

• @ Identification:
• *A viral infection, polio virus(genus: Enterovirus) types
1,2,3 . all types can cause paralysis.
• *Type 1 often isolated from paralytic cases, type 3 less so,
& type 2 least . *commonly,Type 1 most frequently causes
epidemics. Most vaccine associated cases are due to type 2
or 3.
• *One in 200 infections leads to irreversible paralysis
(usually in the legs). Among those paralysed, 5% to 10% die
when their breathing muscles become immobilized.
• *Poliomyelitis most often recognized by acute onset of
flaccid paralysis, polio virus occur in the GI tract spread to
the regional nodes, & in minority of cases to the nervous
system.
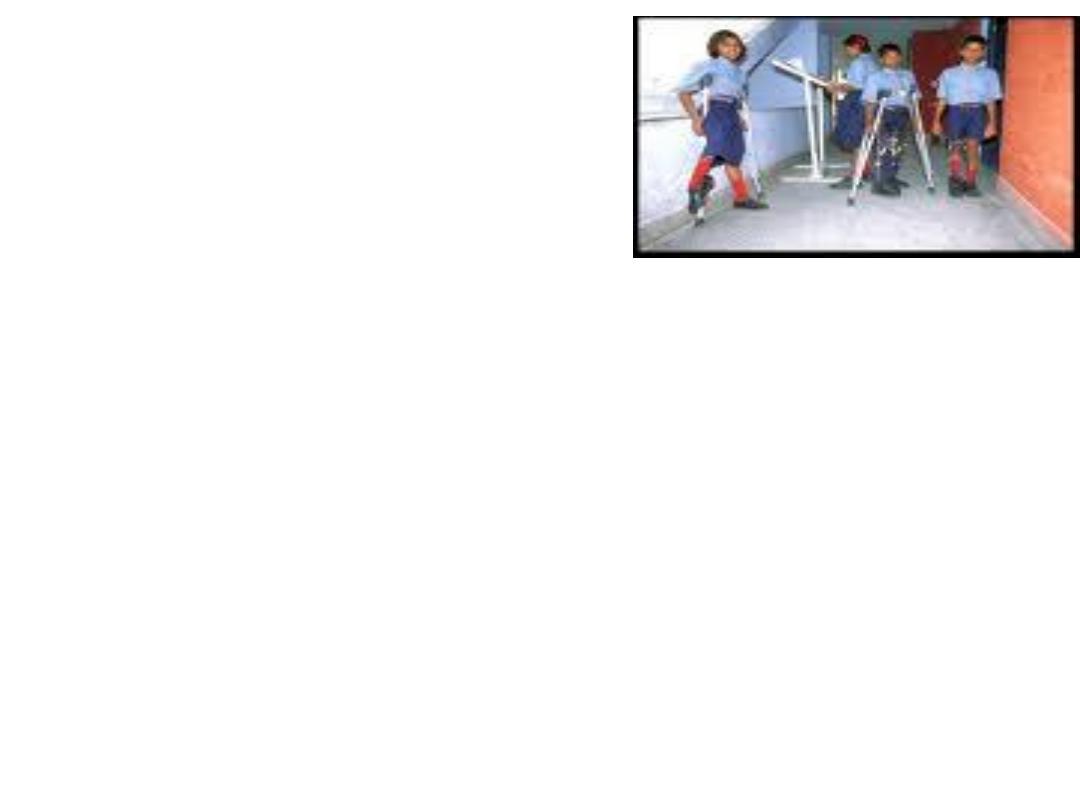

• *Symptoms include :
• fever, malaise, headache, nausea & vomiting.
If the disease progresses to major illness,
severe muscle pain & stiffness of the neck &
back with flaccid paralysis may occur.
• *Flaccid paralysis occur in less than 1% of
polio virus infection, greater than 90% of
infections are either in apparent or a non-
specific fever, Aseptic meningitis occurs in
about 1% of cases.

• *The paralysis of poliomyelitis
• is asymptomatic with fever present at onset.
• The maximum extent of paralysis is reached
within 3-4 days, the site of paralysis depends on
location of nerve cell destruction in spinal cord
or brain stem.
• The legs are affected more often than the arms.
Paralysis of the muscles of respiration &/or
swallowing is life threatening .

• *Any paralysis present after
• 60 days is likely to be permanent.
• *Polio remains primarly a disease of infants &
young childrens, 70-80 % of cases are less than 3
year of age & 80-90 % of cases are less than 5
years of age.
• *WHO has set the end of the year 2000 as the
target for world wide eradication but it still have
little longer to accomplish.

• @Occurrence:World wide, it occur
sporadically or epidemic the greatest risk of
polio occurs in India & to lesser extent in
west & central Africa. with increase in cases
during the late summer & autumn in
temperate countries & in hot , rainy seasons
in tropical countries.
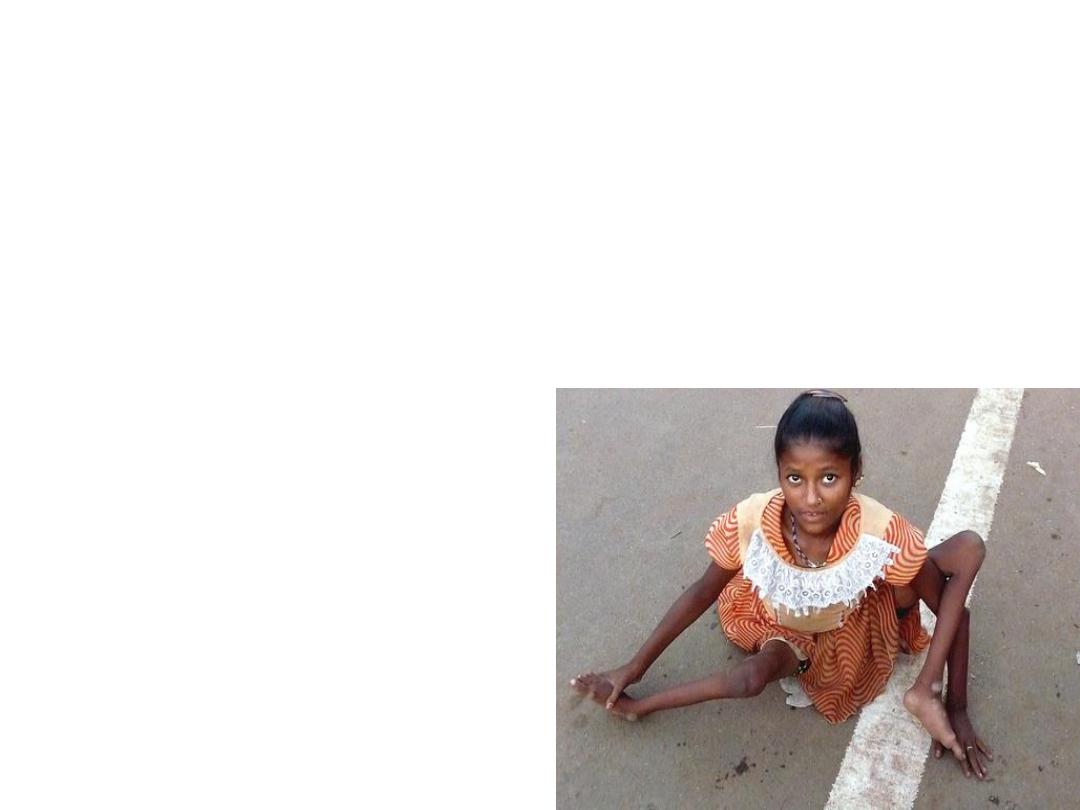

• @Reservoir: Humans, the virus dose not
survive long in environment outside the
human body. There is no long term carriers
state.
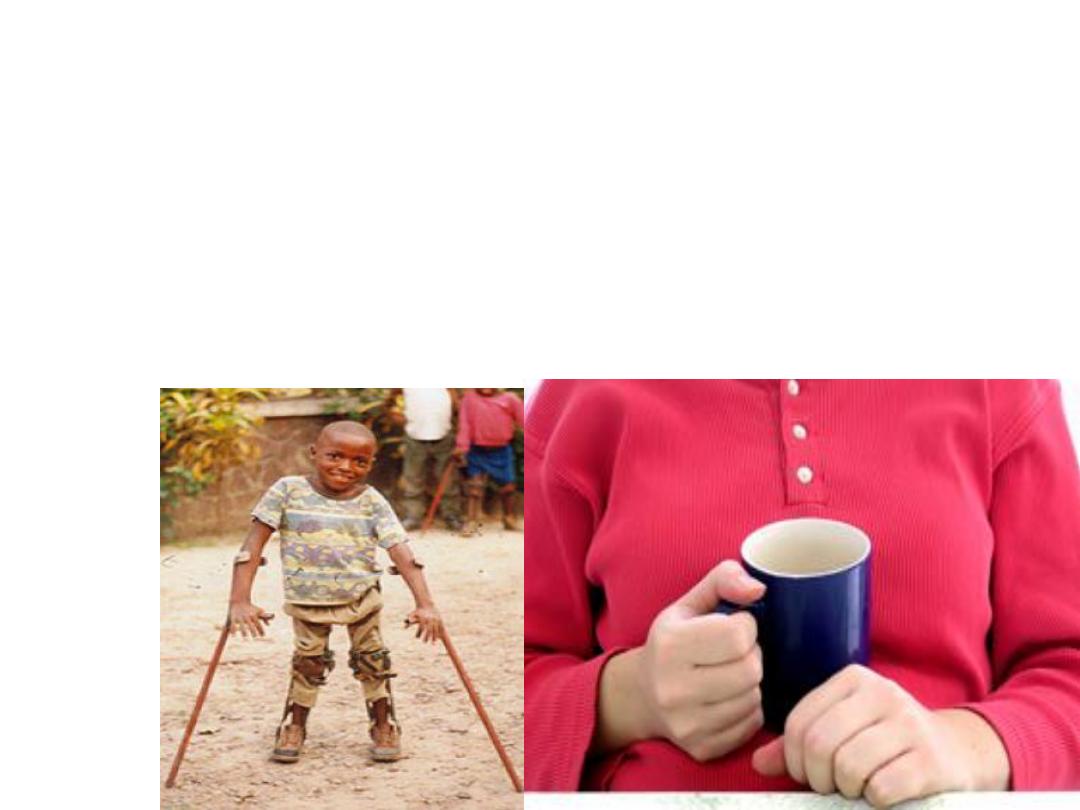

• @Mode of tranismission:
• 1- person to person by feco-oral route &
pharangeal spread .
• 2- milk, food-staffs, & other material
contaminated with feces have been
incremented as vehicles (rare).

• @ Incubation period: 7-14 days for paralytic patients.
• @Period of communicability:
• As long as the virus is excreted. Poloi virus is
demonstrable in throat secretion as early as 36 hr &
in feces 72 hr after exposure to infection in both
clinical & unapparent cases. Virus typically persist in
the throat about 1 week & in the feces for 3-6 weeks
or longer.
• Cases are most infectious during the first few days
before & after onset of the symptoms.

• @Susceptibility & Resistance:
• Susceptibility to infection is universal but paralysis occur
in 1%. The rate of paralysis among infected, non-immune
adult is higher than that among non –immunized infants
& young children.
• The specific immunity is life long duration follows both
clinically & unapparent infection . seconds attacks are
rare & results from infection with a polio virus of a
different type. Infant born to immune mothers have
transient passive immunity .
• IM injection, trauma or surgery during incubation period
or prodromal illness may provoke paralysis in the affected
extremity.

• @Methods of control:
• A- preventive measures:
• 1- educate the public on the advantages of
immunization in early childhood.
• 2- polio vaccines: there are two types of polio
vaccine:
• * trivalent oral polio vaccine & *inactivated or
killed polio vaccine.
• Trivalent oral polio vaccine:
• Consist of life attenuated polio viruses & is a safe
& effective vaccine. OPV stimulates natural
infection by inducing both circulating antiboby &
intestinal resistence. As aresult , children
immunize with OPV are unlikely to spread wild
polio virus to other children. When administered
during a mass campaign, OPV can interrubed
wiled polio virus tranismissin in the community.
These compaign are ideally conducted during the
cool, dry sessons to achieve maximam effect.

• WHO recommends the use of OPV alone for
immunization programs in developing countries
because of low cost, ease to adminsteration &
superior capacity to provide population immunity .
OPV is given in four doses at 0, 2, 4, 6. with 1
st
booster dose at 18 month & 2
nd
booster dose at 4-6
year.
• The three doses of OPV will protect at least 80-85%
of immunized children from paralytic disease.
Lower levels of immunity, specially for type 3, may
occur in developing countries.

•
Disadvantages
• Vaccine-associated paralytic polio — A rare, but
important adverse event associated with OPV
administration is vaccine-associated paralytic
poliomyelitis VAPP.
• VAPP occurs among OPV recipients who are mostly
young infants and also among direct contacts of
OPV recipients, mostly inadequately vaccinated
adult caretakers. The overall risk is about 1 case per
900,000 first dose OPV recipients

• .
• Subsequent doses
• are less likely to be associated with VAPP. Adults
may be at higher risk than young infants and
children . Persons with B cell immunodeficiency
carry the highest risk with an estimated VAPP
rate of 2 per 1000 vaccinees . For this reason,
OPV is contraindicated for persons who are
immunodeficient

•
Contraindication to OPV
:
• congenital immune deficiency , current
immunosuppressive therapy, disease state
associated with immunosuppression (HIV,
lymphoma, leukemia, generalized malignancy),
& the presence of immunodeficient individuals
in household of potential vaccine recipients
(IPV should be used in such people).

• Inactivated or killed polio vaccine:
• It produce sufficient circulating
• antibody that blocks spreads of the virus to the
CNS.
• IPV have no risk of vaccine associated paralysis. It
produce lower levels of intestinal immunity
compared to OPV so person immunized with IPV is
more likely to spread wiled polio virus to other
children compared to OPV.
• IPV is more expensive, must be injected by trained
personals, & required additional equipments &
supplies.

• B- control of patient , contacts & immediate
environment:
• 1- obligatory case report to local health authority of
paralytic cases. In countries undertaking polio
eradication, each case of acute flaccid paralysis(AFP) ,
including guillain-barre syndrome , in children less than
15 year of age, or with paralytic illness at any age where
polio is suspected , should be reported immediatly ,
investigated withen 48 hours and two stool specimens
collected 24-48 hours apart and within 14 days of
paralysis onset.
• Non-paralytic cases are also reported to the local health
authority. .

• 2- isolation: enteric precaution.
• 3- concurrent disinfection: throat discharge,
feces & articles soiled therewith, adequate
sewage disposal system, terminal cleaning.
• 4- Quarantine: none.
• 5- protection of contact : immunization of
familial & other close contact is
recommended.

• 6- investigations of contact
• & source of infection: occurrence of a single
paralytic case in community should prompt
immediate investigations. Through search for
additional cases of AFP in the area around the case
assures early detection, facilitate control & permits
treatment of unrecognized & unreported cases.
• 7- specific treatment : none, special treatment as
respirotery assistance, physical therapy may be
needed.

• C- epidemic measures: in countries
undertaking polio eradication, a single case
of poliomyelitis is considered a public health
emergency & public health authorities will
determine the need for supplemental
immunization program in the community.
•

THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE
• Objectives
• The objectives of the Global Polio Eradication
Initiative are:
• To interrupt transmission of the wild poliovirus
as soon as possible;
• To achieve certification of global polio
eradication;
• To contribute to health systems development
and strengthening routine immunization and
surveillance for communicable diseases in a
systematic way.

Strategies
• 1- High infant immunization coverage with four doses of
oral
(OPV) in the first year of life in
developing and endemic countries, and routine
immunization with OPV and/or IPV elsewhere.
• 2- Organization of “National immunization days” to
provide supplementary doses of oral polio vaccine to all
children less than five years of age.
• 3- Active surveillance for wild poliovirus through reporting
and laboratory testing of all cases of acute flaccid paralysis
among children less than 15 years of age.
• 4- Targeted "mop-up" campaigns once wild poliovirus
transmission is limited to a specific focal area.

• Before region can be
• certified polio-free, three conditions must be satisfied: (a)
there are at least three years of zero polio cases due to
wild poliovirus; (b) disease surveillance efforts in
countries meet international standards; and (c) each
country must illustrate the capacity to detect, report and
respond to “imported” polio case .
• As indicator of a countrys ability to detect polio , at least
one cases of AFP per 100000 chilidren < 15 years of age
should be detected. The AFP rate in children < 15 years of
age is an indicator of the sensitivity of the surveillance
system .

eradciation
Impact of global polio
:
programe
• 1-More than five million people who would
otherwise have been paralysed are today walking
• 2- it help to reduce poverty
• 3-it access to children everywhere, it“finding”
children in remote villages and households for the
first time, and "mapping" their location for future
health services.
• 4- building effective disease-reporting and
surveillance systems
• 5- it highly successful measles vaccination
campaigns that have saved millions of young lives ,
since it give with polio vaccine.
•
•

• 6-Vitamin A is often administered during
polio vaccine. Since 1988, more than 1.2
million childhood deaths have been
prevented through provision of vitamin A
with polio vaccine.
• 7-It give a model for regional and
international cooperation for health & have
significant financial benefits will also accrue
from eradication.
