Sinusitis
What`s sinusitis?
• An acute inflammatory process involving one or more of the paranasal sinuses.• A complication of 5%-10% of URIs in children.
• Persistence of URI symptoms >10 days without improvement.
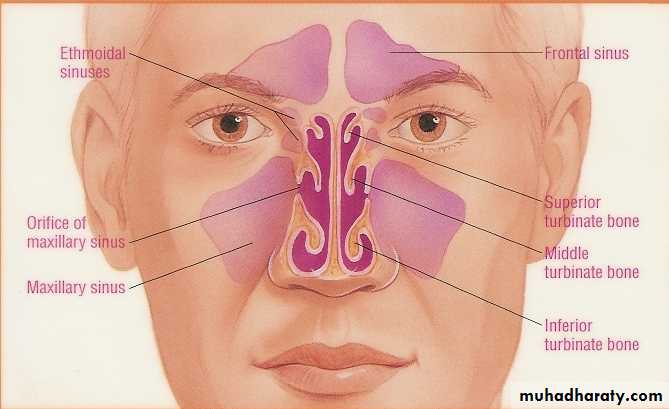
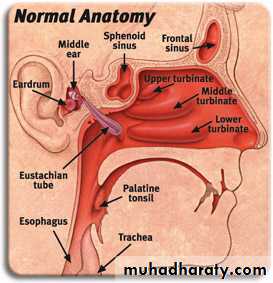
• Maxillary and ethmoid sinuses are most frequently involved
Acute sinusitisCauses:1.Acute infective rhinitis.2.Swimming & diving .3.Dental extraction & infection.4.Fractures involving sinus.5.Barotrauma.
Predisposing factors:a.Local: Nasal obstruction. Sinus meatus obstruction. Neighboring infection. Previous infection.b.General: Debilitation & immune deficiency Mucociliary disorders (cystic fibrosis) Irritating atmospheric conditions.
Bacteriology:Usually mixed & preceded by viral infection * Strep. pneumonia, *Staph.aureus , *Moraxella catarrhalis * Kleb. ,E.coli .* Anaerobic infection ( dental origin).
pathophysiology
• With inflammation, the mucosal lining of the sinuses produce mucoid secretion. Bacteria invade and pus accumulates inside the sinus cavities.• Postnasal drainage causes obstruction of nasal passages and an inflamed throat.
• If the sinus orifices are blocked by swollen mucosal lining, the pus cannot enter the nose and builds up pressure inside the sinus cavities
• Acute Sinusitis – respiratory symptoms last longer than 10 days but less than 30 days.
• Subacute sinusitis – respiratory symptoms persist longer than 30 days without improvement.
• Chronic sinusitis – respiratory symptoms last longer than 120 days.
Clinical presentation:1.Preceding URTI.2.Constitutional symptoms.(headache, fatigue, fever)3.Nasal obstruction.4.Nasal discharge ,postnasal drip & halitosis5.Sever facial pain over sinus , increases by bending or coughing.6.Swelling &tenderness over affected sinus.
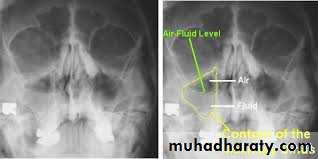
Investigations:1.Endoscopical examinations.2.Radiological examinations. X-ray sinuses ,CT scan, MRI .
Differential diagnosis:1.Dental pain.2.Migraine.3.Trigeminal neuralgia.4.Neoplasms of sinuses.5.Infections eg. erysipelas & H.zoster.6.Temporal arteritis, Angioneurotic oedema & Insect bite.
treatment.:1. Tt. of infections.2. Tt. of pain.3. Decongestant4. Irrigation.
• Antimicrobials-treat for 10-14 days, depending upon severity, with one of the following:
• Amoxicillin:20-40mg/kg/d in 3 divided doses(>20kg, 250mg tid)
• Augmentin:25-45mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses(>20kg, 400mg q12) Use chewable or suspension if child is less than 40kg.
• Analgesia
• Acetaminophen , or ibuprofen
• Codeine – for severe pain
• Nasal douche with saline
• Rhinocort nasal spray – 2 sprays in each nostril every 12 hours for children over 6 years of age.
Non-pharmacological treatment
• Humidifier to relieve the drying of mucous membrane associated with mouth breathing• Increase oral fluid intake
• Saline irrigation of the nostrils
• Moist heat over affected sinus
• Prolonged shower to help promote drainage
Chronic Sinusitis
Predisposing Factors:1. VMR ,AR.2. Smoking & other pollutions.3. Nasal polyposis.4. Endocrine disorder e.g. Myxedema.5. Cong.mucociliary disorders.Bacteriology:Usually mixed*Strep. Including some anaerobic.*Pneumococci.*Proteus ,Pseudomonus &E.colli
Clinical features:Same as acute but lesser degree*Nasal &post nasal discharge of mucoid or purulent.*Headache; heavy or dull ache.*Anosmia or cacosmia.*Less sever constitutional symptoms.
Principles of Tt.:*Decongestants; - topical decongestants for a short time, - systemic may be of value.*Steroid may of benefit (systemic or local).*Systemic antibiotics.*Surgical drainage .
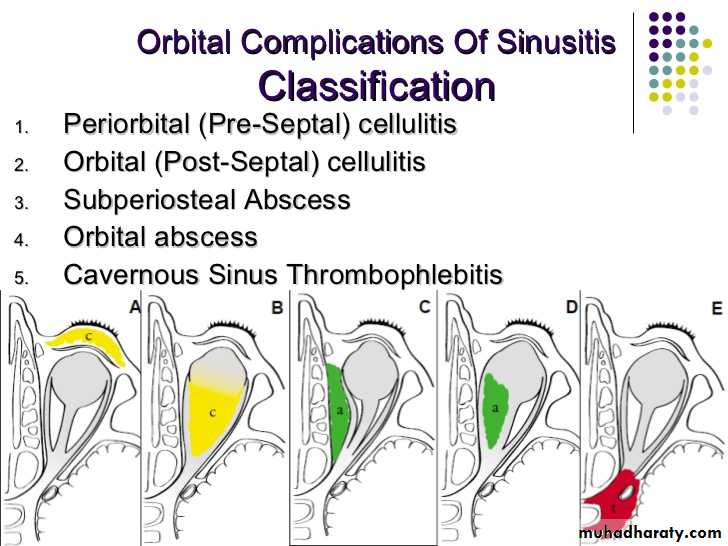
Complications of sinusitis:
the orbit is the most common complication of acute sinusitis in childrenMode of spread:1.Direct;through bony wall.2.Venous.3.Lymphatics.4.Via perineural space of Olfactory n.to subarachnoid space.
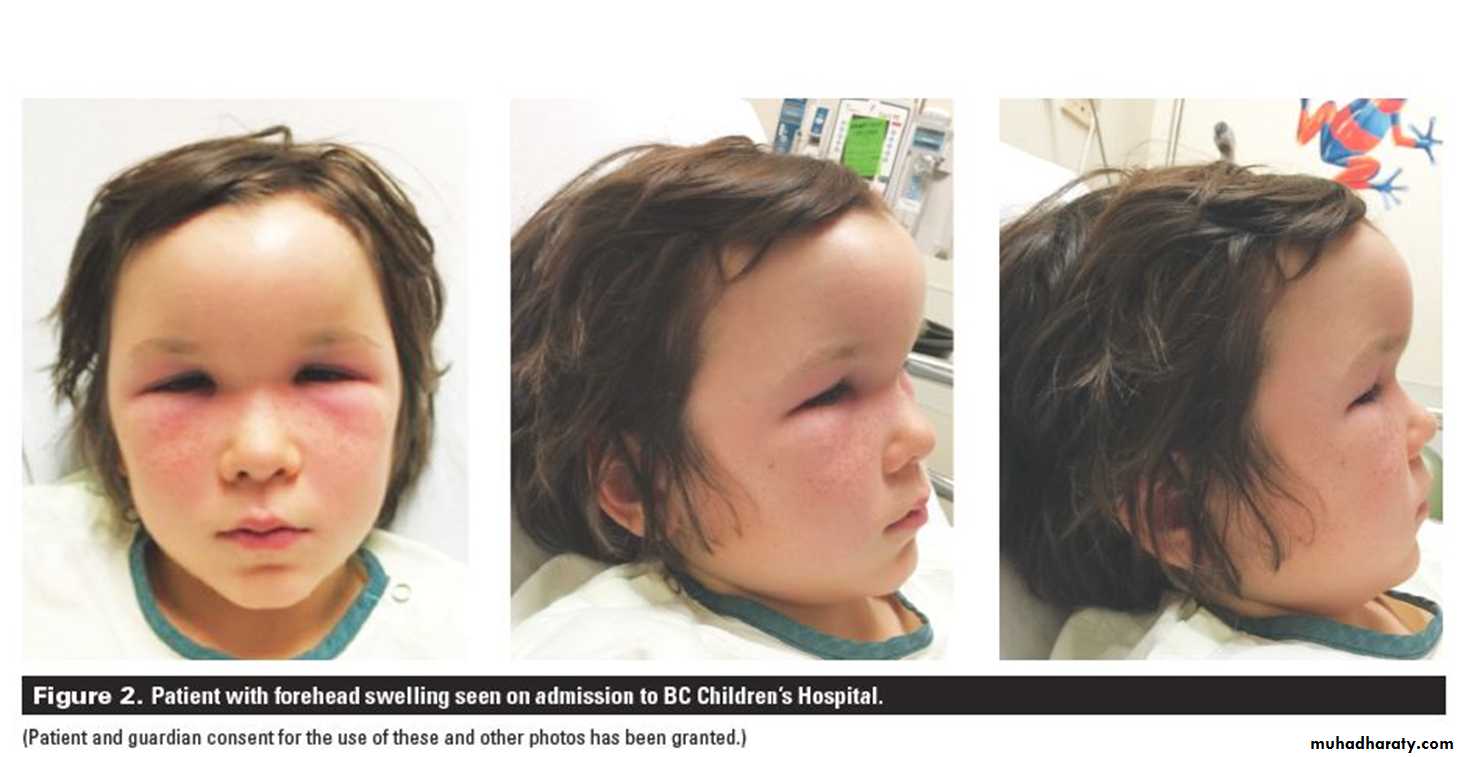
Types:1.Extracranial cx.s a.Osteomayelitis: Rare ,usually of frontal sinus, increases in young adults. Forehead oedema (Pott’s puffy tumor).b. orbital cx.s:Rare but more in children due to ethmoiditis
c.Others:1.Infection of nasopharynx.2.Lateral pharyngitis & Tonsillitis.3.Otitis media.4.Laryngotracheitis.5.Bronchitis.6.Association with bronchiectasis.7.Association with asthma.8.Polyarteritis,Tenosynovitis.
2.Intracranial cx.s:a. Meningitis +/- extradural or subdural abscesses.b. Cavernous sinus thrombosis.c. Brain lesion; according to affected sinus; 1.Frontal lobe abscess.(frontal). 2.Diffuse supp. Meningitis near cribriform plate(ethmoid). 3.Diffuse meningitis(sphenoid). 4.Max.sinusitis rarely causes ICCx.