Benign cystic lesions of
The oral cavityA cyst is a cavity occurring in either hard or soft tissue with a liquid,semiliquid, or air content. It is surrounded by a definite connectivetissue wall or capsule and usually has an epithelial lining.
Classification:
A. Congenital cysts.B. Developmental cyst which divided into:
1. Non odontogenic cysts.
2. cysts of dental origin
A.Congenital cysts:
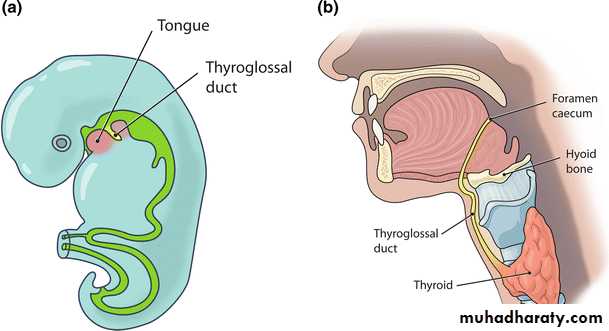
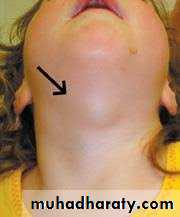
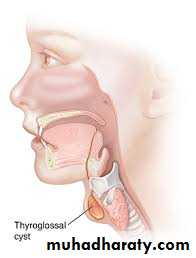
1. Thyroglossal duct cyst:which may arise from any portion of thyroglossal duct they are therefore in a midline position at any point between the thyroid isthmus and the base of the tongue. The cyst may be asymptomatic or may cause symptoms as a result of pressure on other structures. Swallowing will cause the mass to move upward.
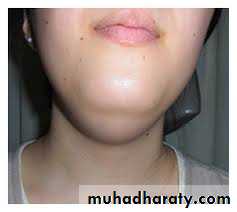
2.Dermoid cysts:D. cyst are relatively uncommon in oral cavity. The cyst consists of a fibrous wall lined with stratified squamous epithelium which contains hair, sebaceous and sweat glands. As well as tooth structures. They may occur on the hard and soft palate, on the dorsum of the tongue or more commonly in the floor of the mouth above or below the geniohyoid muscle usually in the midline.Treatment is the surgical removal.
D. cyst are not easily discovered unless they cause swelling beneath the chin or up into the floor of the mouth on palpation. These cyst have a rubber like sensation.
3.Branchiogenic cysts:These cysts arise from persistence's of the second branchial cleft. They are characteristically located along the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle at any level in the neck. The cyst are linedwith ciliated arid stratified squamous epithelium and contain a milky ora mucoid fluid. Treatment consists of complete surgical excision.
B. Developmental cysts:
Nonodontogenic cysts:1.Median palatine cysts:It is bone cysts that forms in a median fissure of the palate from embryonic remnants. Median cysts are differentiated from incisive canal cysts primarily by their location. Since they usually occur more posteriorly in the palate. The median cyst has a connective tissue sac lined by squamous epithelium.2. Incisive canal cysts (Nasopalatine cysts)Which located in the center of the bone but don't expand inside the bone nor do they alter significantly the overlying mucosa and these cyst give no clinical symptoms unless they become secondarily infected.
3. Globulomaxillary cysts:G. cyst are epithelial lined sacs formed at the junction of the globular and maxillary processes between the lateral incisor and canine teeth They usually cause a divergence of the roots of these teeth and appears as a pear-shaped radiolucency's on x-ray film. As is true with other cysts of the oral-cavity, they become secondarily infected and undergo acute inflammatory changes. Treatment is surgical and consists of careful excision.
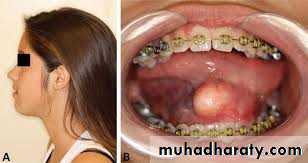
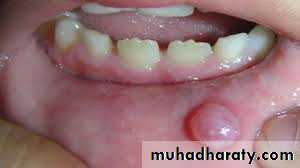
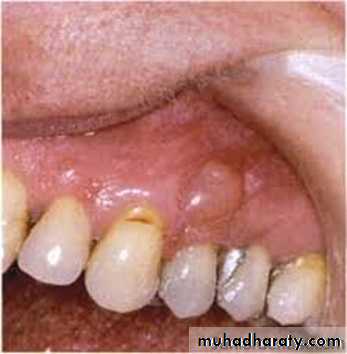
4. Mucoceles:Result from obstruction of a glandular duct or ( minor salivary gland duct) and are commonly located in the lip, cheek and floor of the mouth. They may also be found on the anterior portion of the tongue. Where glands are located at the inferior surface. These are small, round or oval, translucent swellings, some times having a bluish color. The mucocels is freely movable and usually found right underneath the mucosa. The preferred treatment is complete excision. If the mucocele is incompletely removed, it has a marked tendency to recur but the lesion is not known to become malignant.
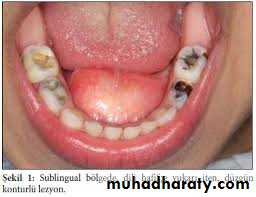
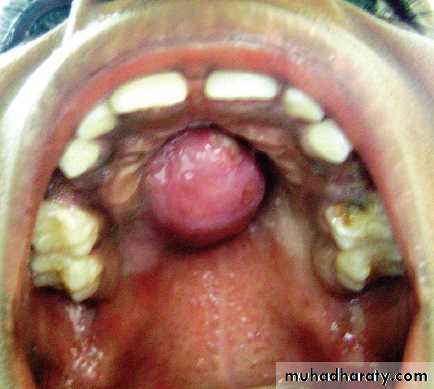
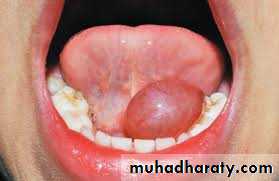
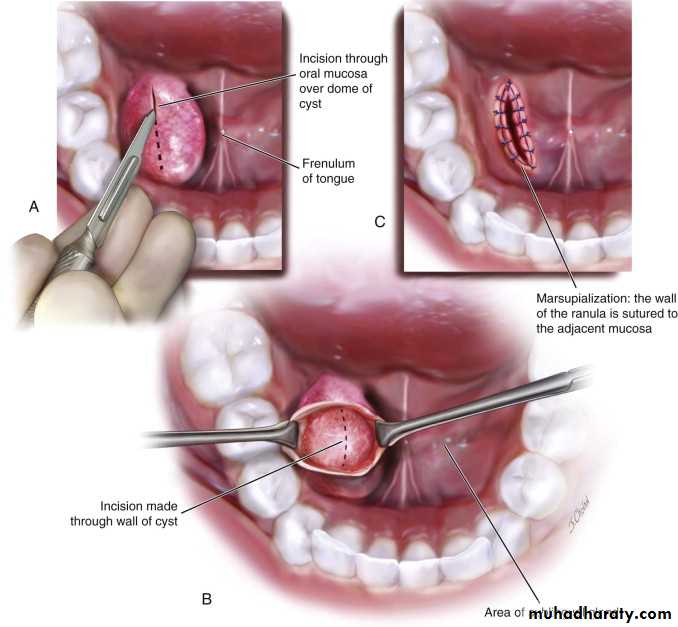
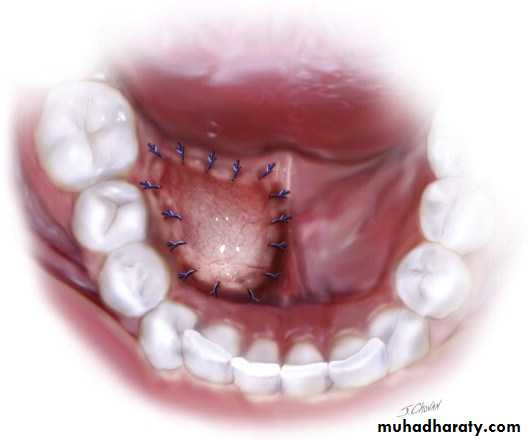
5. Ranula:A ranula is a cyst forming in the floor of the mouth, generally from sublingual gland. The ranula forms in a manner similar to the mucocele but develop to a much larger size. The mucosa is thinned out and the cyst assumes a bluish color. It is non painful lesions. But the tongue may be raised and it's motion obstructed, thus impairing mastication and speech. The ranula is subject to rupture when injured, with escape of a mucoid fluid that re-accumulates as the area heals. The best treatment for a ranula is surgery in the form of marsupialization.
Odontogenic cysts ( dental cysts):1-periodontal cysts:is formed from epithelial rests or remnants in the periodontal membrane. These cysts are all of inflammatory origin. The usual location is along the lateral surface of the teeth. Which termed lateral cyst or at the apex of Cysts of inflammatory nature in edentulous area are termed residual. These result from incomplete surgical removal of pathological tissue at the time an infected tooth is extracted. These cysts are commonly lined by stratified squamous epithelium.
Round cell inflammation and other signs of chronic inflammation are usually found. The small periodontal cyst can often be enucleated through the alveolar socket after removal of the involved tooth. It is frequently much better to elevate a surgical flap and remove the cyst by the labial or buccal approach. Large periodontal cyst treated either by enucleation or marsupialization tooth roots that protrude into a bone cavity after enucleation of a cyst should be amputated after proper root canal therapy.
2. Primordial cysts: (Follicular):It is developed when the restrogression of the stellate-reticulumin the enamel organ take place before any calcified tooth structure isformed. The word primordial means most simple and most undeveloped in character. These cyst may lined by stratified squamous epithelium and may be either locular-multilocular or multiple.
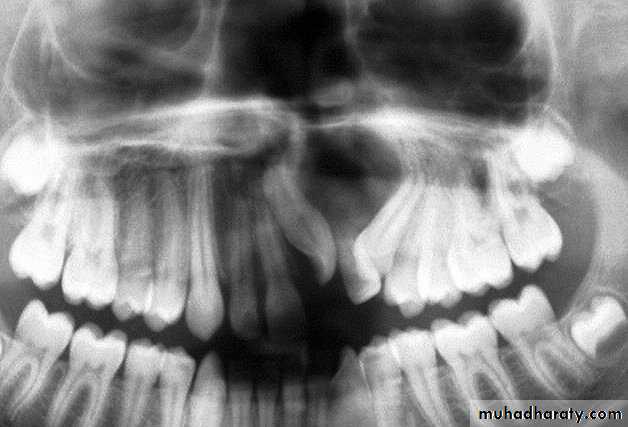
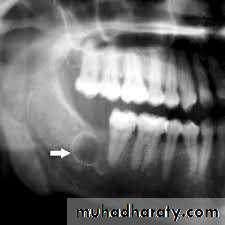
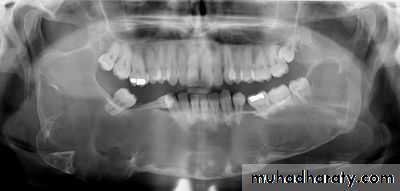
3. Dentigerous cysts:These cysts develop after deposition of enamel and are probable,result of degenerative changes in the reduced enamel-formingepithelium. The fact that the epithelium of a dentigerous cyst isattached to the neck of the tooth is fairly strong evidence that in mostcases the cyst is formed by the enamel organ and not independently of it A dentigerous cyst contain a crown of un erupted tooth or dentalanomaly such as odontoma. Enlarge D.cysts can cause a markeddisplacement of teeth. Pressure of accumulated fluid usually displacesthe tooth in an apical direction.
D.cysts may found any where in the mandible or the maxilla butare more frequently located at the angle of the jaw. The cuspid regionsmaxillary third molar areas. Treatment by complete surgical enucleation
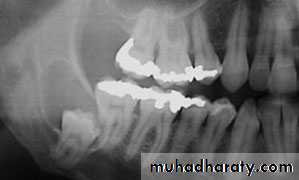
4. Keratocysts:Many follicular and dentigerous cysts contain keratinizing material and are known as keratocysts. These cysts differ from other odontogenic cysts in their microscopic appearance and clinical behavior. Keratocysts in crease in size principally by a process of epithelial cell multiplication and have a greater tendency toward recurrence.
Methods of treatment of cysts:
• Enucleation.• Marsapialization.
• Combination of Marsupialization and enucleation .
• Enucleation with chemical cauterization of the base.
• Enblock excision.
• Segmental resection.
Regardless of the etiology nature or location of the cyst, two methods of treatment are generally accepted:1. Enucleation of the cystic sac :
complete enucleation of the cyst sac is indicated in developmental dental cysts. A partial excision is dangerous and any small part left behind may contain the potential of developing into a true dental tumor.
The surgical procedure must be based on sound fundamental principles.
(1) Preservation of he blood supply to the area(2) avoidance of undue trauma to nerve in the region
(3)control of hemorrhage,
(4) Aseptic technique,
(5) a traumatic handling of the soft tissue.
2. The marsupialization
operation by which the cyst is un covered or de roofed and cystic lining made continuous with the oral cavity or surrounding structures. Like surrounding periosteum, and held in place with dressings, if gauze dressings are used. They may be removed in about 7 to 10 days.
Indications for marsuplization of a cyst include: those conditions in which adjacent vital structure such as teeth may be involved if the cystic contents are completely enucleated or danger exists of entering adjacent paranasal sinuses or a marked bone defect is to be avoided. The possible occurrence of paresthesia from surgical trauma or severance of a nerve is also eliminated
Thank
YouFor
Listening