Mohanad N Noaman Electronic Engineering College Ninevah University
Method of construction Polygon
1- Regular hexagon knowing the length of one side.
After doing this
Your work should look like this
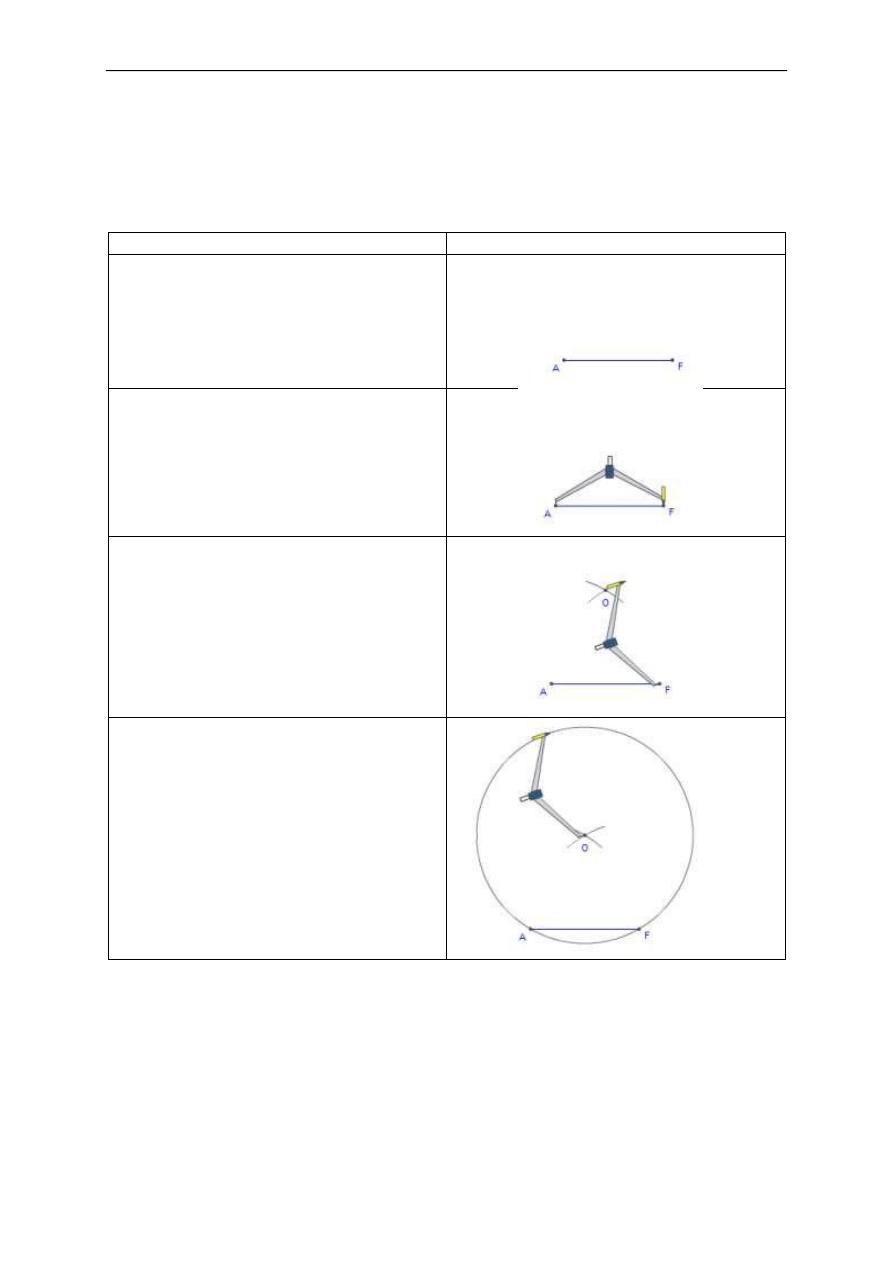
We start with a line segment AF. This will
become one side of the hexagon. Because we
are constructing a regular hexagon, the other
five sides will have this length also.
1. Set the compasses' point on A, and set its
width to F. the compasses must remain at this
width for the remainder of the construction.
2. From points A and F, draw two arcs so that
they intersect. Mark this as point O.
This is the centre of the hexagon's circumcircle.
3. Move the compasses to O and draw a circle.
This is the hexagon's circumcircle - the circle that
passes through all six vertices
Mohanad N Noaman Electronic Engineering College Ninevah University
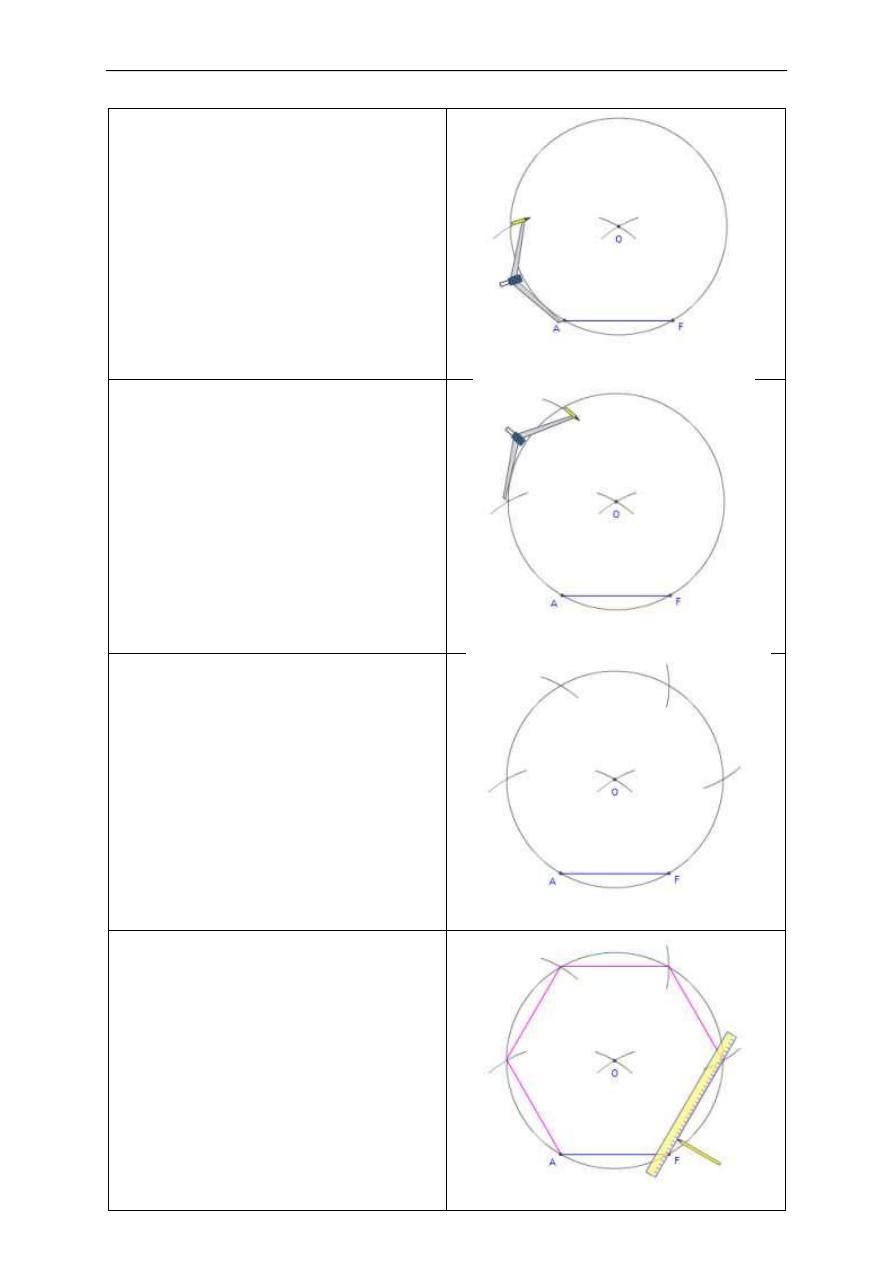
4. Move the compasses on to A and draw an arc
across the circle. This is the next vertex of the
hexagon.
5. Move the compasses to this arc and draw an
arc across the circle to create the next vertex.
6. Continue in this way until you have all six
vertices. (Four new ones plus the points A and F
you started with.)
7. Draw a line between each successive pairs of
vertices.
Mohanad N Noaman Electronic Engineering College Ninevah University
8. Done. These lines form a regular hexagon
where each side is equal in length to AF.
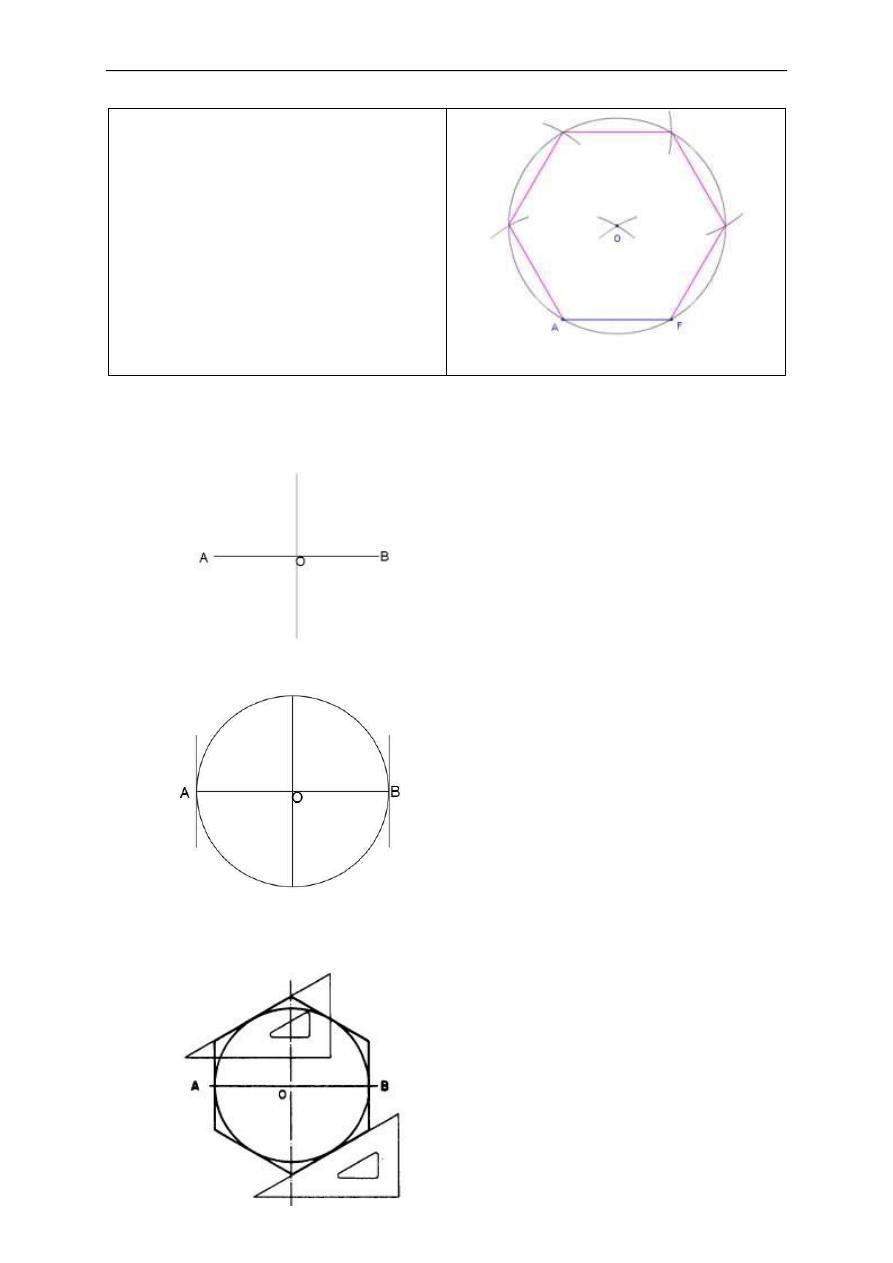
2- Regular Hexagon on a Given Inscribed Circle.
A. Draw horizontal diameter AB and vertical centre line.
B. Draw lines tangent to the circle and perpendicular to AB at A and B.
C. Use a T square and a 30°/60° triangle to draw the remaining sides of the figure tangent
to the circle and at 30° to the horizontal.
Mohanad N Noaman Electronic Engineering College Ninevah University
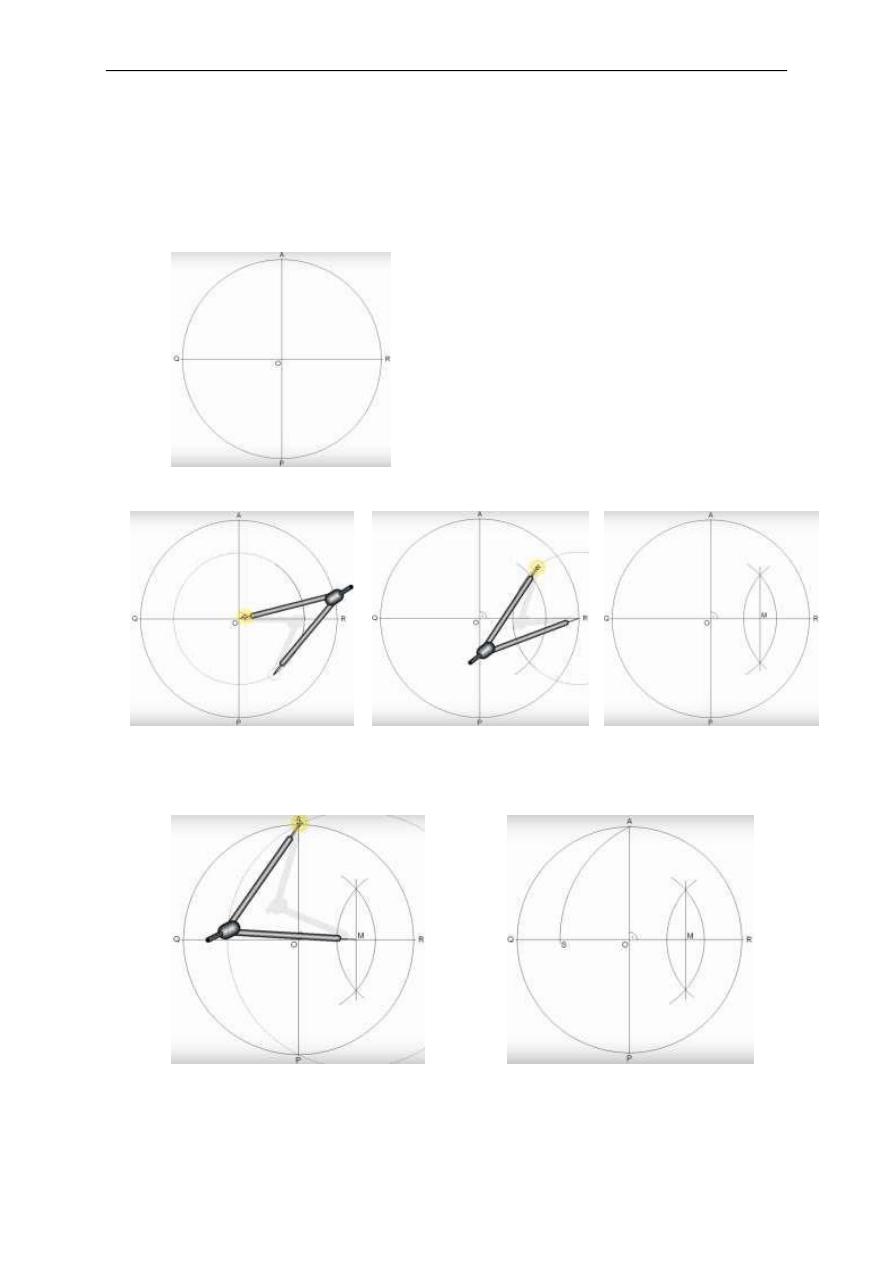
3-
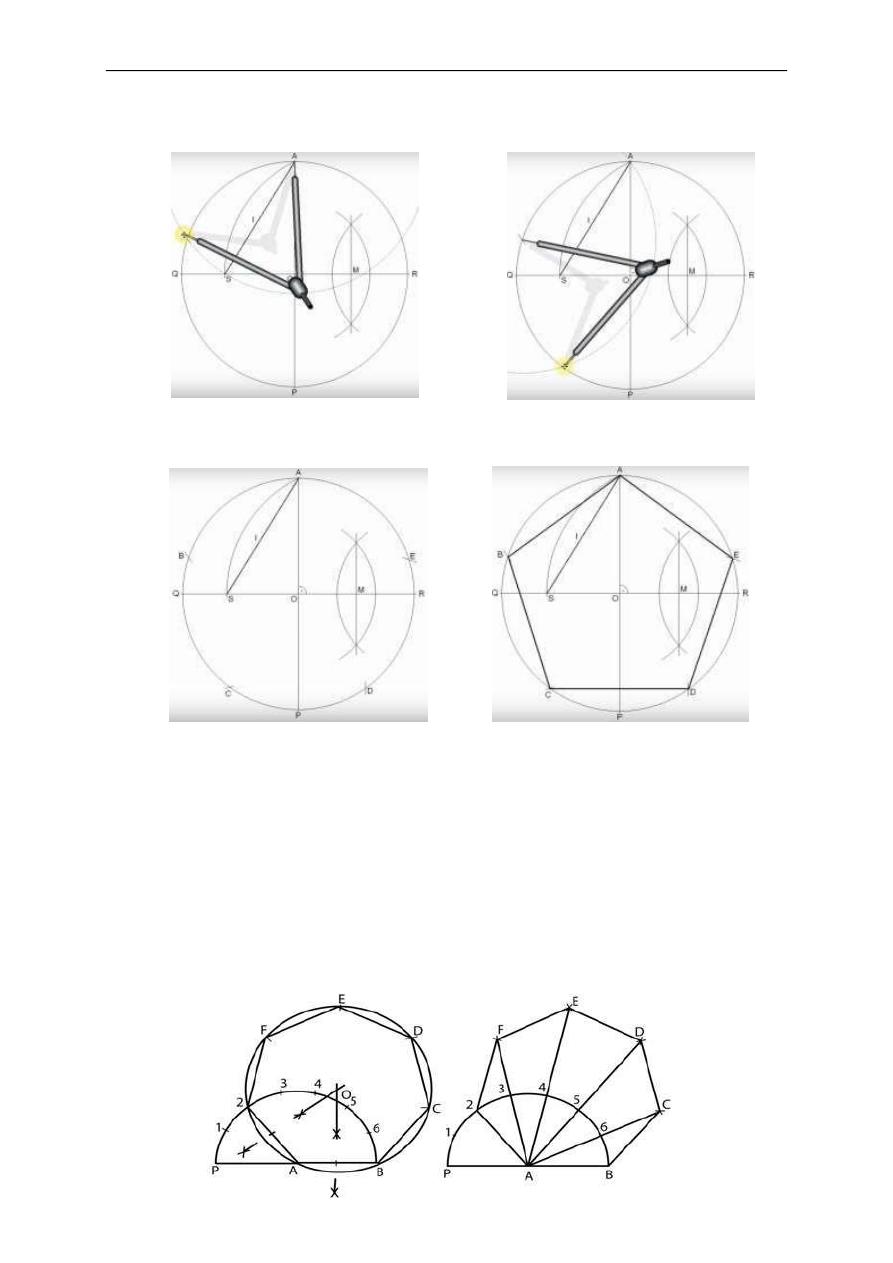
REGULAR PENTAGON IN A GIVEN CIRCUMSCRIBED
CIRCLE
A. Draw a horizontal diameter QR and vertical diameter AP.
B. Locate M, the midpoint of the radius OR.
C. Set a compass to the spread between M and A, and, with M as a centre, strike the arc
AS.
Mohanad N Noaman Electronic Engineering College Ninevah University
D. Set a compass to the spread between A and S, and, with A as a centre, strike the arc.
E. A line from A to B forms one side of the pentagon. Set a compass to AB and lay off
this interval from A around the circle. Connect the points of intersection.
4- Constructing a Regular Polygon, with A Given
Length of Side.
To construct a regular polygon with length of edge AB us shown in figure below. To
draw any polygon with any number of sides, for example, 7 sides:
Half circle (180°), to find number of devisions that we should divide the half circle to.
We can divide the angle of 180 over No. of sides we need to draw.
(180°/7) = 25.7° so, we can divide the half circle into 7 devisions with 25.7° per each.

Mohanad N Noaman Electronic Engineering College Ninevah University
A.
Draw a line of length AB. With A as center and radius AB, draw a semicircle.
B.
With the divider, divide the semicircle into the number of sides (example of number
of side 7 is shown in figure above) of the polygon.
C.
Draw a line joining A with the second division-point 2.
D.
The perpendicular bisectors of A2 and AB meet at O. Draw a circle with center O and
radius OA.
E.
With length A2, mark points F, E, D & C on the circumferences starting from 2
(Inscribe circle method)
F.
With center B and radius AB draw an arc cutting the line A6 produced at C. Repeat
this for other points D, E & F (Arc method).
