LAB-8-
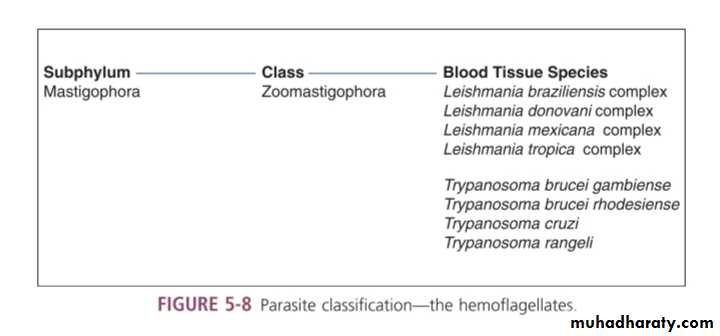
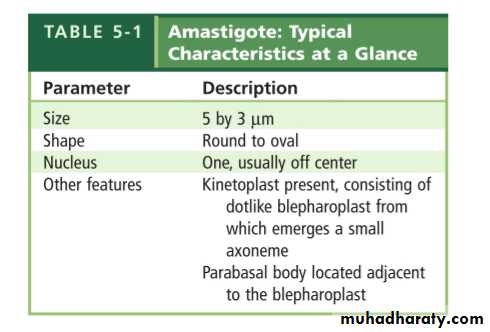
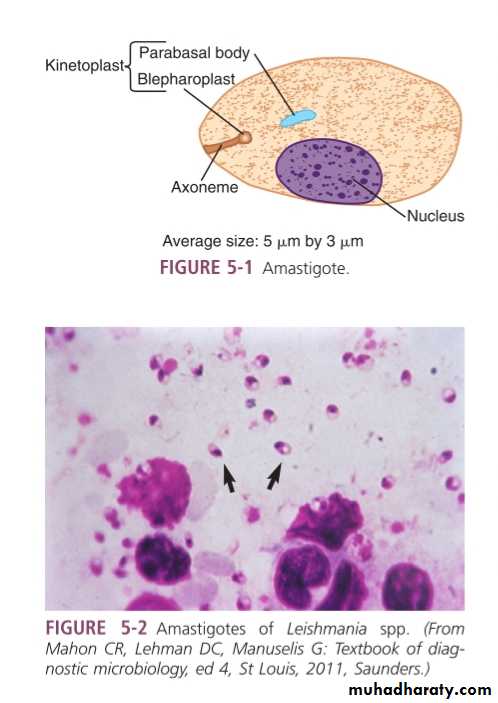
TrypanosomaAmastigotes
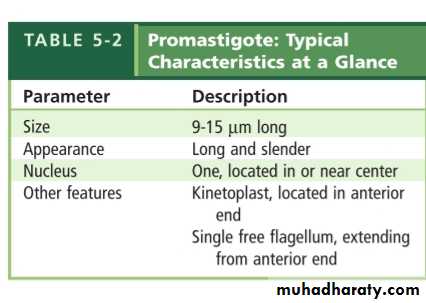
Promastigote
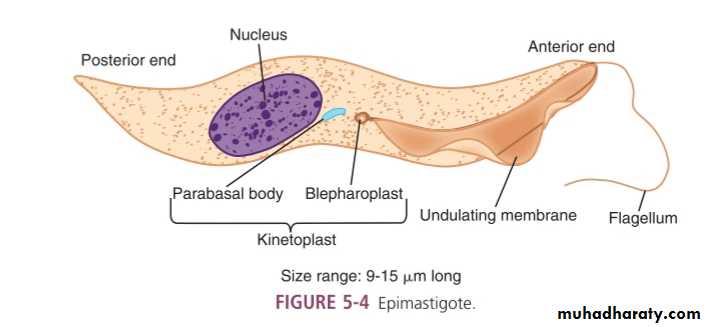
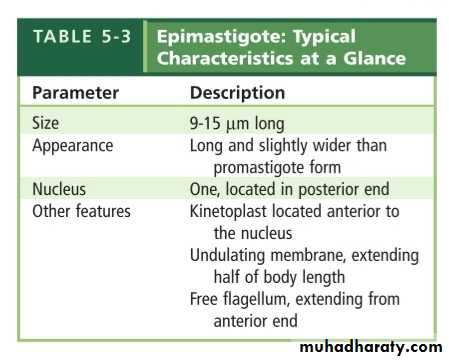
Epimastigote
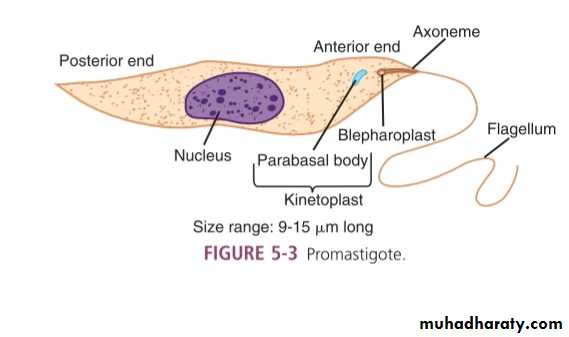
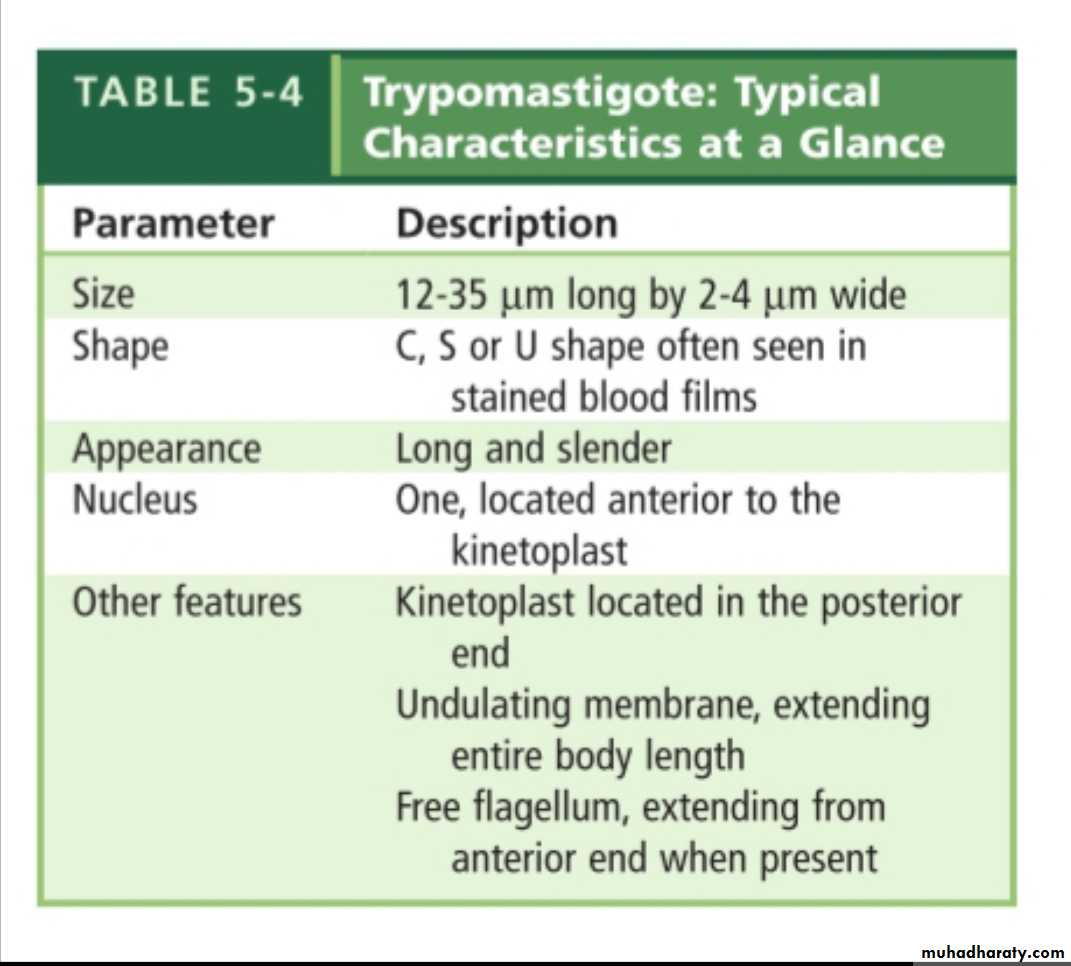
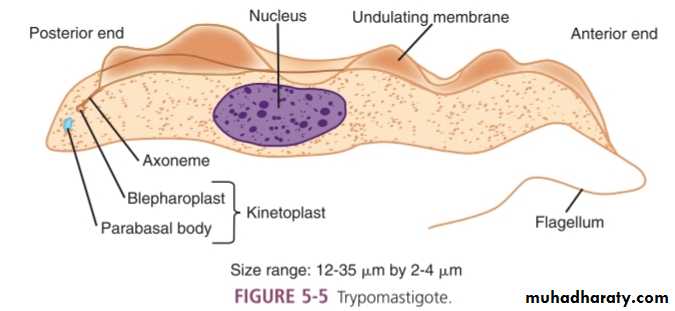
Trypomastigote
Trypanosoma spp
include :Trypanosoma cruzi.
Trypanosoma brucei.
which include gambiense and rhodesiense.Trypanosoma cruzi
Cause the disease : chagas disease,American trypanosomiasis.
The vector : reduviid bug (kissing bug).
The host : human and animal(dogs,cats).
Diagnostic stage : trypomastigote.
Infective stage : metacyclic trypomastigote.
Mode of transmission: bite of vector,blood transfusion,sexual intercourse,transplacental.
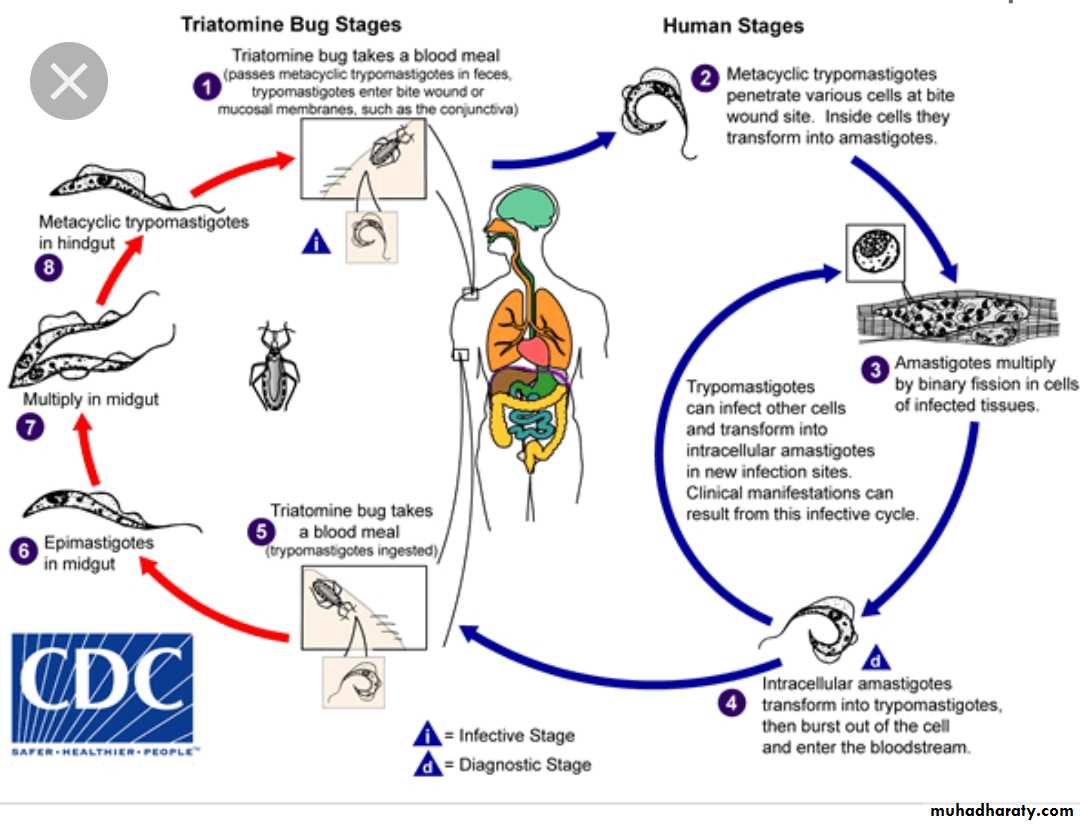
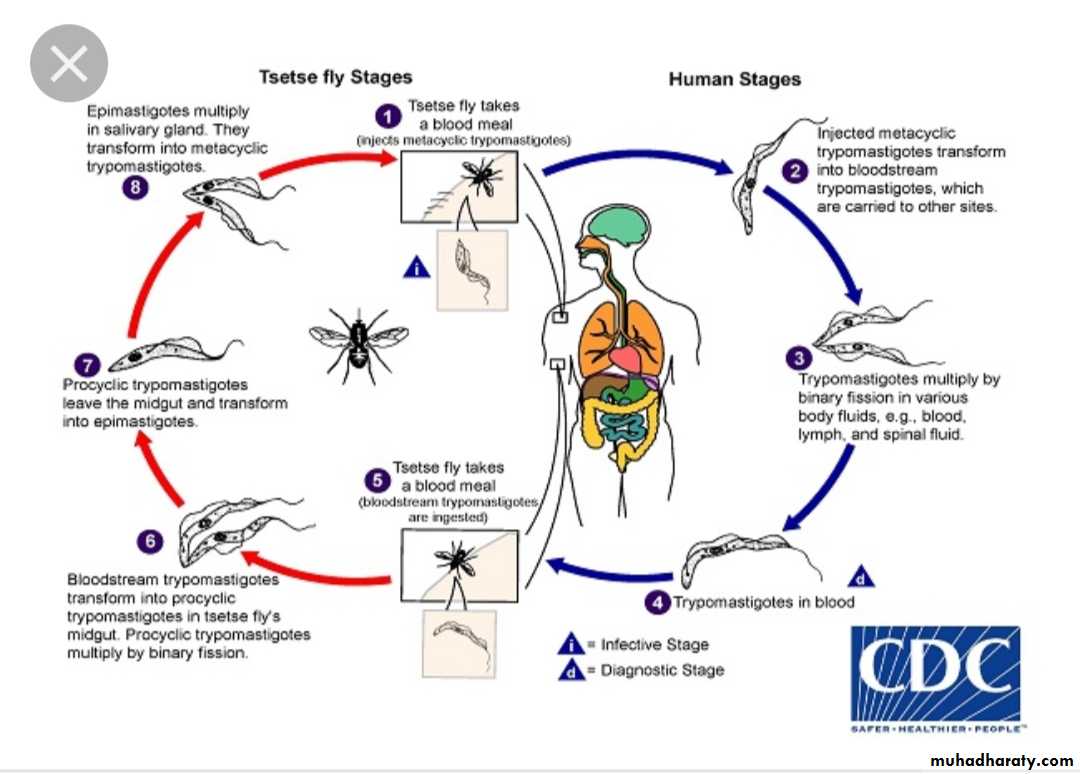
Life cycle
The vector defecates infective trypomastigotes near the site of its blood meal.
As the host scratches the bite area,the trypomastigotes enter the host and invade surrounding cells,where they transform into amastigotes.The amastigotes multiply,destroy the host cell and convert back to trypomastigotes.
Infect the heart muscle,liver and brain.In the reduviid bug:
When it feeds via a blood meal,on an infected human, the trypomastigotes transmitted back to the bug.
On ingestion the trypomastigotes transform into epimastigotes in the midgut.
Multiplication of the epimastigotes in to trypomastigotes again in the hindgut.
Lab diagnosis
• Giemsa –stained blood slides for detection of the T.cruzi trypomastigotes.• Lymph node biopsy giemsa-stained slides,blood culture ,may reveal the typical amastigotes stage.
• Serology : complement fixation (CF),DAT,indirect immunofluorescence(IIF),PCR and ELISA.
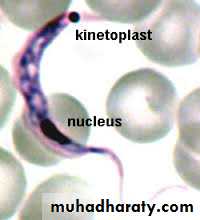
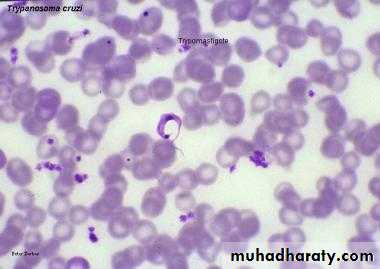
Trypansoma cruzi parasite in a thin blood showing C shaped trypomastigoite with bulging kinetoplast posteriorly
Trypanosoma brucei
Include: T.b gambiense,T.b rhodesiense.Disease: African trypanosomiasis, sleeping sickness.
Vector : testes fly.(Glossina).
Host : Humans are the reservoir for T. gambiense, whereas T. rhodesiense has reservoirs in both domestic animals (especially cattle) and wild animals.
Infective stage: metacyclic trypomastigotes.
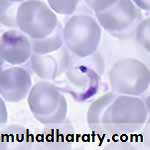
Diagnostic stage: trypomastigotes in blood.
Mode of transmission: bite by the vector.
Life cycle
Human become infected following the injection of trypomastigotes by the testes fly.
The trypomastigotes migrate through the blood stream and to the lymphatic system,multiplying by binary fission.Some of it destroyed by the immune system.
Invation of the CNS.
The trypomastigotes are transmitted back to the testes fly vector when it feeds on an infected human.
Once ingested by the testes fly ,the trypomastigotes continue to multiply and eventually migrate back to the salivary gland,converting into epimastigotes
Once in the salivary gland they transform back to the trypomastigotes.
Lab diagnosisBlood,lymph node aspiration,and CSF are the specimens of choice,( Giemsa-stained slides) reveal the typical trypomastigotes.
Microscopic :detection of the presence of (IgM) and proteins.(infected pt typically have high levels of both IgM and proteins in their CSF.
Serology.
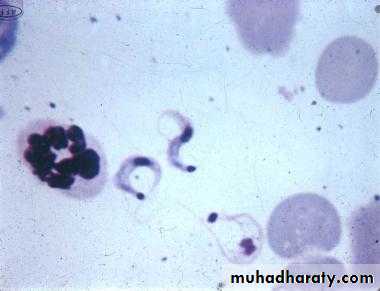
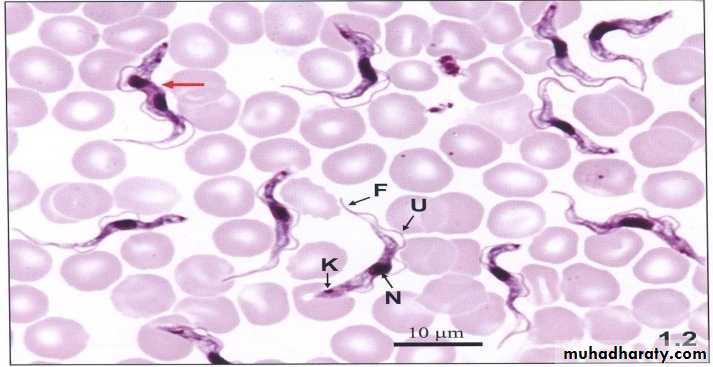
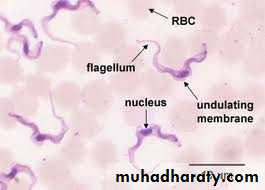
trypomastigoite appear as wavy or curved S shaped with central nucleus and post kinetoblast but not bulging and with undulating membrane at hole length of trypomastigoite arise from post kinetoblast