Sinuses, Orbits, and Neck imaging
ByDr. Firas Abdullah
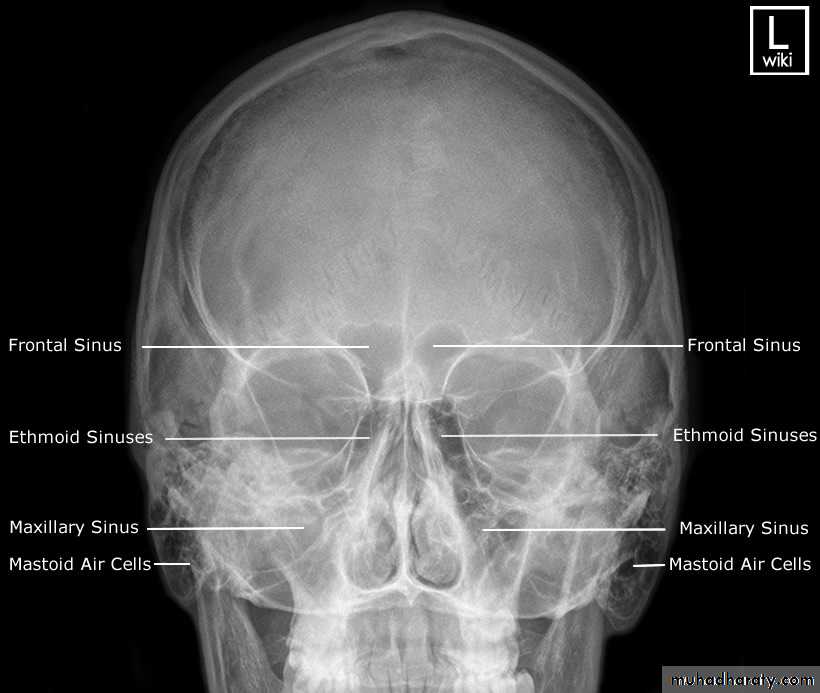
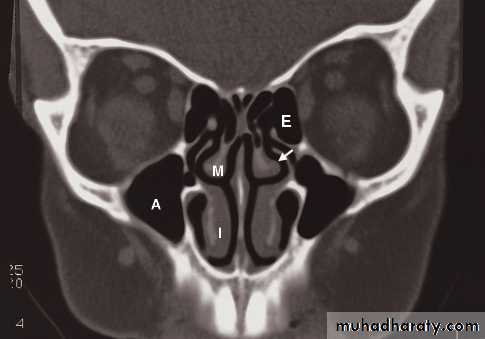
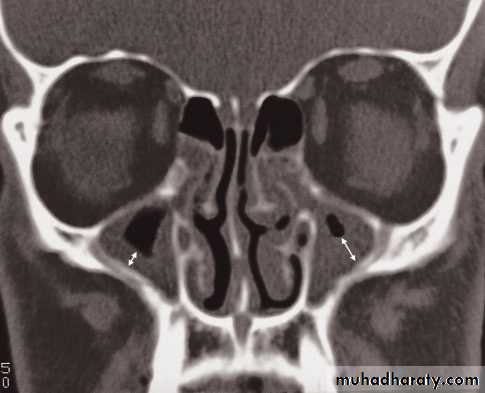
Sinuses:
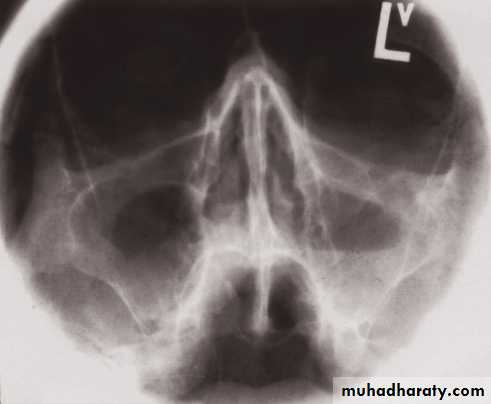
• On plain radiographs the normal sinuses are transradiant because they contain air.• Plain films have a role in showing mucosal thickening, fluid levels, bone destruction and fractures.
• However, CT is often the preferred technique in sinus disease
• MRI) also demonstrates the sinuses well, but is rarely needed as the primary investigation.
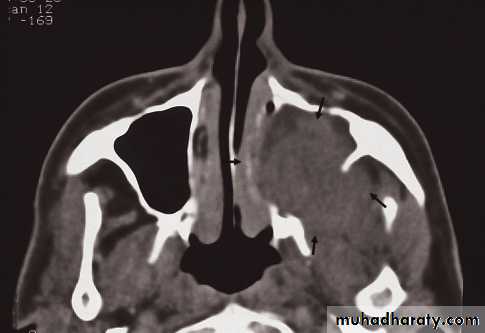
• The causes of an opaque sinus are:
• Infection or allergy.
• Mucocele.
• Carcinoma of the sinus or nasal cavity.
Mucosal thickening and a fluid level
Nasopharynx
• Computed tomography and especially MRI give excellent visualization of the nasopharynx.• Demonstrate the presence of tumour, the most common being a nasopharyngeal carcinoma as a mass disrupting the symmetry of the nasopharynx.
• Imaging can detect any spread into the skull base and lymphadenopathy in the neck
Orbits
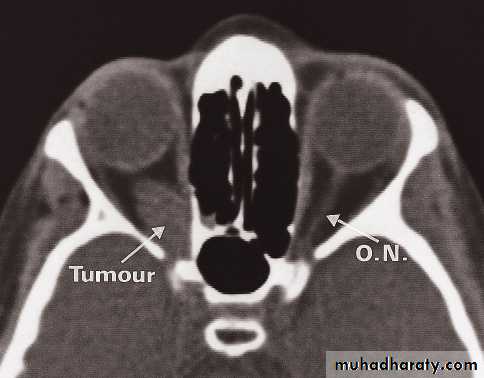
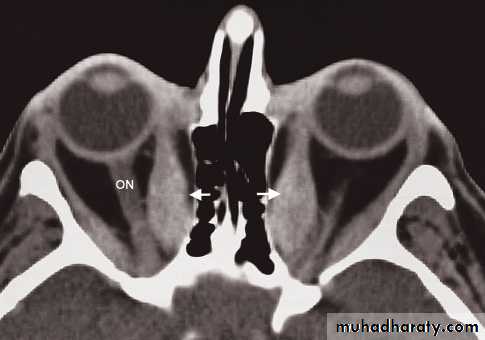
• Computed tomography and MRI clearly demonstrate the anatomy of the orbits.
• To distinguish between masses arising within the orbit, masses arising outside the orbit and thyroid eye disease. With an intraorbital mass, its relationship to the optic nerve can be determined.
• The main causes of intraorbital masses include various tumours, including tumours of the optic nerve, vascular malformations and granulomas.
• The most common orbital masses originating outside the orbit, which often present with exophthalmos, are tumours or mucoceles of the frontal or ethmoidal sinuses, and a meningioma arising from the sphenoid ridge.
• In thyroid eye disease, there is enlargement of the extraocular muscles which is frequently bilateral and may affect one, several, or all the eye muscles. There is also infiltration of the fat behind the eye which adds to the exophthalmos.
Blow out fracture
A direct blow to the eye raises the intraorbital pressure and can result in a fracture of the orbital floor, which is the weakest part of the orbit. The break in the orbital floor allows herniation of orbital contents into the antrum,Salivary glands
• Ultrasound is the initial investigation choice• Magnetic resonance imaging is the preferred method for the investigation of masses thought to be in the salivary glands. The commonest salivary gland tumour is a benign adenoma.
• Magnetic resonance imaging is excellent for demonstrating the presence of a mass and its relationship to the facial nerve
Sialography
• Calculi, which occur most commonly in the submandibular duct or gland, normally contain calcium and can, therefore, be seen on plain films.
• To show the duct system, a sialogram is performed by injecting contrast into the ducts of the salivary glands. Stones and strictures in the ducts can be identified. Dilatation of small ducts, which is known as sialectasis, may occur with obstruction to the main duct
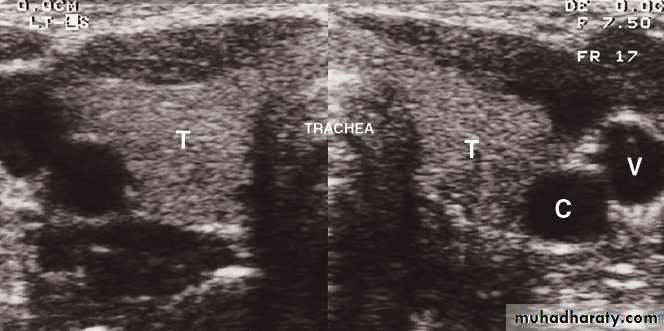
Neck
• Ultrasound: is recommended as the first line investigation, which may demonstrate the extent of the mass, LNs• Doppler studies: will indicate its vascularity
• CT : for cervical LNs enlargement or cervical mass (calcification)
• MRI: is the best method of imaging the neck because of the superior contrast between normal soft tissues and tumour
Thyroid imaging
Carcinoma of the thyroid
Thank you