1
Fifth Stage – ENT – Dr.Mushtaq – Lecture 9
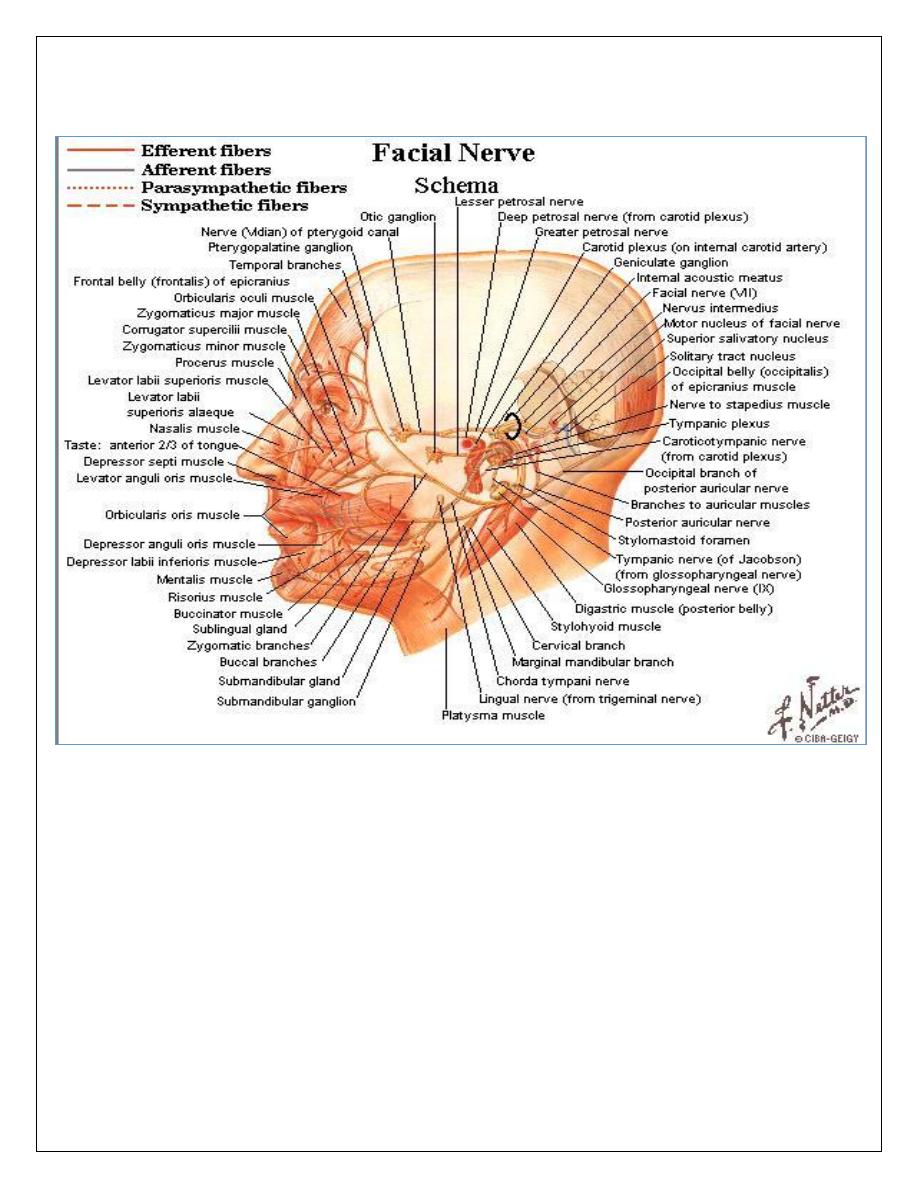
Facial nerve
Anatomy
—
7
th
cr n.
—
Mixed
—
Pons & medulla
—
Motor part arises from the facial n. nucleus in the pons
—
Sensory part arises from the nervus intermedius
—
Secretomotor part arises from the sup. Salivatory nucleus

2
Motor part
Motor part arises from motor neuclus & enters the petrous part of the temporal bone
through the internal auditory meatus with the VIII cr.n. then run within fallopian canal
crossing the middle ear cavity then it exits from the stylomastoid foramen and emerges
through parotid gland to supply the m.m. of facial expressions.
Branches:
Inside facial canal :
1. greater petrosal n.(secretomotor) parasympathetic n. to lacrimal gland
2. Nerve to stapedius m.
3. Chorda tympani (secretomotor) parasympathetic n . to submandibular & sublingual
gl.
Outside the canal
1. Posterior auricular .
2. N.to the post. belly of the digastric m.
3. N. to the stylohyoid m
4. Five major brs. Supply muscles of facial expression
A. Temporal
B. Zygomatic
C. Buccal
D. Mariginal
E. cervical
Sensory part
—
Receives taste sensation from ant.2/3 of the tongue
—
Supratonsillar fossae
—
Small fibers from auricle
Secret motor part
—
Salivary glands except parotid
—
Lacrimal gland

3
Causes of facial n. dysfunction
1) Bell`s palsy
2) Trauma
3) Infection
4) Tumors
5) Central causes
6) General medical causes
1-Bell`s palsy
—
Commonest cause 15-30/100,000
—
Lower motor lesion of unknown cause
—
Possible theories , viral, vascular, or autoimmune ,but none is proven
—
Path:
inflammation of the perineural sheath can cause swelling of the sheath which
may compress the nerve within the bony canal>>FN. paralysis
Clinical features:
—
Any age & sex
—
Rapid progressive stiffness or numbness of the face
—
lost of forehead wrinkling
—
Incomplete closure of the eye
—
Cannot blow the cheek
—
Lost of the nasal wrinkle
—
Flattening of the nasolabial fold
—
Deviation & lowering of the angle of the mouth of the affected side.
Diagnosis
❖
History : onset ,duration, ass’symptoms of
other disease, trauma, pregnancy,
DM, allergy, viral inf….ect,

4
❖
Ex: severity ,ear , full neurological ,
assessment of the muscles of the face
Investigations:
—
C.B. F.
—
E.S.R.
—
B.S.
—
E.M.G.
—
E.N.G.
—
Audiological tests
—
Radiological test // c-ray( sarcoidosis)
—
Salivary flow rate
Treatment
—
Medical:
➢
steroid (controversial)
➢
Antiviral(controversial)
➢
Relieve of pain
➢
Eye care / oint. Artificial tear
➢
Physiotherapy // massage & electrical stimulation
Surgical decompression.
—
Prognosis :
- usually good if dx. In 1st . Wk. 80%
- rarely residual facial paralysis
2-trauma // external or surgical
—
Neuropraxia : physiological block
—
Axonotmesis : intact sheath with divided
axon>>>mismatch
regeneration >> synkinesis

5
—
Neurotmesis : whole n. is divided>>poor
prognosis
3-infection
—
Herpes zoster oticus
—
I.M.N.
—
O.m.
—
Malignant O.EXT.
—
Spirochaetal infections
Herpes zoster oticus (ramsay hunt syndrome)
—
c/f :
- usually elderly
- pain around the ear
- vesicles on the auricle & ext. ear & facial palsy
- s/t S.N.H.L.
- vertigo
—
R, : - anti inflammatory analgesics .
- antiviral
- topical R, for vesicles
* Poor prognosis
4-Tumours :
v. schwannoma ,parotid gl. Tumour
5-Central causes :
e,g; c.v.a
6- General medical causes:
-sarcoidosis
- m.s
- Guillian – Barre syndrome
- D.M.
Thank you,,,
