FIFTH STAGE
E.N.T
DR.MUSHTAQ – LECTURE 20
1
Sinusitis
WHAT`S SINUSITIS?
•
An acute inflammatory process
involving one or more of the
paranasal sinuses.
•
A complication of 5%-10% of URIs in
children.
•
Persistence of URI symptoms >10 days
without improvement.
•
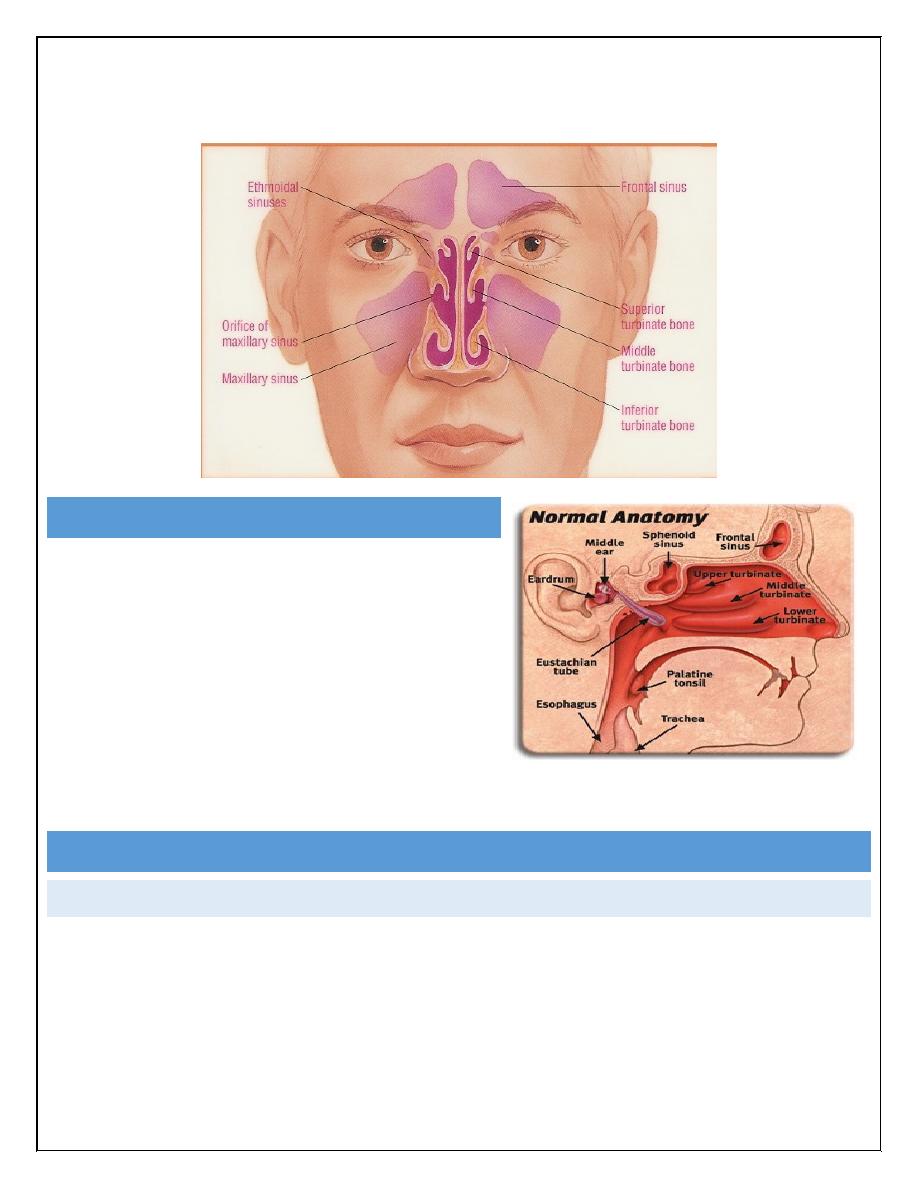
Maxillary and ethmoid sinuses are most frequently involved
Acute sinusitis
Causes:
1.Acute infective rhinitis.
2.Swimming & diving .
3.Dental extraction & infection.
4.Fractures involving sinus.
5.Barotrauma.

2
Predisposing factors:
a.Local:
Nasal obstruction.
Sinus meatus obstruction.
Neighboring infection.
Previous infection.
b.General:
Debilitation & immune deficiency
Mucociliary disorders (cystic fibrosis)
Irritating atmospheric conditions.
Bacteriology:
Usually mixed & preceded by viral infection
*Strep. pneumonia,Staph.aureus ,Moraxella
catarrhalis
*Kleb. ,E.coli .
*Anaerobic strep. in dental origin.
Pathophysiology:
•
With inflammation, the mucosal lining of the sinuses produce mucoid drainage.
Bacteria invade and pus accumulates inside the sinus cavities.
•
Postnasal drainage causes obstruction of nasal passages and an inflamed
throat.
•
If the sinus orifices are blocked by swollen mucosal lining, the pus cannot enter
the nose and builds up pressure inside the sinus cavities
•
Acute Sinusitis – respiratory symptoms last longer than 10 days but
less than 30 days.
•
Subacute sinusitis – respiratory symptoms persist longer than 30 days
without improvement.
•
Chronic sinusitis – respiratory symptoms last longer than 120 days.

3
CLINICAL PRESENTATION:
1.Preceding URTI.
2.Constitutional symptoms.(headache, fatigue, fever)
3.Nasal obstruction.
4.Nasal discharge ,postnasal drip & halitosis
5.Sever facial pain over sinus , increases by bending or coughing.
6.Swelling &tenderness over affected sinus.
INVESTIGATIONS:
1.Endoscopical examinations.
2.Radiological examinations. X-ray sinuses ,CT scan, MRI .
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
1.Dental pain.
2.Migraine.
3.Trigeminal neuralgia.
4.Neoplasms of sinuses.
5.Infections eg.erysipelas & H.zoster.
6.Temporal arteritis, Angioneurotic oedema & Insect bite.
TREATMENT.:
1.Tt. of infections.
2.Tt. of pain.
3. Decongestant
4. Irrigation.
Antimicrobials-treat for 10-14 days, depending upon severity, with one of the
following:
•
Amoxicillin:20-40mg/kg/d in 3 divided doses(>20kg, 250mg tid)
•
Augmentin:25-45mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses(>20kg, 400mg q12) Use chewable
or suspension if child is less than 40kg.
•
Codeine – for severe pain
•
Rhinocort nasal spray – 2 sprays in each nostril every 12 hours for children
over 6 years of age.
4
NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT:
•
Humidifier to relieve the drying of mucous membrane associated with mouth
breathing
•
Increase oral fluid intake
•
Saline irrigation of the nostrils
•
Moist heat over affected sinus
•
Prolonged shower to help promote drainage
CHRONIC SINUSITIS
PREDISPOSING FACTORS:
1.VMR ,AR.
2.Smoking & other pollutions.
3.Nasal polyposis.
4.Indocrine disorder e.g. Myxedema.
5.Cong.mucociliary disorders.
BACTERIOLOGY:
Usually mixed
*Strep. Including some anaerobic.
*Pneumococci.
*Proteus ,Pseudomonus &E.colli

5
CLINICAL FEATURES:
Same as acute but lesser degree
*Nasal &post nasal discharge of mucoid or purulent.
*Headache; heavy or dull ache.
*Anosmia or cacosmia.
*Less sever constitutional symptoms.
PRINCIPLES OF TT.:
*Decongestants; avoid use topical decongestants for a long time, systemic may be
of value.
*Steroid may of benefit (systemic or local).
*Systemic antibiotics.
*Surgical drainage .
COMPLICATIONS OF SINUSITIS:
the orbit is the most common complication of acute sinusitis in children
MODE OF SPREAD:
1.Direct;through bony wall.
2.Venous.
3.Lymphatics.
4.Via perineural space of Olfactory n.to subarachnoid space.
TYPES:
1.Extracranial cx.s
a.Osteomayelitis:
Rare ,usually of frontal sinus, increases in young adults.
Forehead oedema (Pott’s puffy tumor).
b. orbital cx.s:
Rare but more in children due to ethmoiditis

6
c.Others:
1.Infection of nasopharynx.
2.Lateral pharyngitis & Tonsillitis.
3.Otitis media.
4.Laryngotracheitis.
5.Bronchitis.
6.Association with bronchiectasis.
7.Association with asthma.
8.Polyarteritis,Tenosynovitis.
2.INTRACRANIAL CX.S:
a. Meningitis +/- extradural or subdural abscesses.
b. Cavernous sinus thrombosis.
c. Brain lesion; according to affected sinus;
1.Frontal lobe abscess.(frontal).
2.Diffuse supp. Meningitis near cribriform
plate(ethmoid).
3.Diffuse meningitis+CSF (sphenoid).
4.Max.sinusitis rarely causes ICCx.
Thank you, and good luck ^^
