
Parathyroid gland
lecture 2
1
Parathyroid Hormone
PTH is synthesized and secreted by the parathyroid gland which lie
posterior to the thyroid glands.
The dominant regulator of PTH is plasma Ca
2+
.
Secretion of PTH is inversely related to [Ca
2+
].
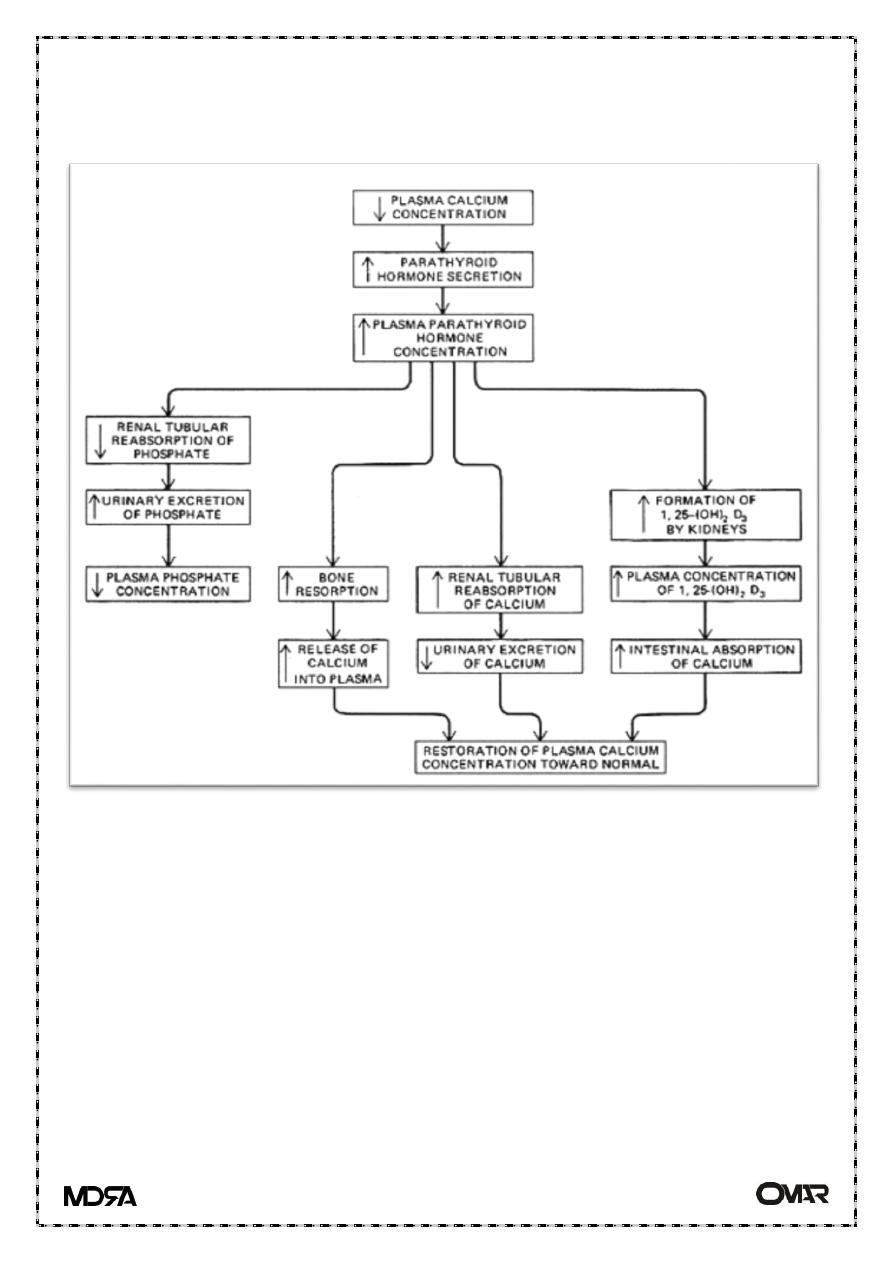
Regulation of PTH
PTH secretion responds to small alterations in plasma Ca
2+
within
seconds.
calcium receptor within the parathyroid cell plasma membrane senses
changes in the extracellular fluid concentration of Ca
2+
.
a typical G-protein coupled receptor that activates phospholipase C and
inhibits adenylate cyclase—result is increase in intracellular Ca
2+
via
generation of inositol phosphates and decrease in cAMP which prevents
exocytosis of PTH from secretory granules.
When Ca
2+
falls, cAMP rises and PTH is secreted.
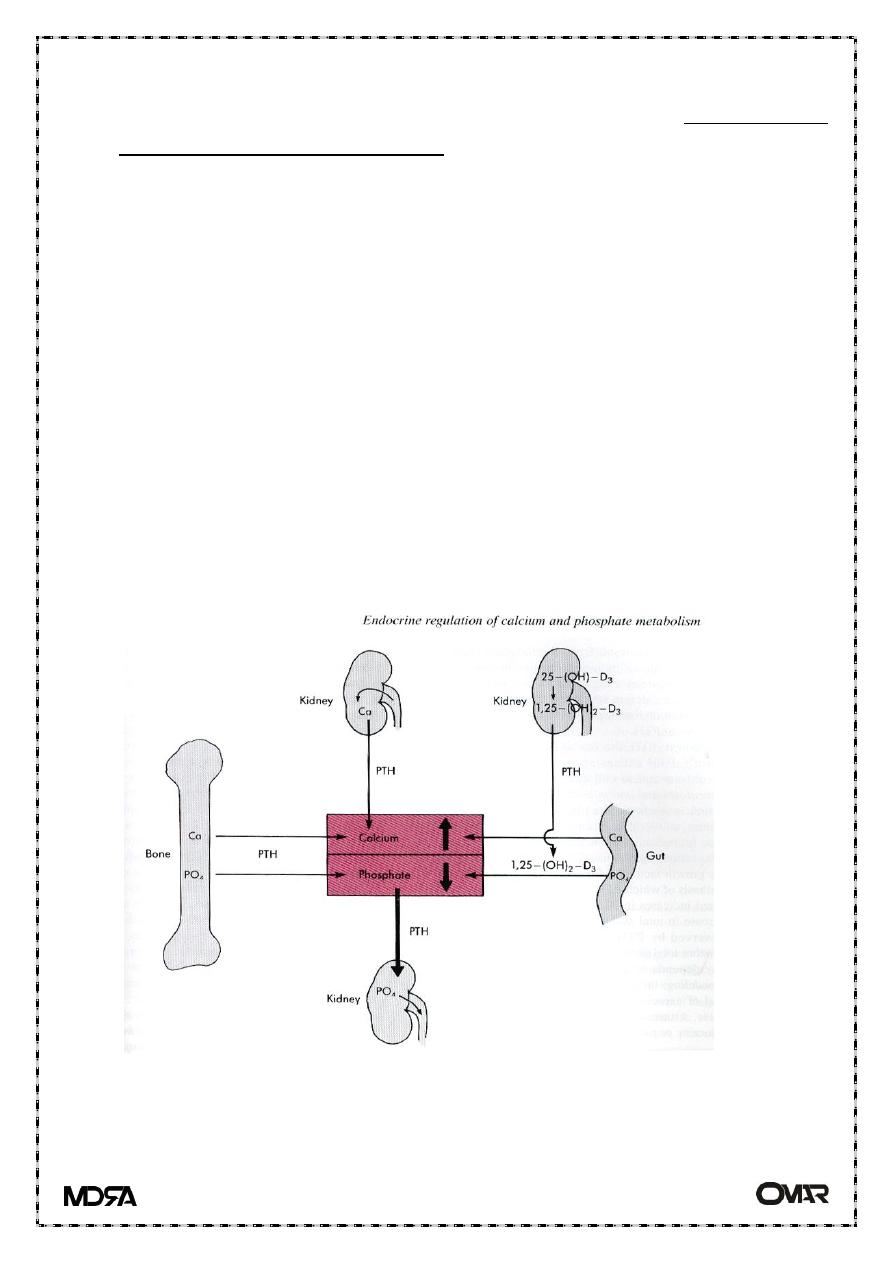
PTH action
The overall action of PTH is to increase plasma Ca
++
levels and decrease
plasma phosphate levels.
PTH acts directly on the bones to stimulate Ca
++
resorption and kidney to
stimulate Ca++ reabsorption in the distal tubule of the kidney and to
inhibit reabsorption of phosphate (thereby stimulating its excretion).
PTH also acts indirectly on intestine by stimulating 1,25-(OH)
2
-D
synthesis.
Calcitonin
Normal calcium level 8.5 – 10 mg/dl in plasma
Calcitonin acts to decrease plasma Ca
++
levels.
Parathyroid gland
lecture 2
2
While PTH and vitamin D act to increase plasma Ca
++
-- only calcitonin
causes a decrease in plasma Ca
++
.
Calcitonin is synthesized and secreted by the parafollicular cells of the
thyroid gland.
The major stimulus of calcitonin secretion is a rise in plasma Ca
++
levels
Calcitonin is a physiological antagonist to PTH with regard to Ca
++
homeostasis
The target cell for calcitonin is the osteoclast.
Calcitonin acts via increased cAMP concentrations to inhibit osteoclast
motility and cell shape and inactivates them.
The major effect of calcitonin administration is a rapid fall in Ca
2+
caused
by inhibition of bone resorption.
Calcium homeostasis
Parathyroid gland
lecture 2
3
