1
Preventive Dentistry
Systemic Fluoridation
Fluoride Supplements
Lec.6 Dr.Jihan Abdulhussein
Fluoride tablets, Lozenges and drops
– Fluoride supplements were originally designed to provide the
systemic fluoride that a child would not consume living in a
non-fluoridated area.
– Supplements contain a measured amount of fluoride typically
0.25mg, 0.5mg, and 1mg usually as sodium fluoride
– An early study by Bibby et al. (1955) a 1-year caries trial with
242 children comparing fluoride lozenges that were sucked and
swallowed with fluoride tablets that were swallowed right away,
he found only four new caries in the children who consumed the
lozenges versus 6.6 new caries in the children who swallowed
the tablets.
– Fluoride supplements should only be prescribed by dentists
where there is clear evidence for high risk of caries and non-
compliance with using other fluoridated products; and the
parents must be cooperative.
Indications: children living in area with non or low level of
fluoride in water
1- To children with high risk to dental caries.
2- To children with chronic systemic disease.
3- To handicapped children.
136
وقاية نظري / خامس اسنان
د.جيهان
25
\
11
\
2018
2
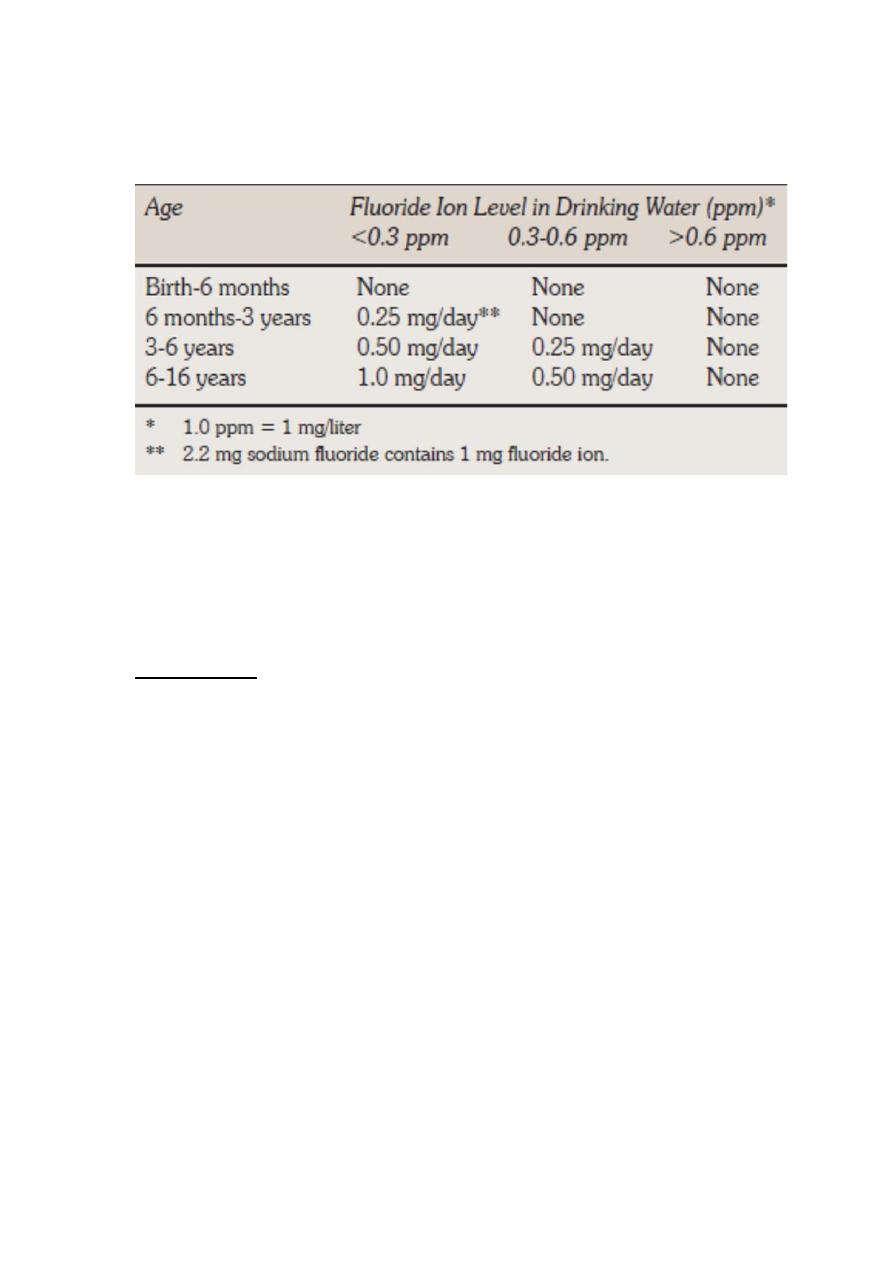
Fluoride supplement dosage schedule according to F
concentration in drinking water Approved by American Dental
Association
To maximize the topical effect of fluoride, tablets and lozenges
are intended to be chewed or sucked for 1–2 minutes before
being swallowed. It is daily used from 6months to 16 years to
give their maximum effect. It should not be given with milk.
Effective on:
Primary teeth: The studies concluded that a caries preventive
effect of about 40-50% was found when entail age was 2 years
or younger.
Permanent teeth: In studies
fluoride tablets were taken from 1
to 7 years give caries reduction 39-80%percent and the show
that sucking tablets, for as long as possible gives better results in
caries prevention.
Prenatal: results from few studies found caries reduction in
children their mothers received fluoride tablets during
pregnancy is greater than others.
Fluoride may be supplemented during pregnancy until dental
formation is completed through pharmaceutical products, i.e.
tablets or drops, according to variable doses (0.25 and 1 mg).

3
During pregnancy and breast feeding, mothers should take 1 mg
a day. In fact, theoretically, during intrauterine life, the fluoride
taken by the mother may work in the pre-eruptive phase, during
the amelogenesis of deciduous teeth with a consequent
beneficial effect on the newborn’s deciduous teeth. Fluoride
passes through the placenta freely, until it reaches excessively
high levels in the mother’s blood, and thus triggers this passage
(barrier effect) to protect the fetus from excessive doses. The
threshold concentration that pushes the placenta to trigger this
function is 0.4 ppm of fluoride in maternal blood. Some Authors
consider the systemic administration of fluoride as a further
supplement during pregnancy, as it is identified as the first step
to caries prevention
Fluoride Drops ; they are available as 0.125mg,0.25mg,0.50mg
drops .The drops are prescribed to the children until they are old
enough to swallow.10 drops equal to 1mg,if 10 drops placed in a
liter of water the result concentration of 1ppm of fluoride.
It may be given with multivitamins drops for young children.
Fluoridated Salt
Where water fluoridation could not be initiated, some countries
have introduced salt fluoridation. Caries remain a significant
problem in some Latin America countries, as well as some
countries in the Caribbean, and some of these countries have
converted their salt supplies to fluoridated salt. Switzerland
started the practice in 1955.
Salt is usually fluoridated at 250 ppm (which is 250 mg F/kg
salt, or 0.25 mg/gm salt). Table salt in the kitchen can contribute
1 to 4 g of the daily salt intake. Thus, a person could potentially
ingest 1 mg of fluoride a day at a salt intake of 4 grams a day.
The evidence that fluoridated salt effective is weak.

4
Advantages:
1- Wide coverage
2- Need little action by the individual
3- Low cost
4- Freedom for the consumers as both fluoridated and non-
fluoridated salt is available
5- It is safe
6- Minimum possibilities of fluorosis.
Disadvantages:
1- Salt fluoridation need community education and promotion.
2- International efforts to reduce sodium intake to help control
hypertension.
3- Consumption of fluoridated salt is lowered during early life
when the need for fluoride is the maximum.
Fluoridated Milk
Milk fluoridation is the addition of a measured quantity of
fluoride to bottled or packaged milk to be drunk by children
.both bovine and human milk contain low level of fluoride about
0.03ppmF. Milk fluoridation is suggested instead of water
fluoridation.
– Concentration of 2.5 ppm fluoride to 6 ppm
– In a study done in UK: The children generally consumed one
typical serving (200 mL) at level 5mg/L(5ppm) of the beverage
(test and control milk). In the trial by Stephen (1984) it took
about 5 years to achieve a 31.2% reduction in DMFT. No
correction was made for delay in tooth eruption.

5
– A high concentration of fluoride is needed for two reasons:
(1) the children did not drink the beverage throughout the day.
(2) calcium in the milk complexes with fluoride, which would
reduce its availability for topical benefits.
Some studies could not show any benefit of fluoridated milk.
Disadvantages:
1- Consumption of milk varies between different socioeconomic
groups .
2- Consumption decrease with age so long term benefit is less
than water fluoridation
3- Require high level of technical expertise
4- Procedure can be relatively coast.
In warm climates fluoridated fruit juices may be alternative to
Milk fluoridation.
Fluoride Vitamin Preparation
Fluoride supplements may be obtained as fluoride vitamin
combinations. There is no evidence that vitamins enhance the
effect of fluoride.
Disadvantage
Disadvantage of fluoride vitamin combination in capsule form is
that they cannot provide a topical effect to the erupted teeth
because they have to be swallowed directly.
