneuploidies (T21, 18 and 13) within 48 hours for an amniocentesis sample.
Full culture results take approximately 7–10 days and results for genetic disorders take varying amounts of time.
This is similar to CVS.
Amniotic fluid may be used to check for viral infections, for example cytomegalovirus.
The advantage of CVS over amniocentesis is that it can be performed earlier in pregnancy, at a stage when surgical termination is possible in the event of a ‘bad result’, and at a stage in pregnancy before a woman has needed to disclose the pregnancy to family, friends and employers.
The disadvantage of CVS compared with amniocentesis is that it may be associated with a higher risk of miscarriage.
Cordocentesis
Cordocentesis is performed when fetal blood is needed, or when a rapid full culture for karyotype is needed.The most common reason for performing a cordocentesis as a diagnostic prenatal test is to check the fetal platelet count, when alloimmune thrombocytopenia is suspected.
A needle is passed under ultrasound guidance into the umbilical cord at the point where it inserts into the placenta. This point is chosen because the umbilical cord is fixed and does not move.
Cordocentesis can be performed from about 20 weeks gestation.
The risk of miscarriage varies with indication and position of the placenta
Down’s syndrome
In the UK, prenatal diagnosis of Down’s syndrome is the most common reason for performing invasive testing.Most prenatal diagnostic tests arise following a ‘high risk’ screening test.
Several different screening tests are available but the option approved test which is performed between 11 and 14 weeks gestation.
This tests involves the combination of an ultrasound scan to measure the nuchal lucency and a blood test to measure the levels of human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG) and pregnancy associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) inmaternal blood.
The nuchal lucency measurement is a mea surement of the thickness of a pad of skin in the nuchal (neck) region of the fetus. Fetuses with Down’s syndrome tend to have a thicker nuchal lucency. If a thick nuchal lucency measurement is obtained it increases the risk of the fetus having Down’s syndrome.
The risk of Down’s syndrome increases with maternal age. For each woman, the individual risk can be calculated by taking her age-related risk and then adjusting this up or down based on the measurements obtained for the nuchal lucency, HCG and PAPP-A. Based on her individual result, the woman can then choose whether to have an invasive test or not.
Prior to performing the screening test, the woman should be encouraged to consider
what action she would take, and how she would feel if she screened positive.explain to women that this initial test is simply a screening test and not a diagnostic test.
A low risk result does not rule out the possibility of Down’s syndrome completely
The accuracy of the screening test for Down’s syndrome can be refined by adding further markers such as measuring the nasal bone, frontomaxillary nasal angle and looking for the presence of tricuspid regurgitation and at the ductus venosus wave form.
These increase the sensitivity of the test and reduce the false-positive rate. However, they are resource intensive, and a prenatal diagnostic test must still be performed to reach a definitive diagnosis