Compound Staining
2
Compound Staining:
• Compound Staining method consist of more than one dye, used to identify organisms according to their type of reaction .
• Examples:
• 1. Gram Stain.
• 2. Acid Fast Stain.
• 3. Spore Stain.
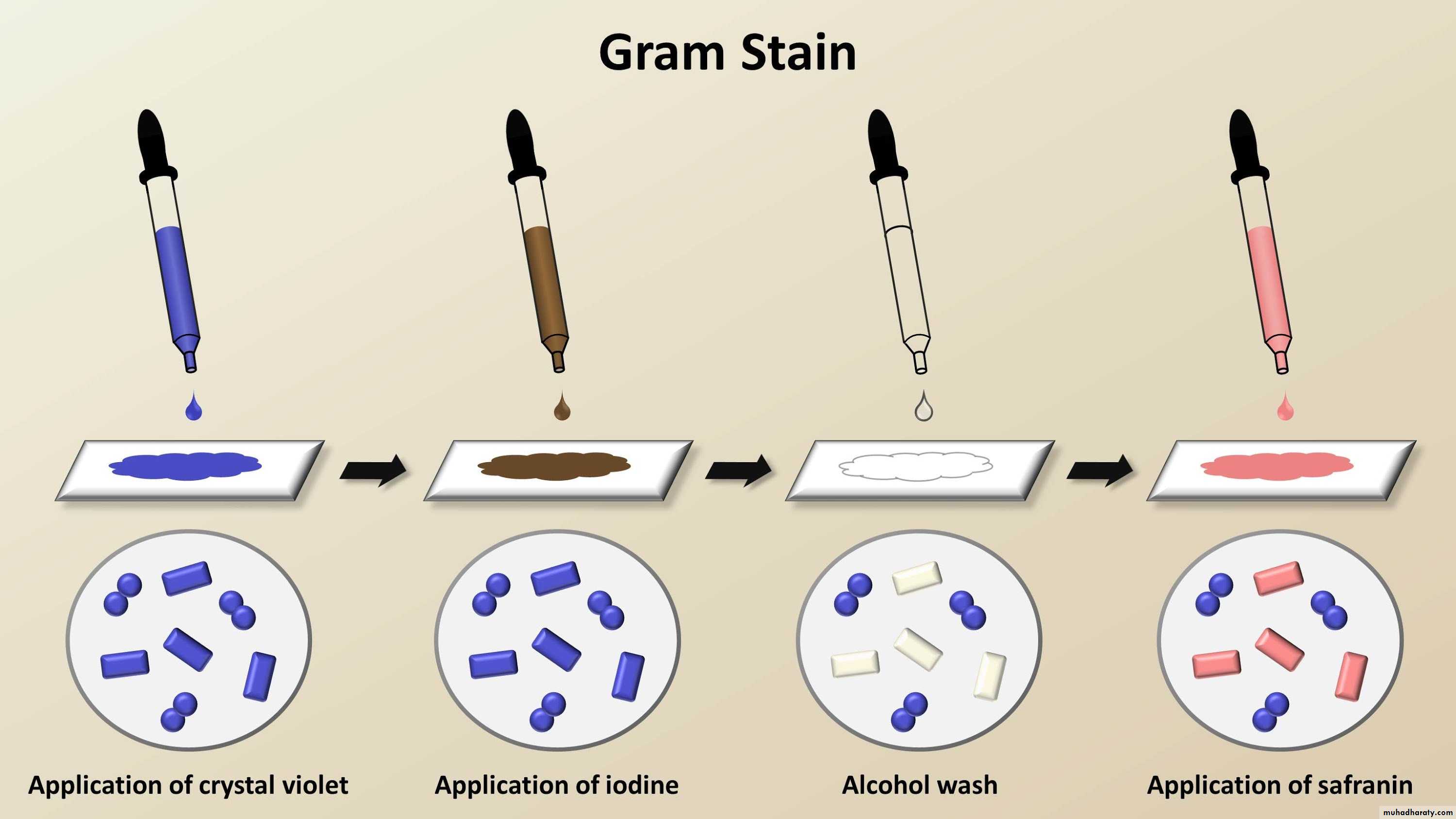
Gram stain
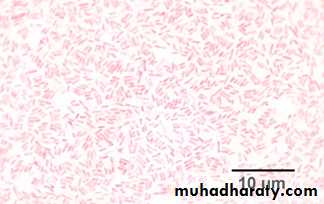
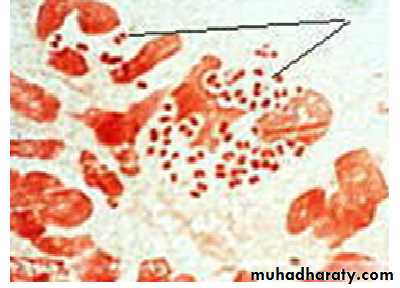
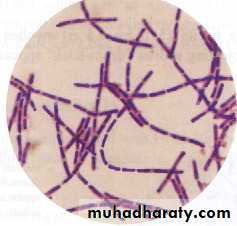
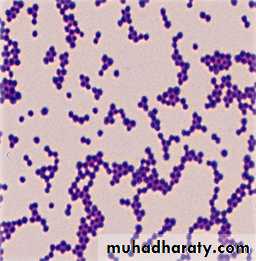
It is the most important differential stain used in bacteriology , it classified bacteria into two major groups:• Gram positive:
which retain the first dye (crystal violet).
Appears violet after Gram’s stainb) Gram negative:
which lost the first dye after decolourization & stain with the second dye.
Appears red after Gram’s stainGram stain
It is possible to differentiate between bacteria of the same morphology.
Is used to determine the relative number & morphology of bacteria in a smear taken directly from a patient.
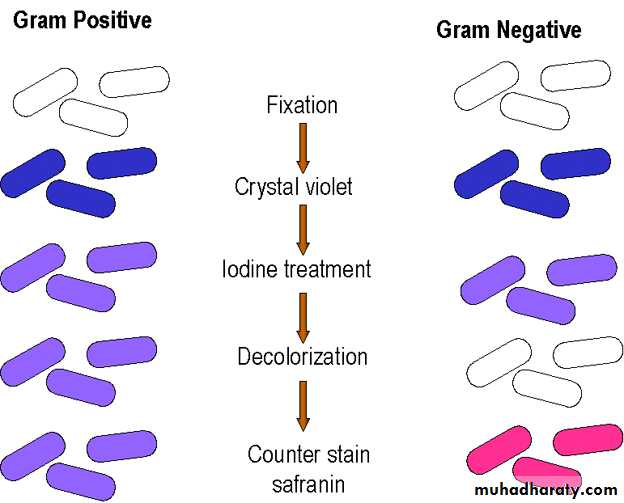
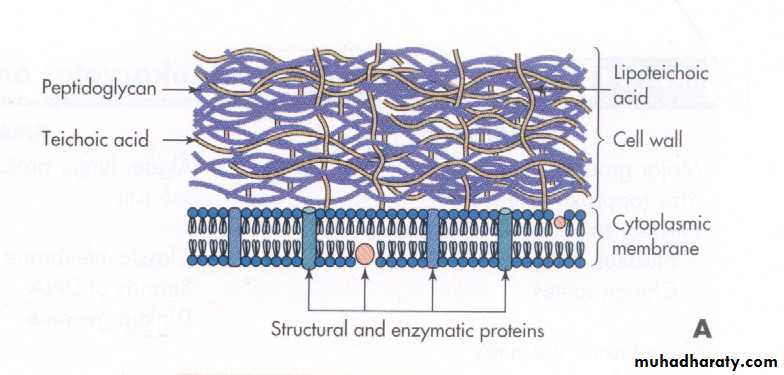
• 1. Difference in the cell wall structure:
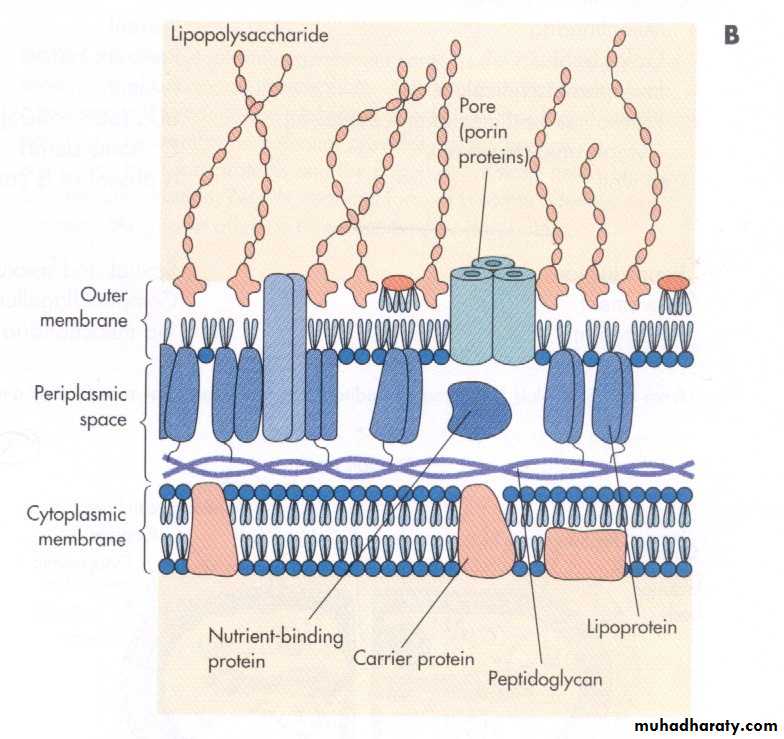
Gram-positive bacteriaHave a thick peptidoglycan layer surrounds the cell.
The stain gets trapped into this layer and the bacteria turned purple.
Retain the color of the primary stain (crystal violet) after decolourization with alcohol
Gram-negative bacteria
have a thin peptidoglycan layer that does not retain crystal violet stain.Instead, it has a thick lipid layer which dissolved easily upon decolourization with Alcohol.
Therefore, cells will be counterstained with safranin and turned red.
7
Mechanism of staining
8
Gram’s +ve Bacteria
Gram’s -ve Bacteria
2. The acid character of the protoplasm of gram positive bacteria.
3. Integrity of the cell wall.