
Complications of Preeclampsia

Complication of severe pre-eclampsia are:
• Eclampsia
• HELLP syndrome
• DIC
• ARDS
• Pulmonary oedema
• Acute renal failure
• Placental abruption
• Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
• Intrauterine fetal death

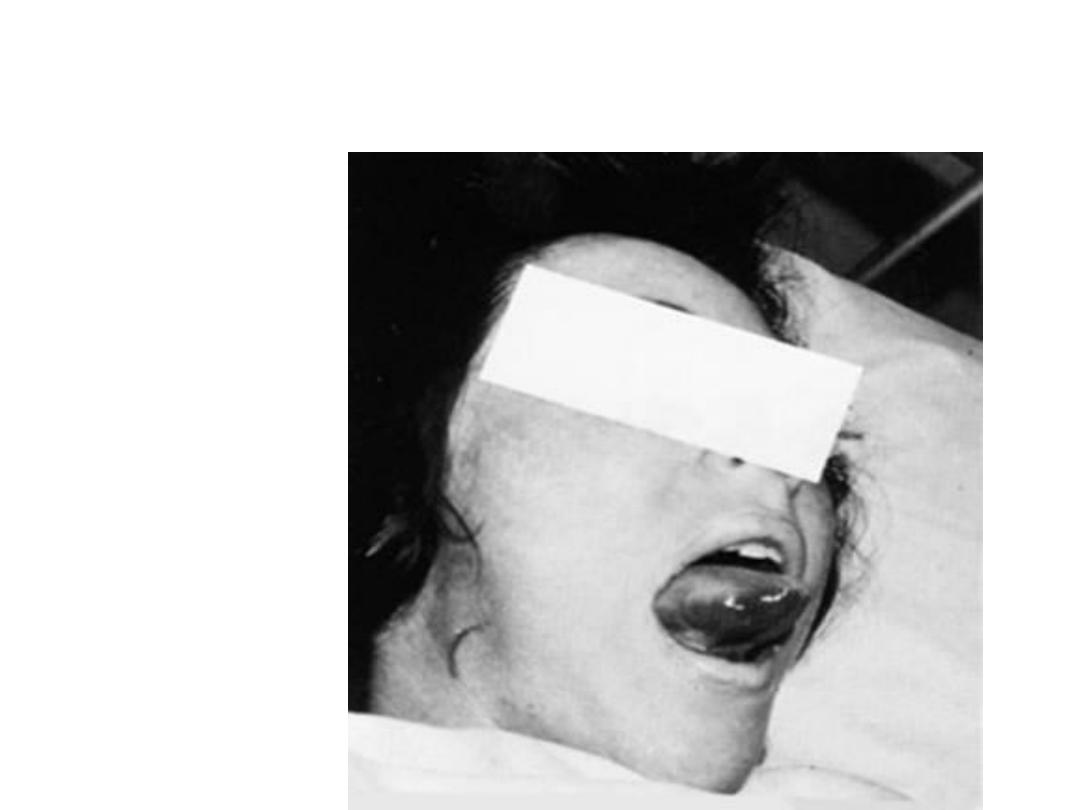
Eclampsia:
• defined as new-onset
in an otherwise healthy woman
with hypertensive disorder of pregnancy
• 44% occur postnatally, 38% antepartum &
18% intrapartum.
• The pathophysiology
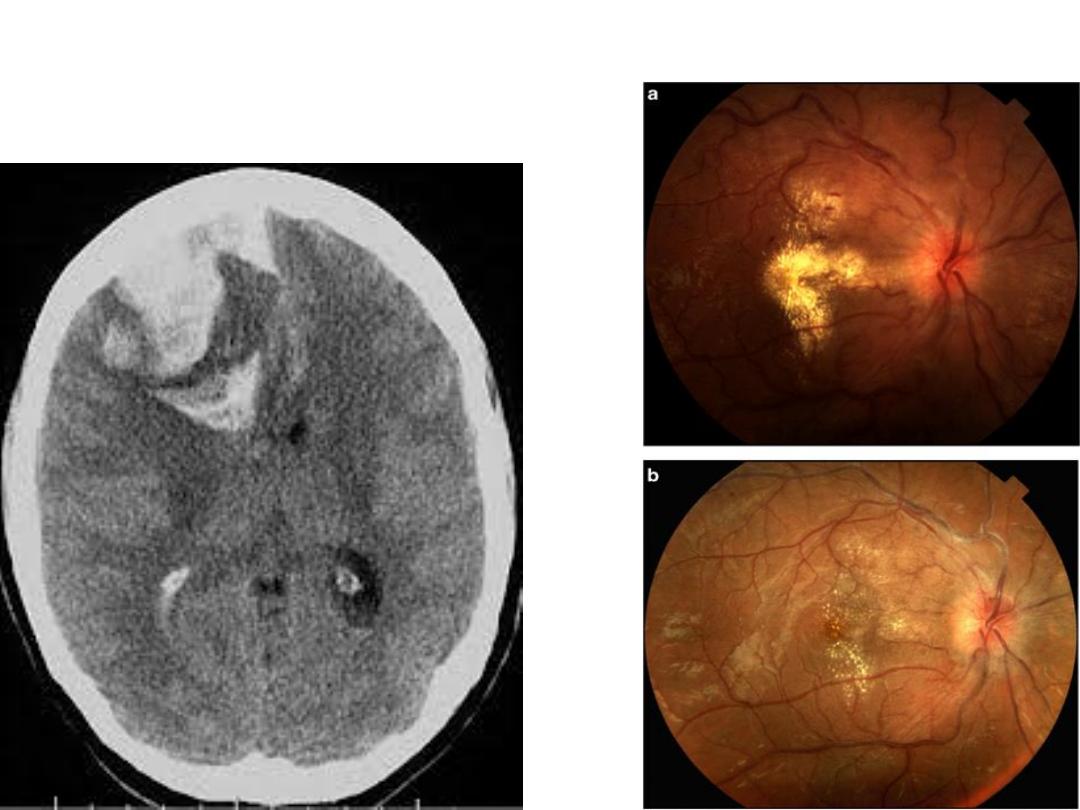
•is associated with high maternal and neonatal
morbidity and mortality.

Management:
• General measures:
• Do not leave the patient alone
• Call for help
• Inform consultant
• Prevent maternal injury during
convulsion

–Air way:
–Breathing:
–Circulation:
–Secure intravenous access
–Urinary catheter to assess
urinary out put
–Fluid input/output chart

anticonvulsant therapy
• Magnesium sulphate:
membrane stabilizer
& vasodilator & reduces intracerebral ischaemia
• Loading dose 4gm bolus iv over 15-20 min
followed by continuous infusion of 1gm/hr
signs of magnesium toxicity
• loss of deep tendon reflexes
• respiratory depression
• cardiac standstill.
• So, the patient should be monitored hourly
by patellar reflex, respiratory rate &
oxygen saturation. & urine output

• BP should be controlled using intravenous
hydralazin or labetolol
• Delivery
• Postpartum care
• Transfusion of red cells, platelets, fresh
frozen plasma and cryoprecipitate or
fibrinogen concentrate are required as
indicated clinically and by blood and
coagulation tests.
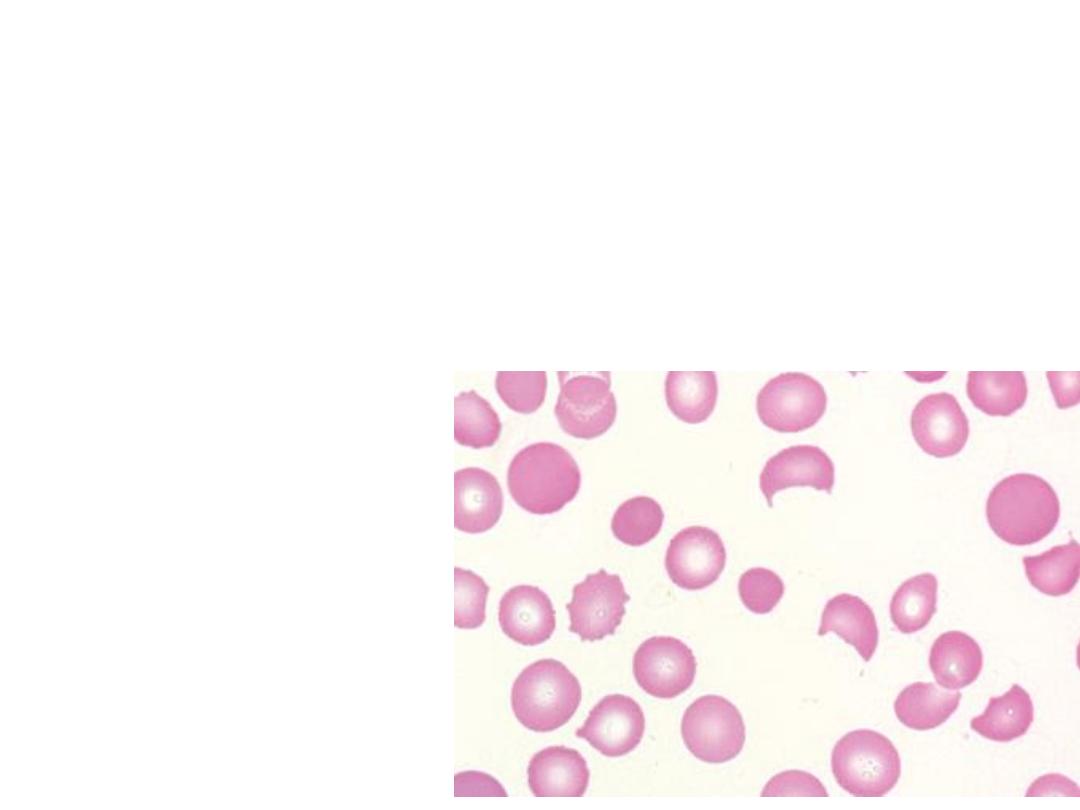

• HELLP Syndrome: the association of
haemolysis (H) elevated liver enzymes
(EL) & low platelet count ( LP)
• DIC with low fibrinogen may coexist.

• Definitive treatment of severe pre-
eclampsia and HELLP requires delivery
of the fetus
• dexamethasone can reduce the risk of
respiratory distress in the newborn and
reduce liver enzymes and possibly the
risk of adult respiratory distress
syndrome in the mother.

Chronic Hypertension:
• 2-4 % of pregnant women. Over 90% of cases
are due to essential hypertension
• causes of chronic hypertension ( secondary)
include:
• Chronic renal disease
• Renal artery stenosis
• Coarctation of the aorta
• Collagen vascular disease
• Pheochromocytoma
• Cushing's syndrome
• Conn's syndrome

High-risk characteristics in women with CHT
include:
• Maternal age >40 years
• Duration of hypertension > 15 years
• BP ≥160/110 mmHg
• Diabetes
• Renal disease
• Cardiomyopathy
• Connective tissue disease
• Coarctation of the aorta
• Previous pregnancy with perinatal loss

Preconception assessment & councelling:
• life style modification
• anti-hypertensive therapy:
• Physical examination
• Investigations:
renal function test,
urinalysis,
24 h urine collection for protein excretion
creatinine clearance
CXR
ECG
echocardiography

Complications of CHT in pregnancy:
• Superimposed PE
• Abruptio placentae
Antihypertensive therapy: reduces the risk of
severe hypertension but does not reduce the
risk of superimposed PE, preterm delivery or
perinatal death
• diuretics decrease blood volume & cause
undesirable physiological effect.
• beta-blockers cause IUGR
• ACE inhibitors & angiotensin receptor blockers
cause renal toxicity in the fetus & should be
changed
