
M.C.H.
VITAL STATISTICS
Dr.Sijal Fadhil Farhood Al Joborae
F
.I
.
C
.
M
.
S
Community Med.
M.Sc. Community Med.
M.B.Ch.B.

Why do we need vital statistics?
Health is difficult to measure directly, so it is
done indirectly by measuring its converse,
i.e.
disease and death or morbidity and mortality
rates.
Absolute numbers are not informative or
comparable,due to the difference in the total
population number,so we have to use rates that
include…….

Maternal Mortality
• Pregnancy and child birth are wonderful and life
changing events,they can also bring potential for
illness, suffering and even death
.
•
WHO definition:
• Death of women while pregnant or within
42
days
of termination of pregnancy,irrespective of the
duration and site of pregnancy, from any cause
related to or aggravated by pregnancy or it’s
managemant but not from accidental or incidental
causes.

one woman or more dies every minute
from pregnancy related causes
•
from obstetrical complications of pregnancy,
:
Direct maternal death
labor, or puerperium, and from interventions ,omissions, incorrect
treatment ,or chain of events resulting from the above.
•
: death resulting from previous existing disease or
Indirect maternal death
a disease that developed during pregnancy, labor, or perperium and
aggravated by the maternal physiological adaptation to pregnancy.
•
resulting from accidental or incidental cause in
:death
death
Non maternal
no way related to pregnancy.
•
death of women from direct or indirect maternal
:the
death
Late maternal
causes occurring after 42 days of termination of pregnancy

Definitions
continued:
Pregnancy related death
:
death of women while pregnant or within 42 days of termination
of pregnancy, irrespective of the cause of death.
Maternal disability:
short or long term illnesses caused by obstetric
complications(fistula, incontinence).
CAUSES OF MATERNAL DEATH
•
Direct obstetrical complications:the main killers in
developing countries( ¾).
• 1-Haemorrhage(APH,PPH)
• 2-Sepsis
• 3-Hypertensive diseases of pregnancy
• 4-Obstructed labour
• 5-Unsafe criminal abortion
• 6-Ectopic pregnancies
• 7-Unsafe operative procedures
• 8-Pulminary embolism
Indirect obstetrical complications:are due to
pre-existing conditions,(1/4)of maternal
deaths in developing countries.
• Malaria, anaemia ,hepatitis ,cardiac and renal
diseases
•
**IN IRAQ:
•
The leading causes of maternal deaths according
to their proportions are ;
•
APH and PPH.
•
Pulmonary embolism.
•
Hypertention and toxaemia.
•
Purperial sepsis.

But why do these women die
(THREE DELAYS MODEL)
• 1-Delay in decision to seek care.
• Lack of understanding of complications.
• Acceptance of maternal death.
• Low status of women.
• Socio-cultural barriers to seeking care.

• 2-Delay in reaching care:
• Mountain ,Islands ,Rivers , Poor organization.
• 3-Delay in receiving care:
• Supply.
• Personnel.
• Poorly trained personnel with punitive attitude.
• Finances.

Measures of maternal mortality:
• The number of maternal deaths in a population is
essentially the product of two factors , the risk of
mortality associated with a single pregnancy or a
single live birth and the number of pregnancies or
births that are experienced by women of
reproductive age.
•
Maternal mortality ratio
:is defined as the
number of maternal deaths in a population
divided by the number of live births(per
100000),it is represents the risk associated with
each pregnancy, it is the
obstetric risk.

•
Maternal mortality rate:
• Is
defined as
the
number of maternal deaths in
a population divided by the number of women
of reproductive age(usually 15-49)years per
100000
• It measures both the
obstetric risk
and the
frequency
with which women are exposed to
this risk as well as the
level of fertility
in the
population

Prevention and reduction of
maternal deaths
• 1-Ensure
access to medical treatment for obstetric
emergencies
,PPH,APH,infection.
• 2-Improving emergency treatment for obstetric
complications in existing referral facilities.
• 3-Inform the community about the
danger signs
during pregnancy and delivery.
• 4-Work with the community to
improve access to
emergency care.

•
5-Reduce exposure to the risk of unwanted
pregnancy,through accessible and acceptable
family planning
services.
• 6-Improve antenatal care services
,11% of
maternal deaths can be prevented through
ANC,5%due to prevention of infection,5%due to
prevention of anaemia,3.3%due to prevention of
hypertention,and 80% due to prevention of
tetanus.
• 7-Train traditional birth attendants(TBA)
to refer
and treat women with complications.

•
These estimates provide an up-to-date
indication to the extent of the maternal
mortality rate globally,they strongly indicate a
need for both imroved action for maternal
mortality reduction and increased efforts for
the generation of robust data to provide
better estimates in the future, achieving
decline in maternal mortality requires
increased attention to improve health care for
women

• This leads to development of
safe motherhood
programmes, a global effort that aims to reduce
death and illnesses among women and
infants,especially in developing counries,aimed at
reducing maternal mortality.
• These programmes tackle the clinical causes of
maternal deaths through improvements in
maternal services with special emphasis on
EMOC

How to measure maternal
mortality(sources of data)
• 1-Hospital.
• 2-Vital registration system.
• 3-Confedential inquiries into maternal
deaths(CEMD).
• 4-House hold surveys :pregnancy related
deaths,large sample size,expensive.

•
5-Sisterhood methods: retrospective rather than a
current maternal mortality estimate(over 10 years
prior to the survey).
•
6-census(every 10 years).
•
7-verbal autopsy:use to assign cause of death
through an interview with the family .
•
8-Reproductive age mortality surveys (RAMOS).gold
standard method ,if properly conducted ,provides
fairly complete estimation of maternal mortality.
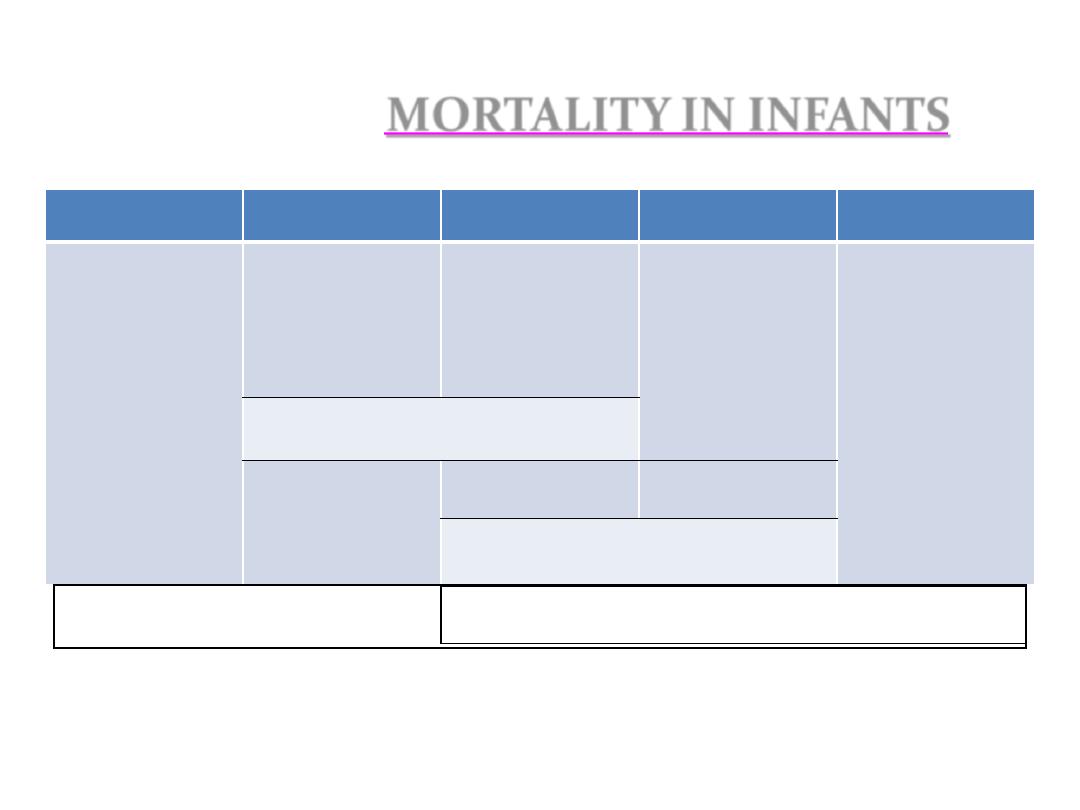
INFANTS
IN
MORTALITY
0 22w
birth
1w
4w
1 y
Miscarriage or
abortion
Still birth
Early neonatal
death
Late neonatal
death
Post neonatal
death
Perinatal death
Neonatal death
Infant death

Mortality in infancy and childhood
Infant mortality rate(IMR):is defined as
the
ratio of infant deaths registered
in a given year to the total
number of live births registered
in the same year.

IMR as an indicator
• IMR is universally regarded not only
as a most important indicator of the
health status of a community but also
of the level of living of people in
general and effectiveness of MCH
services in particular.

Demographic importance of IMR
• 1- The largest single age-category of mortality.
• 2- Deaths at this age are due to a peculiar set of
diseases and conditions to which the adult
population is less exposed or less vulnerable.
• 3- It is affected rather quickly and directly by
specific health programs and hence may change
more rapidly than the general health rate.

CAUSES OF NEONATAL MORTALITY
• 1- Low birth weight and prematurity
• 2-Birth injury and difficult labor
• 3- Sepsis
• 4- Congenital anomalies
• 5- Haemolytic diseases of newborn
• 6- Conditions of placenta and cord
• 7- Diarrhoeal diseases
• 8- Acute respiratory infections
• 9- Tetanus

Causes of post-neonatal mortality
1- Diarrheal diseases
2-Acute respiratory infections
3-Other communicable diseases
4-Malnutrition
5- Congenital anomalies
6- Accidents


1-BIOLOGICAL FACTORS
A-Birth weight
• Birth weight is a major determinant of infant
and perinatal mortality and morbidity .
Babies
of under 2.5 kilogrammes especially if under
1000 g and those exceeding 4 kgs are at a
special risk.
It has been observed that the
mother who was adequately nourished
during her own growing up years has an
excellent chance of delivering a normal size
baby even if she has taken inadequate diet
during her pregnancy

B- age of the mother
There is a definite relationship between the age
of the mother and the fate of the child.
Infant mortality rates is greater when the
mother is either very young or very old.
C-Birth order
:the highest mortality is found
among first born and lowest among those born
second ,the risk of infant mortality escalated
after the third birth.

D-Birth spacing:
Repeated pregnancies exert a great influences
on infant mortality ,they cause malnutrition and
anaemia in the mother, predispose to
LBW,which result in high infant deaths.
E-Multiple births:
Infants born in multiple births face a greater risk
of death than do those in single births due in
large part to the greater frequency of LBW
among the former.
F-Family size:
Studies show that infant mortality
increase with
family size
,the number of episodes of infectious
diarrhea,prevalance of malnutrition ,and sever
respiratory infections have been found to
increase with family size.
G-High fertility:
Fertility is one of the most important factors that
influence infant mortality.

2-ECONOMIC FACTORS
One of the most important factors
affecting infant mortality rates,both
directly and indirectly is socio economic
status,
the availability and quality of health
care and the nature of child environment
are closely related to the socio economic
status
.

3-CULTURAL AND SOCIAL FACTORS:
A-Breast feeding.
B-Religion.
C-Early marriage.
D-Sex of the child(female).
E-Maternal education.
F-Quality of motherhood.
G-Quality of health care.

H-Broken homes(mother or father has
died or seperated).
I-Illegitimacy.
J-Domestic violence.
K-Midwives.
L-Bad environmental sanitation.
