Fifth Stage
Internal Medicine
Dr. Basim - Lecture 11
1
Aplastic Anemia
Definition:
Pancytopenia with hypocellularity (Aplasia) of Bone Marrow
Etiology
Inherited:
Fanconi’s Anemia
Acquired:
1- primary idiopathic aplastic anemia
2- Secondary aplastic anemia
Primary aplastic anemia
50 % of cases
No explanation
Thought to be an autoimmune condition in which there are cytotoxic
T- lymphocytes which destroy the stem cell
2
Secondary aplastic anemia
Causes:
1- Drugs
* Dose related: Alkylating agent
Antibiotics : Chloramphenicol
* Idiosyncratic: Chloramp, gold, NSAID, anticonvulsant, penicillamin
2- Toxins: benzene , insecticides .
3- Viral infection: hepatitis , EPV ,HIV
4- PNH
5- Pregnancy
6- Radiation.
7- Immune disease : Hypogammaglobulinemia
Graft-versus host disease in immunodeficiency .
Pathogenesis
Immune mechanism responsible for most of the cases of Idiopathic acquired
aplastic anemia
Activated Cytotoxic T cells in Blood & Bone marrow
Bone marrow failure
Clinical Features
Signs & symptoms of:
Anemia: ……….
Bleeding: Ecchymoses, Bleeding gums, Epistaxis
Infections: Fever, Mouth ulcers
Lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly are highly atypical of aplastic anemia .
Diagnosis
Blood peripheral smear : Pancytopenia and reticulocytopenia
Bone marrow aspiration & biopsy : Hypocellular / aplastic bone marrow with
increased fat spaces
Tests for underlying cause ( viral titers)
Other causes of Pancytopenia:
Myelofibrosis
Megaloblastic anemia
Bone Marrow infiltration or Replacement:
-Lymphoma, Myeloma, Acute Leukemia, Secondaries
Hyperspleenisn
SLE
Disseminated TB
PNH
Sepsis
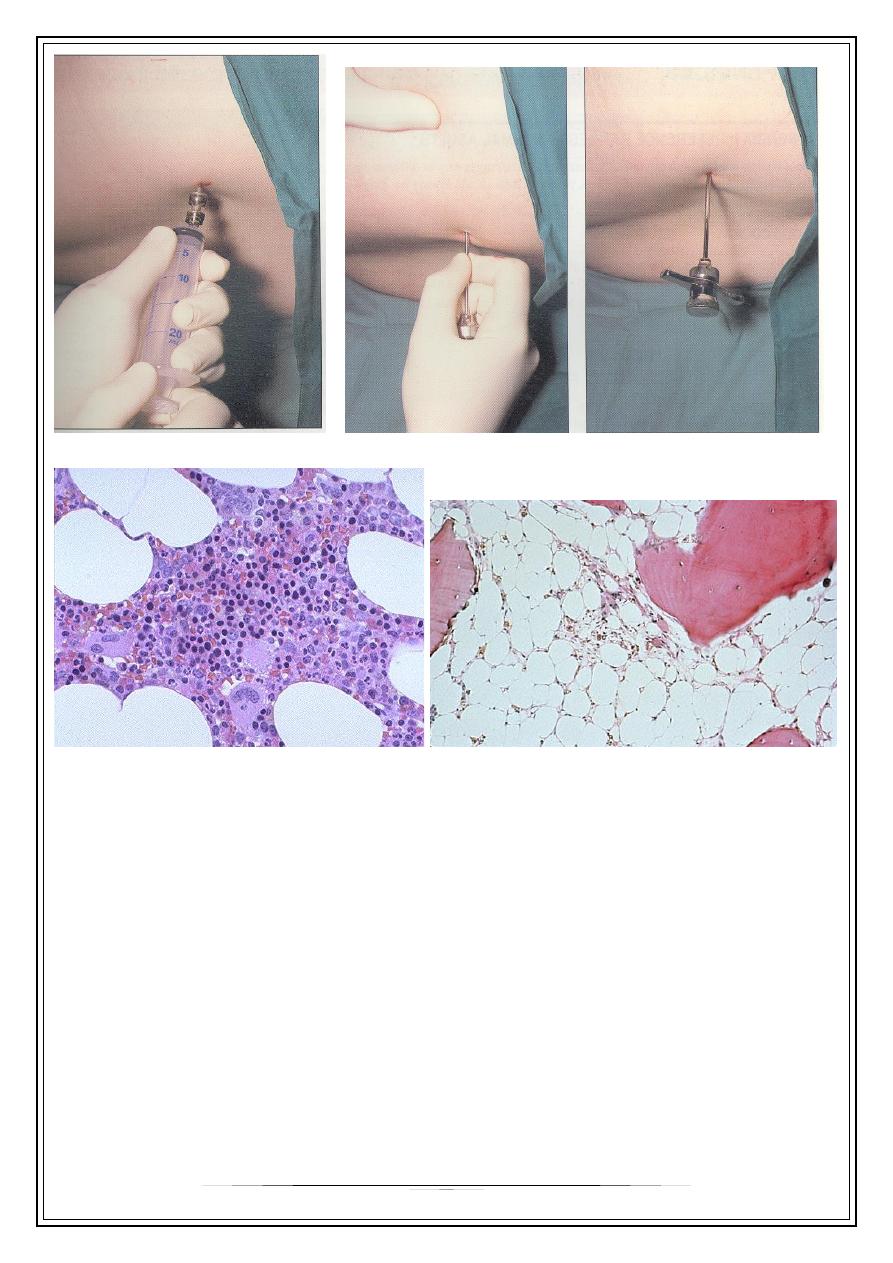
3
BM Aspiration
BM Biopsy
BM biopsy
hypocellular ,increased fat spaces
Treatment
Treatment of underlying cause –if possible
Removal of cause
Supportive care:
-Blood & platelet transfusion
-Infection: Broad spectrum antibiotics
-Asepsis
Bone Marrow Transplant (SCT):
-patient age <40yrs , availability of a HLA-identical sibling marrow donor
Immunosuppression:
-Cyclosporine,
-Glucocorticoids : in cong Pure Red Cell Aplasia
-Antilymphocyte or Antithymocyte globulin (ALG / ATG)
-Cyclophosphomide
4
Androgens
Thymectomy : for Adult Pure Red Cell Aplasia
Severe AA (SAA)
Bad prognosis
Two of three peripheral blood criteria:
Neutrophils < 500 / cmm,
Platelets < 20,000/cmm,
Reticulocyte < 0-0.5%
Thank You,,,
Extra : Case history:
A 41 year old lady
Extreme pallor, gum bleeds, Purpura, Menorrhagia
for one month and fever with mouth ulcers for one week.
No organomegaly
In a patient’s own words:
I had gone to the emergency room after fainting.
I had an extremely heavy period, a terrible headache, a bleeding sinus infection, a
gash from falling onto my glasses, painful mouth sores, bruises from where my cat
jumped on my lap, red spots all over, and no energy.
Initial Counts:
Hemoglobin: 4.7
WBC: 900 GNC: 23 (not 2300) Platelet: 8,400
