
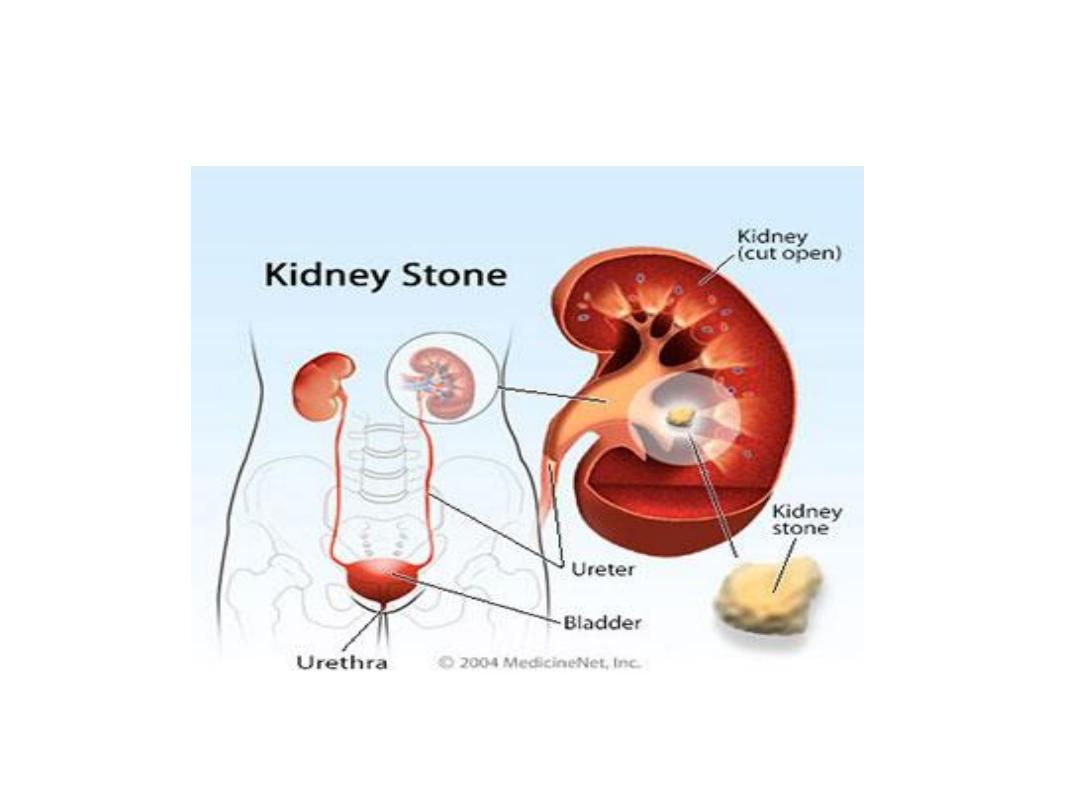
RENAL STONES
EMAD HASAN MAHMOOD
PROFESSOR OF UROLOGY

Learning objective
•
Theories of stone formation
•
Incidence of stones
•
Etiology of stones
•
Clinical feature
•
Diagnosis
•
Treatment
•
Complications
•
Ureteric colic
•
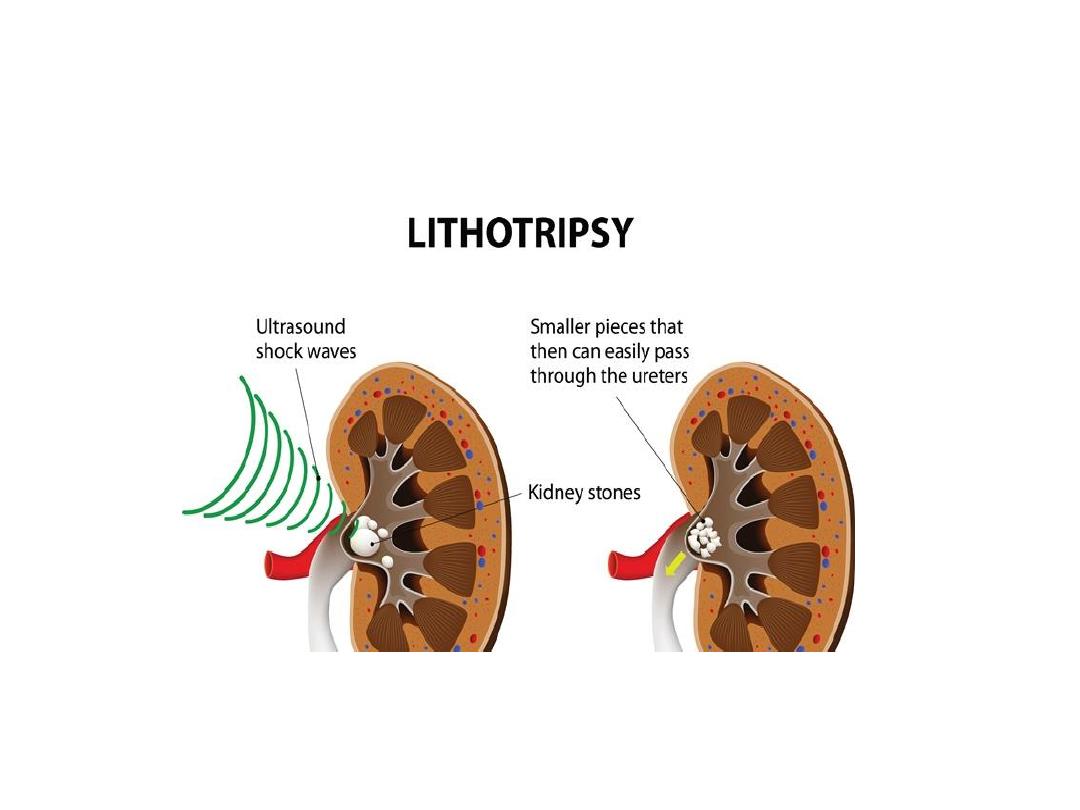
ESWL
•
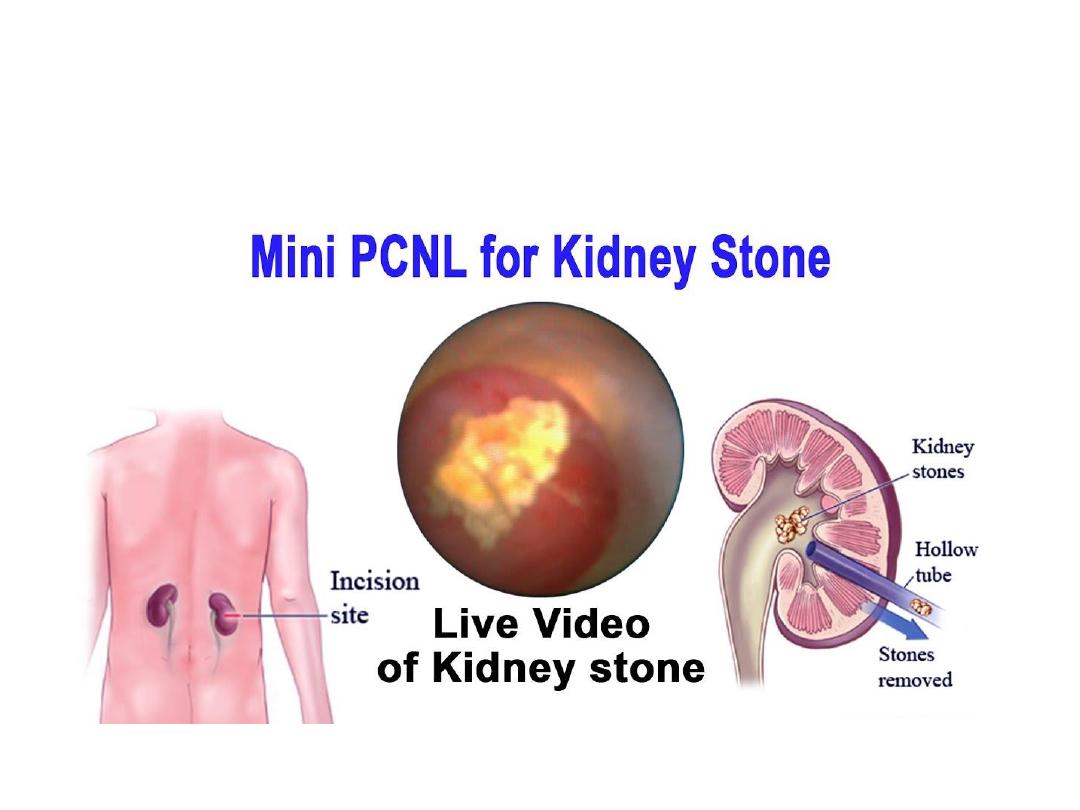
PNL


Theories of stone formations
•
Super saturation solution
•
1-stones fixed to surface of papilla at site of
interstitial appetite plaque ( Randell plaque )
•
as seen in idiopathic calcium oxalate
•
2-stones attached to plugs protruding from
the opening of ducts of Billini as seen in
hyperoxaluria
•
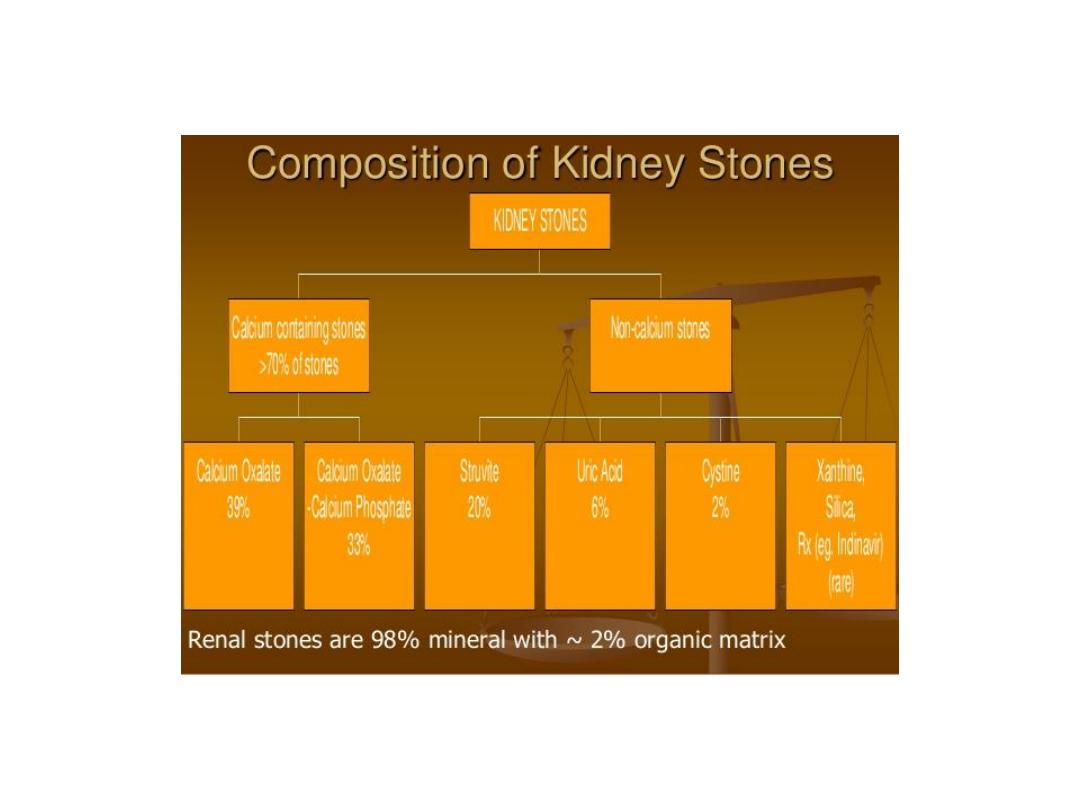
3-stones forming in free solution in the renal
collecting system as in cystinuria


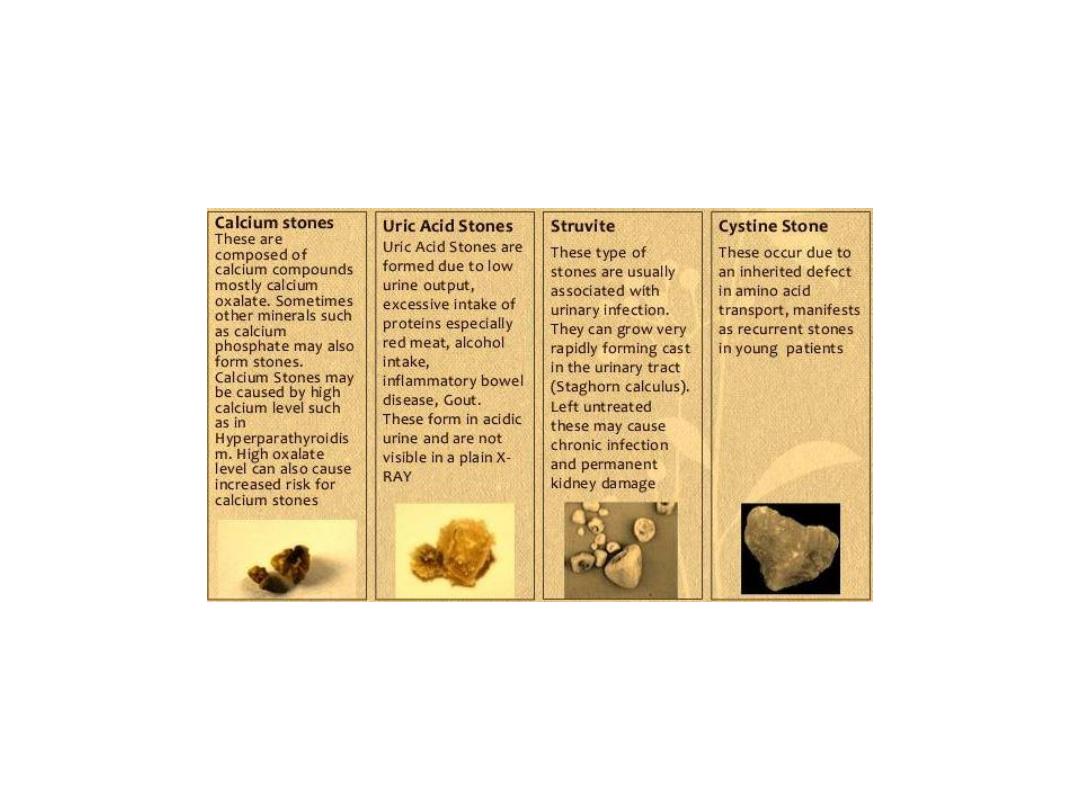
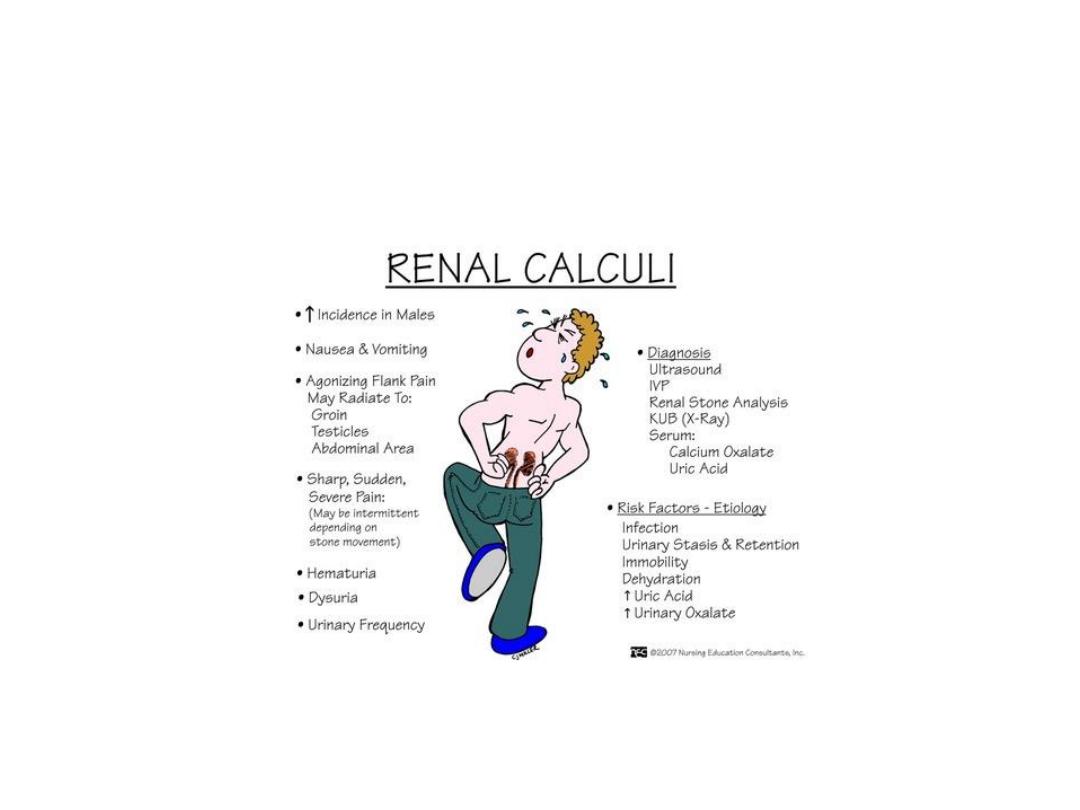
CLINICAL FEATURE

DIAGNOSIS
• URINE
• PH
• RBC
• WBC
• CRYSTALS
• C\S
• 24 hour urine for
calcium,phosphate.oxalate,urate,citrate,sodium
• and cystine

DIAGNOSIS
• Blood test
• Calcium, phosphate , urate , alkaline
phosphatase , albumin , parathroid hormones
• Renal tubular function : sodium , potassium ,
and chloride
• Blood gas analysis

DIAGNOSIS
• Stone analysis
• Chemical
• CT scan
• Spectrophotometry
• XR DIFFRACTION
DIAGNOSIS
•
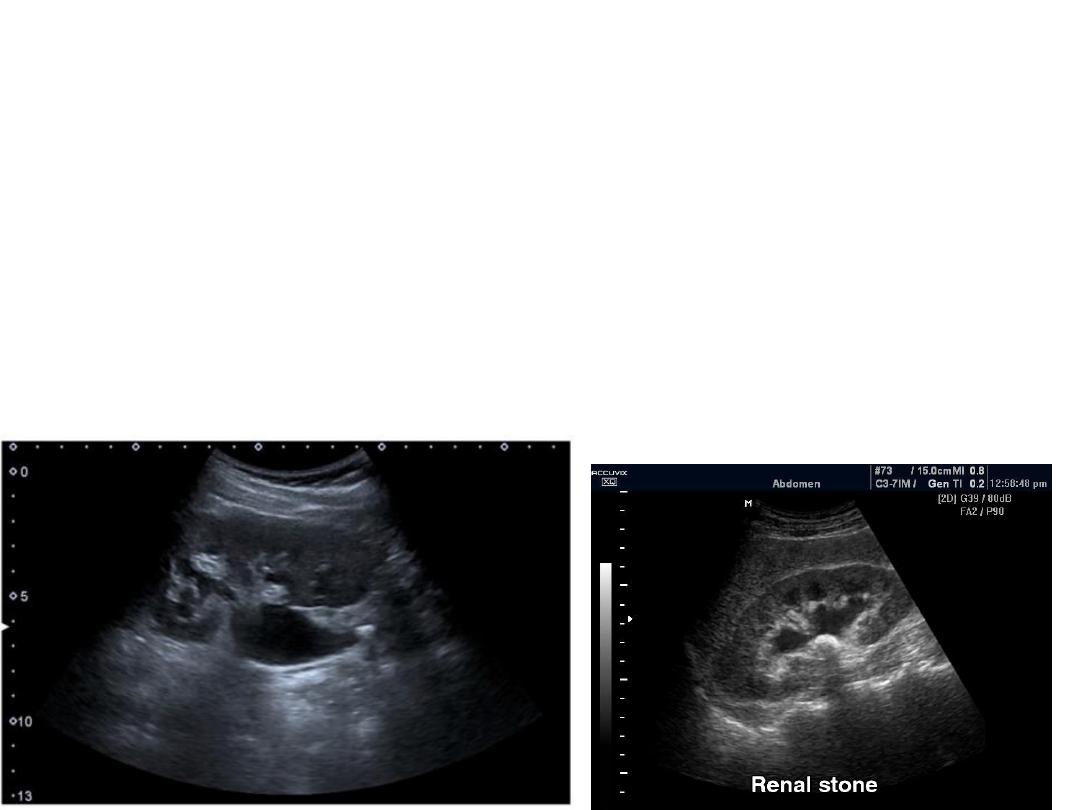
ABDOMINAL U\S
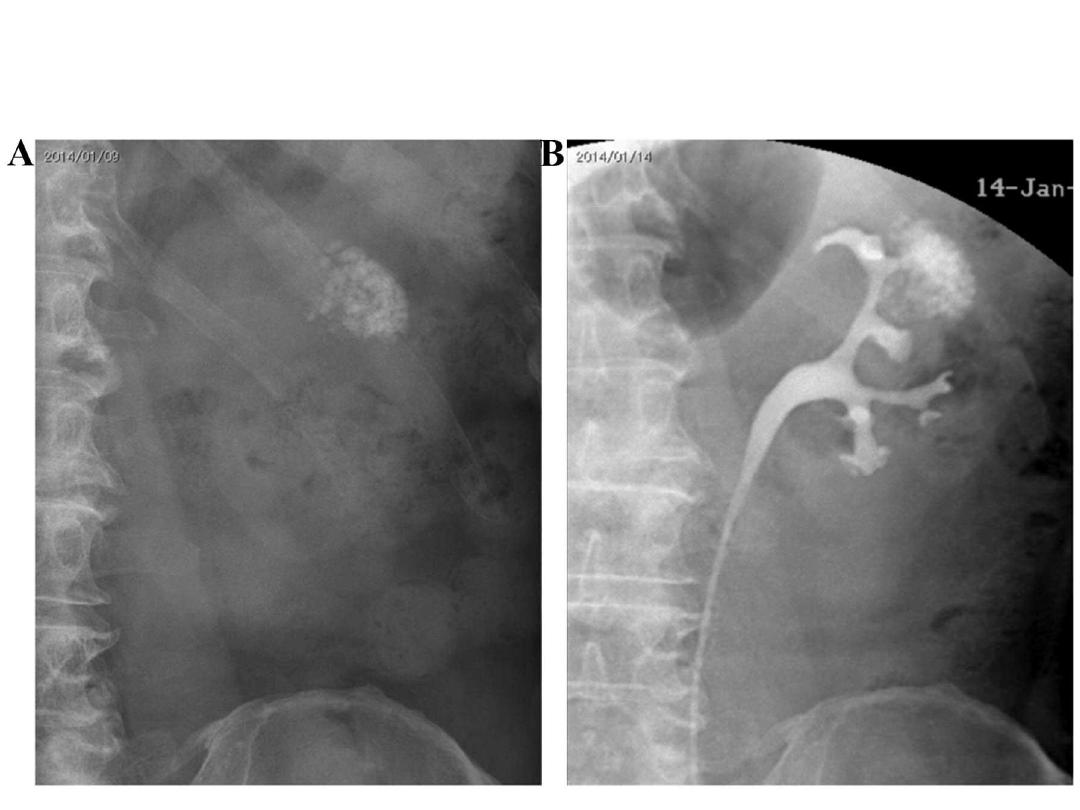
RADIOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS
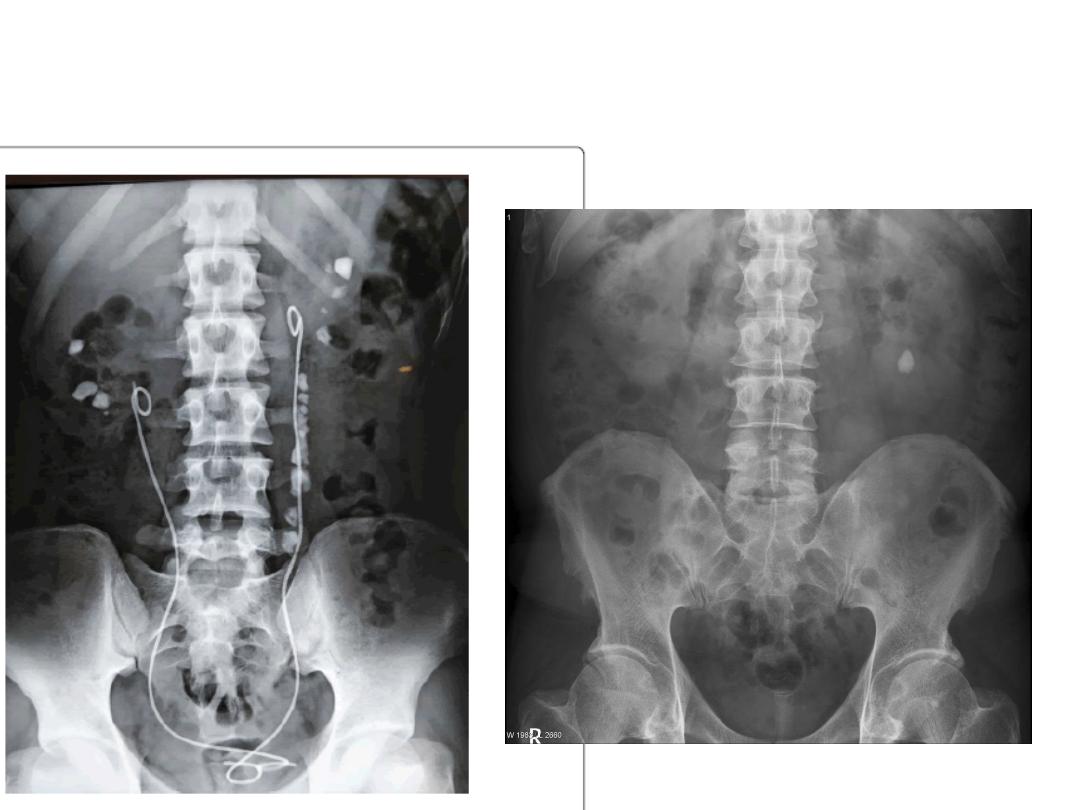
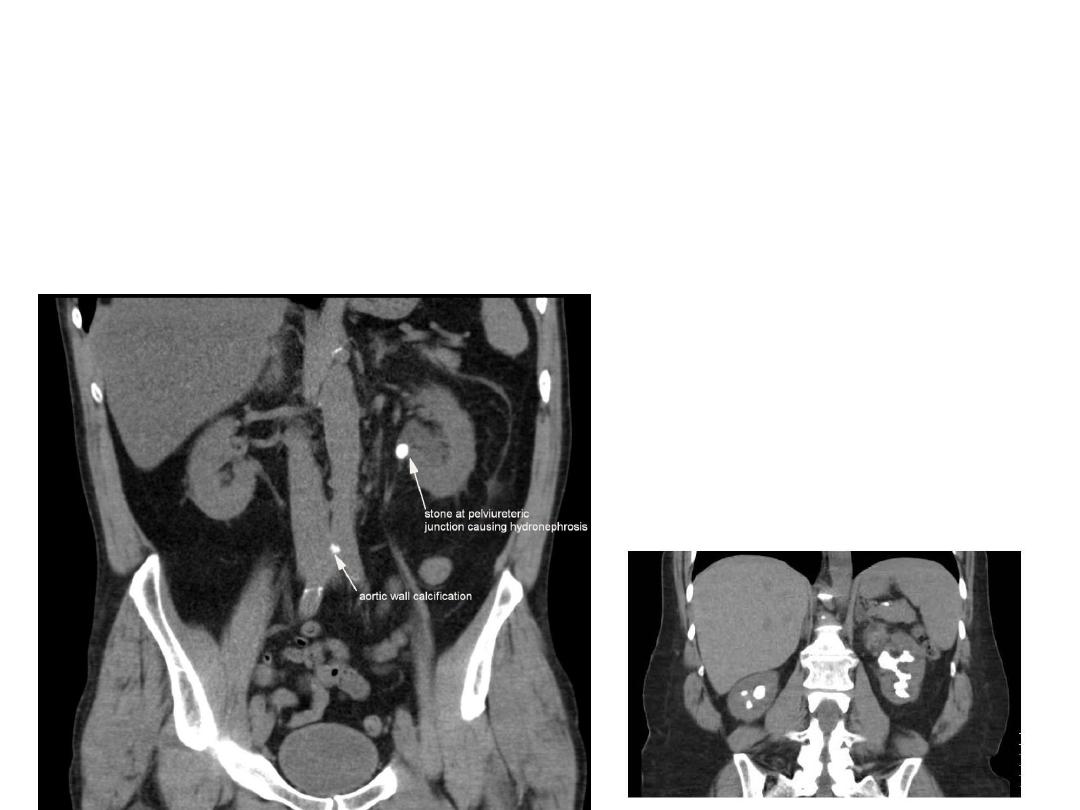

TREATMENT


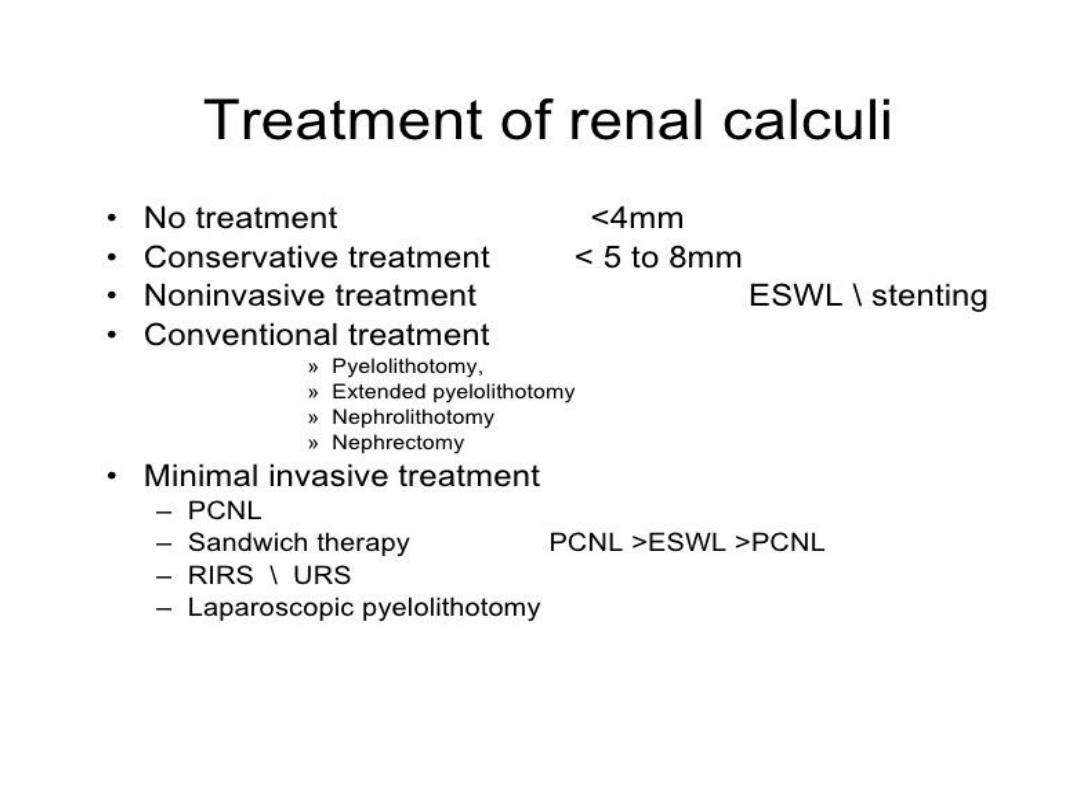

SUMMARY OF TREATMENT
•
NO TREATMENTSTONE SIZE LESS THAN 4mm
•
MRDICAL TREATMENT 5-10 mm
•
ESWL 10-20 mm
•
PCNL STONE MORE THAN 20mm
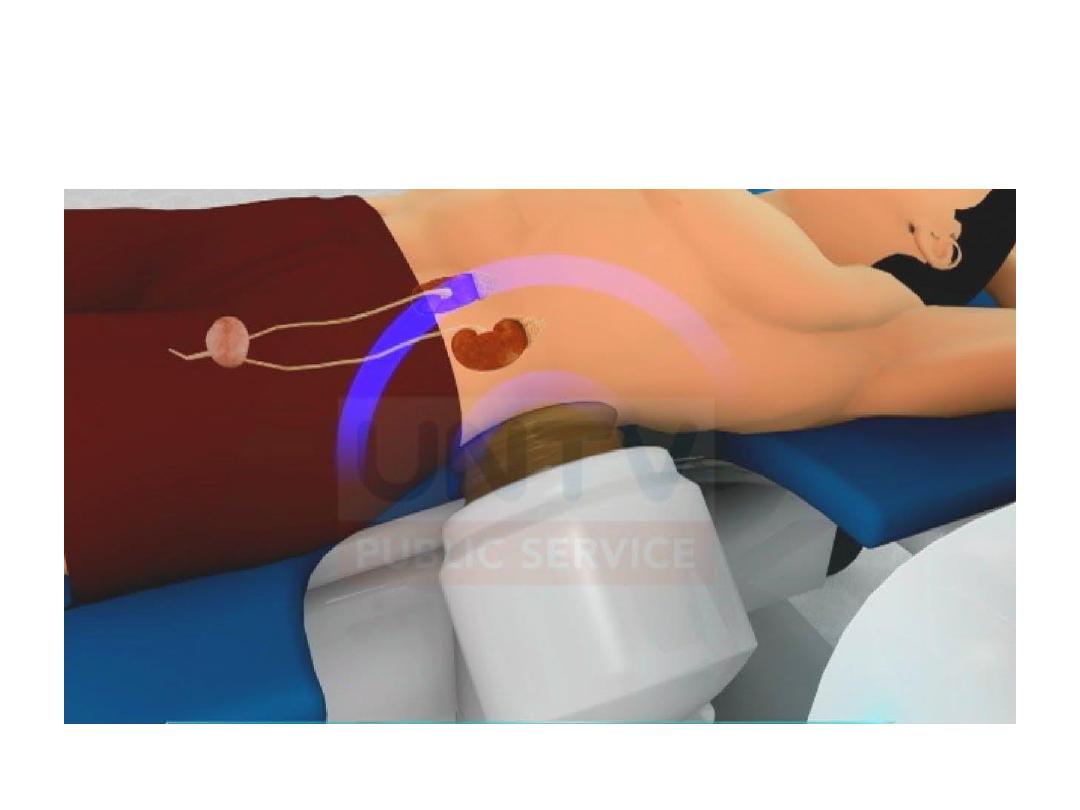
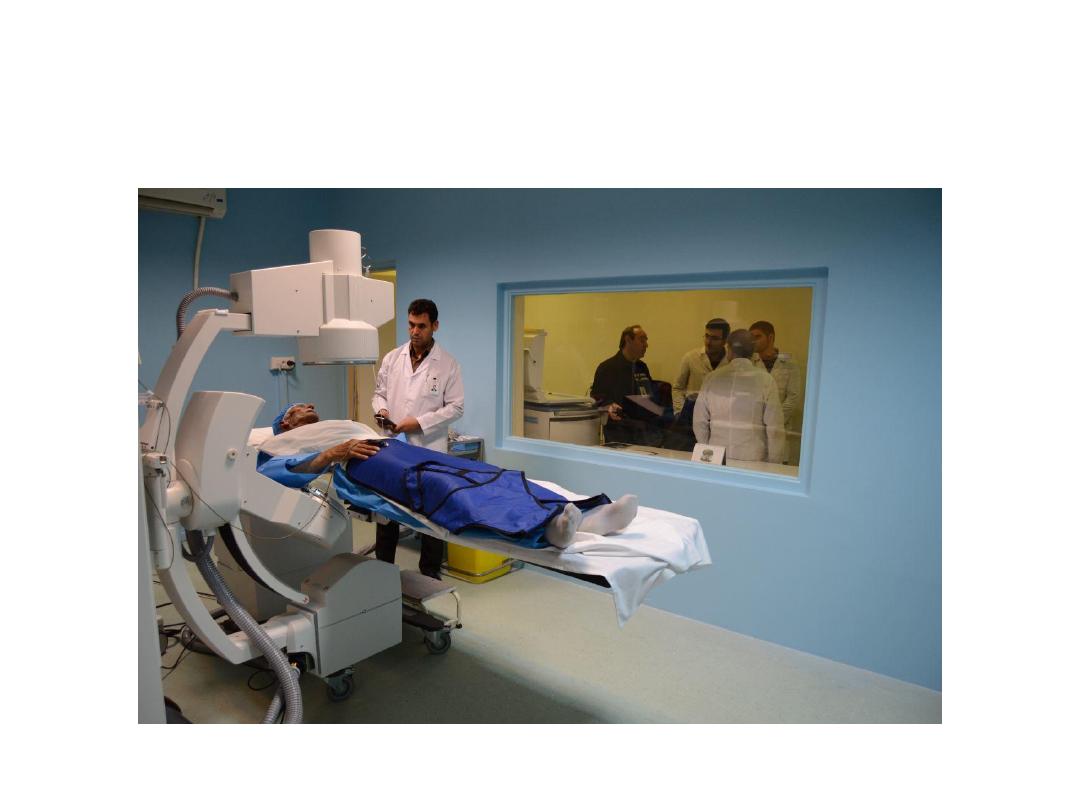
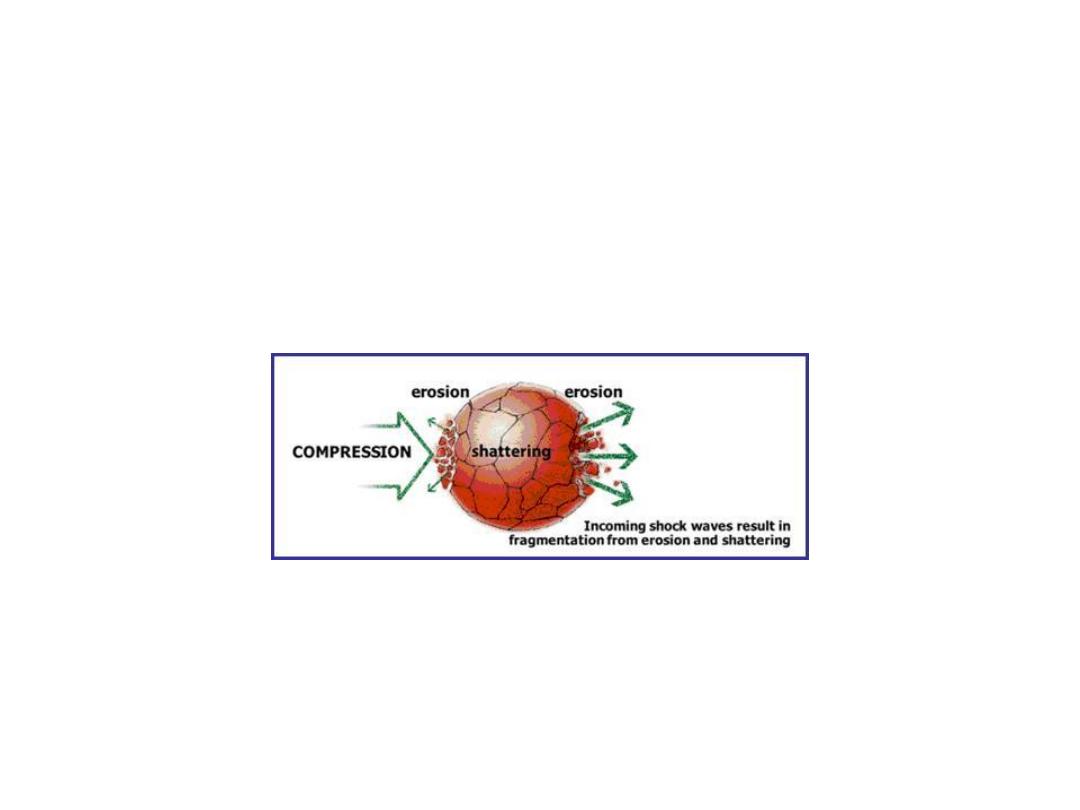
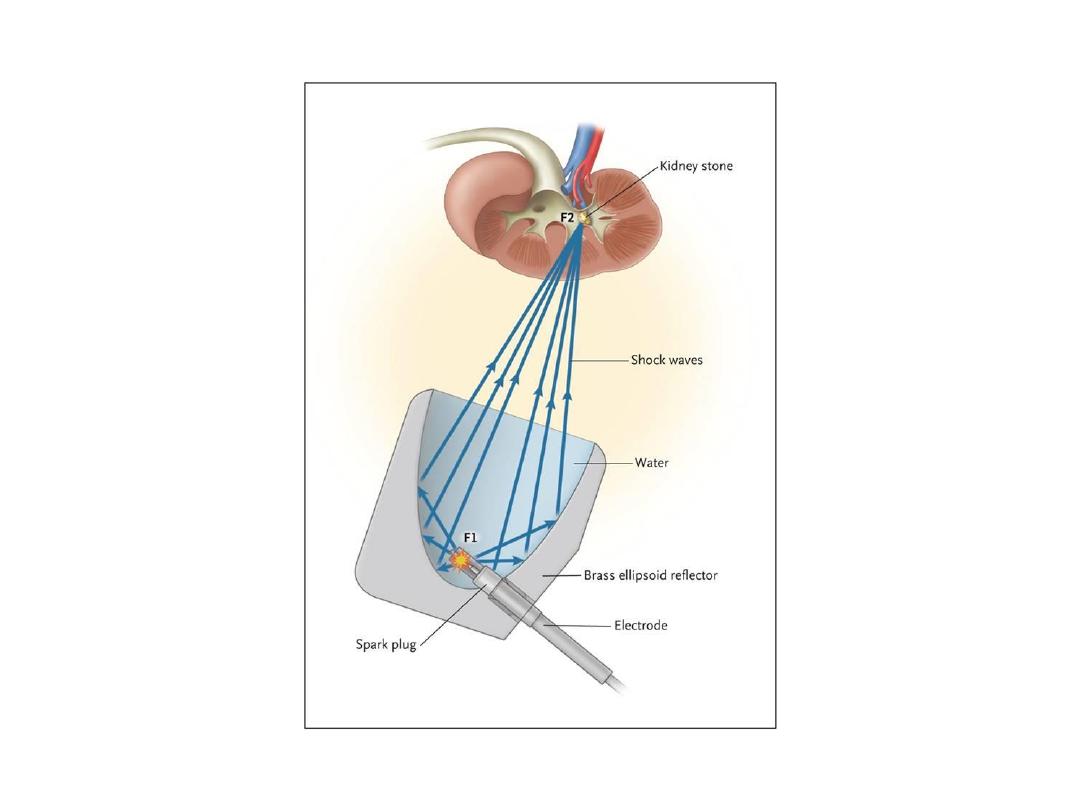
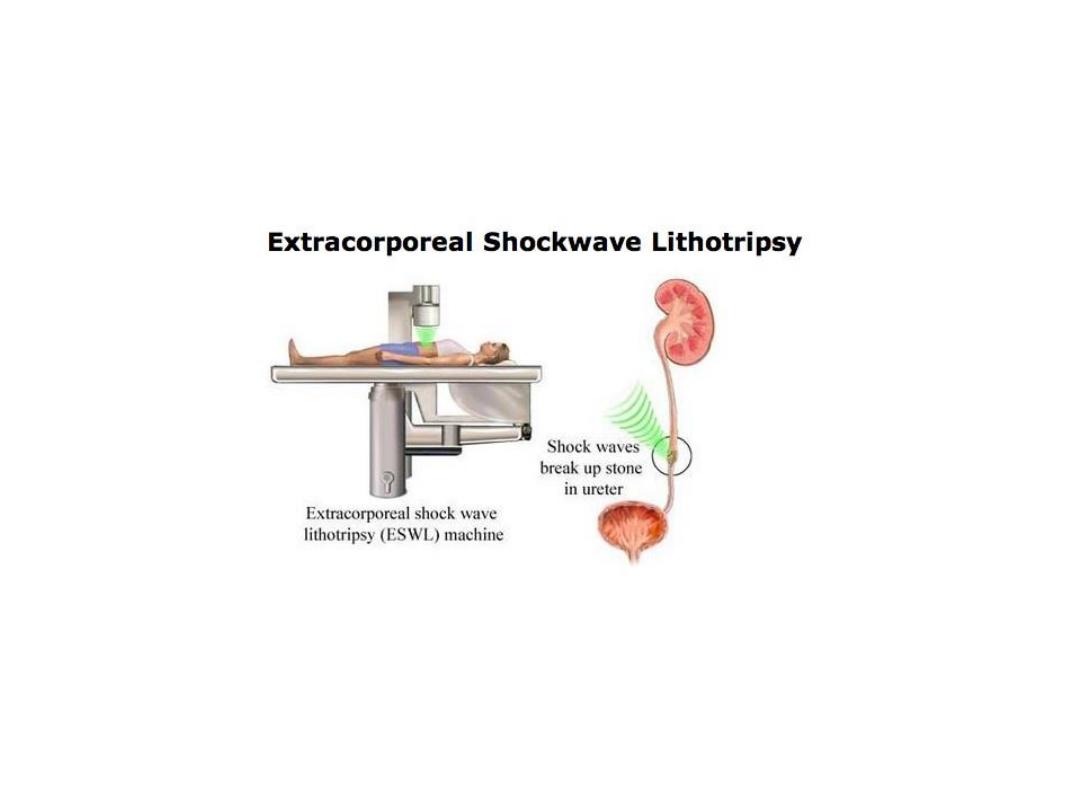
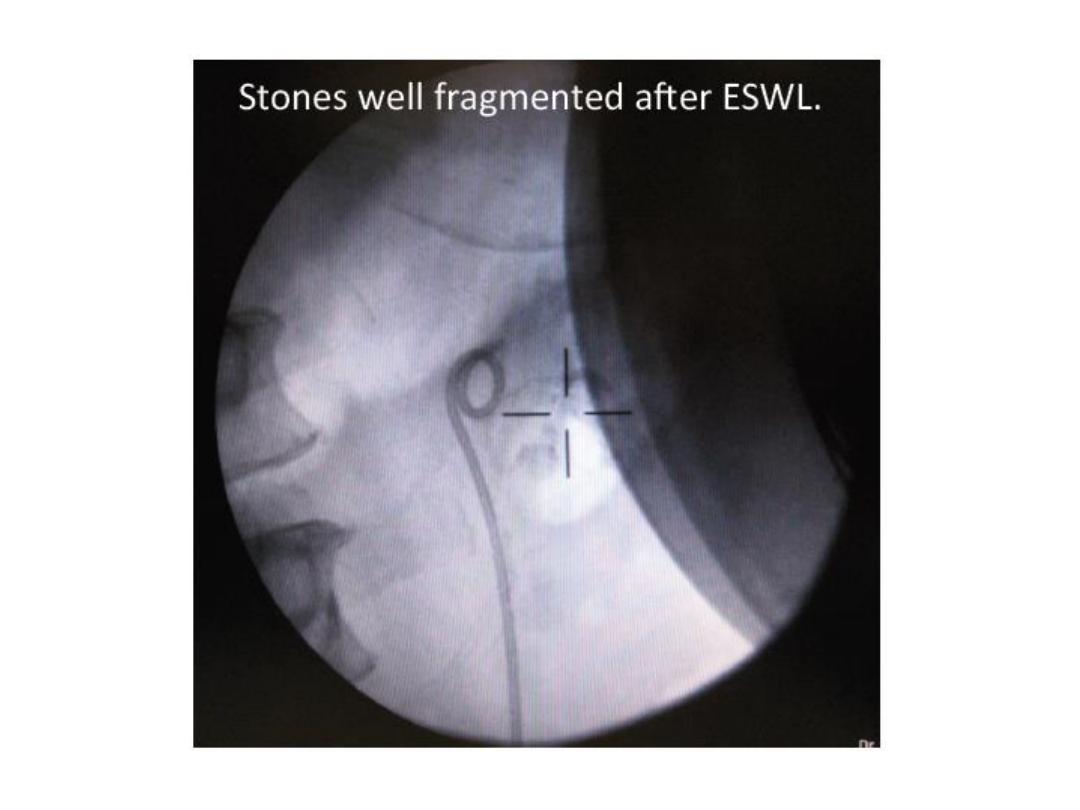
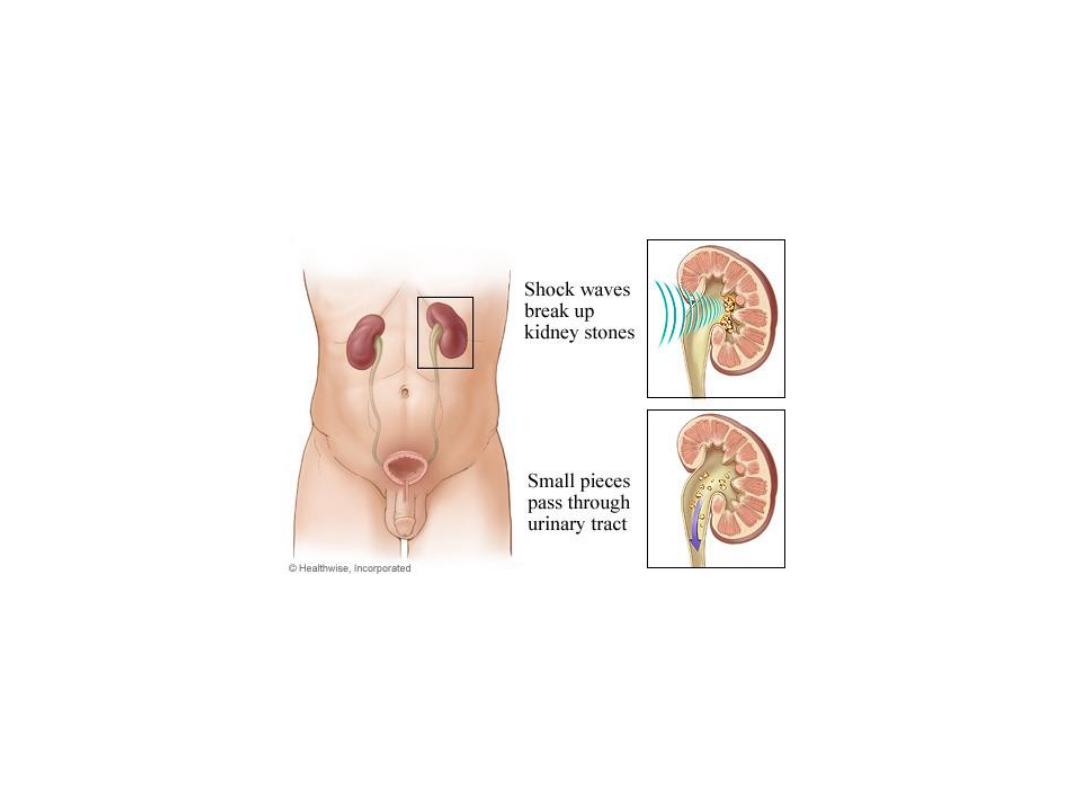
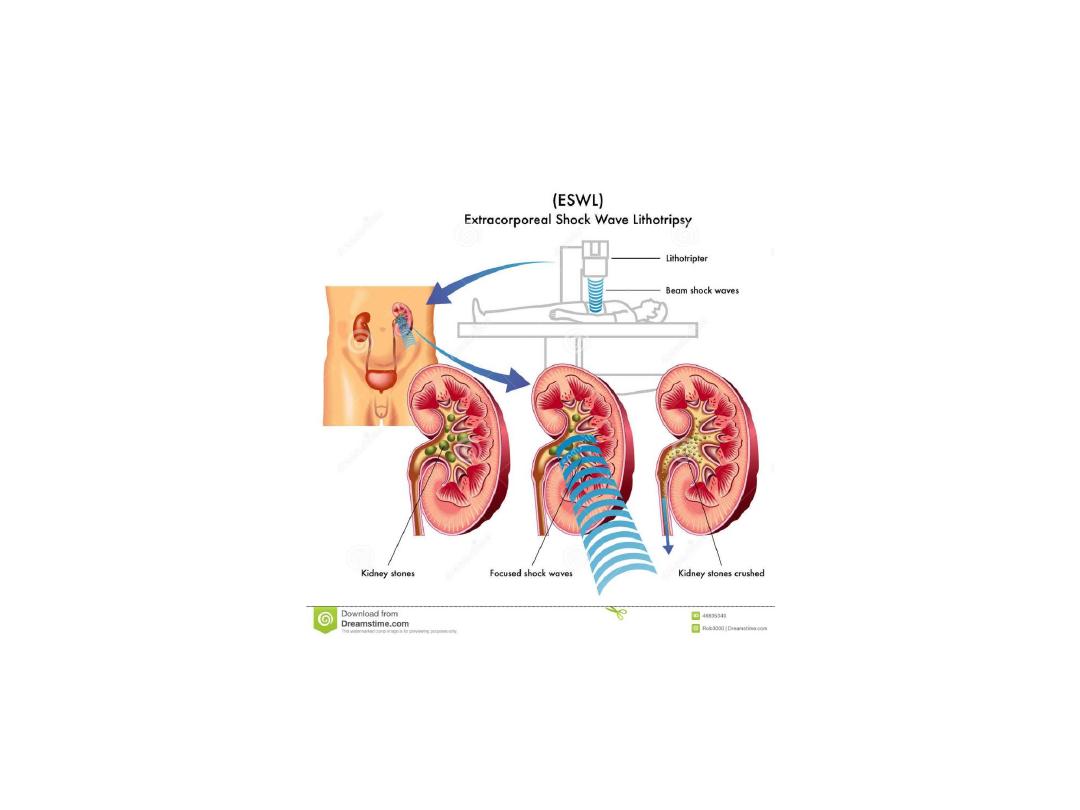

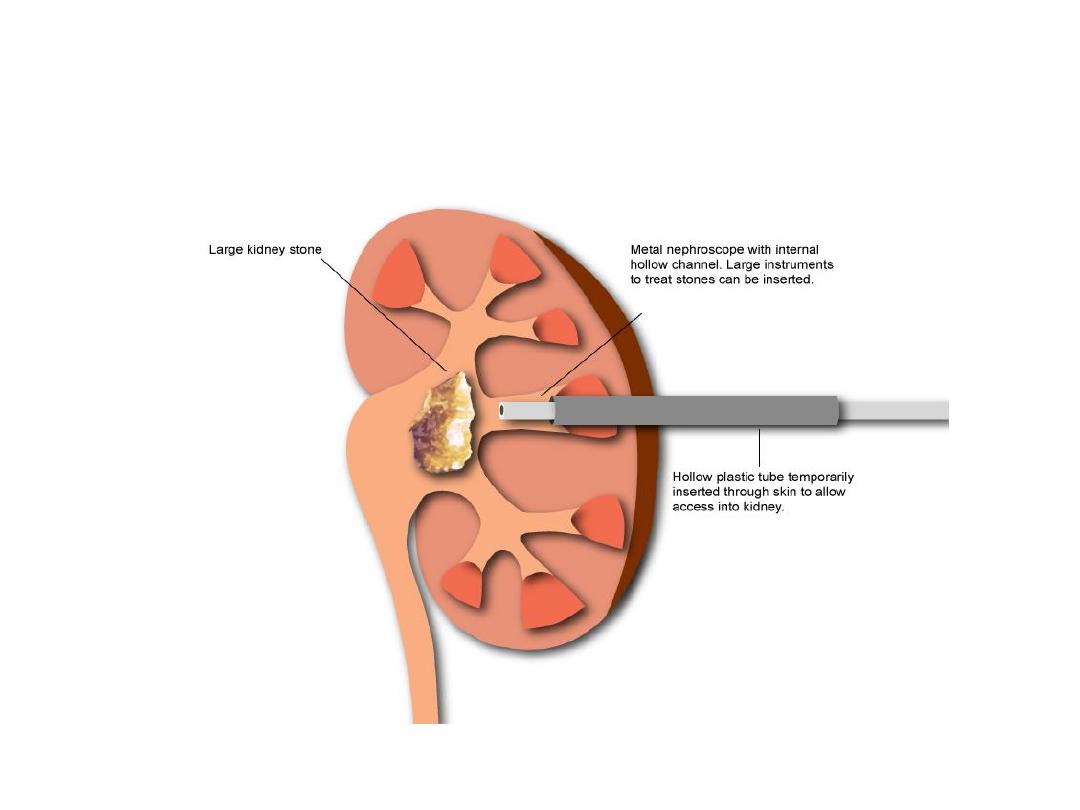
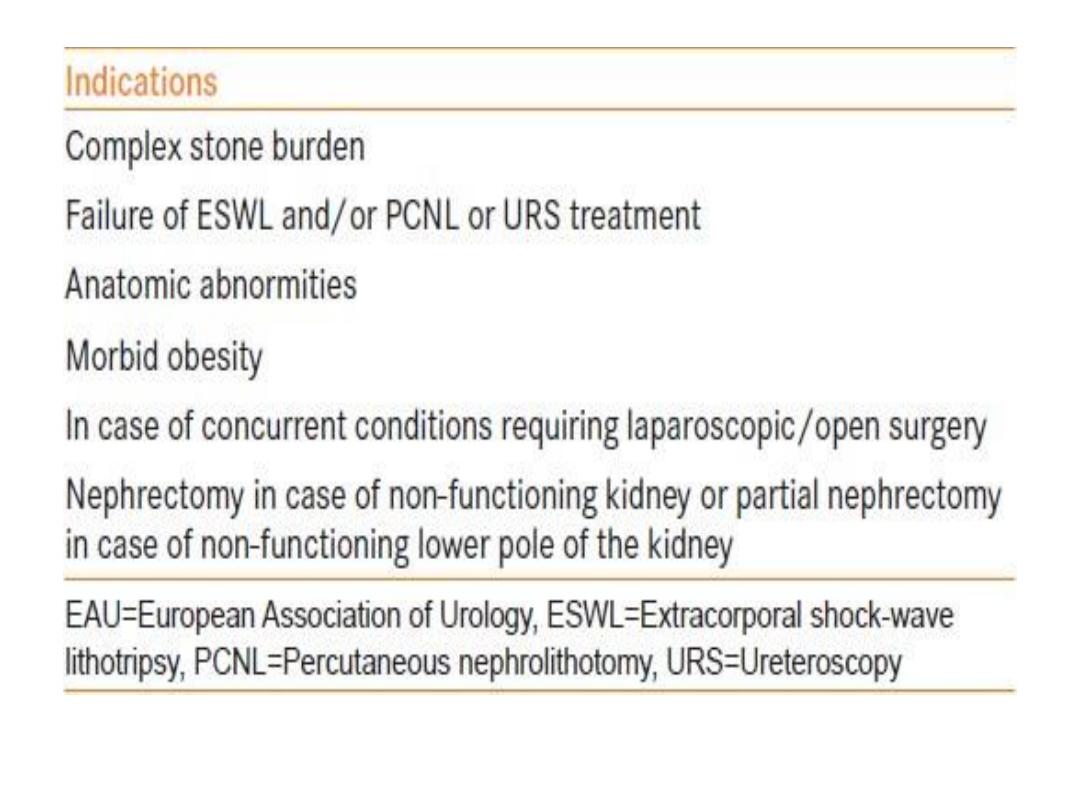
PCNL



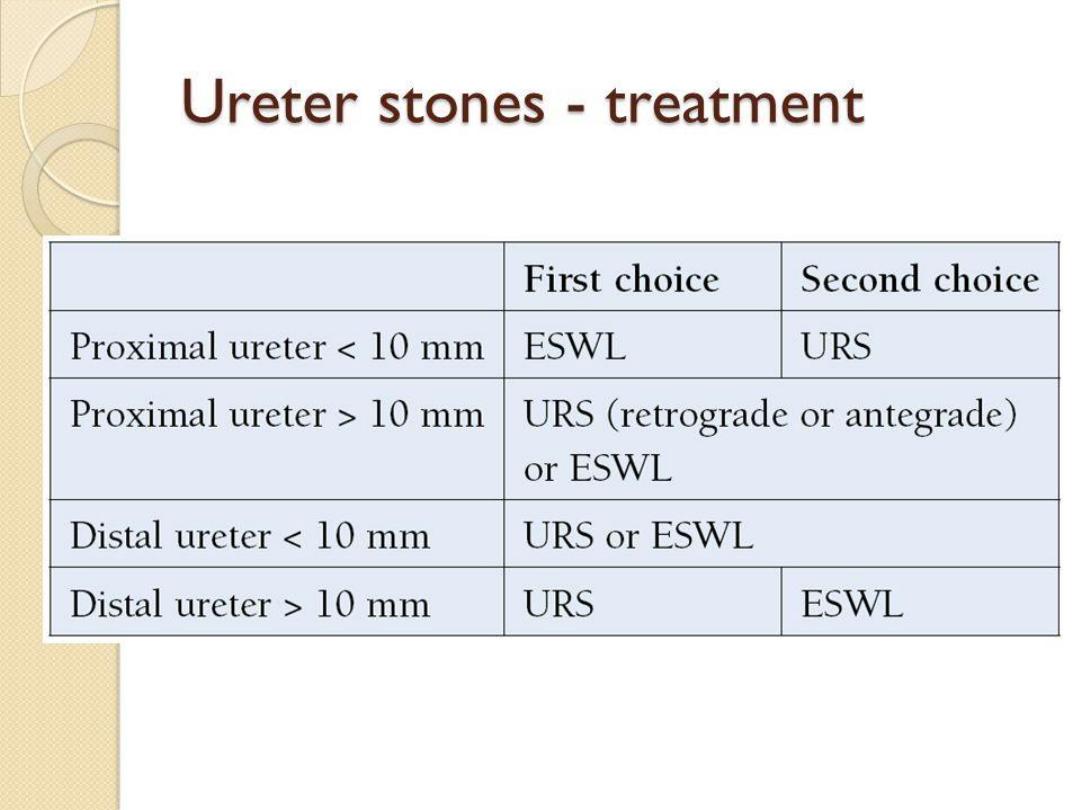
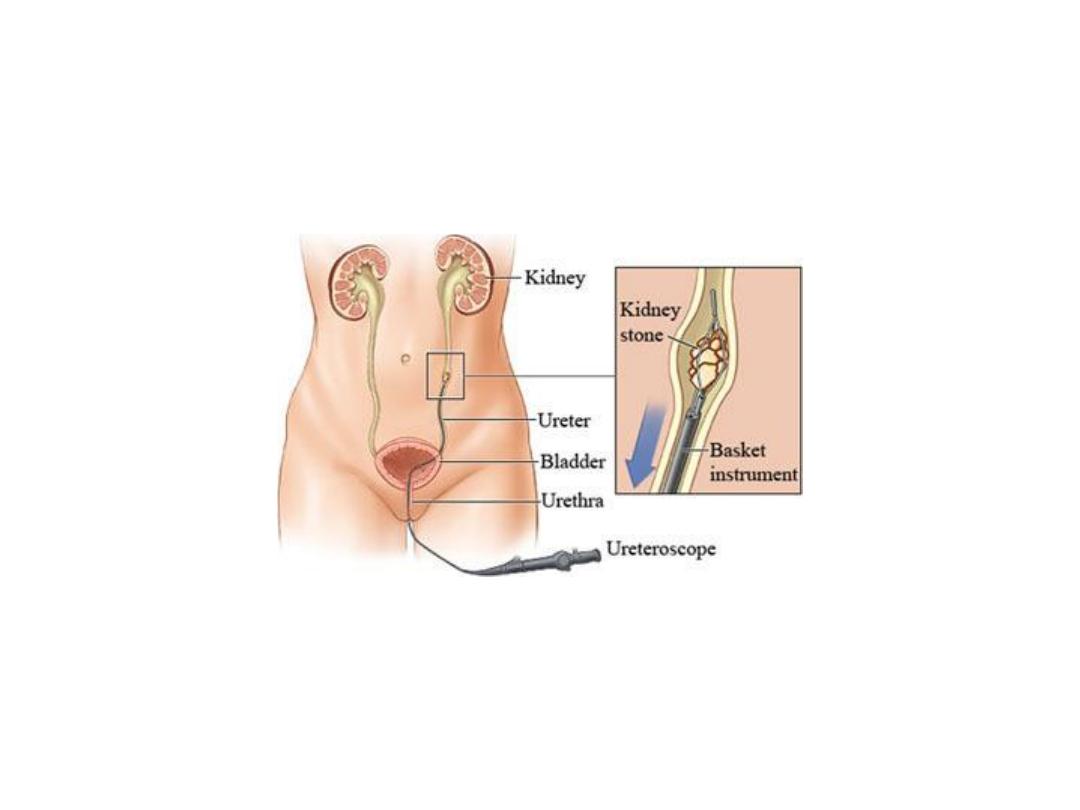


Medical treatment of ureteric colic

THANK YOU
