Aplastic Anemia
ByDr. Teeb M. Jaafar
MBCh.B / F.I.C.M.S. (Path.)
Aplastic Anemia
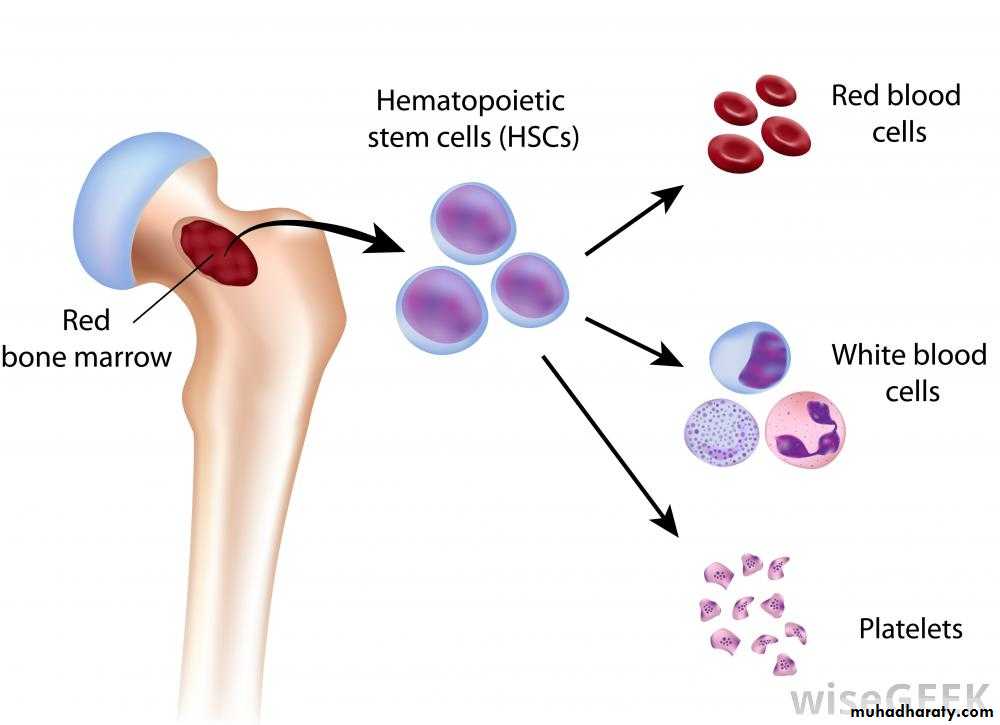
Aplastic anemia is a bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by peripheral pancytopenia and marrow hypoplasia.Bone marrow failure is a term with a larger meaning, referring to disorders of the hematopoietic stem cell which involves either one cell line or all of the myeloid cell lines
Aplastic Anemia - Etiology
Congenital/inherited (20%)• Patients usually have dysmorphic features or physical stigmata. Occasionally, marrow failure may be the initial presenting feature.
• Fanconi anemia
• Dyskeratosis congenita
• Shwachman-Diamond syndrome
• Familial aplastic anemia.
• Acquired:
• 1. Primary (idiopathic) : the most common form 75%
• 2. Secondary:
• .
• Secondary: causes includes
Radiation.
Drugs:
• ( Cytotoxic drugs , Antibiotics : Chloramphenicol , Sulphonamides
• Anti-inflammatory, Anti-convulsant )
• 2-3 months usually between exposure and the development of aplastic anemia.
Chemicals e.g., Benzene and pesticides, chloramphenicol, phenylbutazone, and gold.
Viruses:
• Hepatitis A, Non-A and Non-B, Herpes simplex, E-B virus and Parvovirus: (transient)
Important clinically in patients with hemolytic anemia
5-10% of cases of AA in the West and 10-20% in the Far East.
2-3 months between exposure to the virus and the development of AA.
Immune: SLE, RA (rheumatoid arthritis).
Pregnancy.Aplastic Anemia - Pathogenesis
Potential mechanisms:• Absent or defective stem cells (stem cell failure).
• Abnormal marrow micro-environment.
• Inhibition by an abnormal clone of hemopoietic cells.
• Abnormal regulatory cells or factors.
• Immune mediated suppression of hematopoiesis.
It is believed that genetic factors play a role.
There is a higher incidence with HLA (II) histo comp.Antigen. Immune mechanism is involved.
Aplastic Anemia - Forms of disease:
Inevitable:• dose related e.g. cytotoxic drugs, ionizing radiation. The timing, duration of aplasia and recovery depend on the dose. Recovery is usual except with whole body irradiation.
Idiosyncratic:
• unpredictable to drugs e.g., anti-inflammatory antibiotics, anti-epileptic, these agents usually do not produce marrow failure in the majority of persons exposed to these agents.Common Traits To All Various Causes
Aplasia due to any cause may recover after immunosuppressive therapy indicating that immune mechanisms are involved.Transition to a clonal disorder of hemopoiesis can occur in any patient who has recovered bone marrow function, suggesting that fragility of the hemopoietic system is common to all forms of aplasia.
Aplastic Anemia – Clinical Features
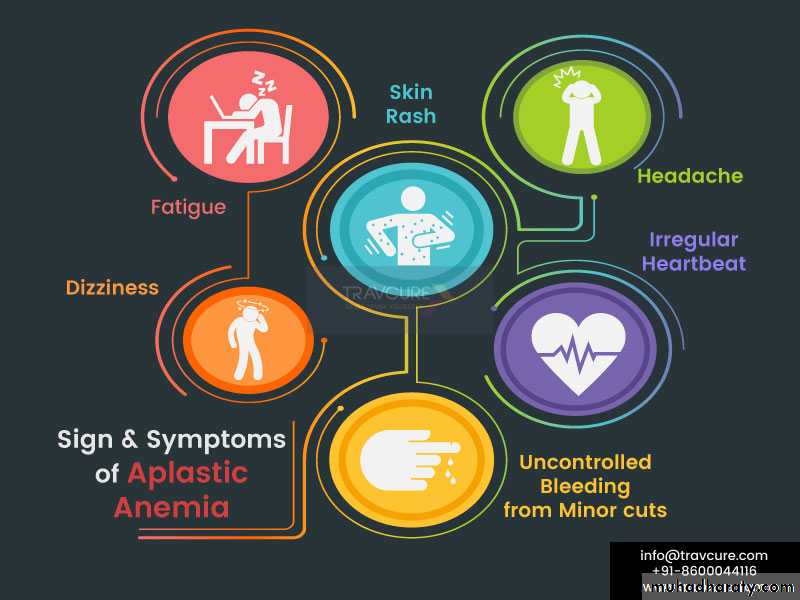
anemia pallor and/or signs of congestive heart failure, such as shortness of breath.
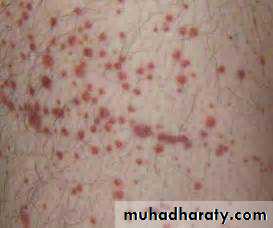
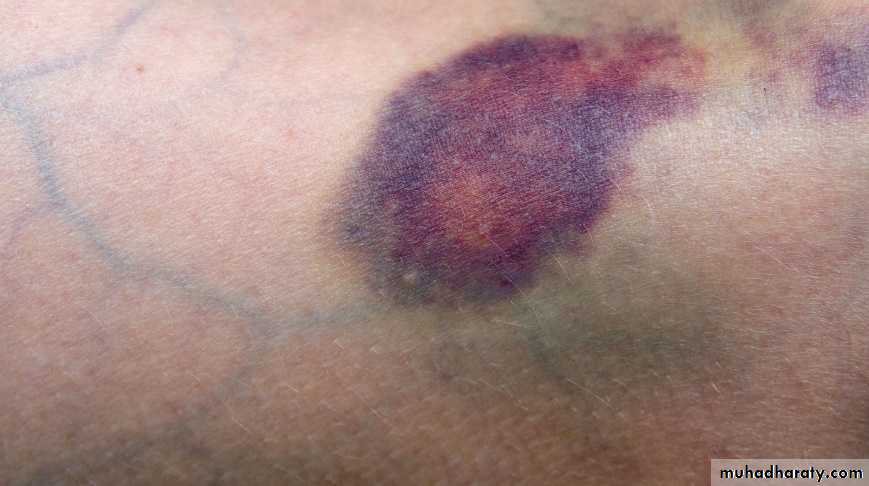
thrombocytopenia bruising (eg, ecchymoses, petechiae) on the skin, gum bleeding, or nosebleeds.
neutropenia fever, cellulitis, pneumonia, or sepsis
jaundice and evidence of clinical hepatitis in subset of patientsAplastic Anemia – Clinical Features
In any case of aplastic anemia, look for physical stigmata of inherited marrow failure syndromes such as
• skin pigmentation,
• short stature,
• microcephaly,
• hypogonadism,
• mental retardation,
• skeletal anomalies.
Aplastic Anemia – Investigations
CBCReticulocyte count
Blood film.
Liver function tests
Virology
Bone marrow aspirate & trephine
Aplastic Anemia – CBC
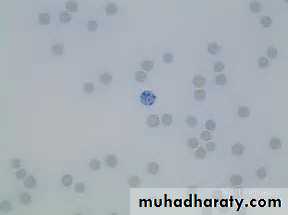
Anemia is common, and red cells appear morphologically normal. The reticulocyte count usually is less than 1%.Thrombocytopenia, with a paucity of platelets in the blood smear.
Agranulocytosis (ie, decrease in all granular white blood cells, including neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and a decrease in monocytes are observed. A relative lymphocytosis occurs.
The degree of cytopenia is useful in assessing the severity of aplastic anemia.
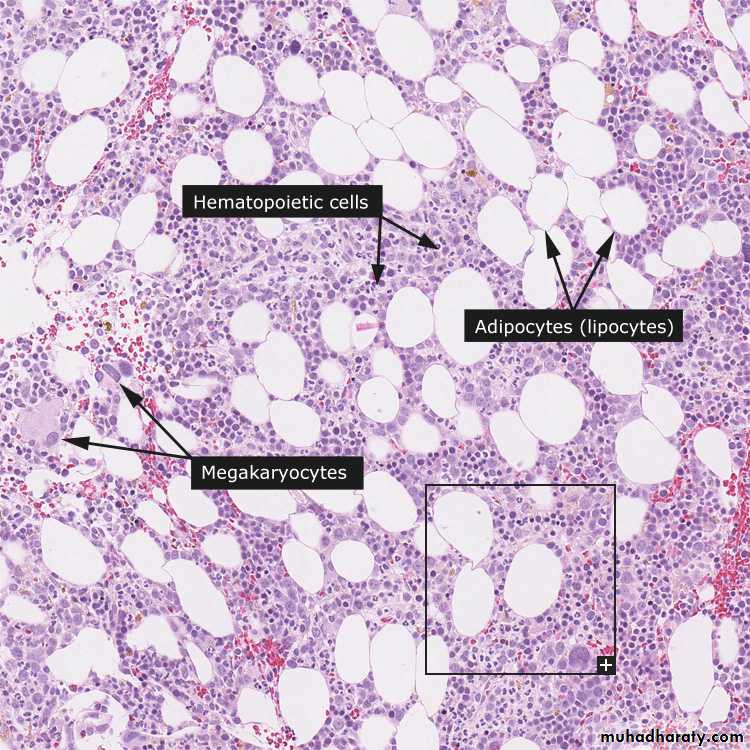
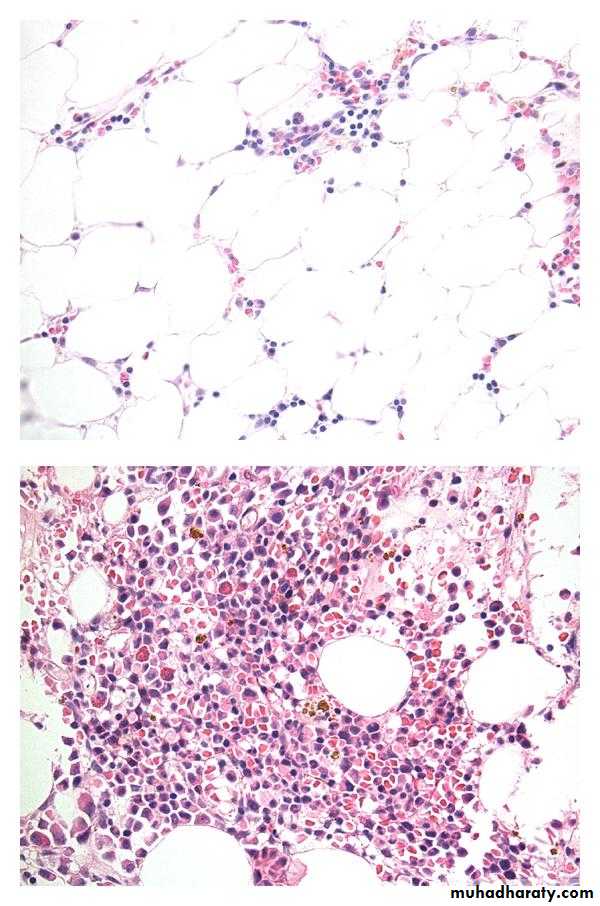
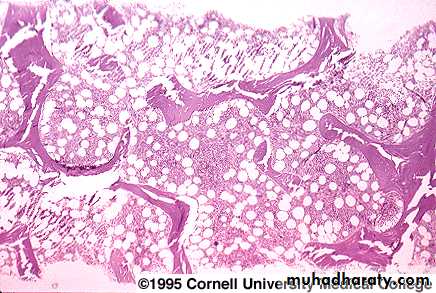
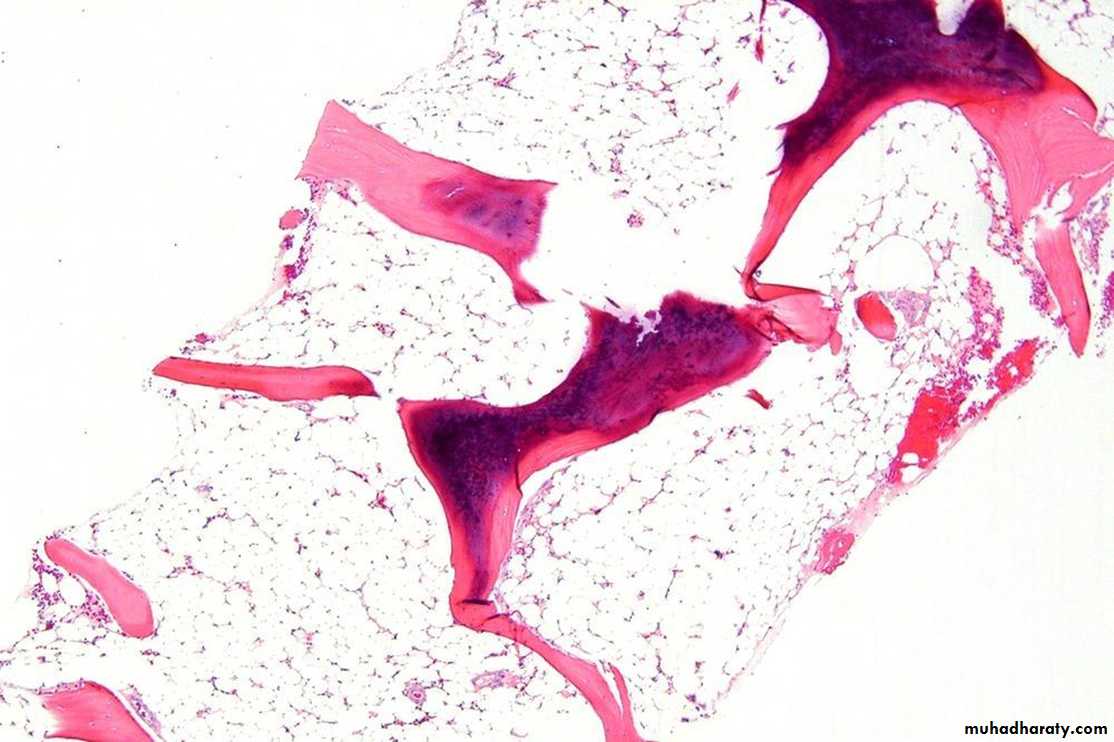
Bone marrow exam
A bone marrow aspirate & biopsy is performed. Both of them are hypocellular.A core biopsy is the most important and provides a better idea of cellularity; the specimen is considered hypocellular if it is less than 30% cellular in individuals younger than 60 years or less than 20% in those older than 60 years.
Aplastic Anemia - Criteria for diagnosis
1. pancytopenia Hb <10g/dLneutrophils <1,5 /L
PLt <100 /L
2. decreased marrow cellularity (< 25%)
- increased fat cells component
- no extensive fibrosis (vi)
- no malignancy or storage disease
Other Causes of pancytopenia
1.Failure of production of blood cellsa) bone marrow infiltration
- acute leukemias
- hairy cell leukemia
- multiple myeloma
- lymphoma
- myelofibrosis
- metastatic carcinoma
b) aplastic anemia
2. Ineffective hematopoesis
- myelodysplastic syndrome
- vit.B12 and folate deficiency
3. Increased destruction of blood cells
- hypersplenism
- autoimmune disorders
- paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
4. Myelosuppression after irradiation or antiproliferative drugs
Aplastic Anemia - Treatment
Withdrawal of etiological agents.
Supportive.
Restoration of marrow activity:
• Bone marrow transplant
• Immunosuppressive treatment
• - Prednisolone - Antilymphocyte glob.
• - Cyclosporin - Anti T cells Abs.
• - Splenectomy
• Androgens
• Growth factors